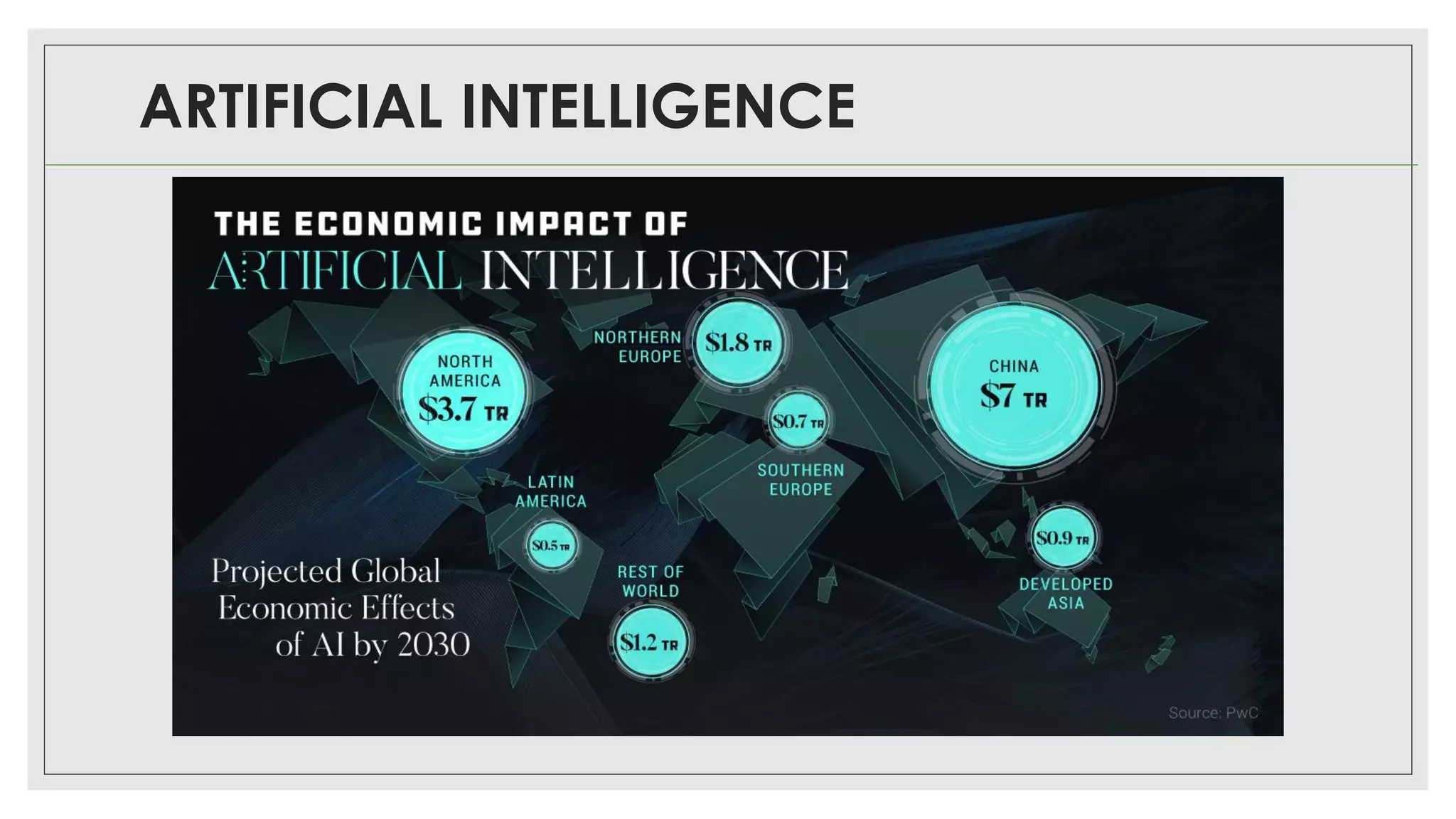
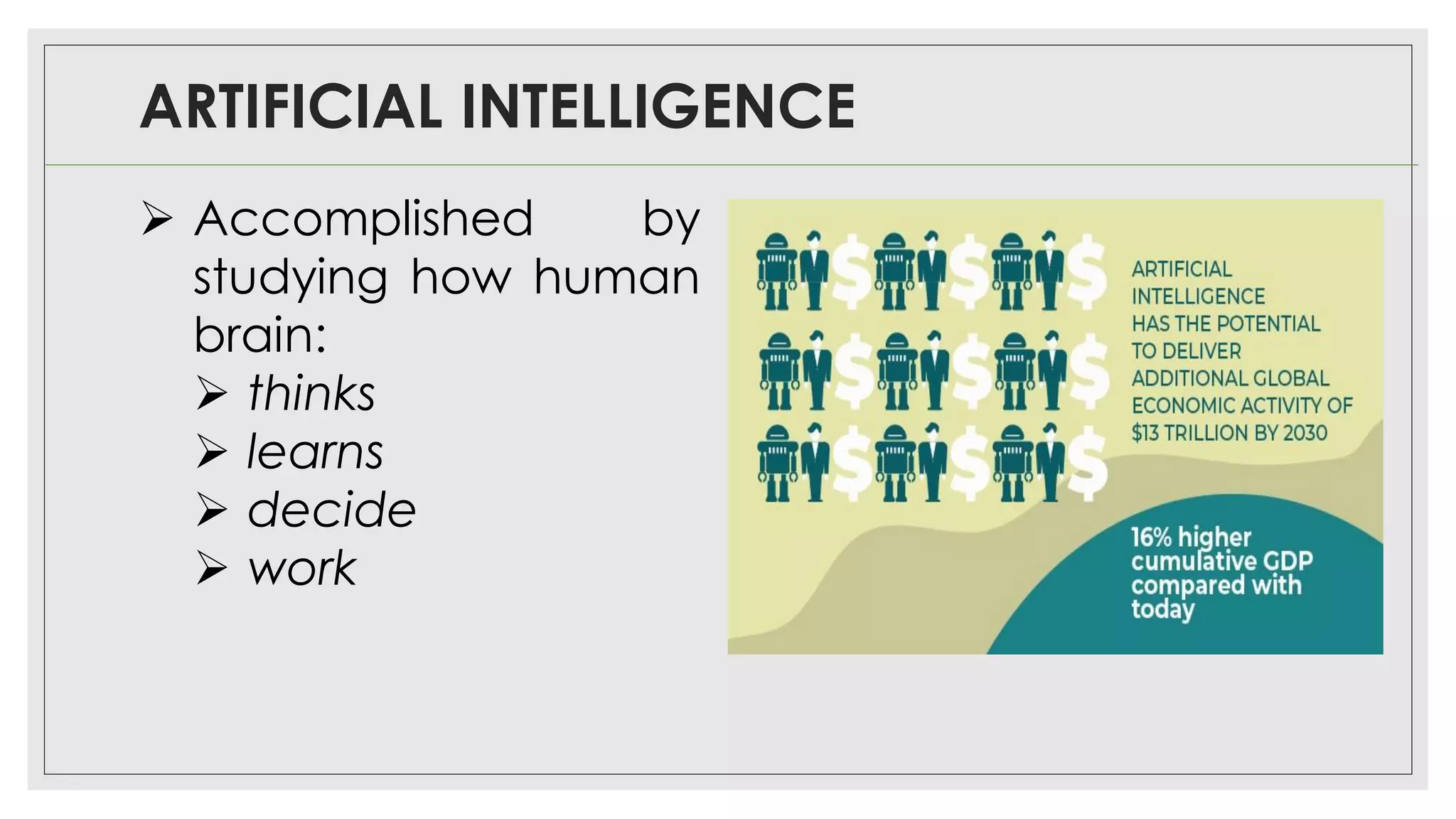
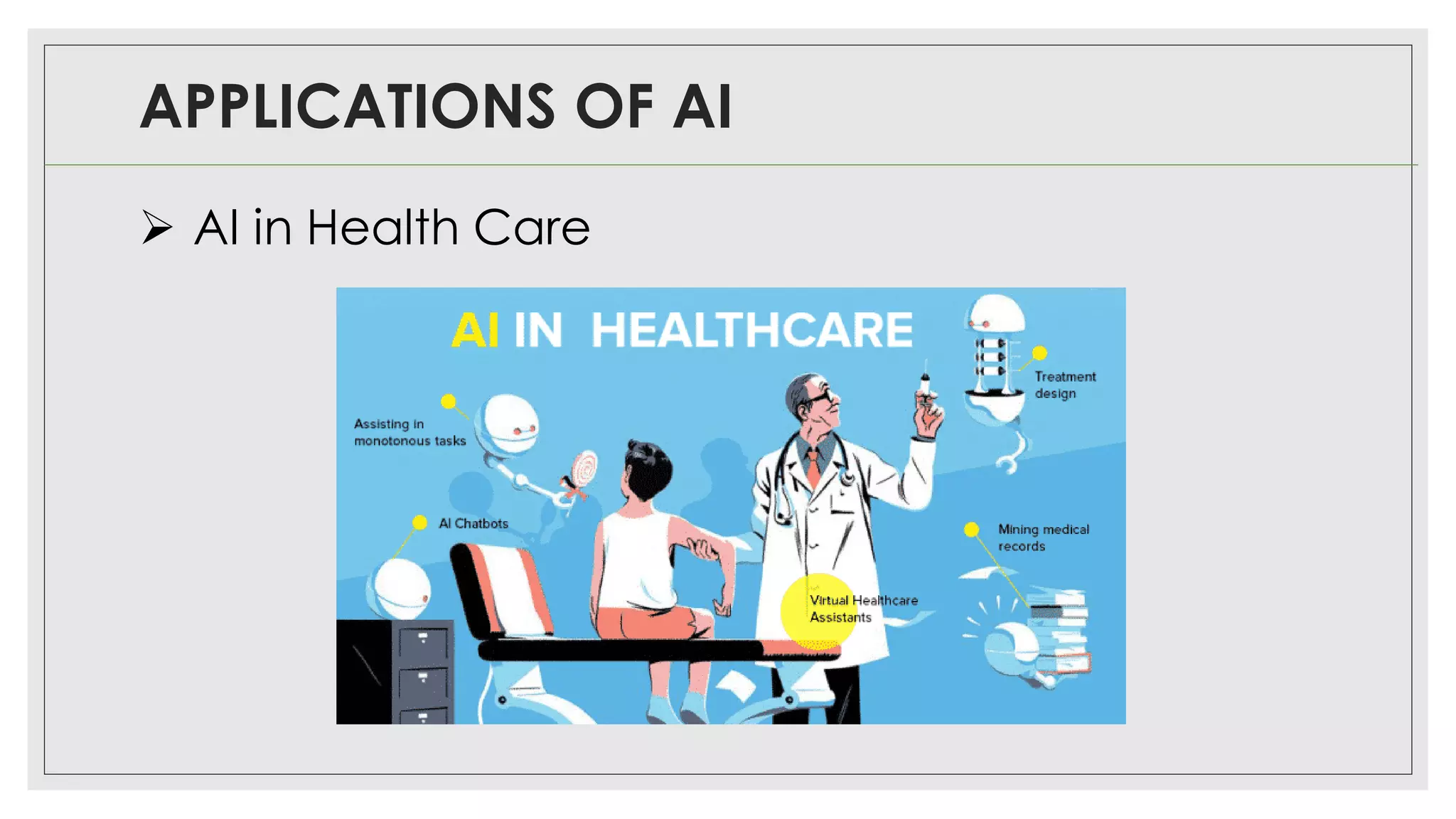
