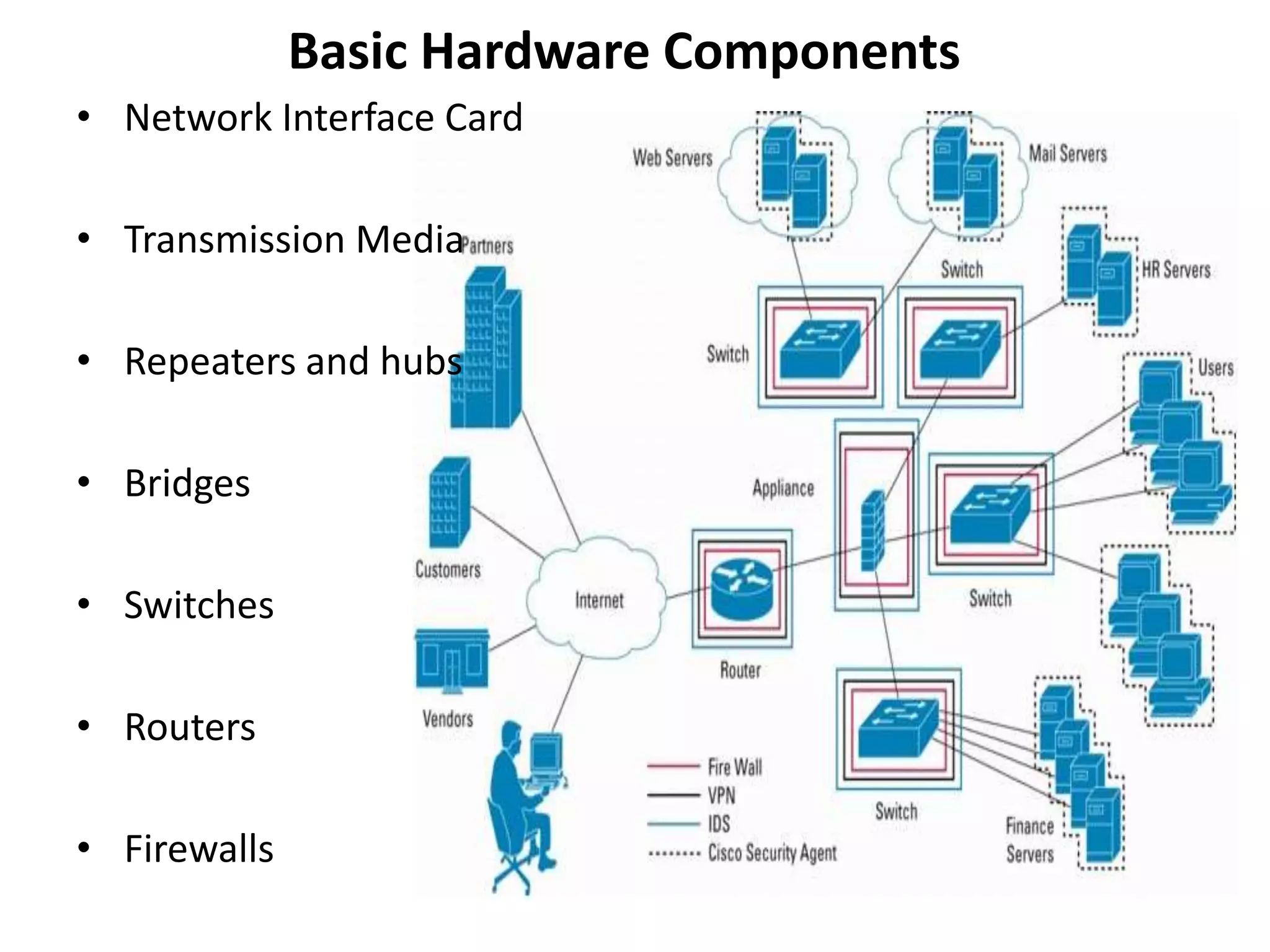
