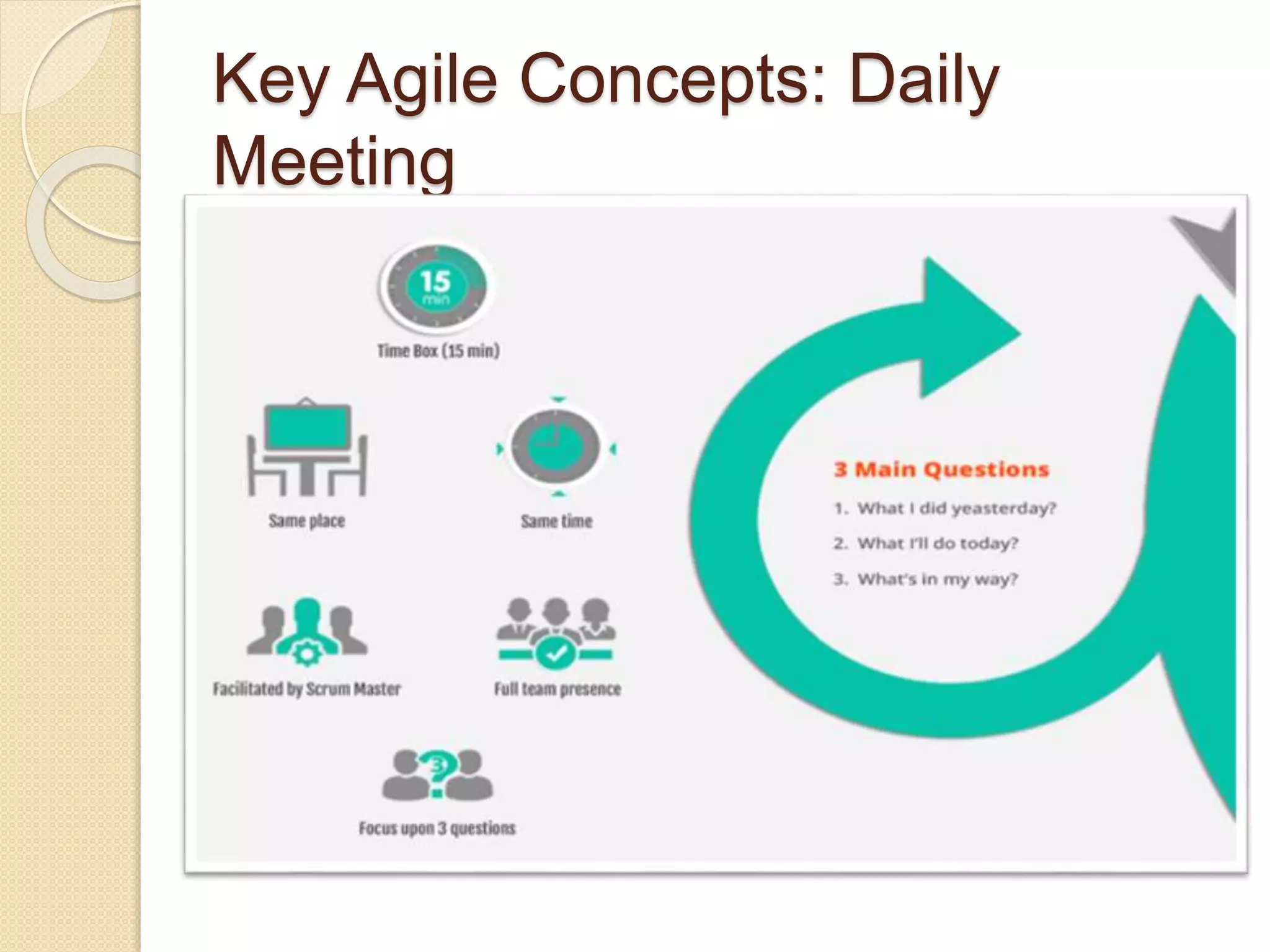
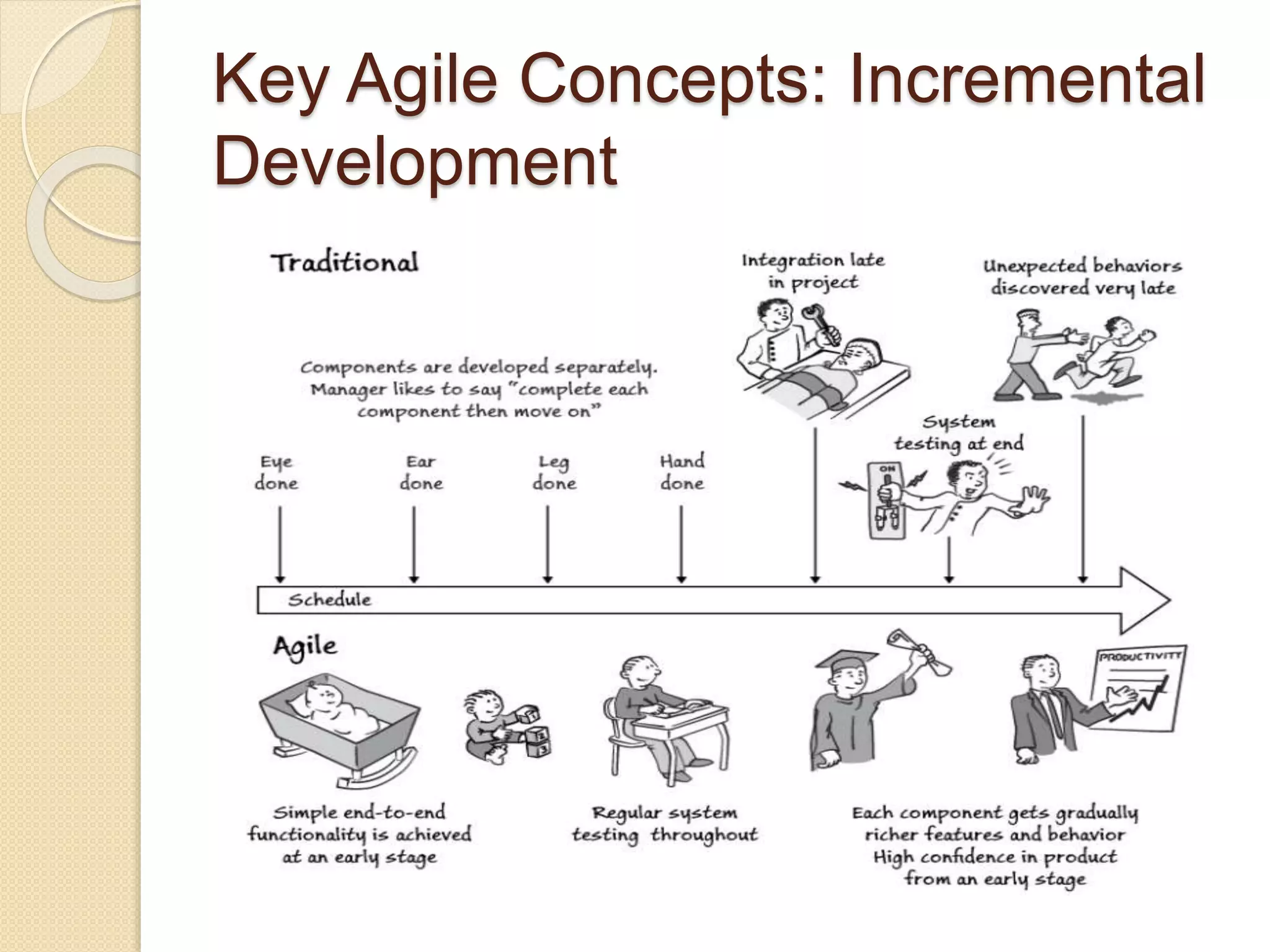
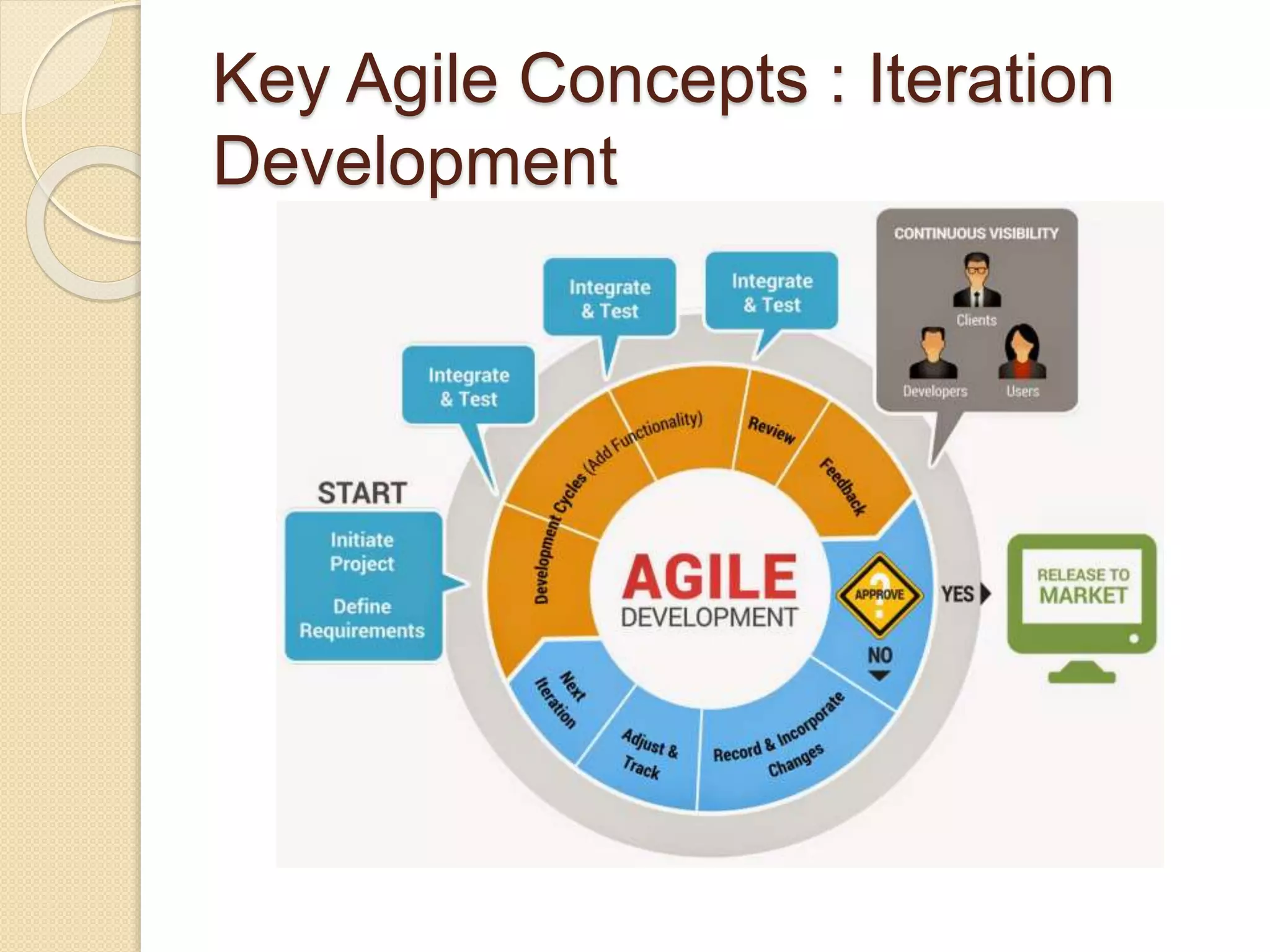
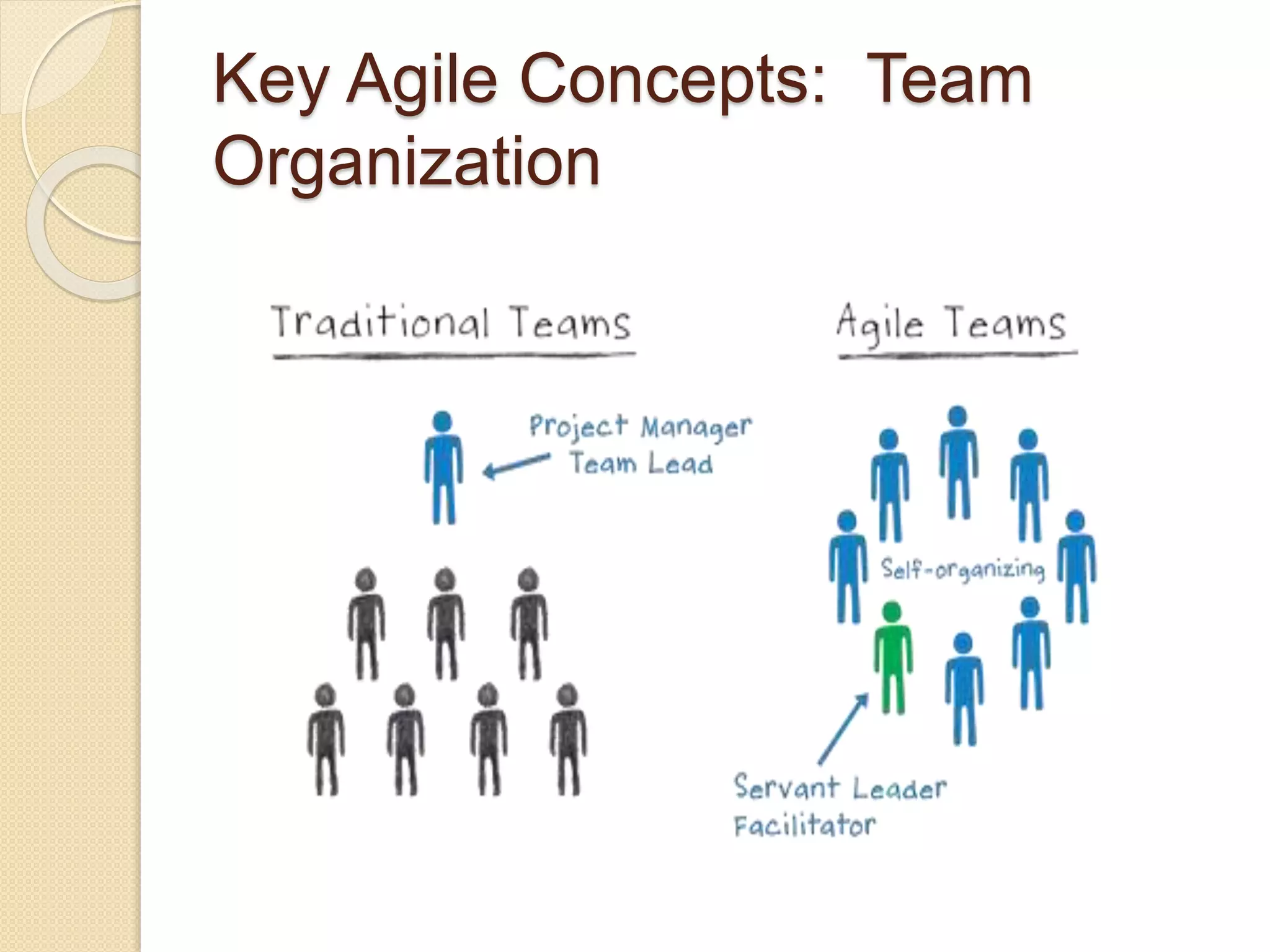
