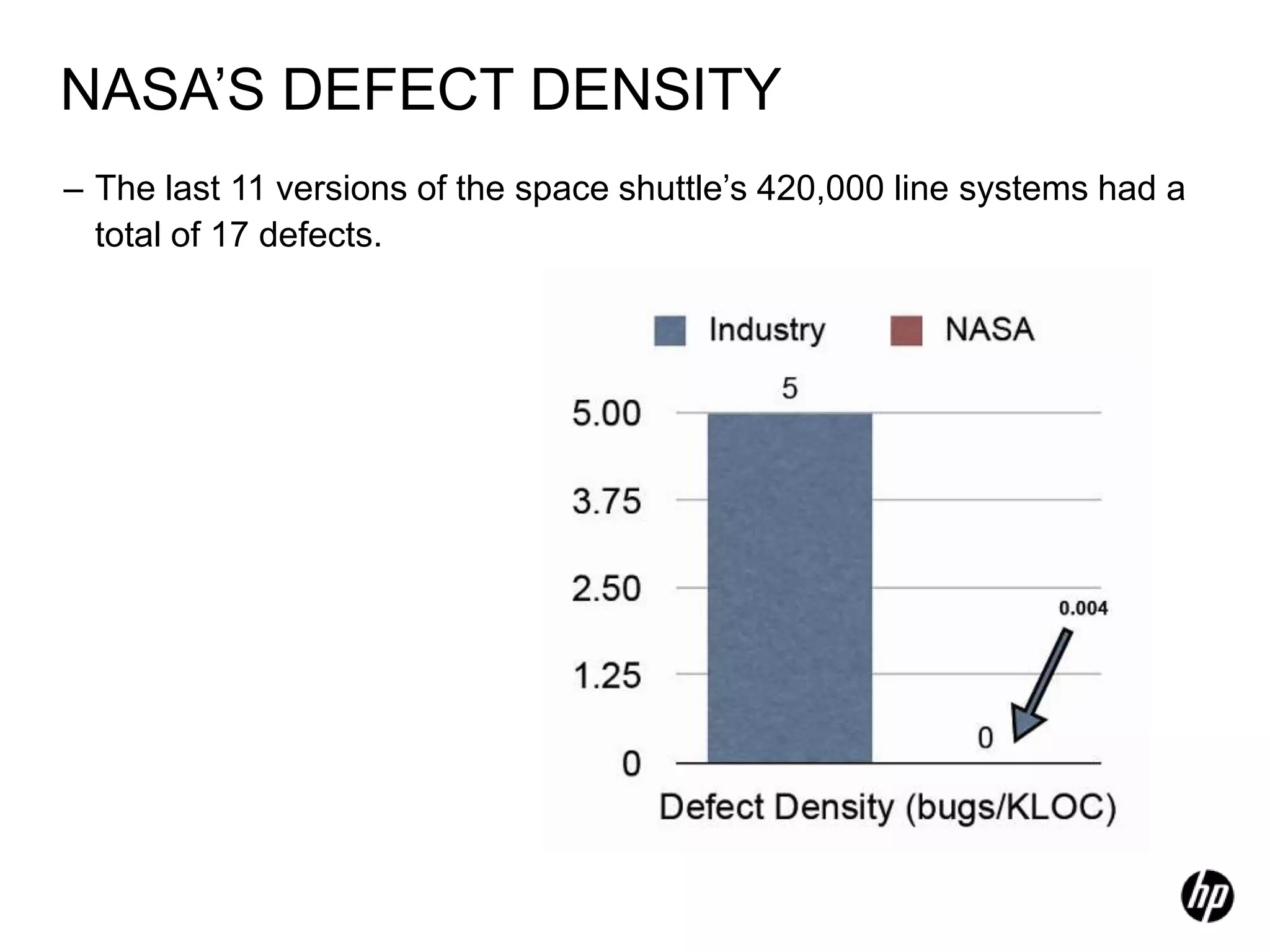
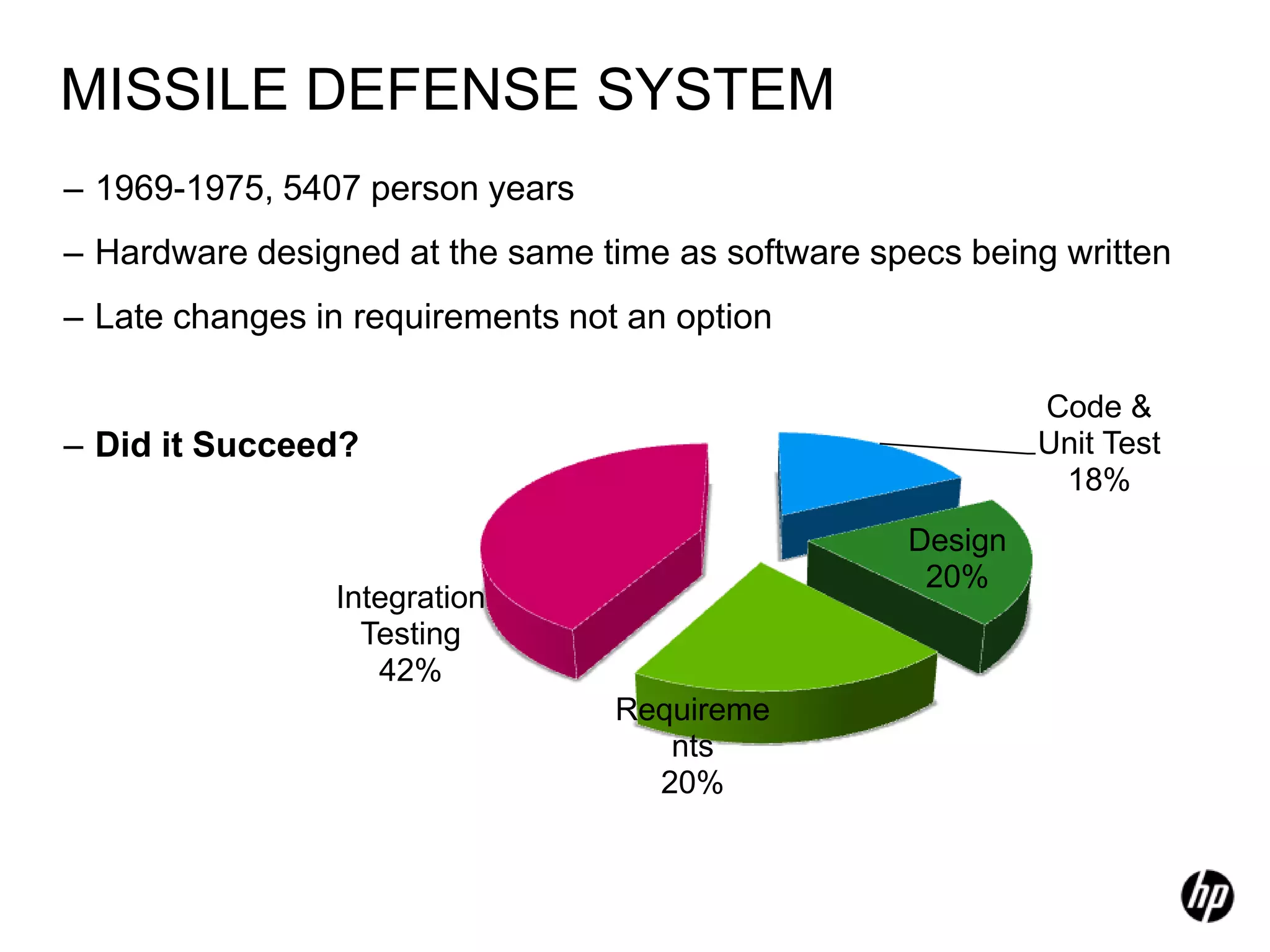
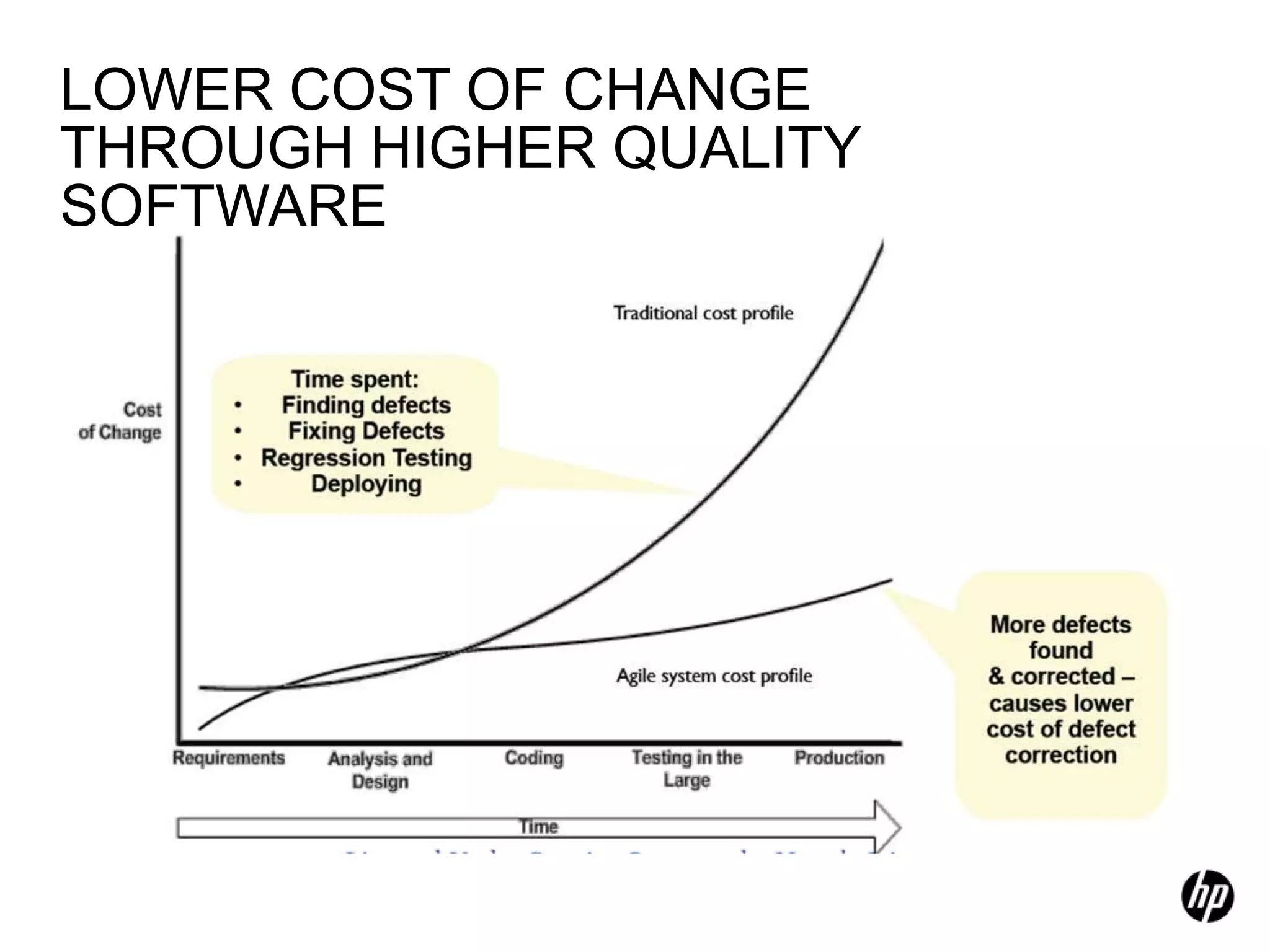