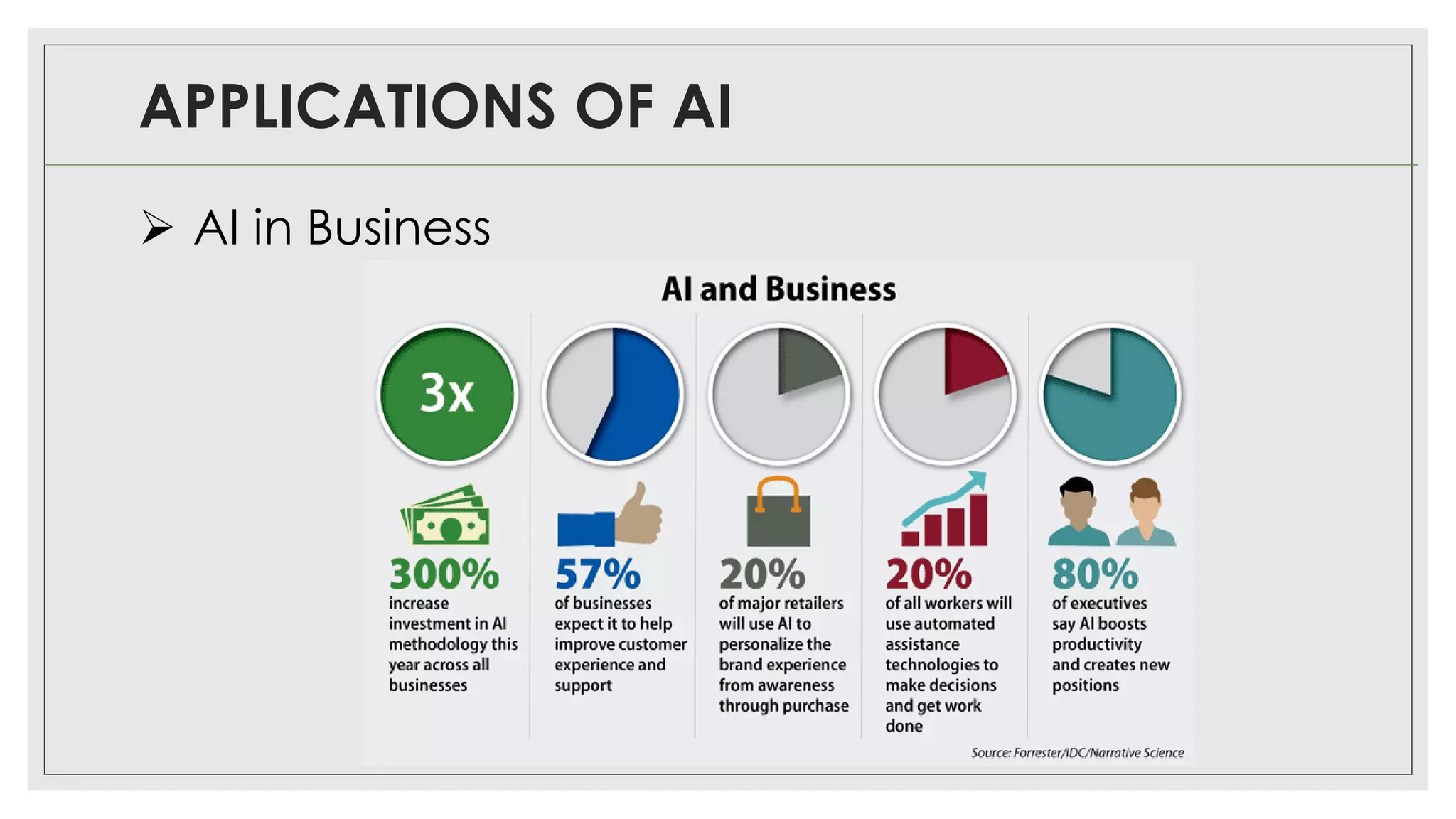
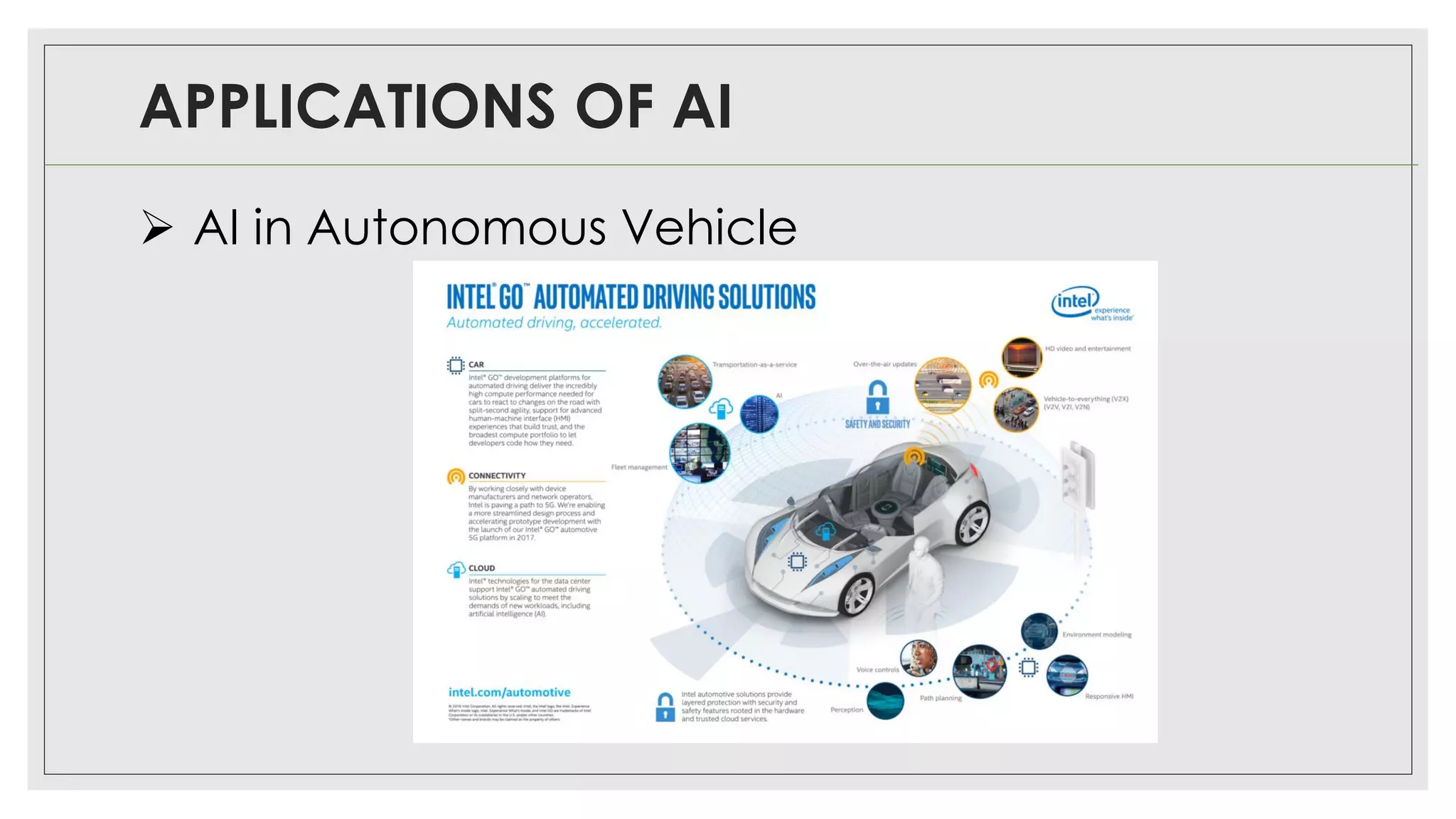
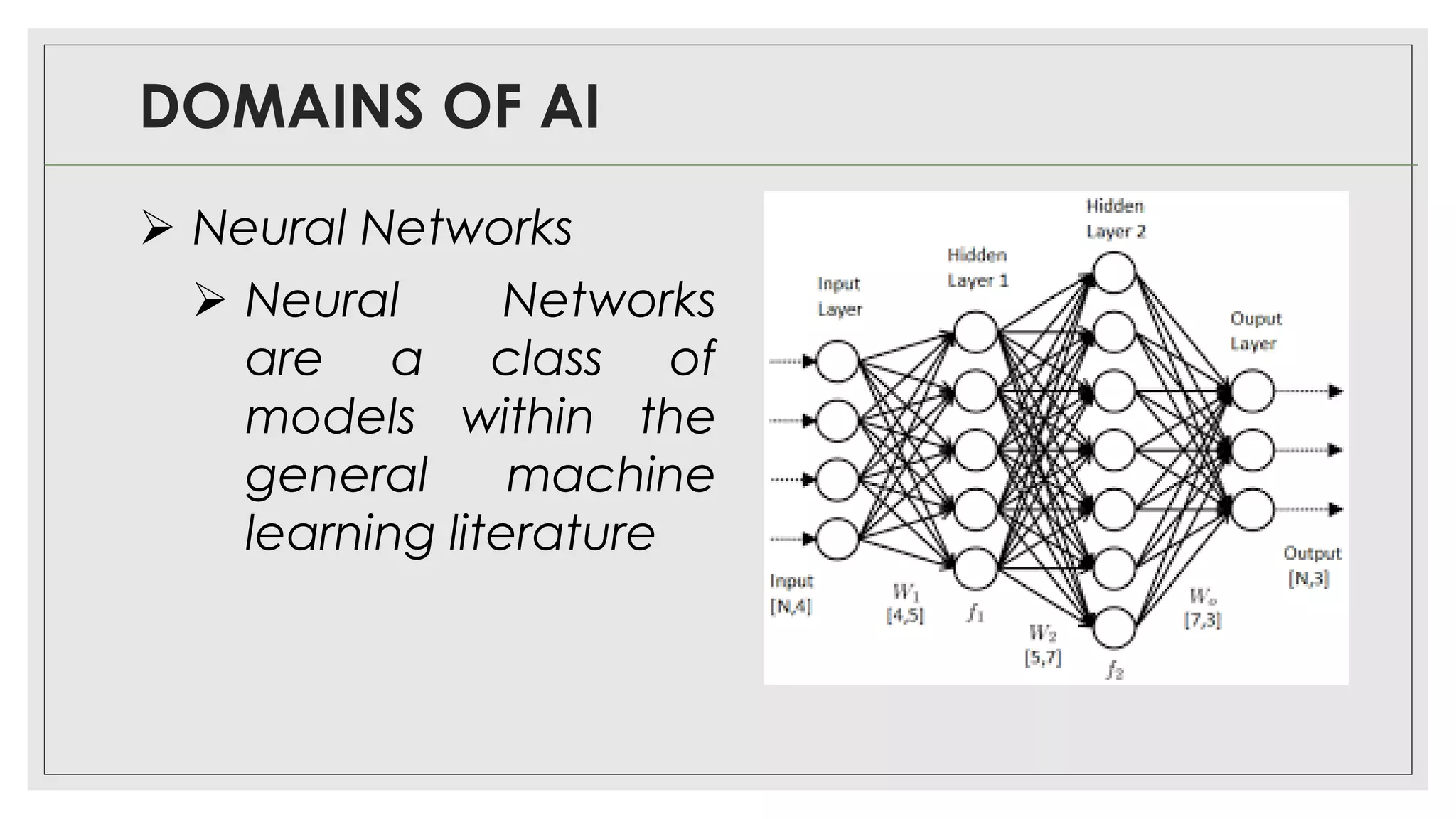