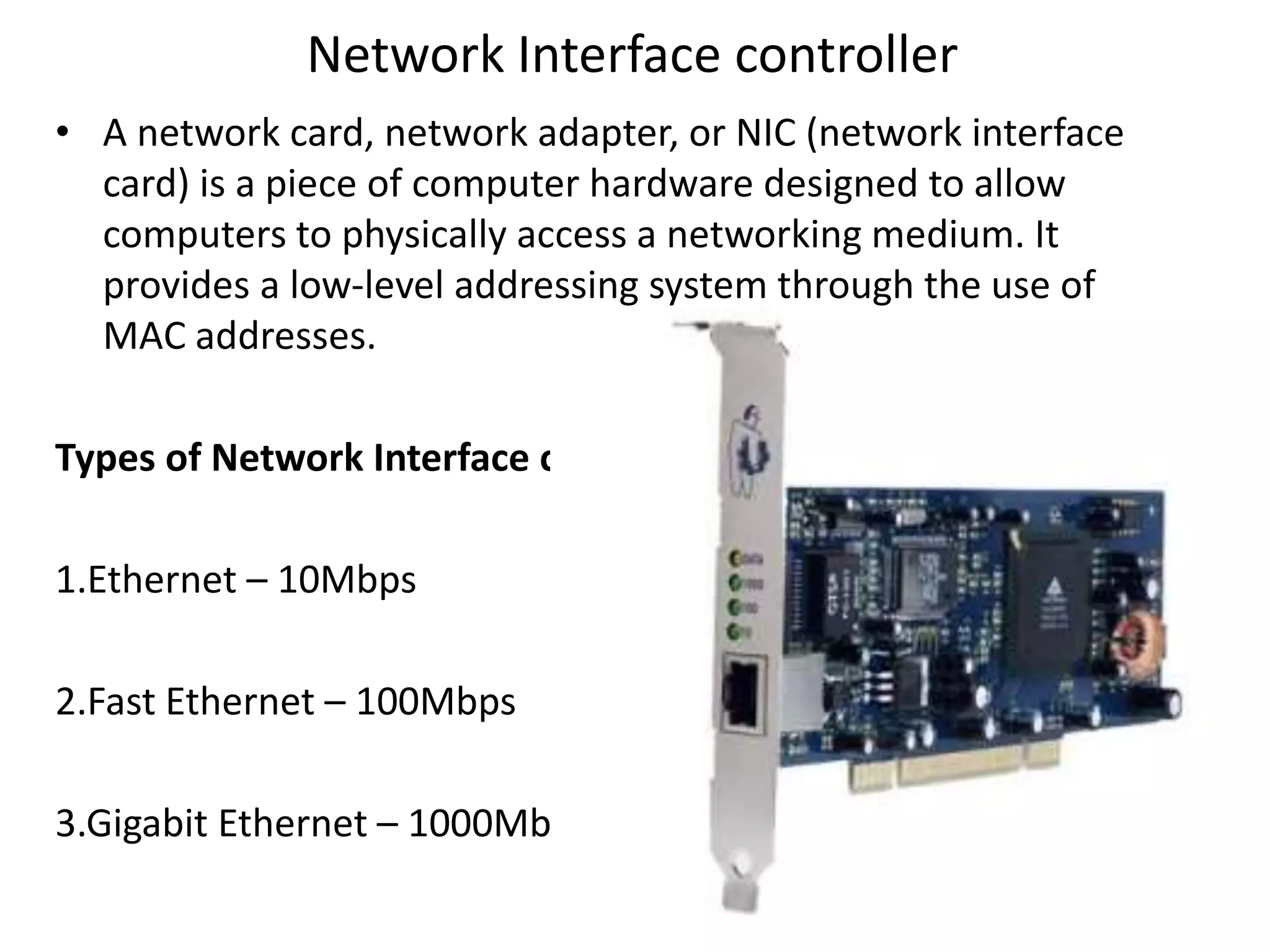
