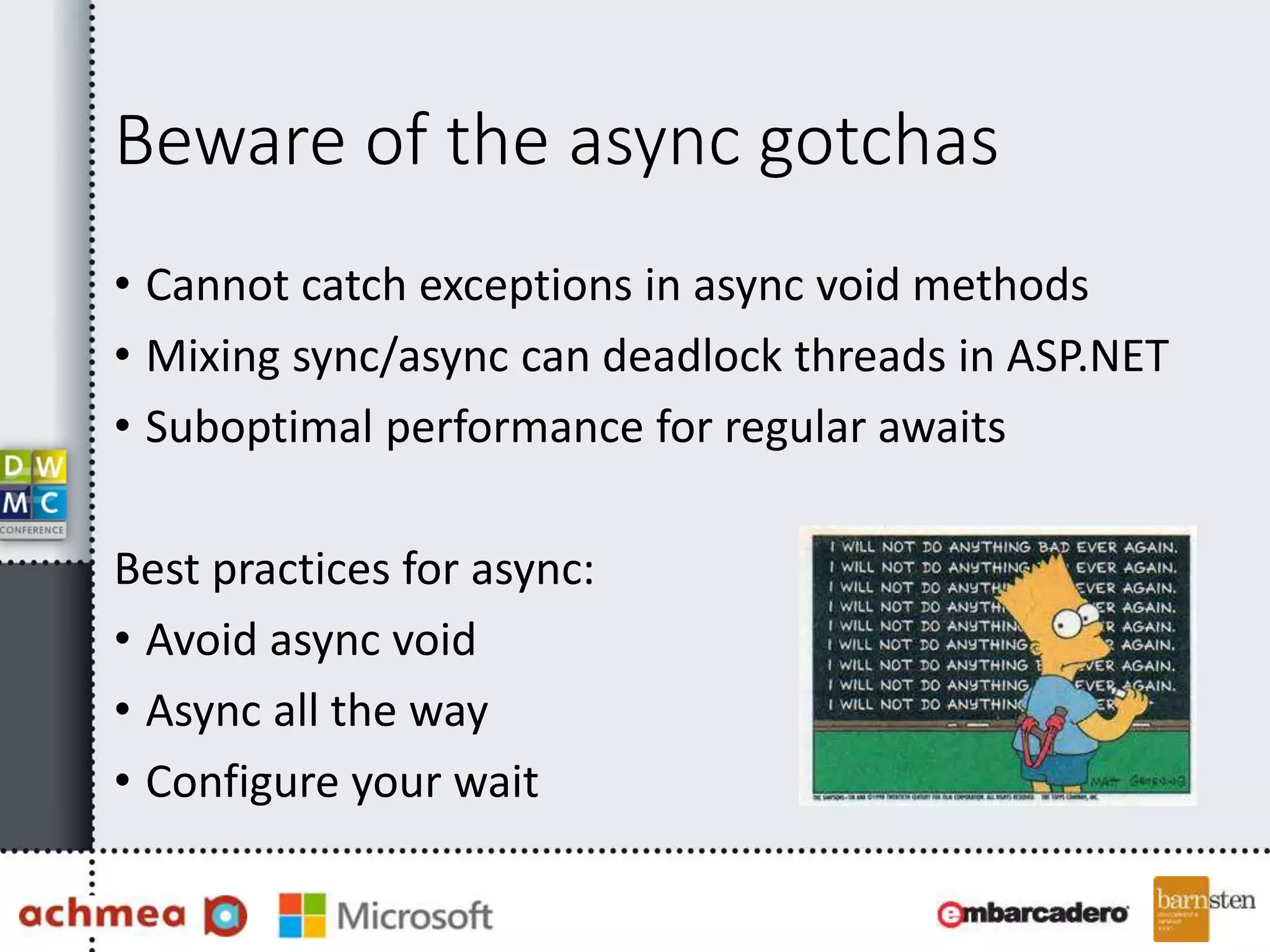
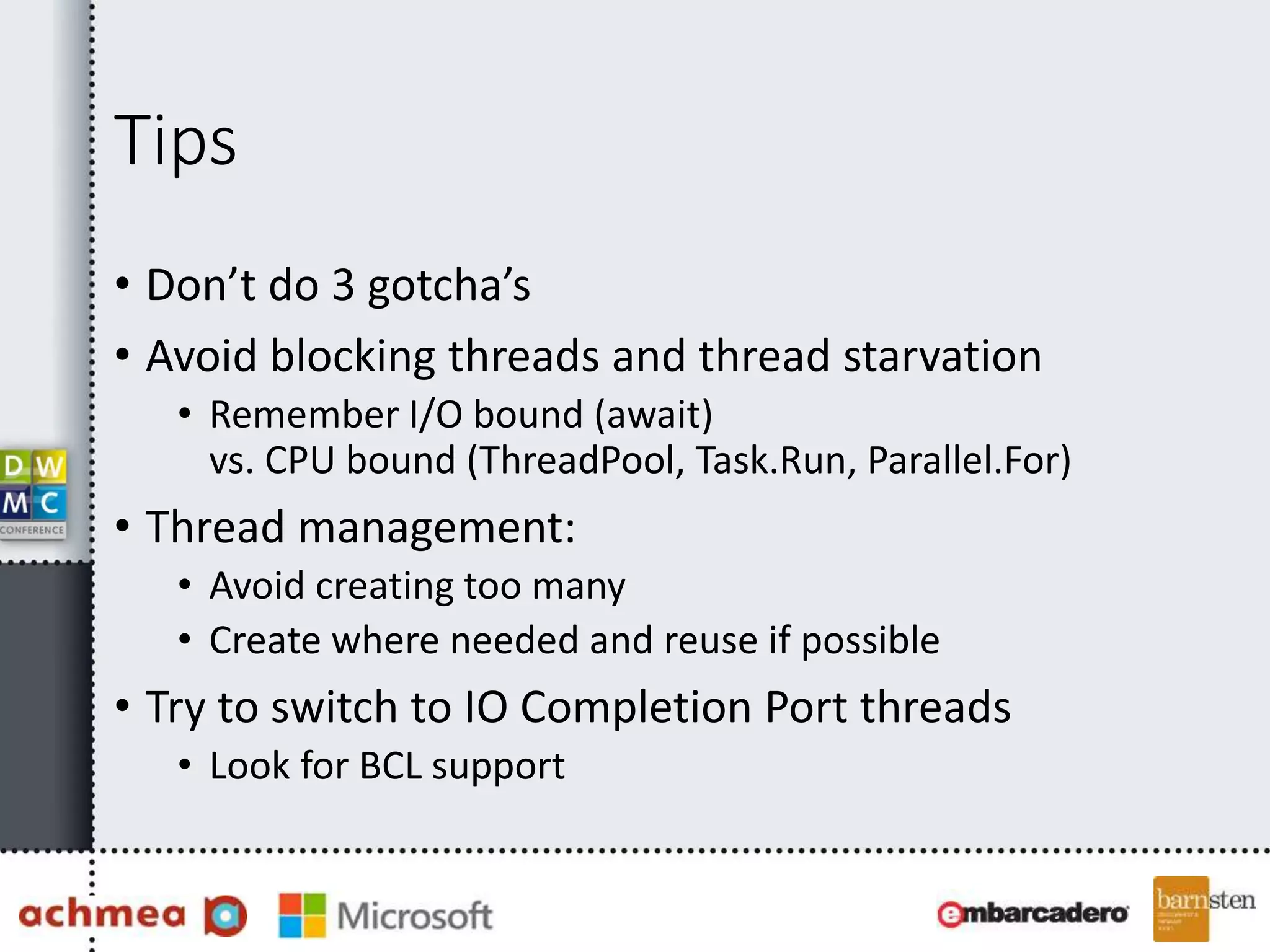
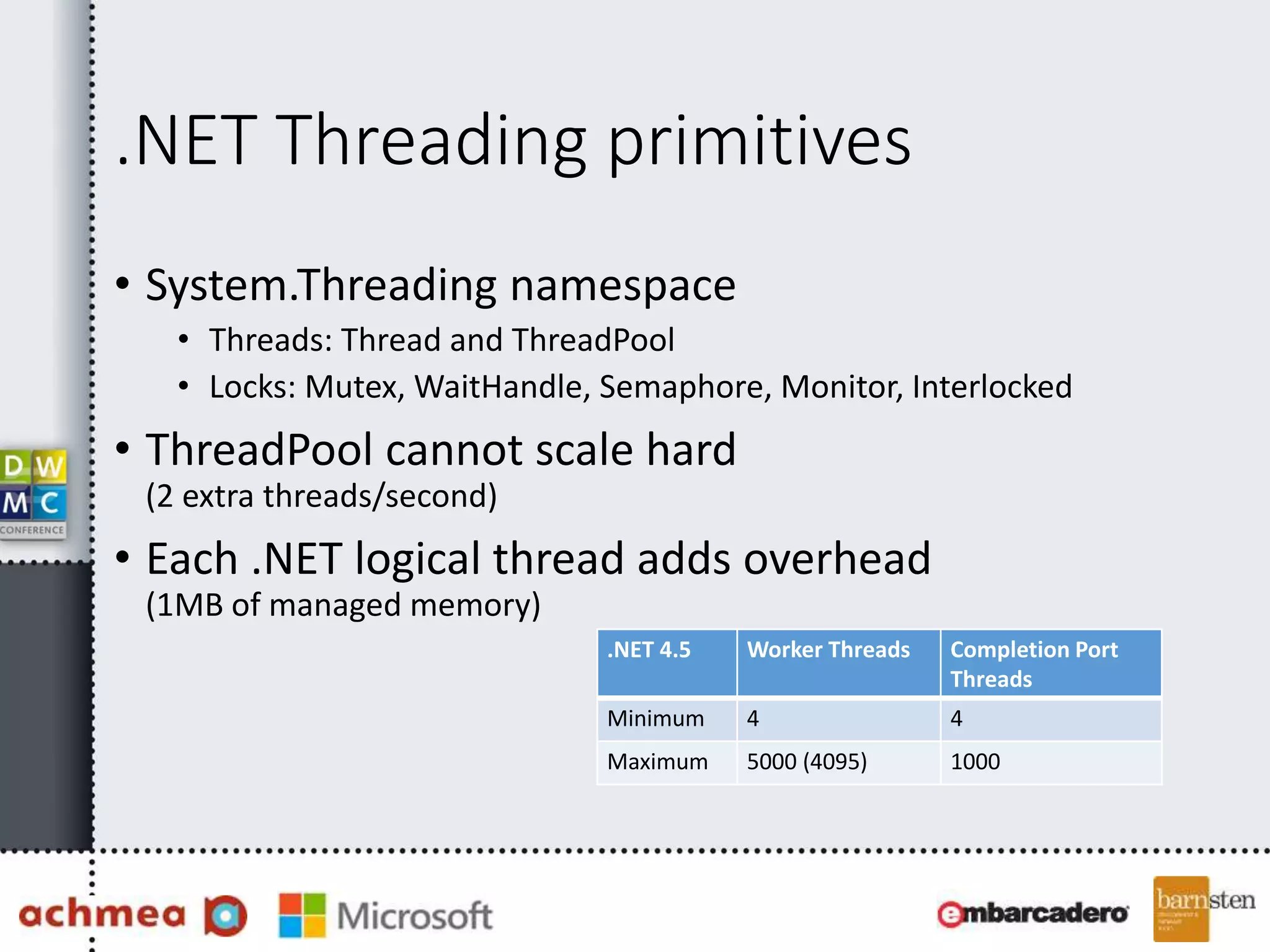