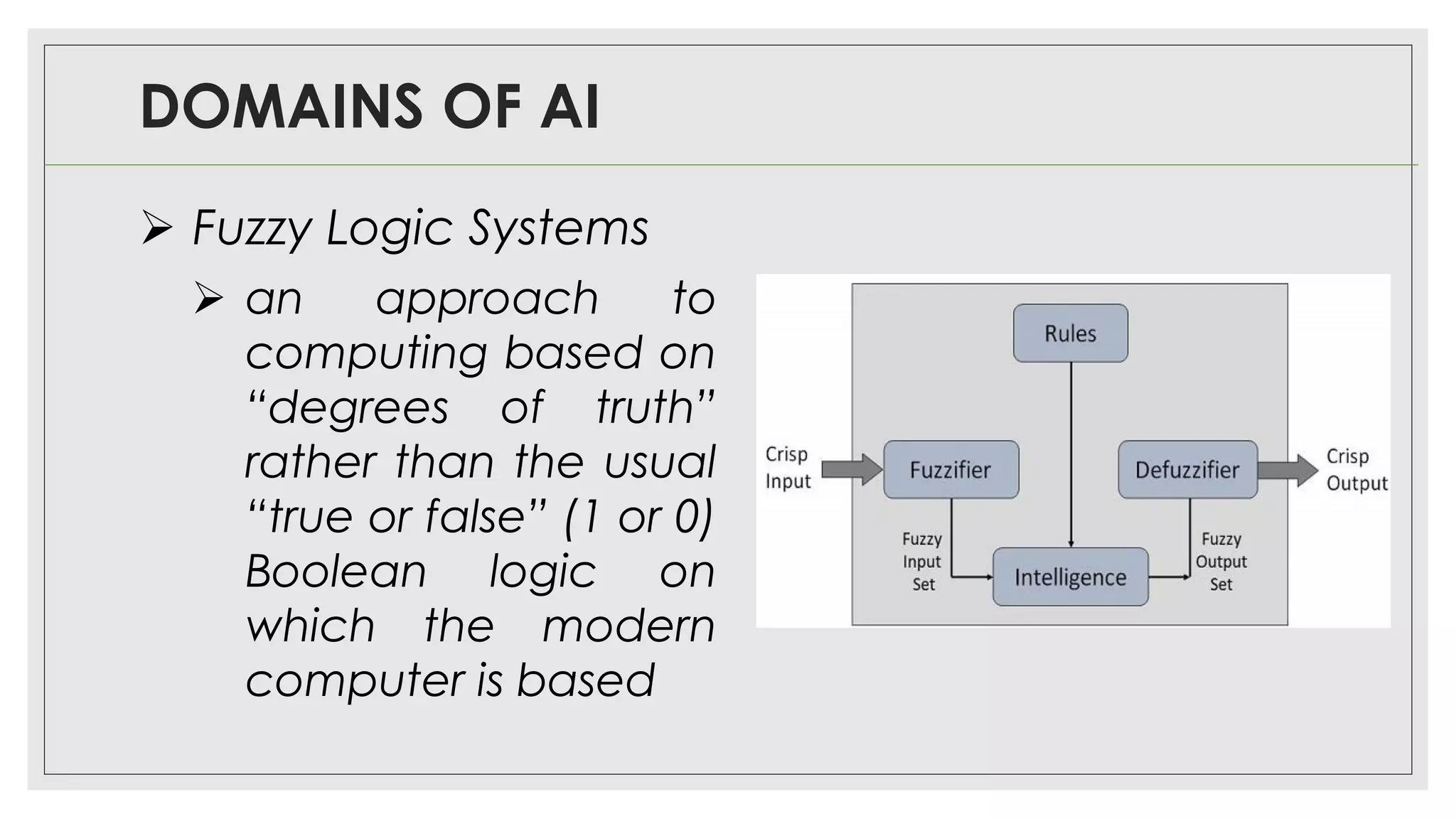
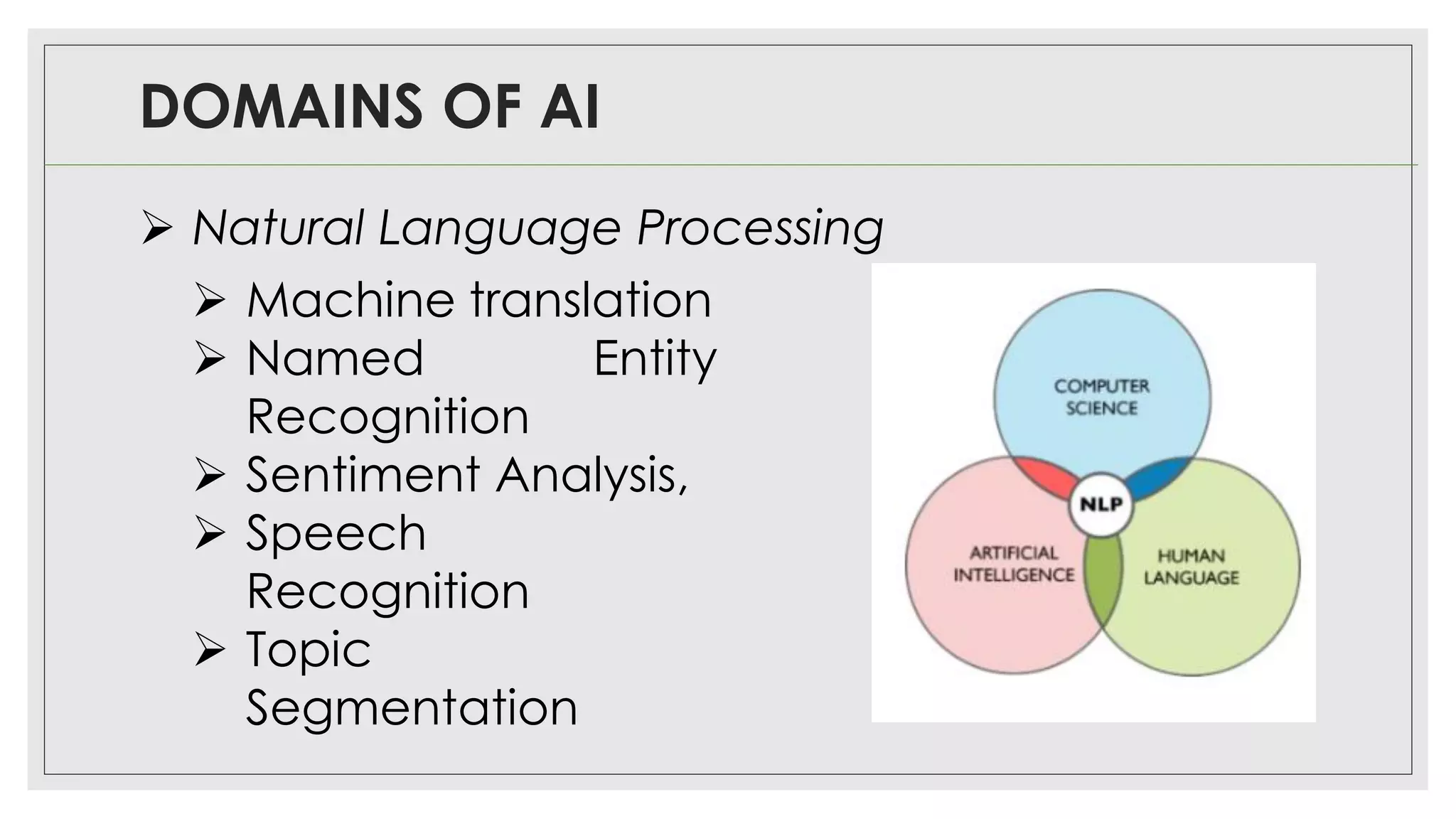
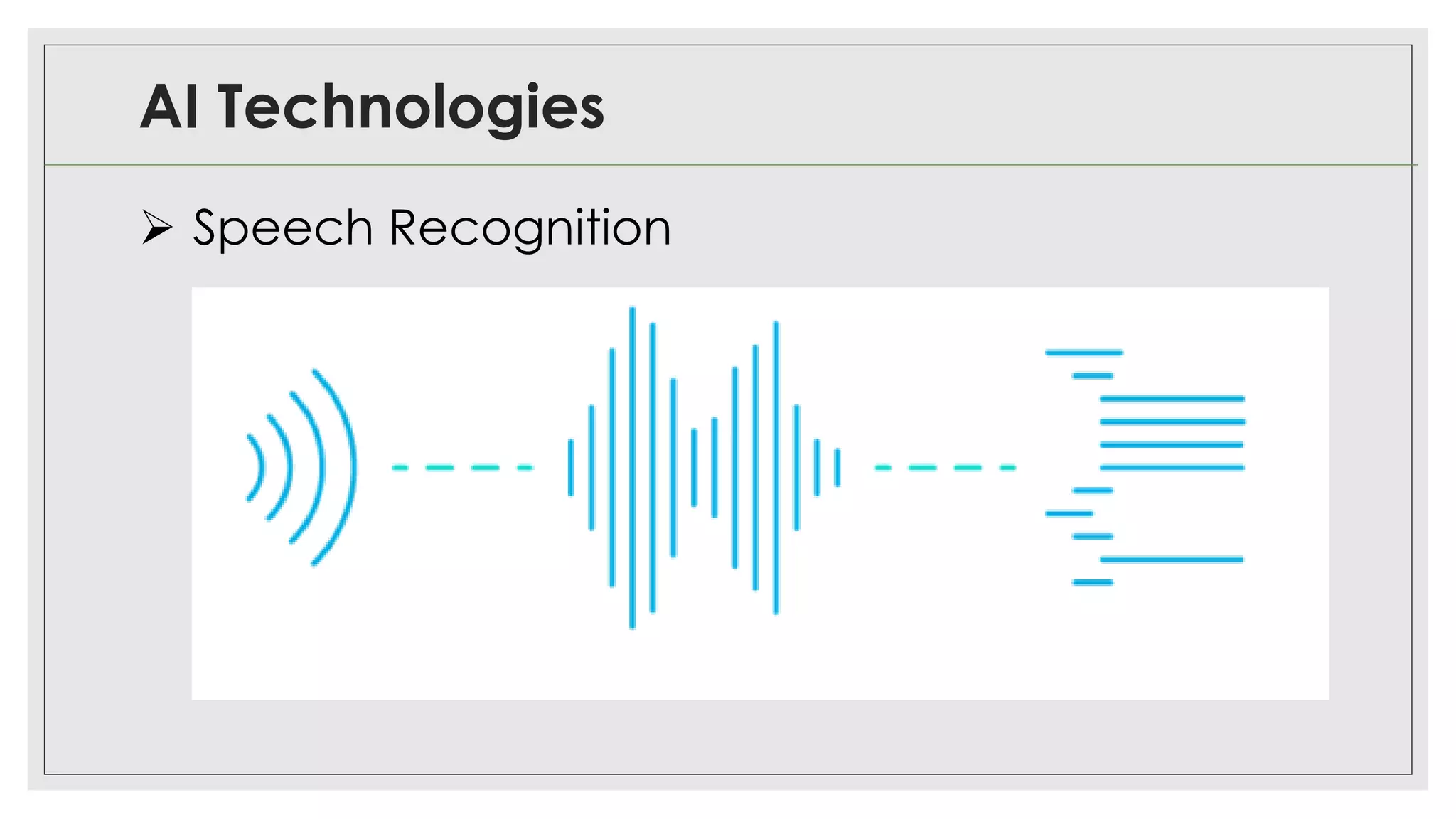