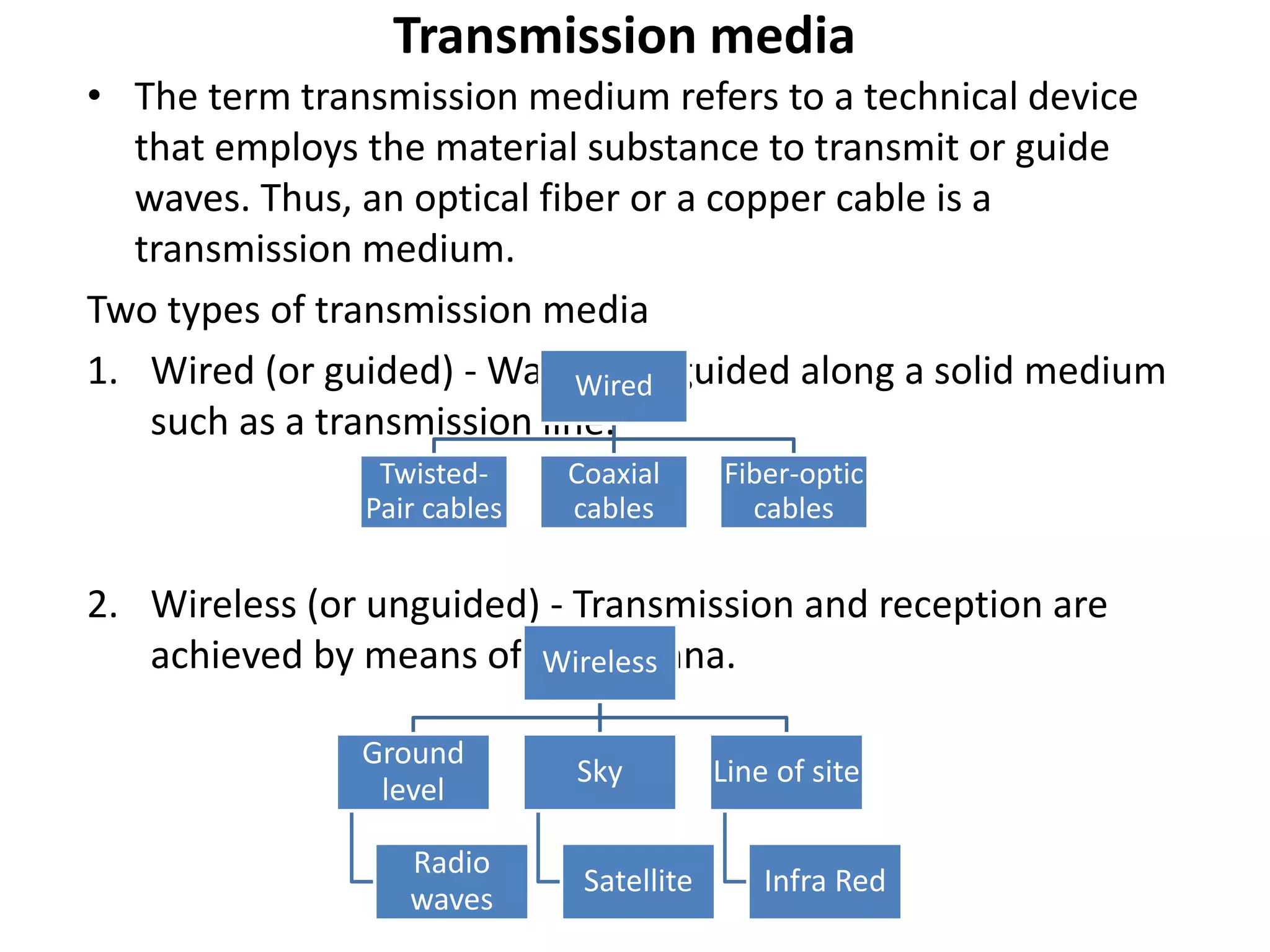