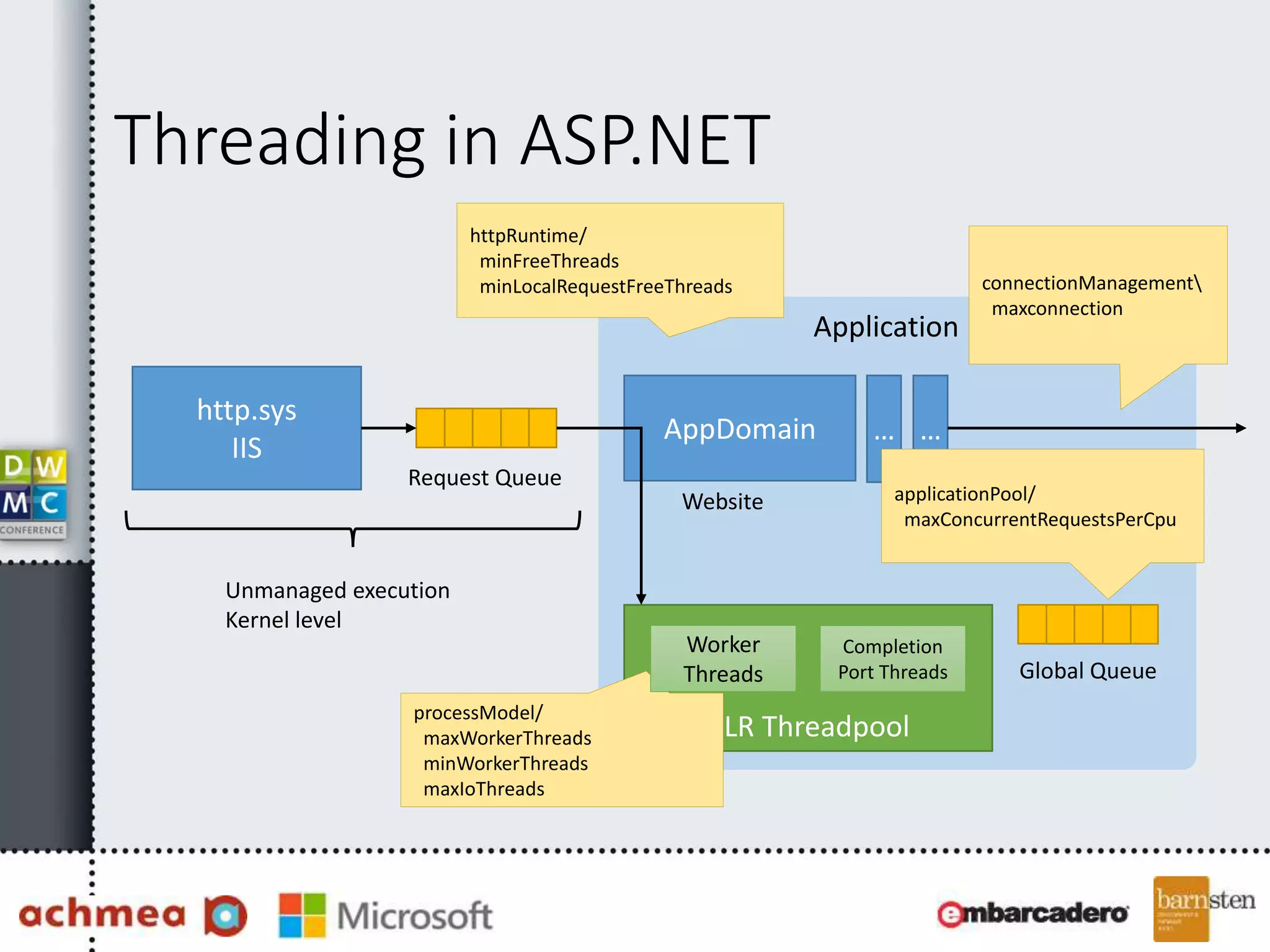
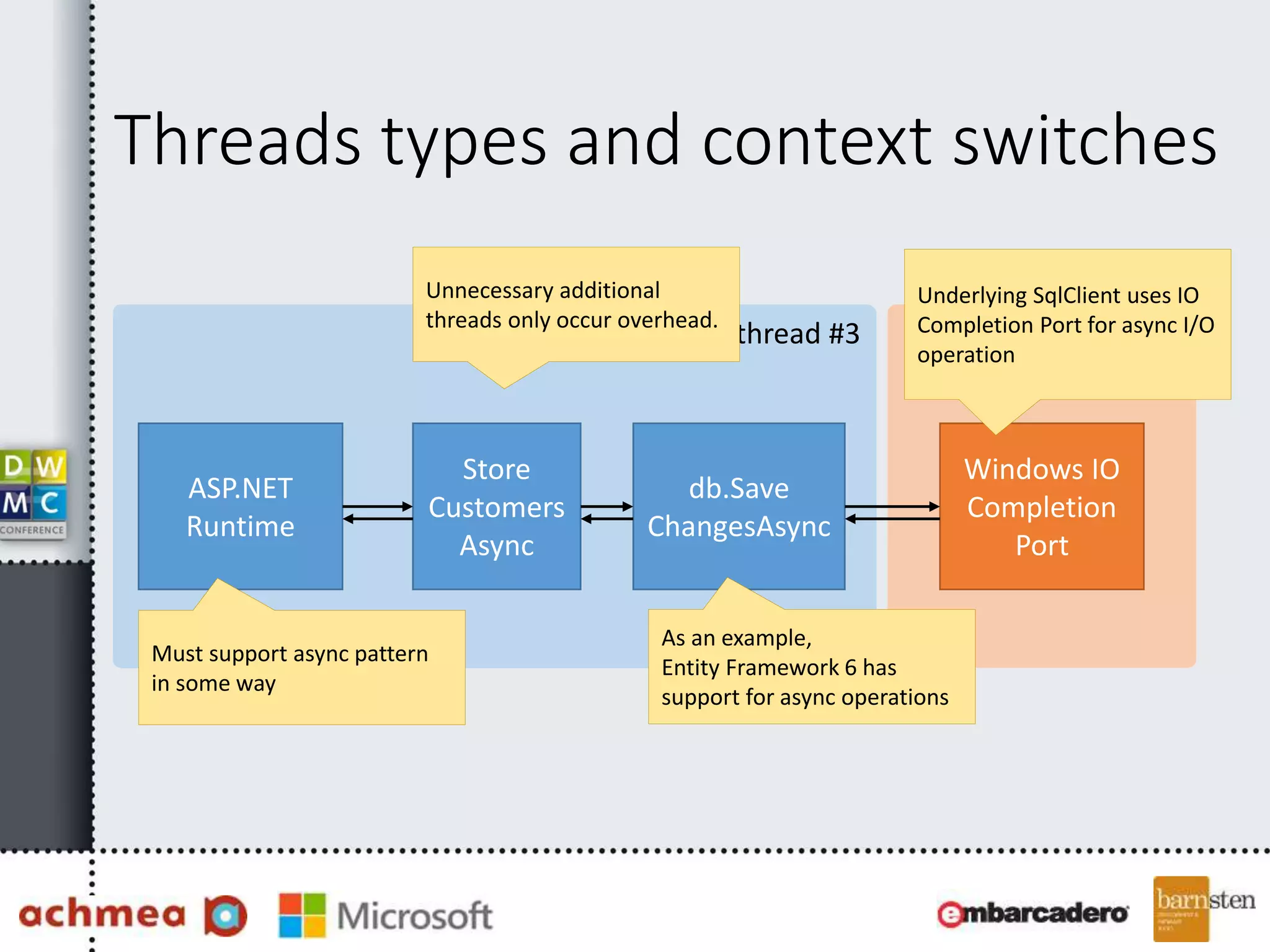
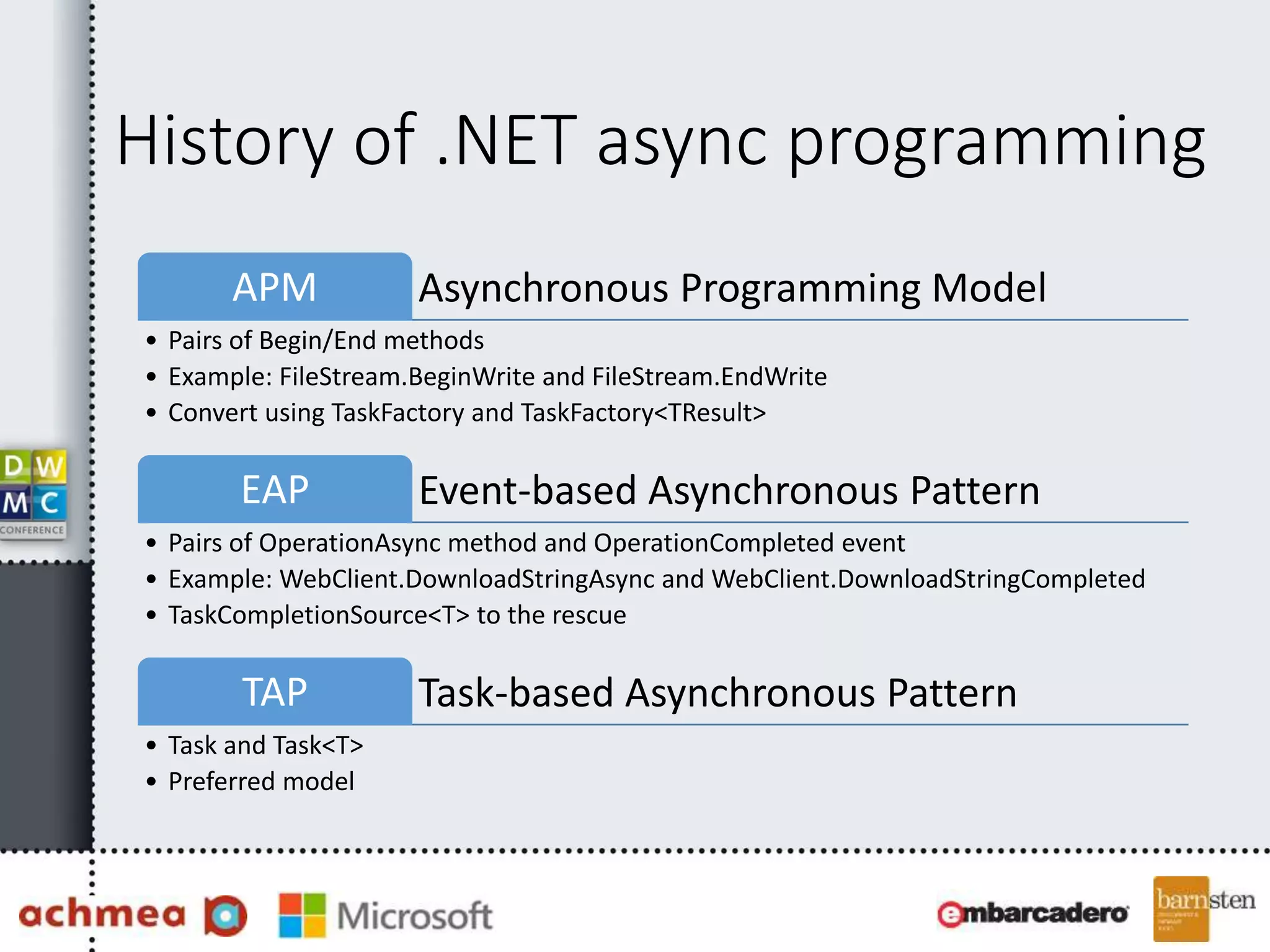