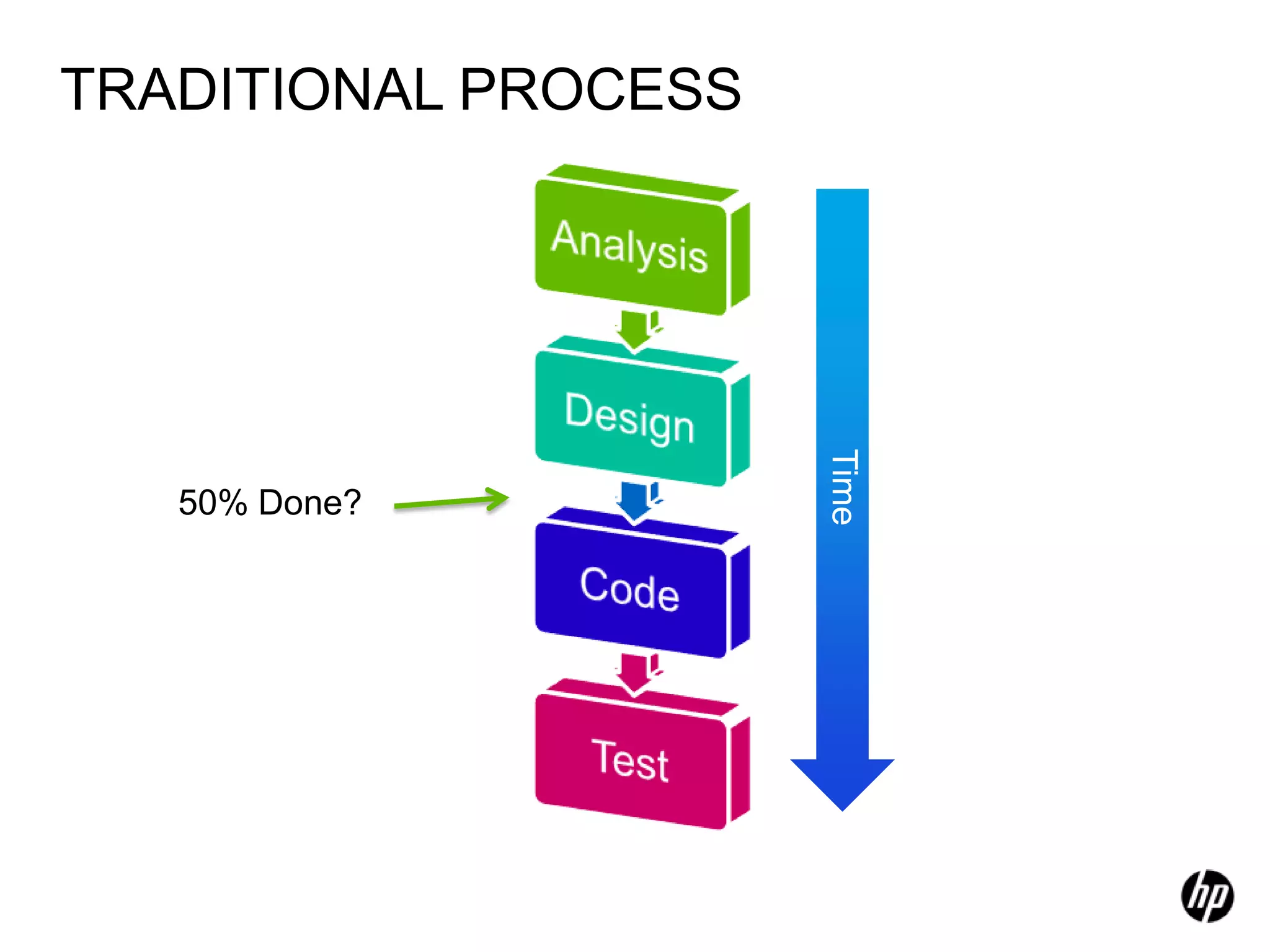
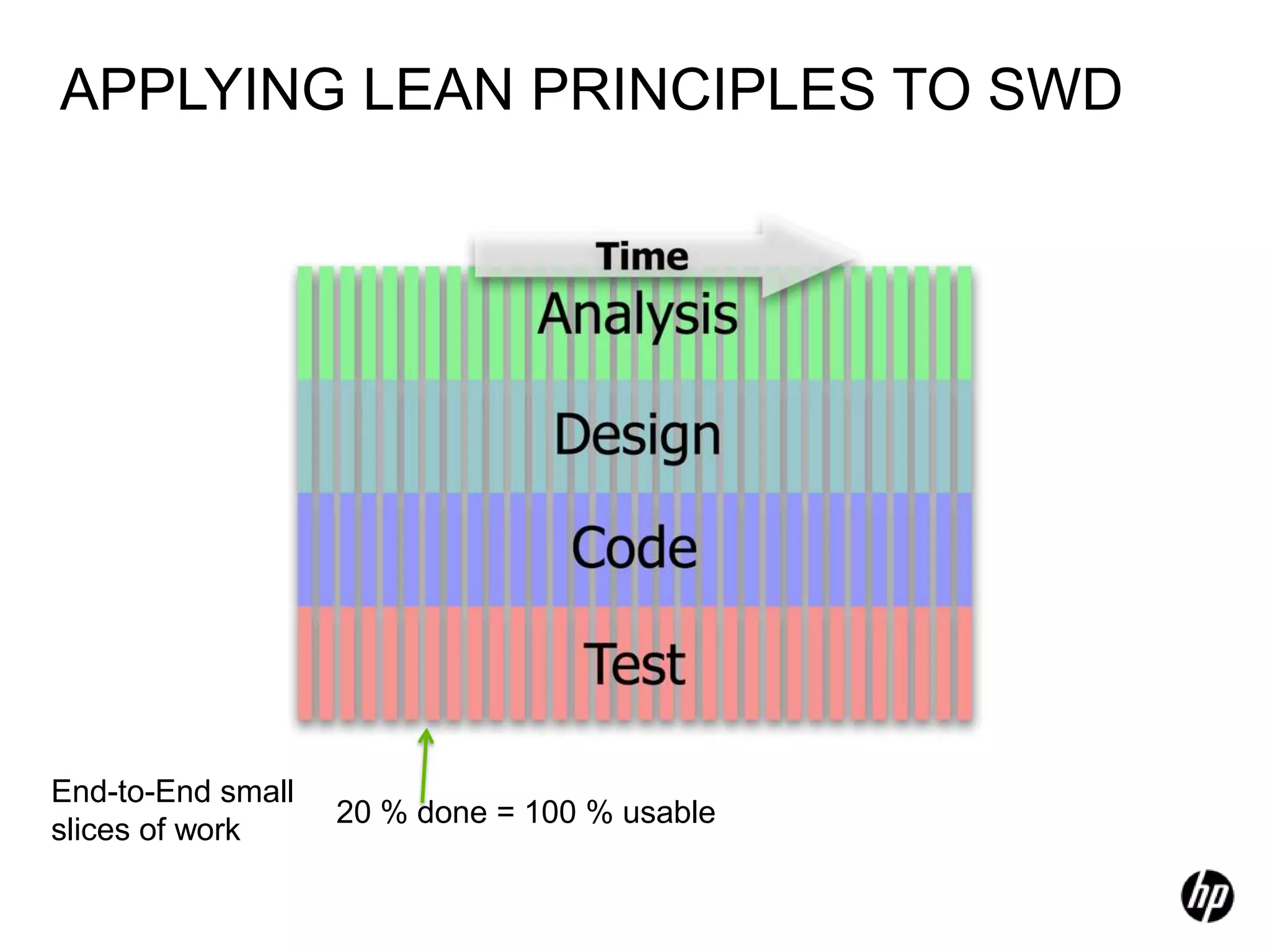
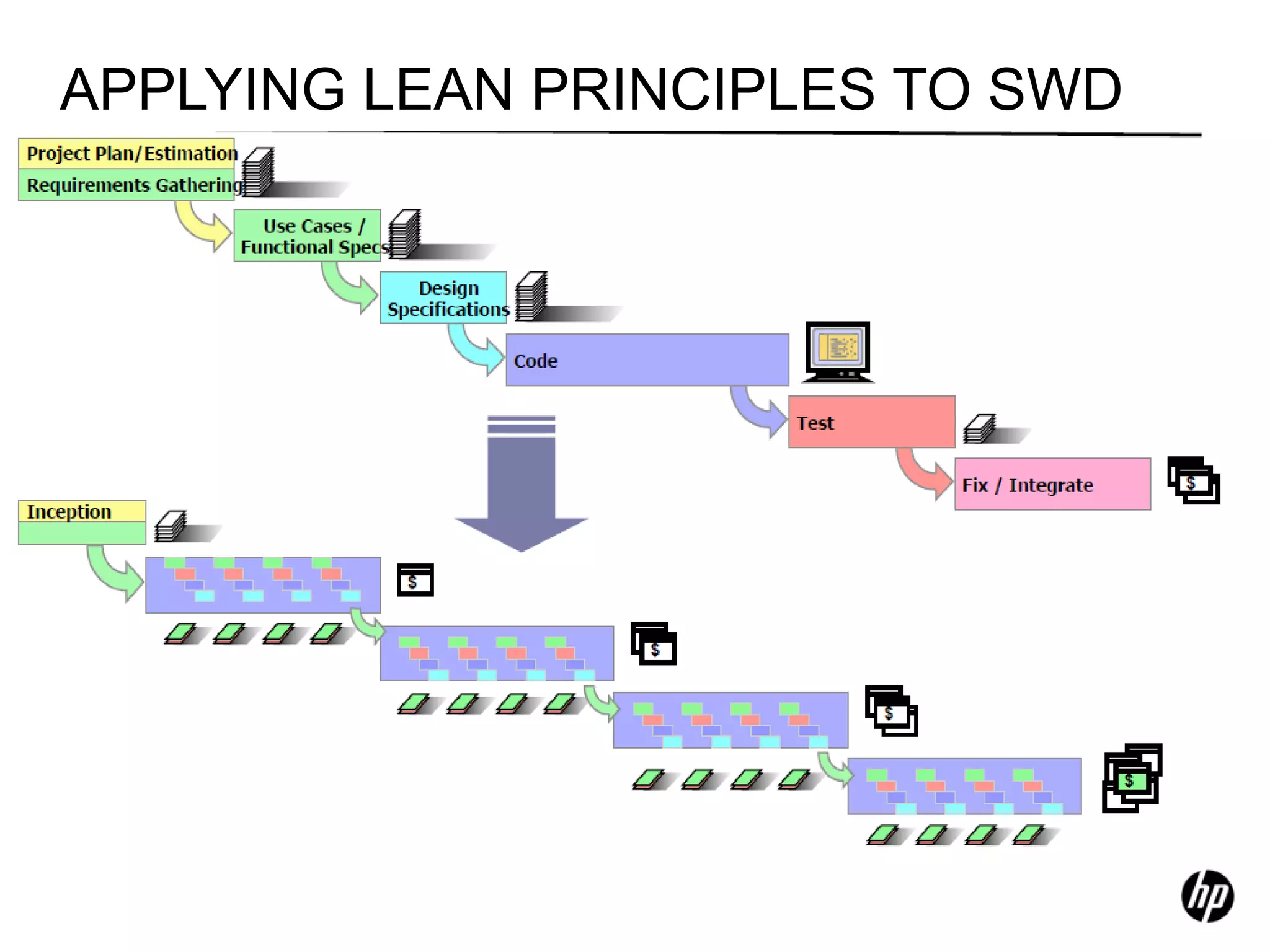
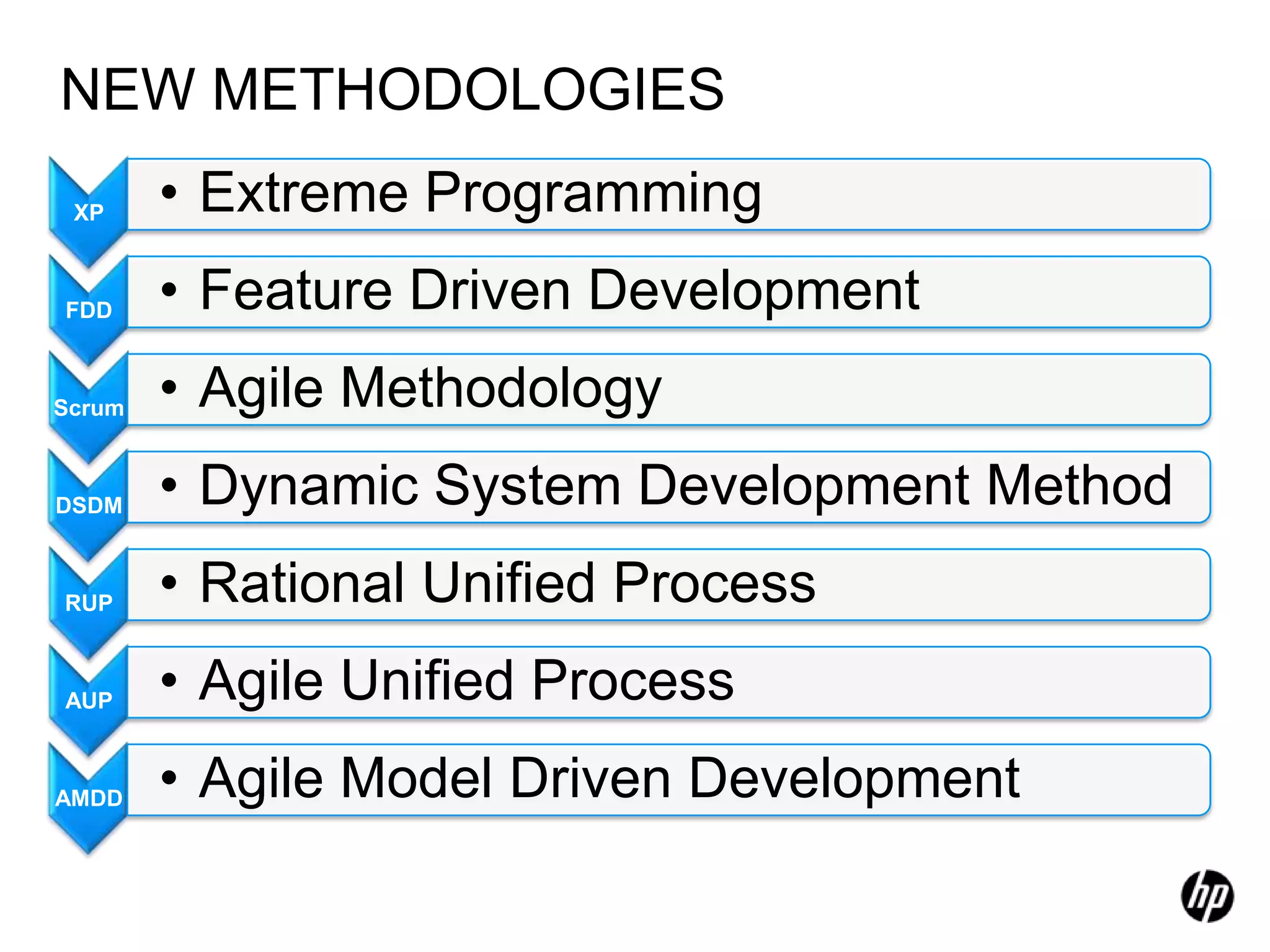