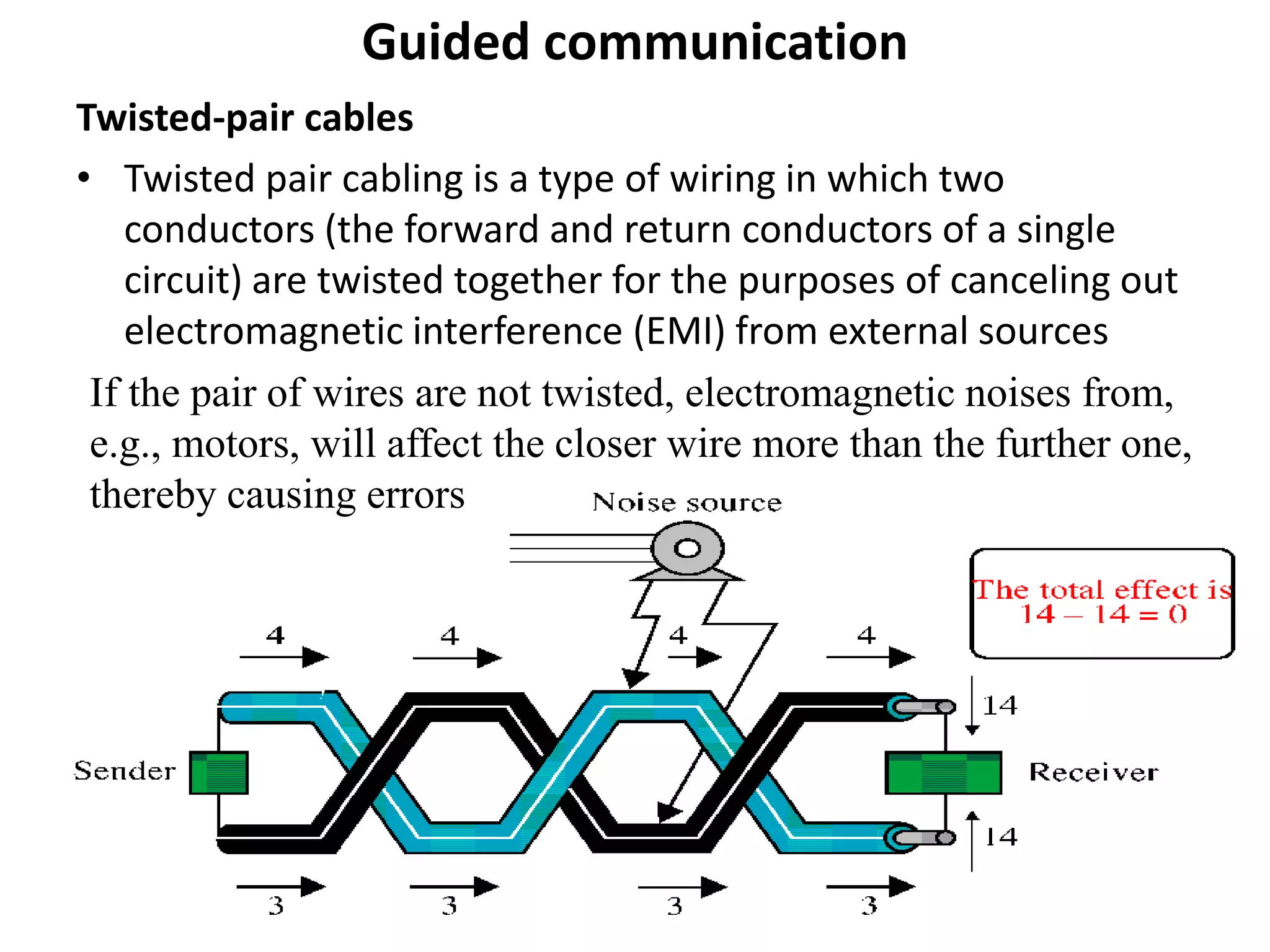