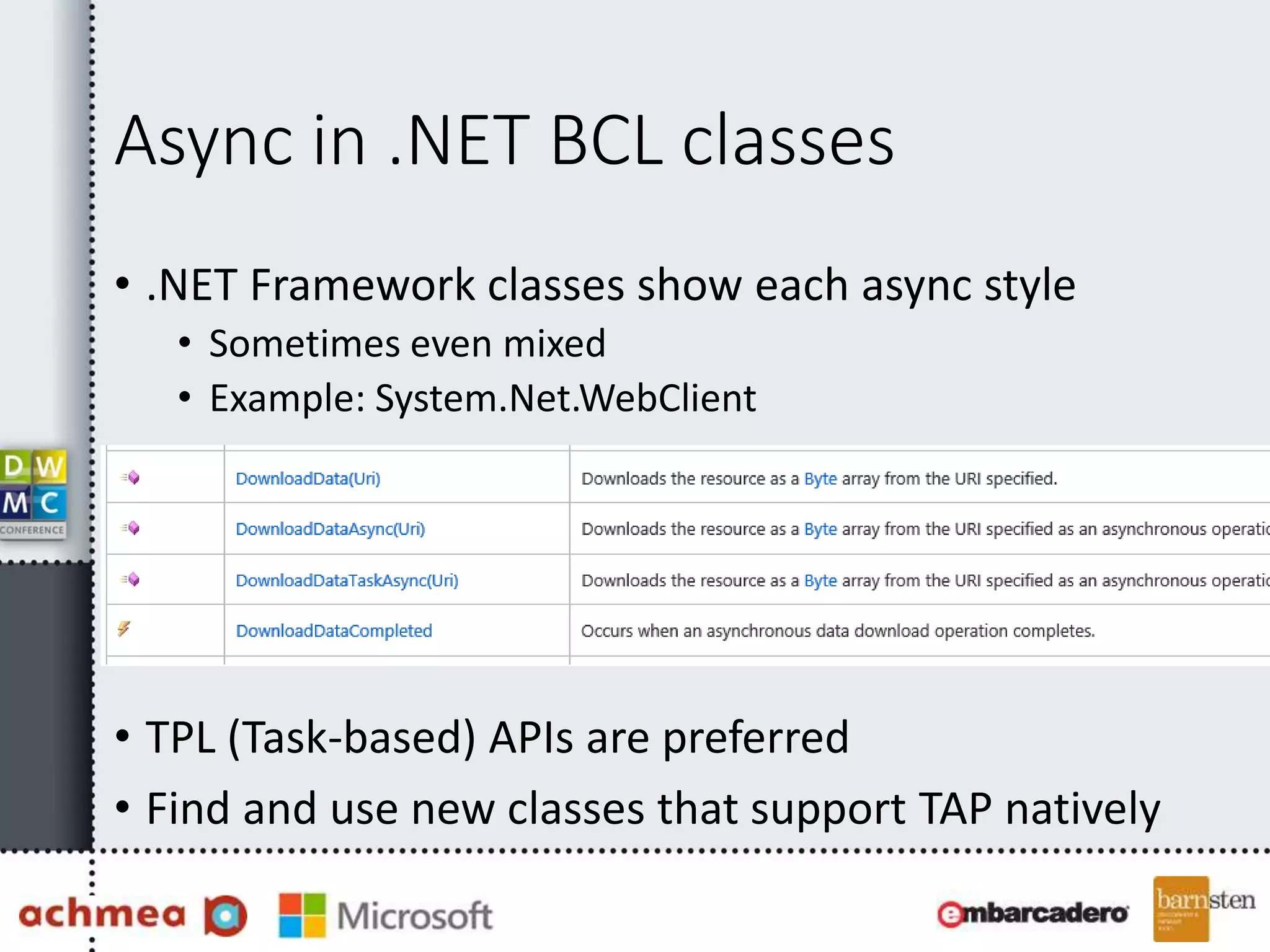
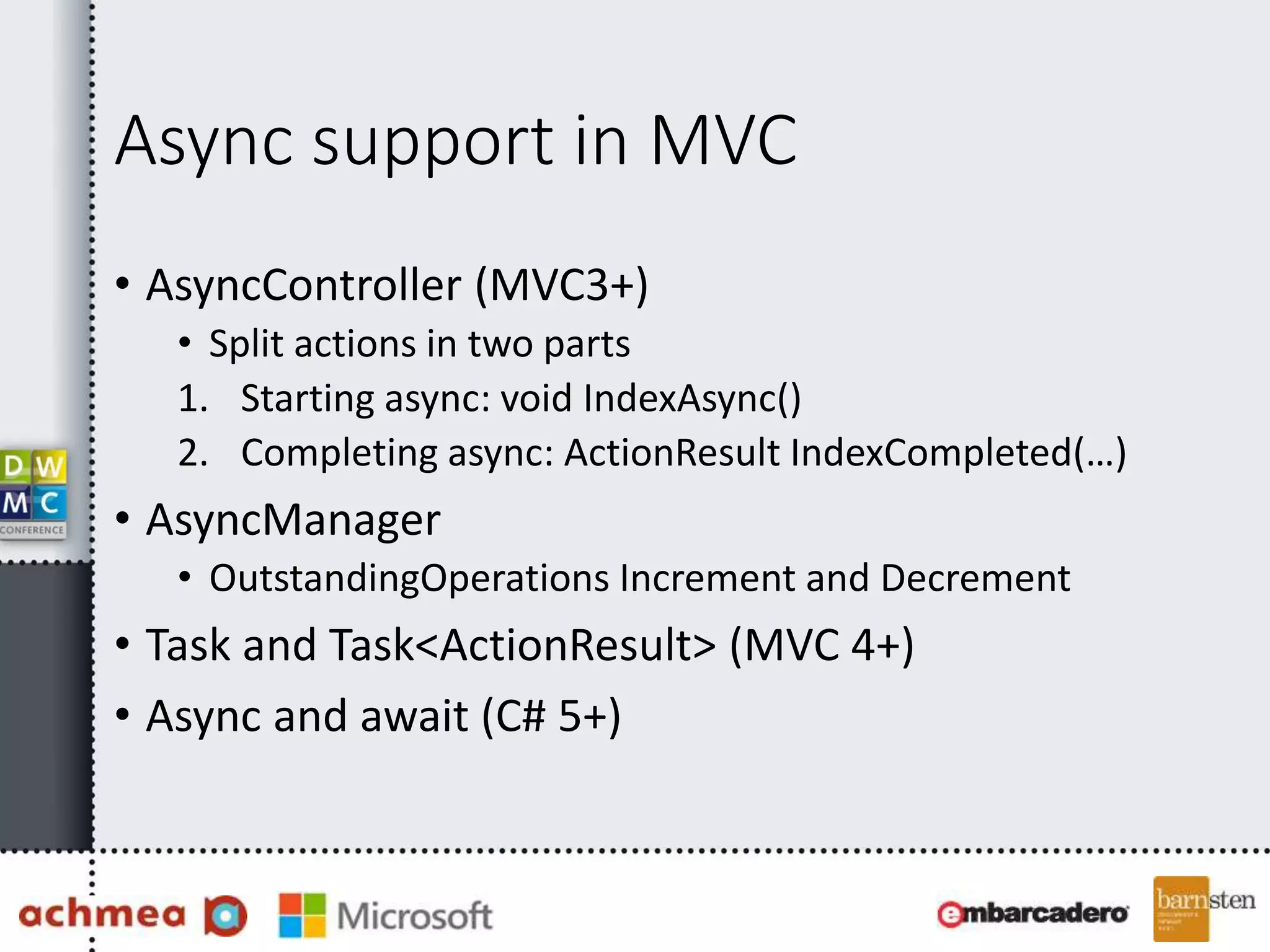
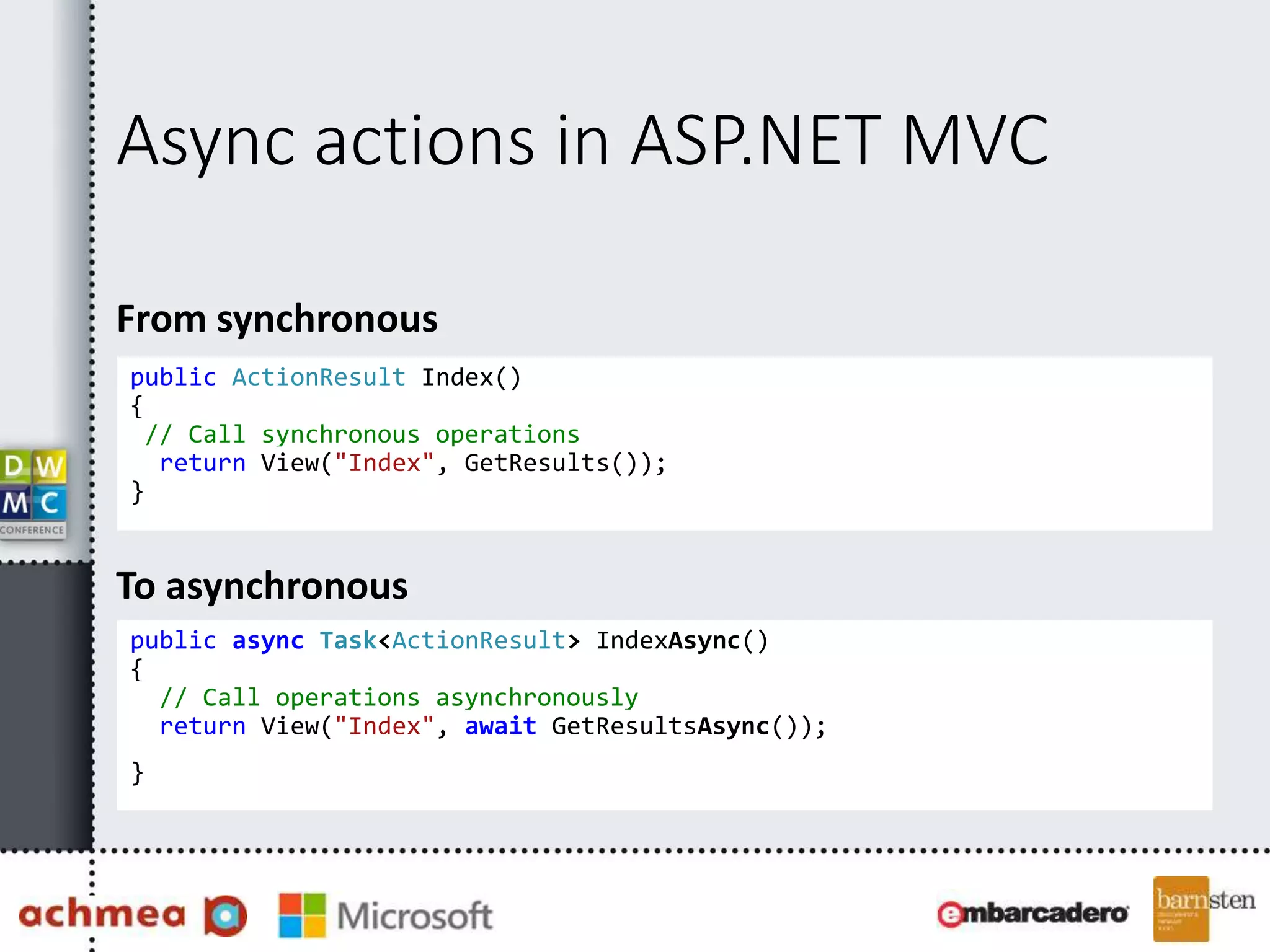