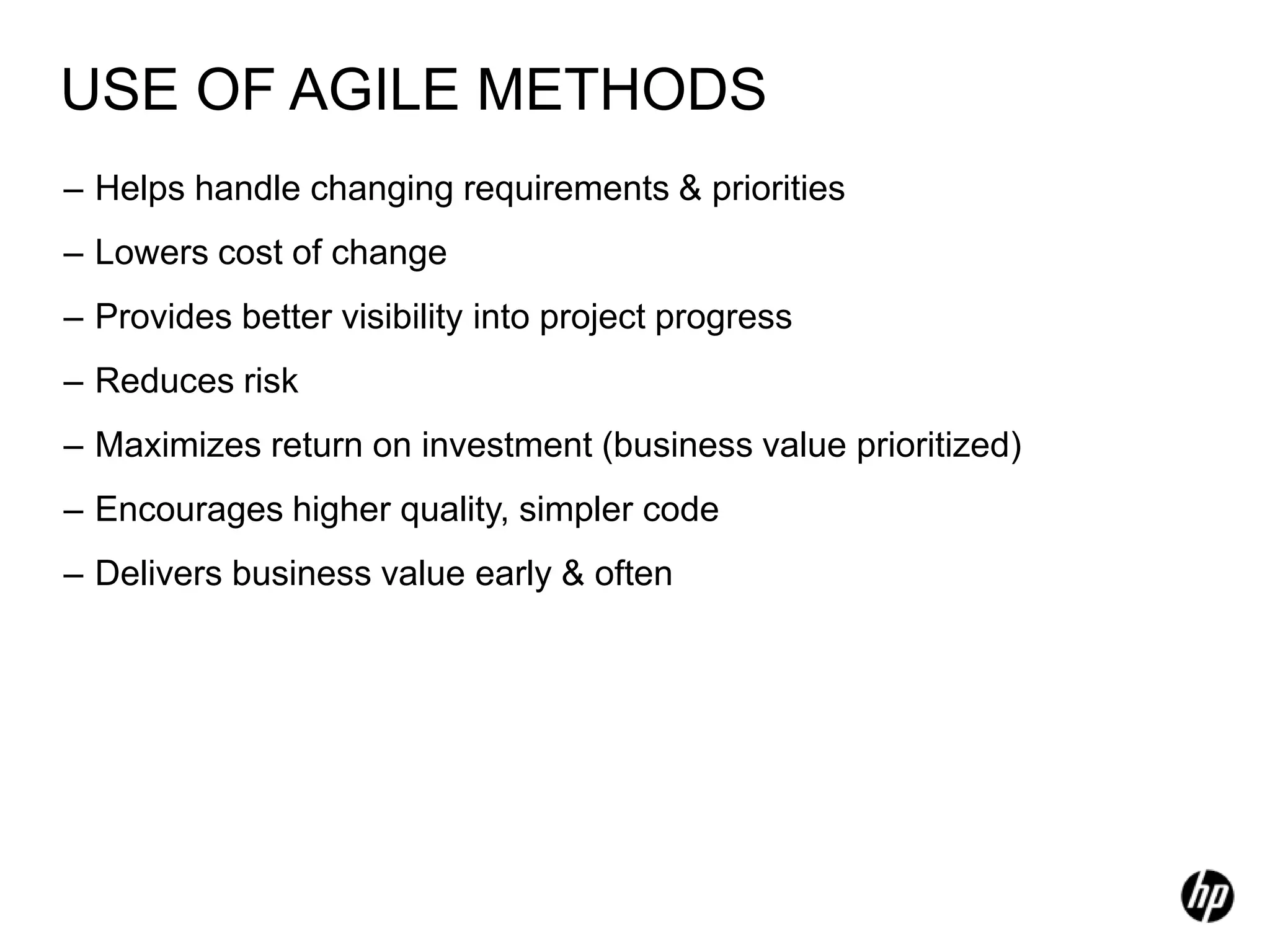
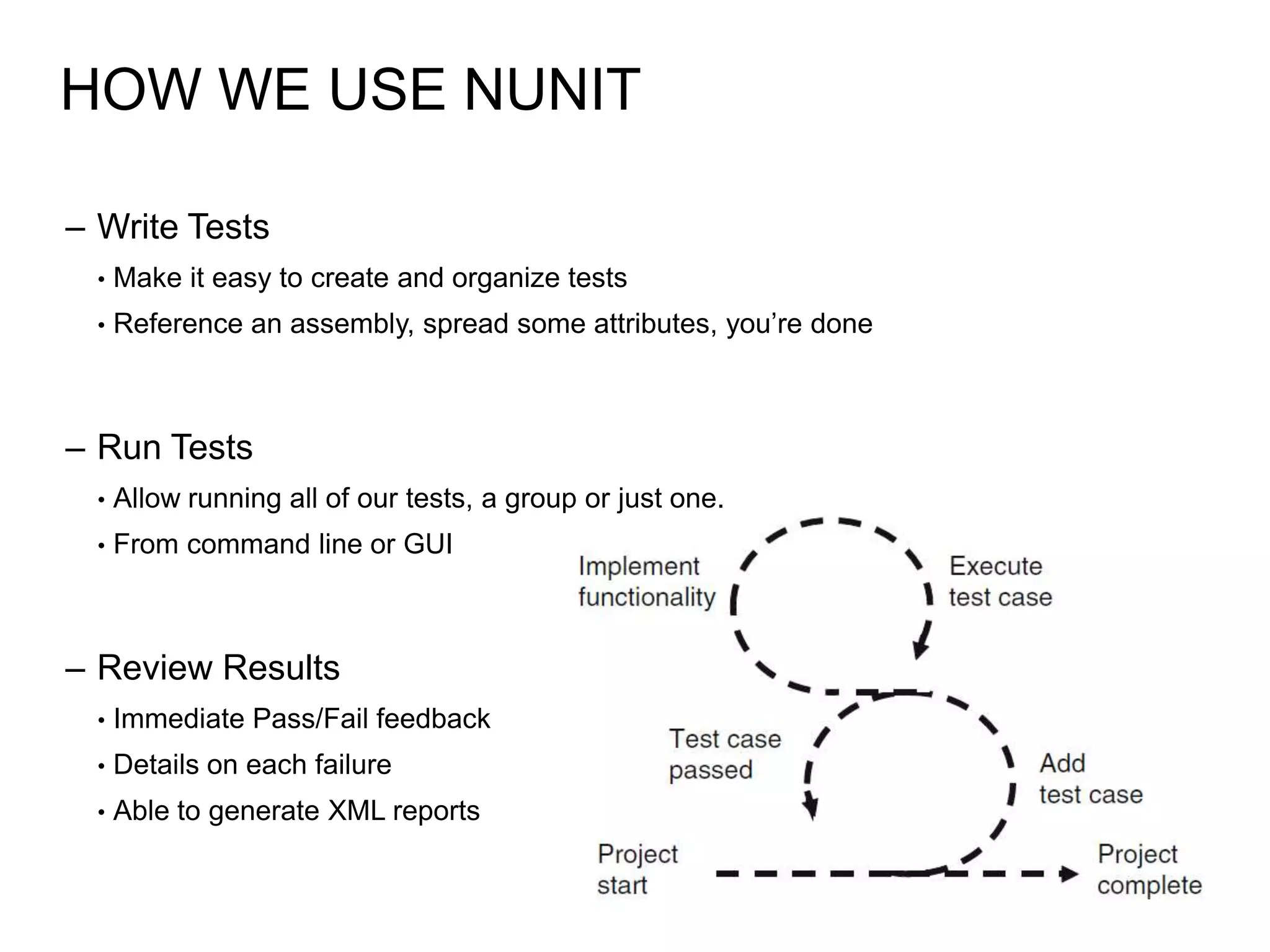
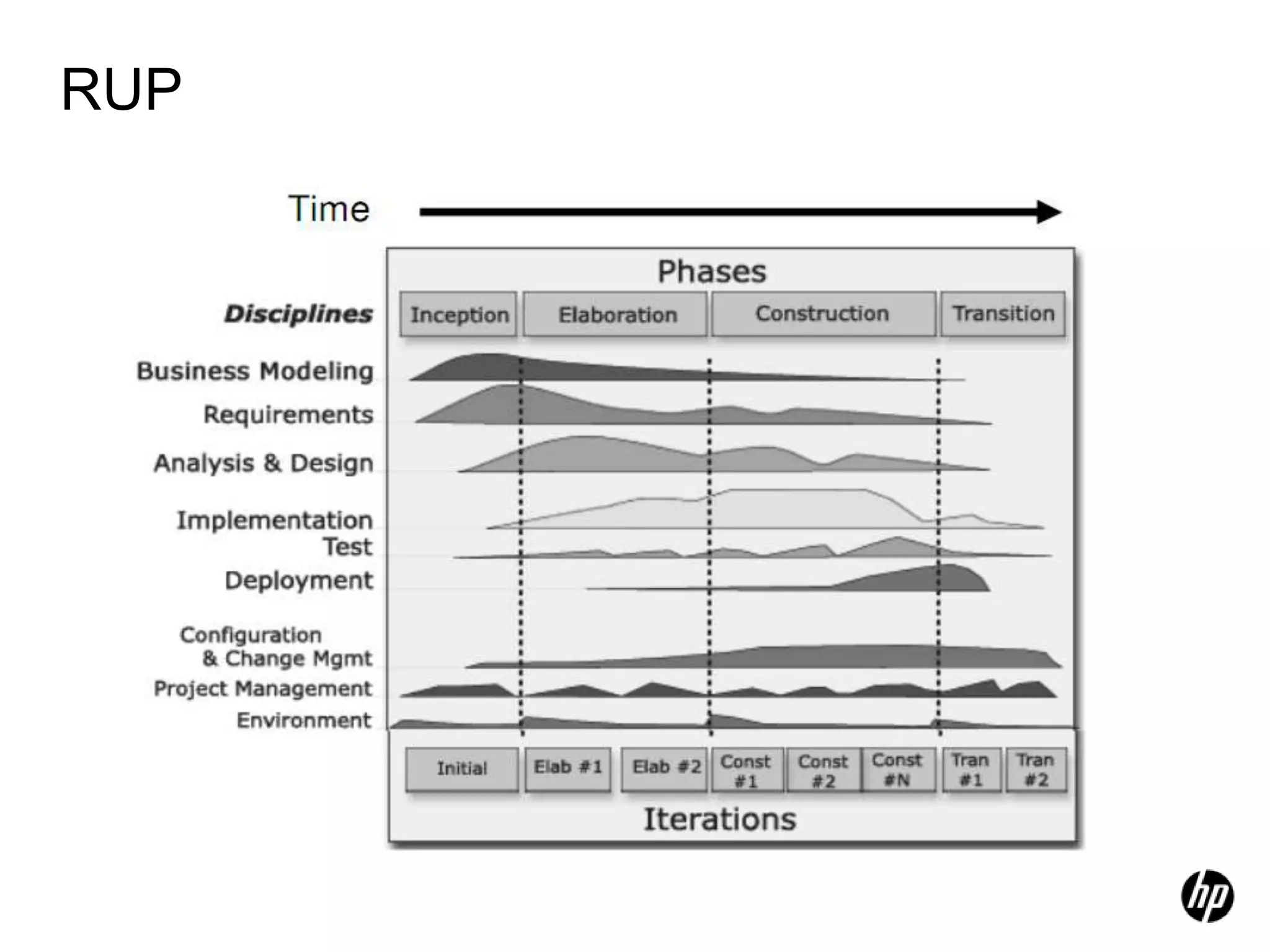