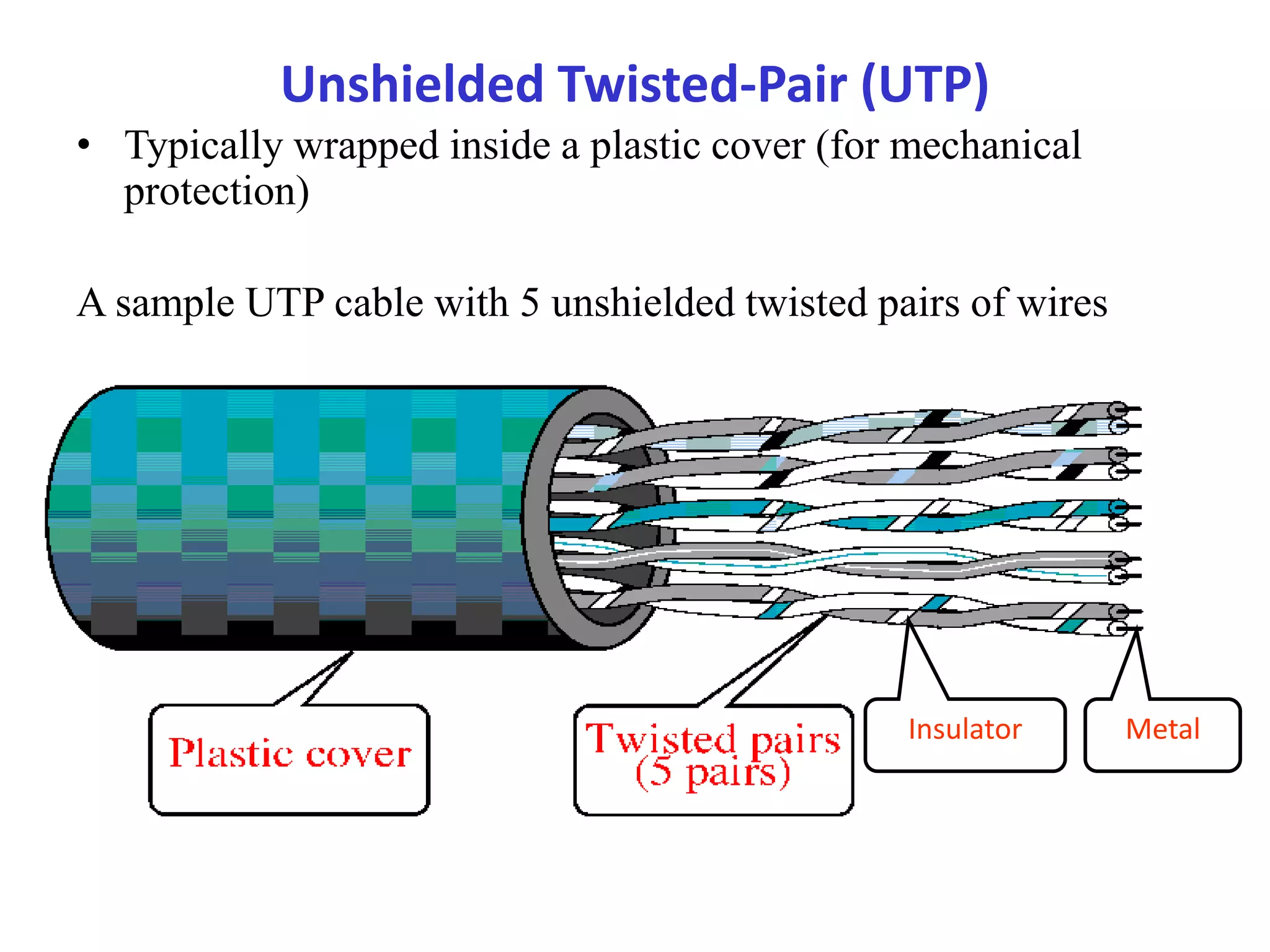