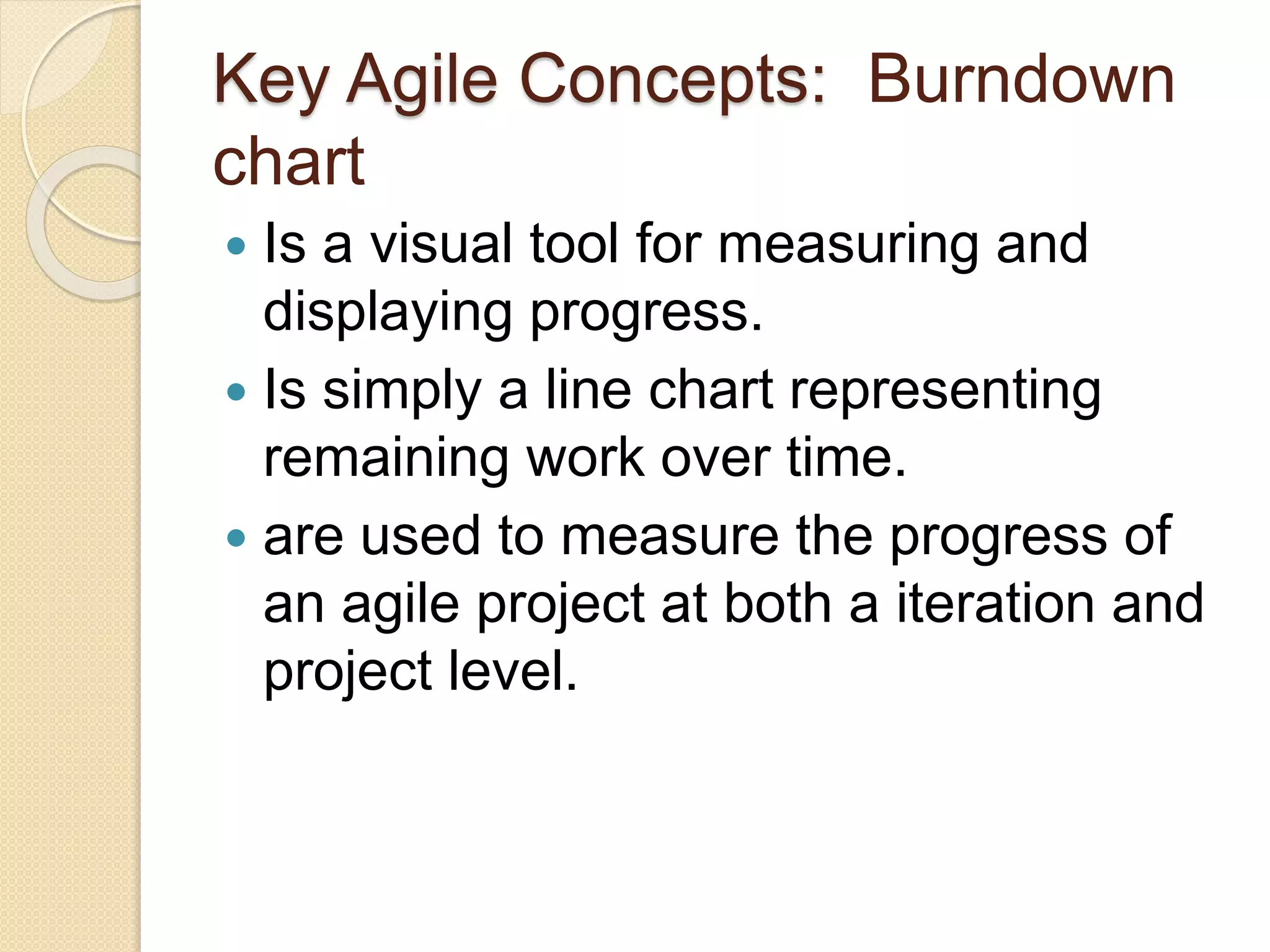
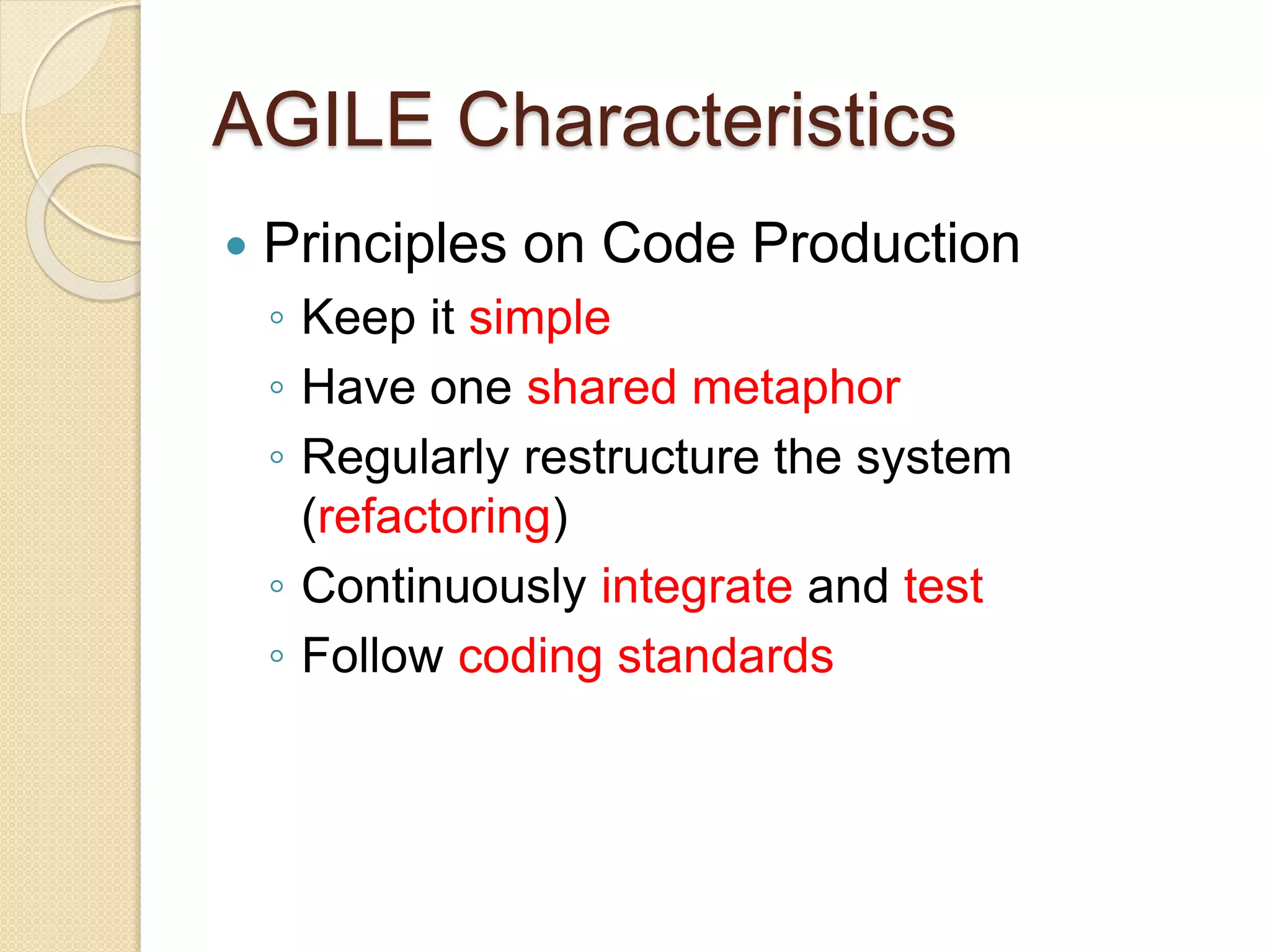
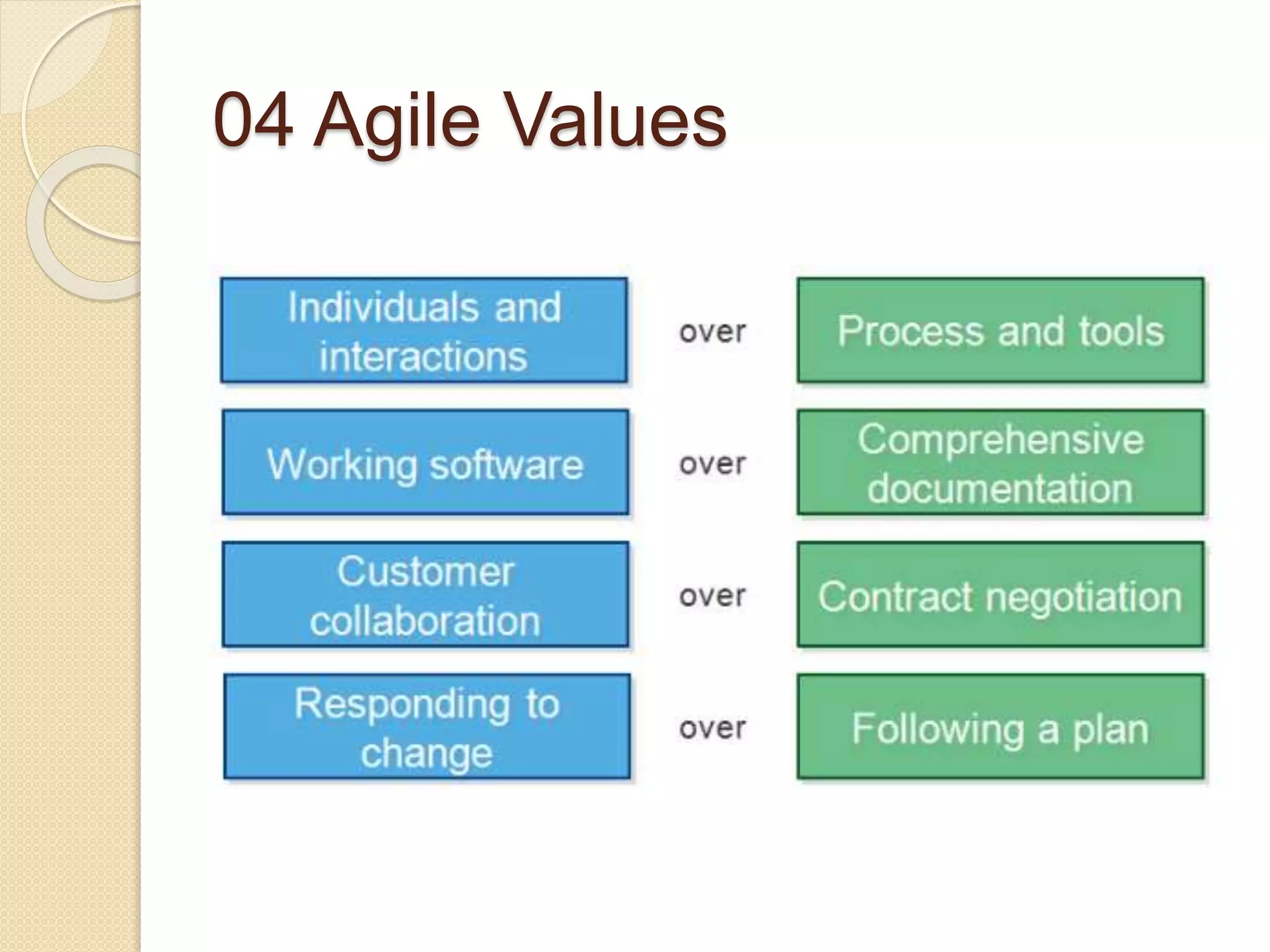
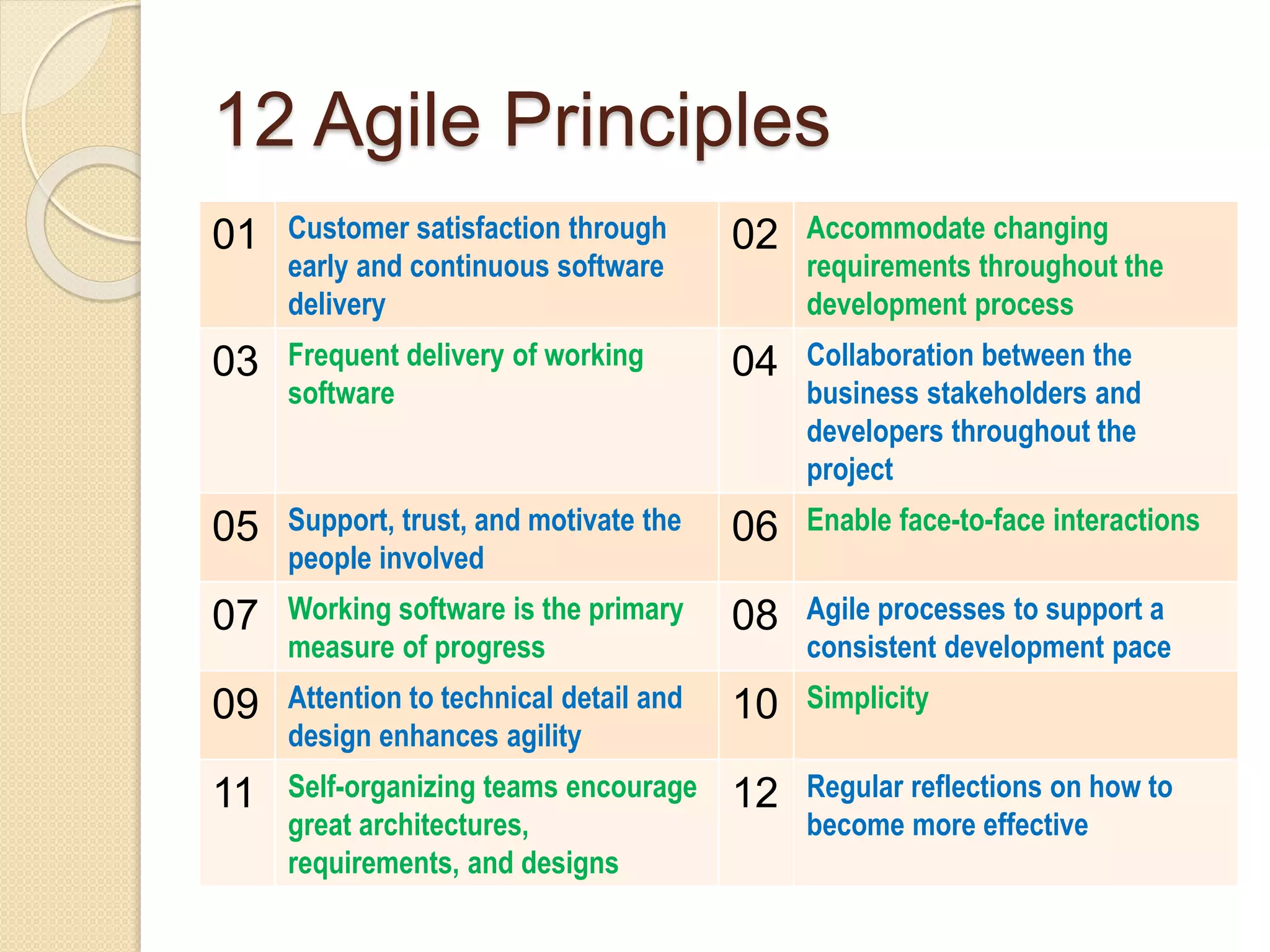