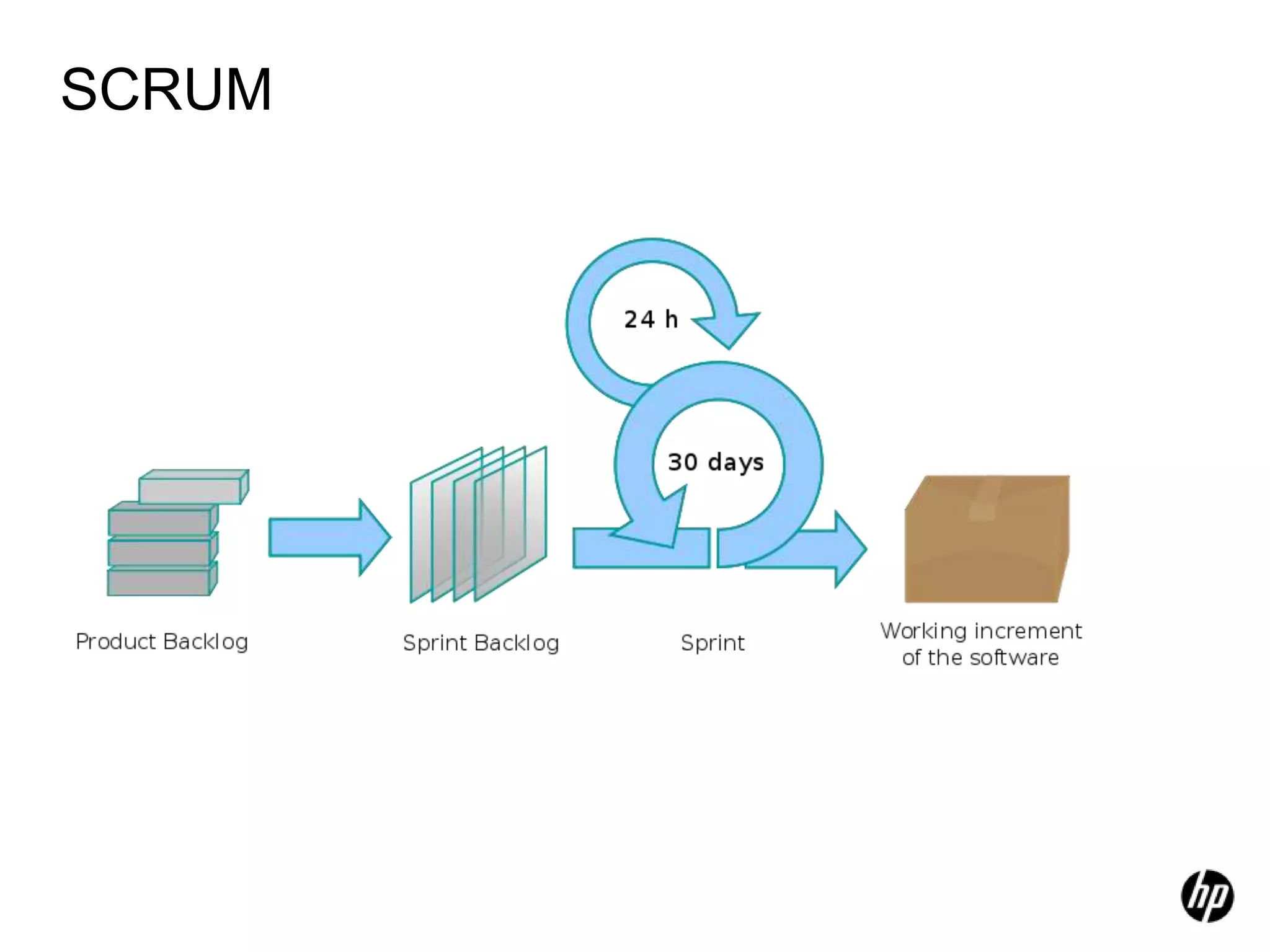
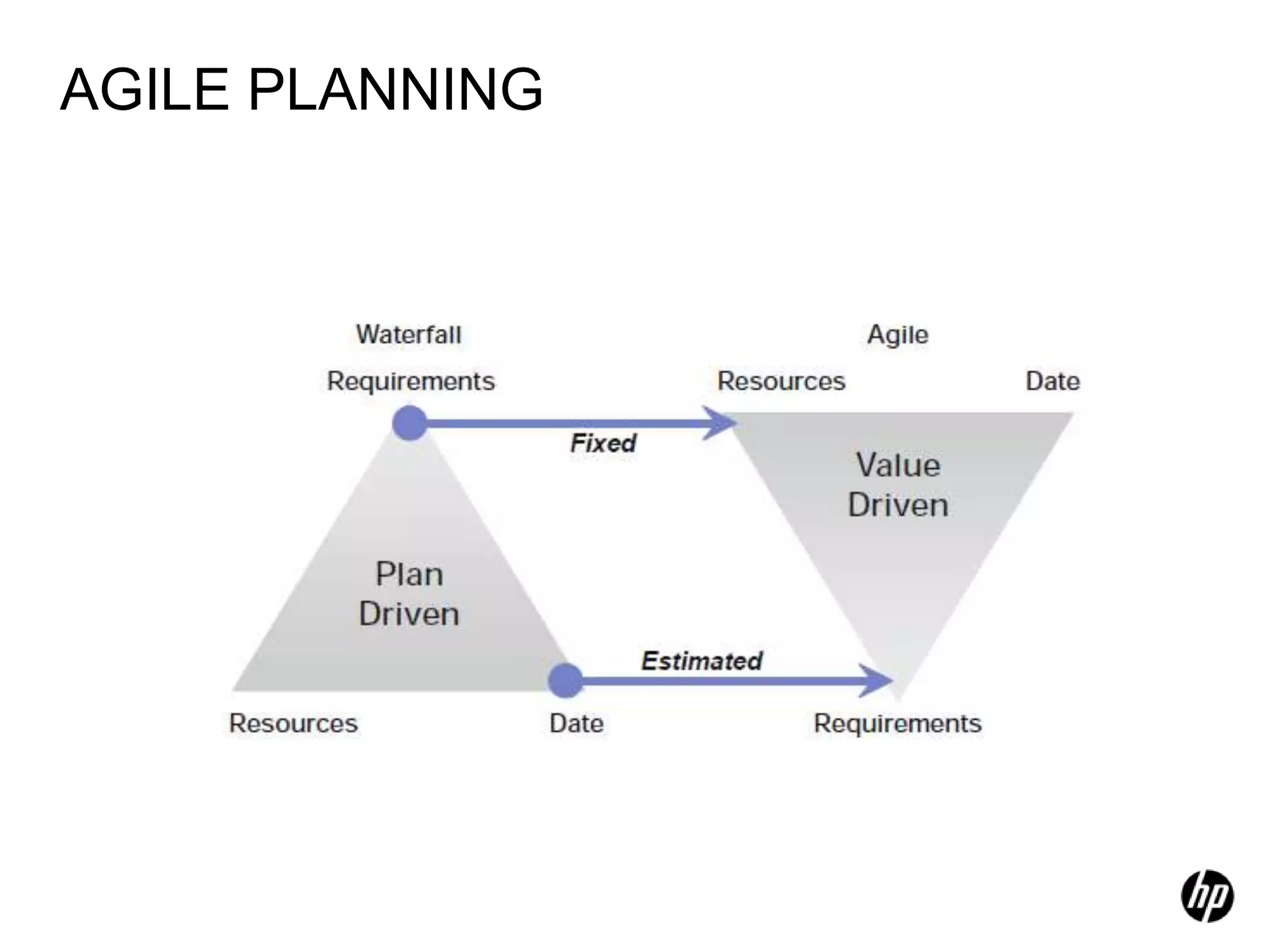
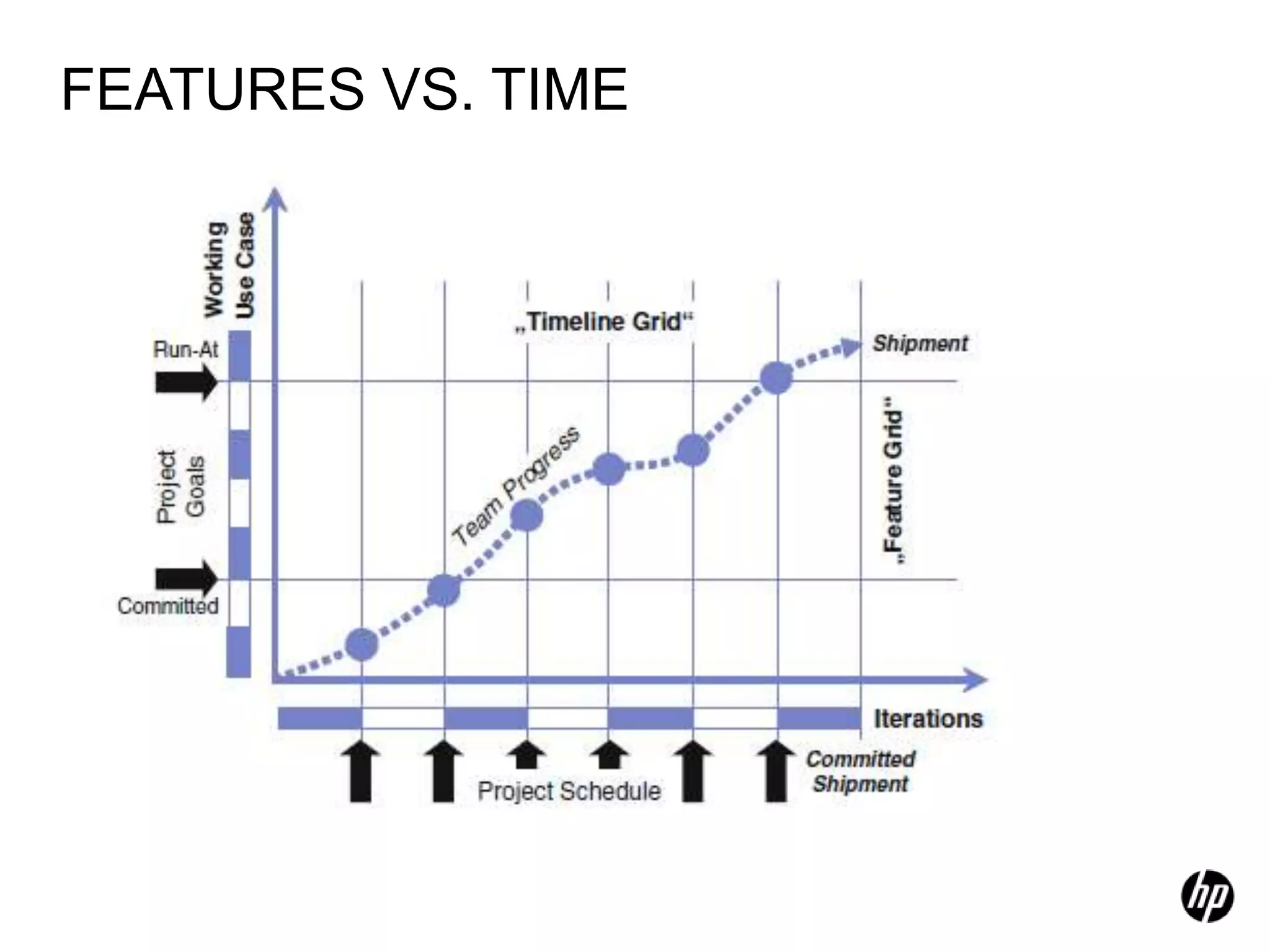