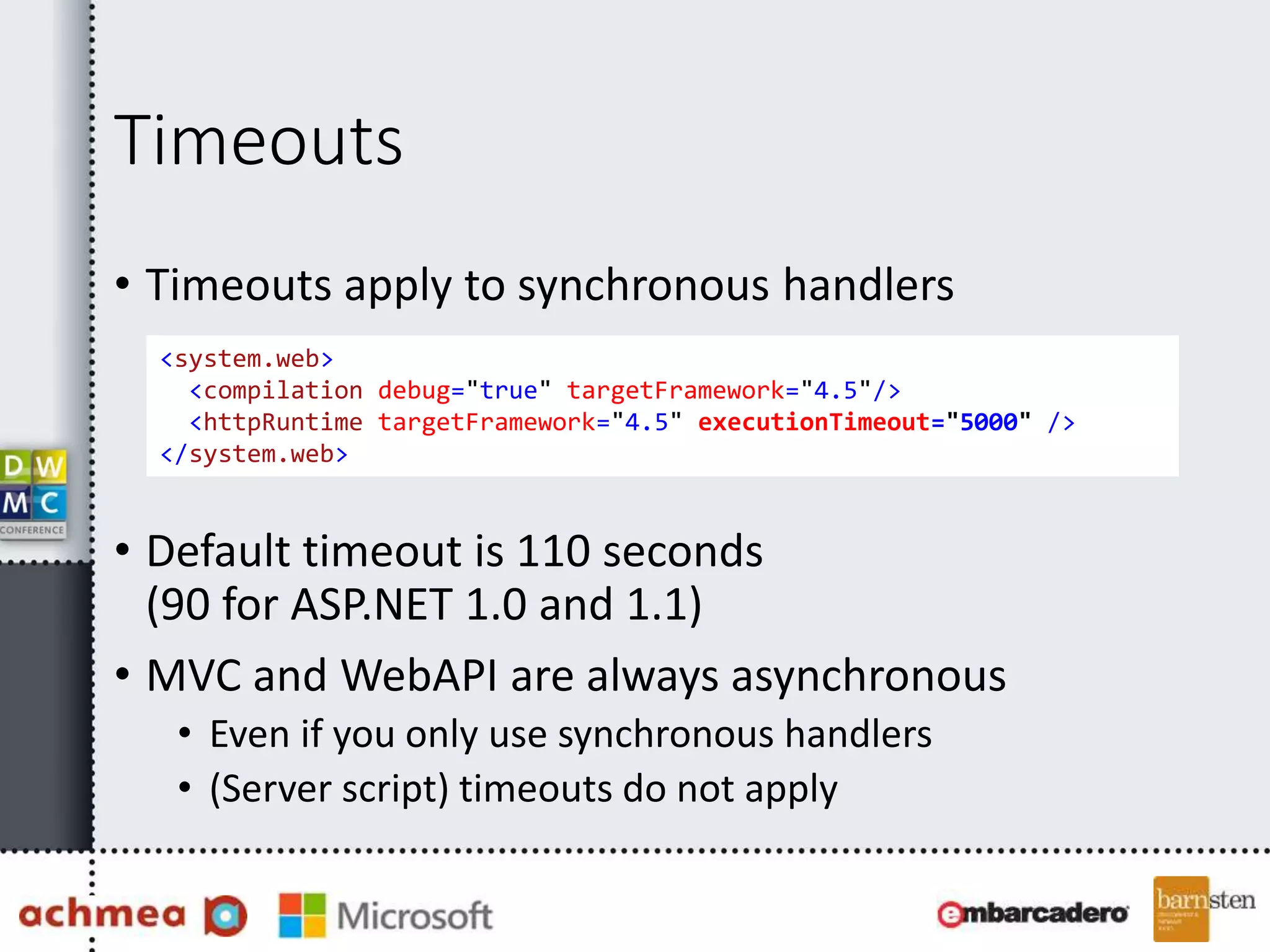
The document covers asynchronous programming in ASP.NET, emphasizing the differences between synchronous and asynchronous operations, threading concepts, and the various async patterns supported by the .NET framework. It details implementations in ASP.NET WebForms, MVC, and WebAPI, including best practices and potential pitfalls. Key topics include handling timeouts, optimizing thread management, and ensuring performance through proper async usage.