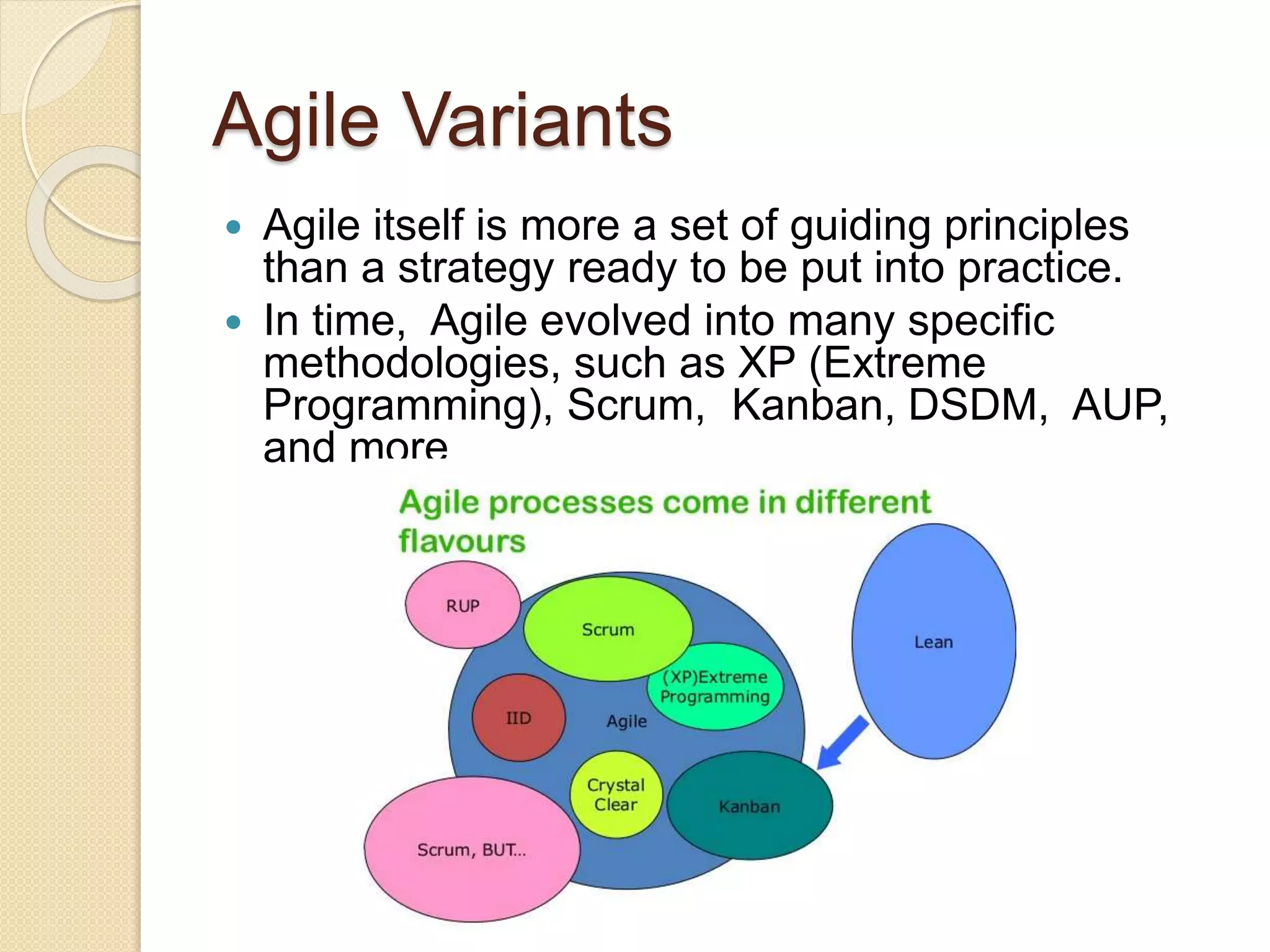
The document provides an introduction to Agile software development, emphasizing its core characteristics such as responsiveness to change, lean governance, and team empowerment. It outlines Agile principles like customer satisfaction, frequent delivery, and collaboration, as well as various Agile methodologies like Scrum and Kanban. Key concepts include user stories, daily meetings, and incremental development, focusing on small, motivated teams and customer involvement for effective outcomes.





![Key Agile Concepts: User
Story
A simple statement about what a user
wants to do with a feature of the
software, written from a user’s
perspective
A User Story should focus on the who,
what and why of a feature, not how.
Fomular
As a [user role], I want to [goal], so I
can [reason]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/agilesoftwaredevelopment-part1agileintroduction-170516042105/75/Agile-Software-Development-Introduction-11-2048.jpg)