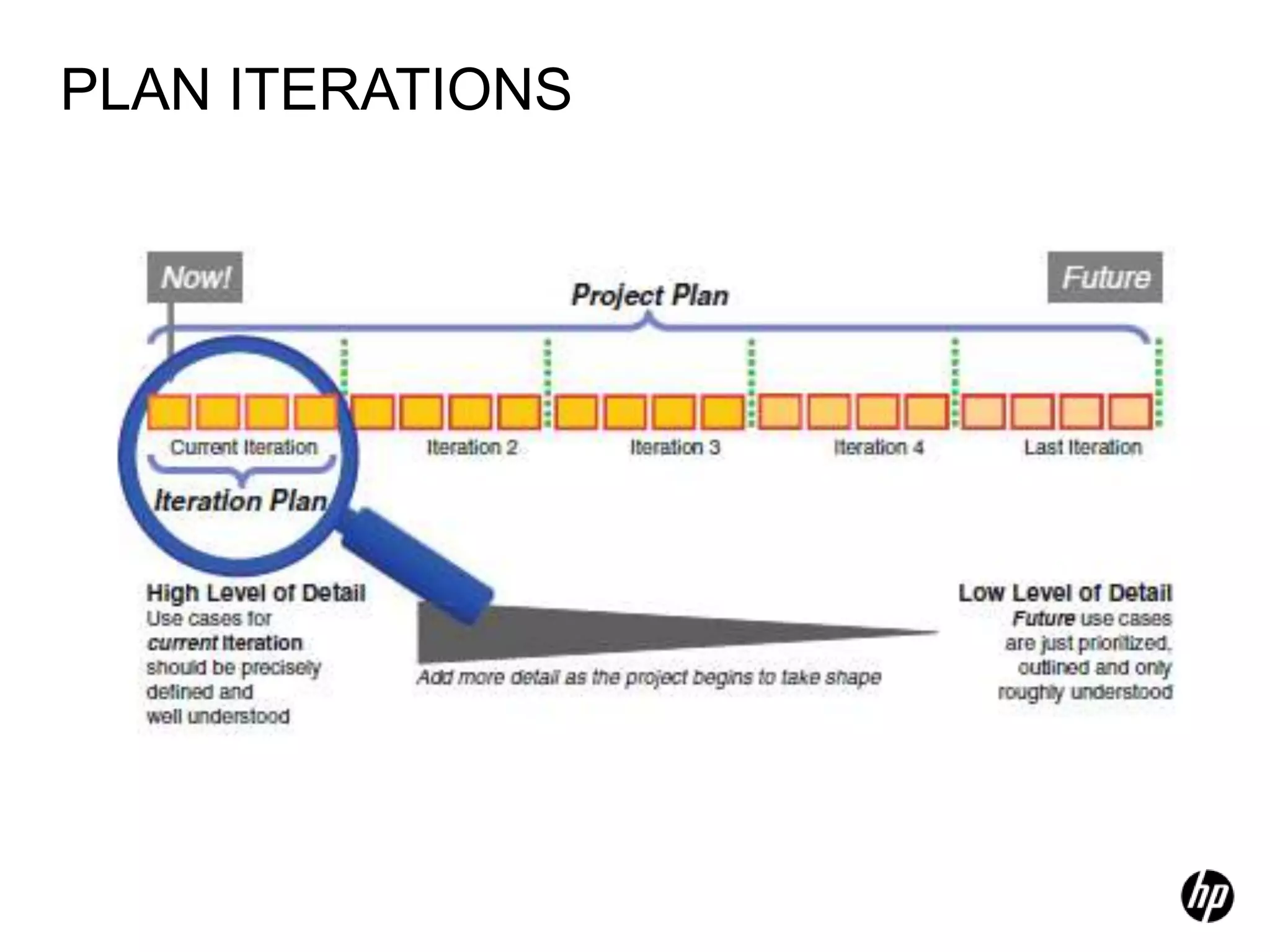
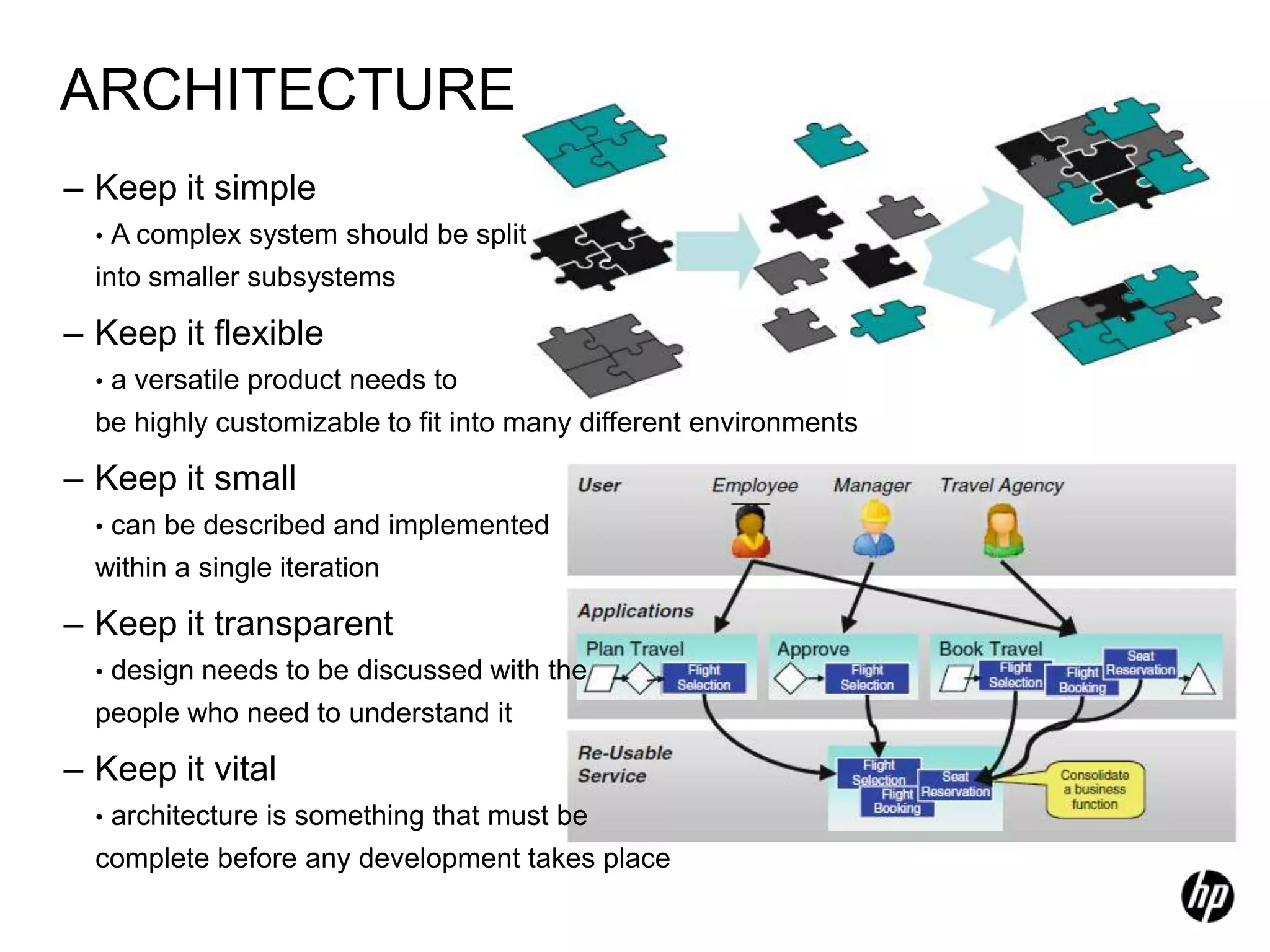
The document provides an overview of agile software development, including its historical context, lean thinking principles, and agile methodologies such as XP, Scrum, and RUP. It emphasizes the importance of flexibility, customer collaboration, and delivering value quickly while advocating for practices like test-driven development. The content also outlines core agile principles aimed at improving software development processes and project outcomes.