This document discusses arrays and structures in programming, highlighting the definitions and types of arrays including one-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays, along with examples. It also explains the concept of records (structs) in C, emphasizing their ability to store varied data types and how they can be combined with arrays to manage complex data. The text concludes with examples showing how to declare and access both arrays and structs.





![6
Example
2 4 8 16 32 64 128 256 512 1024
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
Index
Data
dataType ArrayName[ElementNumber]={<Initialization>};
ArrayName [index];
Declaration
Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-6-2048.jpg)

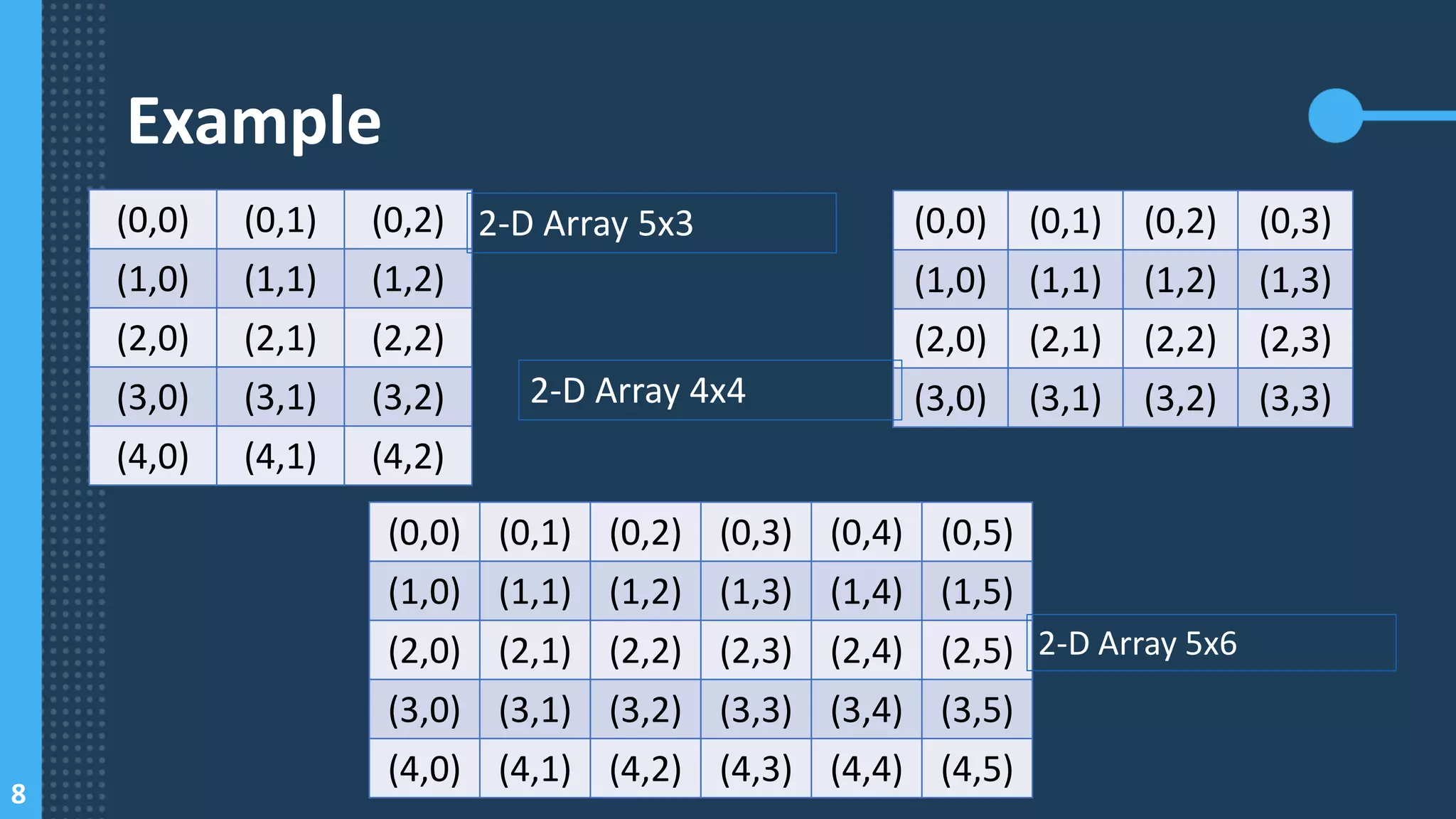
![9
Example (Cont.)
dataType ArrayName [Row][Column] =
{
{<RowInitialization1>},{< RowInitialization2>},{<RowInitializationN>}
{<RowInitialization1>},{< RowInitialization2>},{<RowInitializationN>}
};
ArrayName [Row][Column];
Declaration
Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-9-2048.jpg)


![12
Example (Cont.)
struct mahasiswa { char nama[20]; char npm[10], int nilai;
} nilaiMhs;
nilaiMhs.nama;
nilaiMhs.npm;
nilaiMhs.nilai;
Declaration
Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-12-2048.jpg)

![14
Example
struct nama_type_record {tipe_data1 nm_var1; tipe_data2 nm_var2;
tipe_dataN nm_varN;} var_record[ArrayElement];
General form of record in array](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-14-2048.jpg)
![15
Example (Cont.)
struct mahasiswa { char nama[20]; int nilai;
} nilaiMhs[3];
nilaiMhs[0].nama;
nilaiMhs[0].nilai;
Declaration
Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-15-2048.jpg)

![17
Example
struct nama_type_record {tipe_data1 nm_var1[ArrayElement];
tipe_data2 nm_var2[ArrayElement];
tipe_dataN nm_varN;[ArrayElement]}
var_record;
General form of array in record](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-17-2048.jpg)
![18
Example (Cont.)
struct mahasiswa { char nama[20][3]; int nilai[3];
} nilaiMhs;
nilaiMhs.nama[0];
nilaiMhs.nilai[0];
Declaration
Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-18-2048.jpg)

![20
Example
General form of array in record array
struct nama_type_record {tipe_data1 nm_var1[ArrayElement];
tipe_data2 nm_var2[ArrayElement];
tipe_dataN nm_varN;[ArrayElement]}
var_record[ArrayElement];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-20-2048.jpg)
![21
Example (Cont.)
struct mahasiswa { char nama[20][3]; int nilai[3];
} nilaiMhs[3];
nilaiMhs[1].nama[0];
nilaiMhs[1].nilai[0];
Declaration
Access](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/2arrayandstruct-210222041136/75/Algorithm-and-Data-Structure-Array-and-Struct-21-2048.jpg)