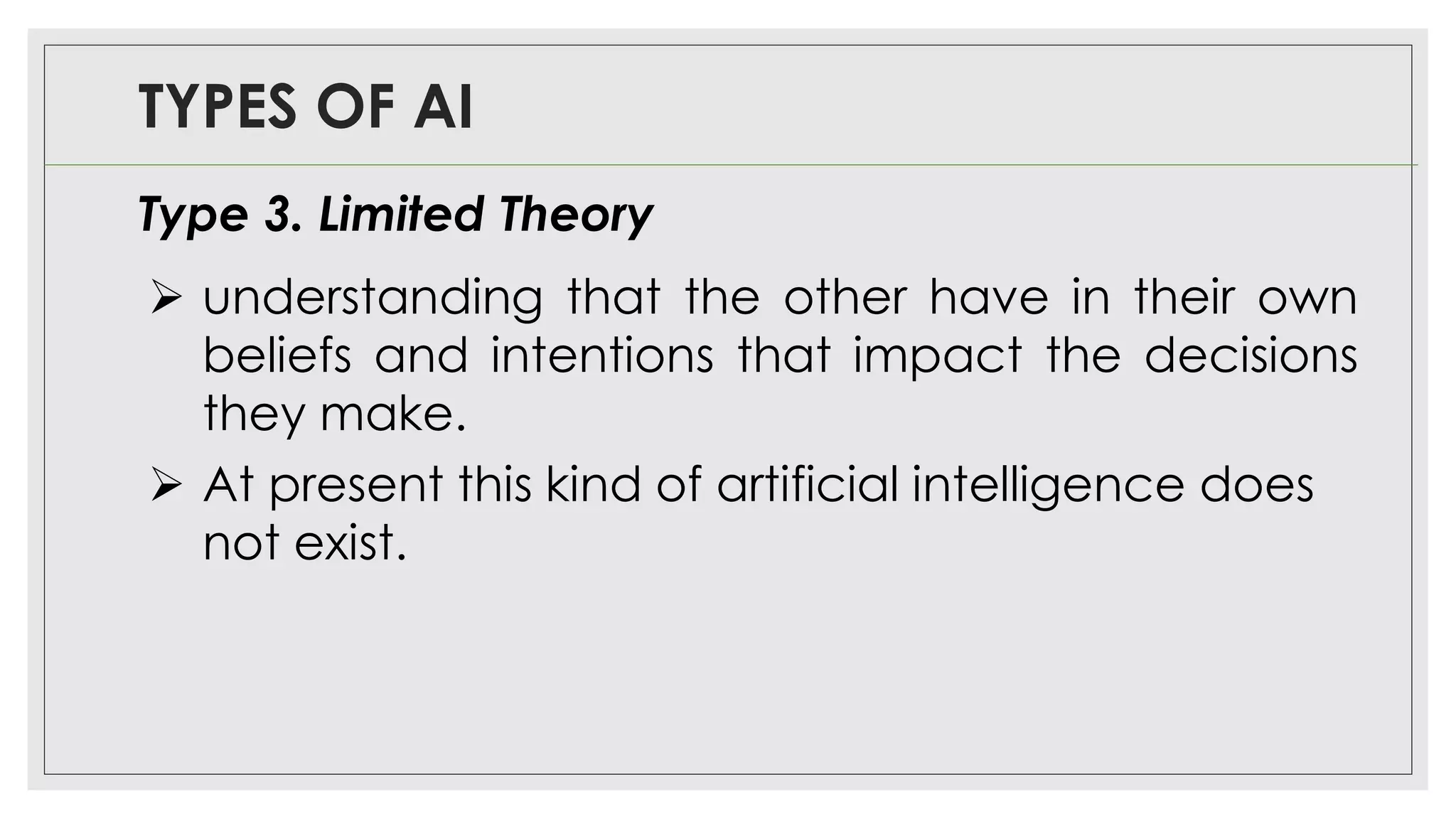
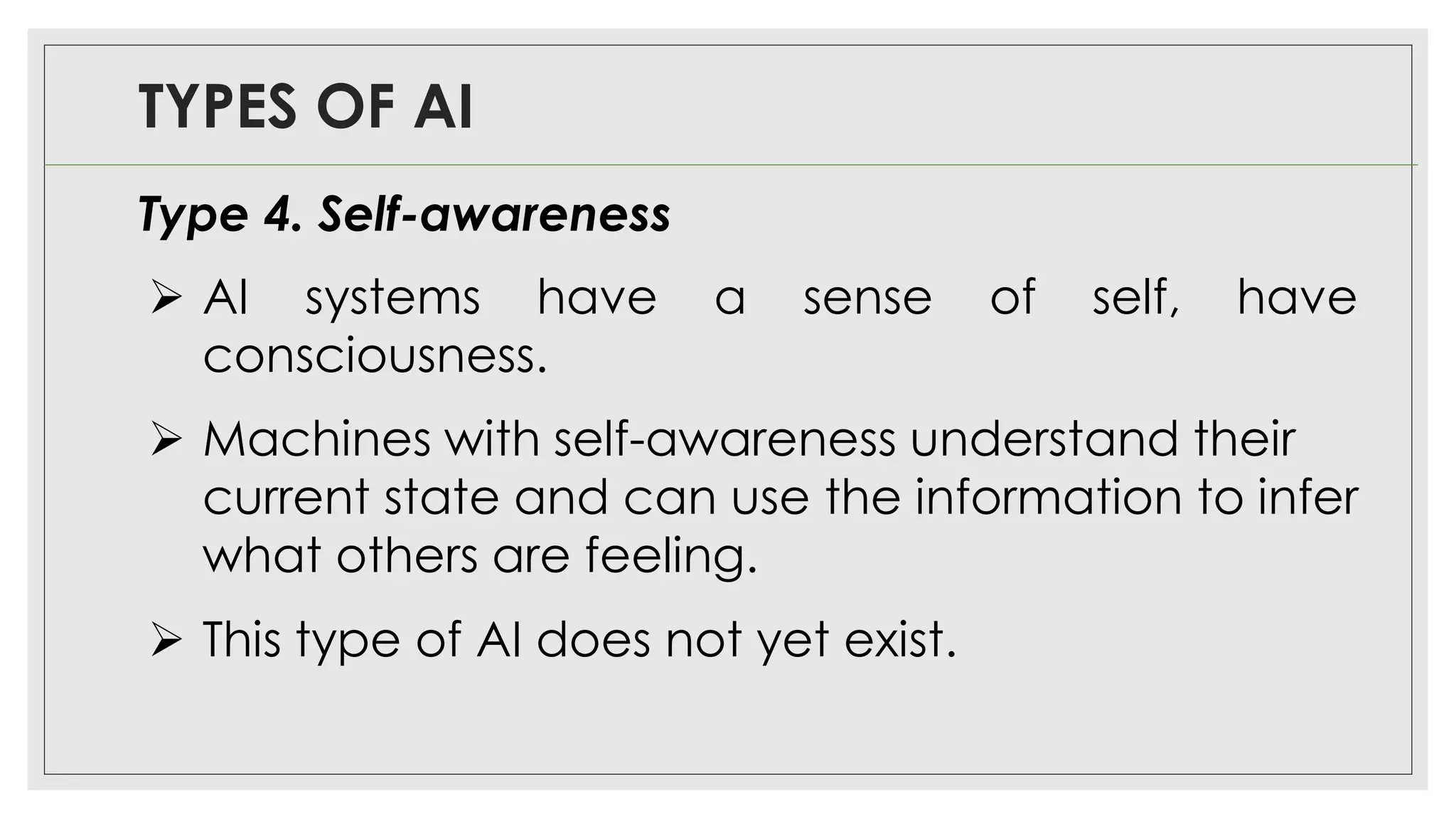
This document provides an overview of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms. It defines AI as using computer systems to mimic human intelligence through processes like visual perception, speech recognition, and decision-making. The document outlines different types of machine learning like deep learning and natural language processing. It also lists several applications of AI in fields such as healthcare, business, education, and autonomous vehicles. Finally, it categorizes different types of AI from reactive machines to the goal of developing self-aware systems.