![Timeouts in MVC and WebAPI
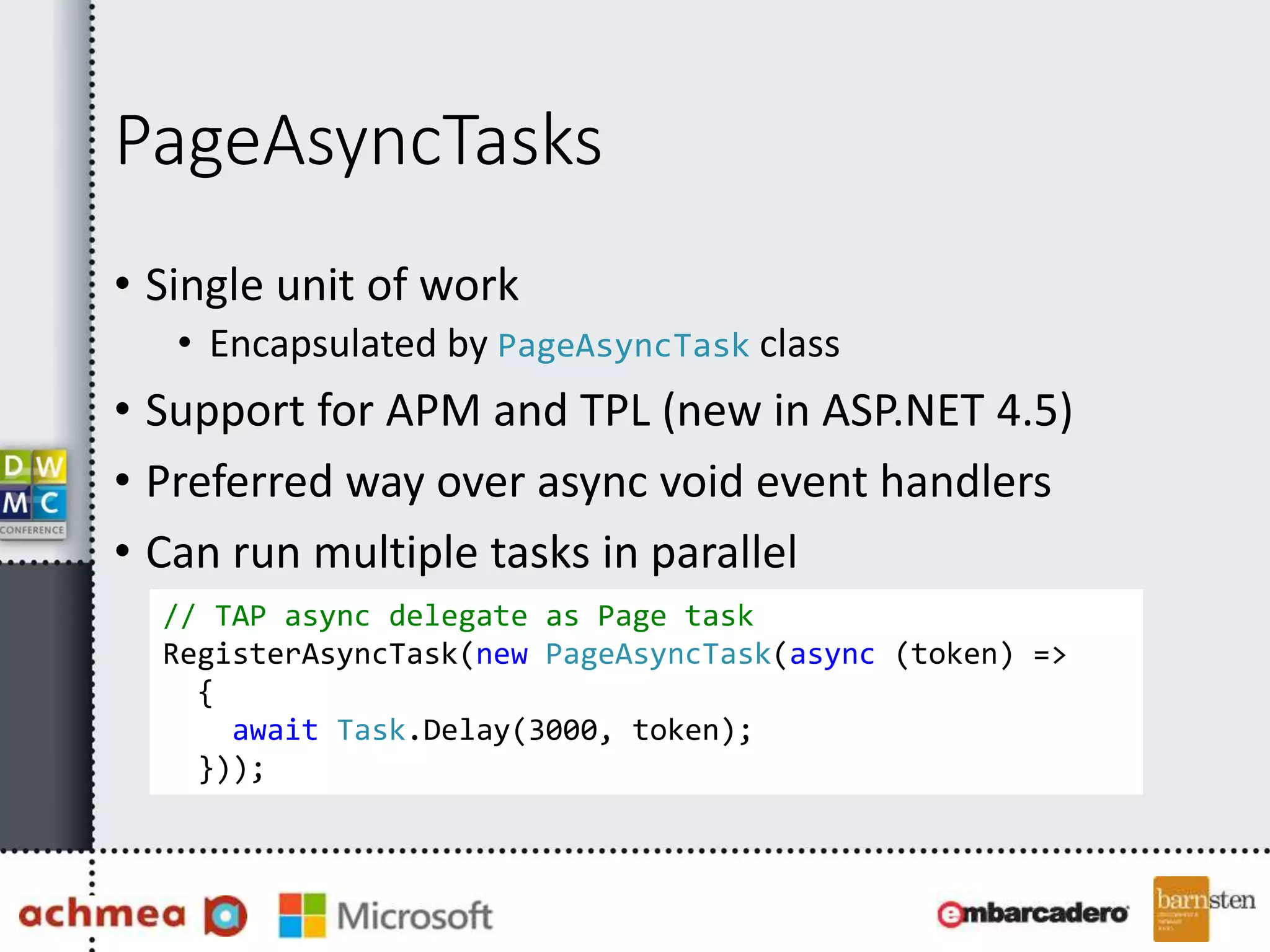
• Use AsyncTimeoutAttribute on async actions
• When timeout occurs TimeoutException is thrown
from action
• Default timeout is AsyncManager’s 45000 milliseconds
• Might want to catch errors
[AsyncTimeout(2000)]
[HandleError(ExceptionType=typeof(TimeoutException))]
public async Task<ActionResult> SomeMethodAsync(CancellationToken token)
{
// Pass down CancellationToken to other async method calls
…
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/asynchronousprogramminginasp-160724223206/75/Asynchronous-programming-in-ASP-NET-26-2048.jpg)