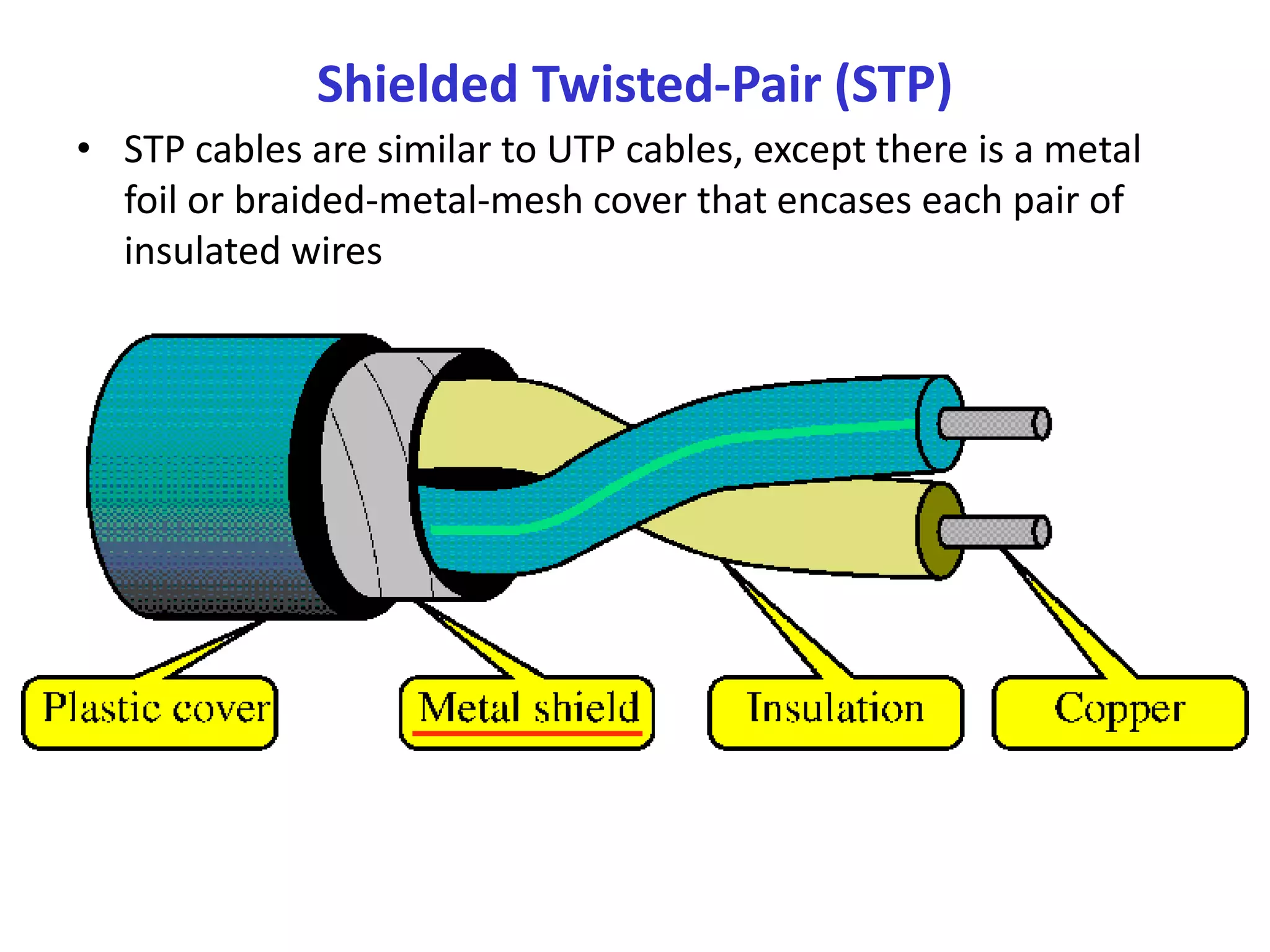
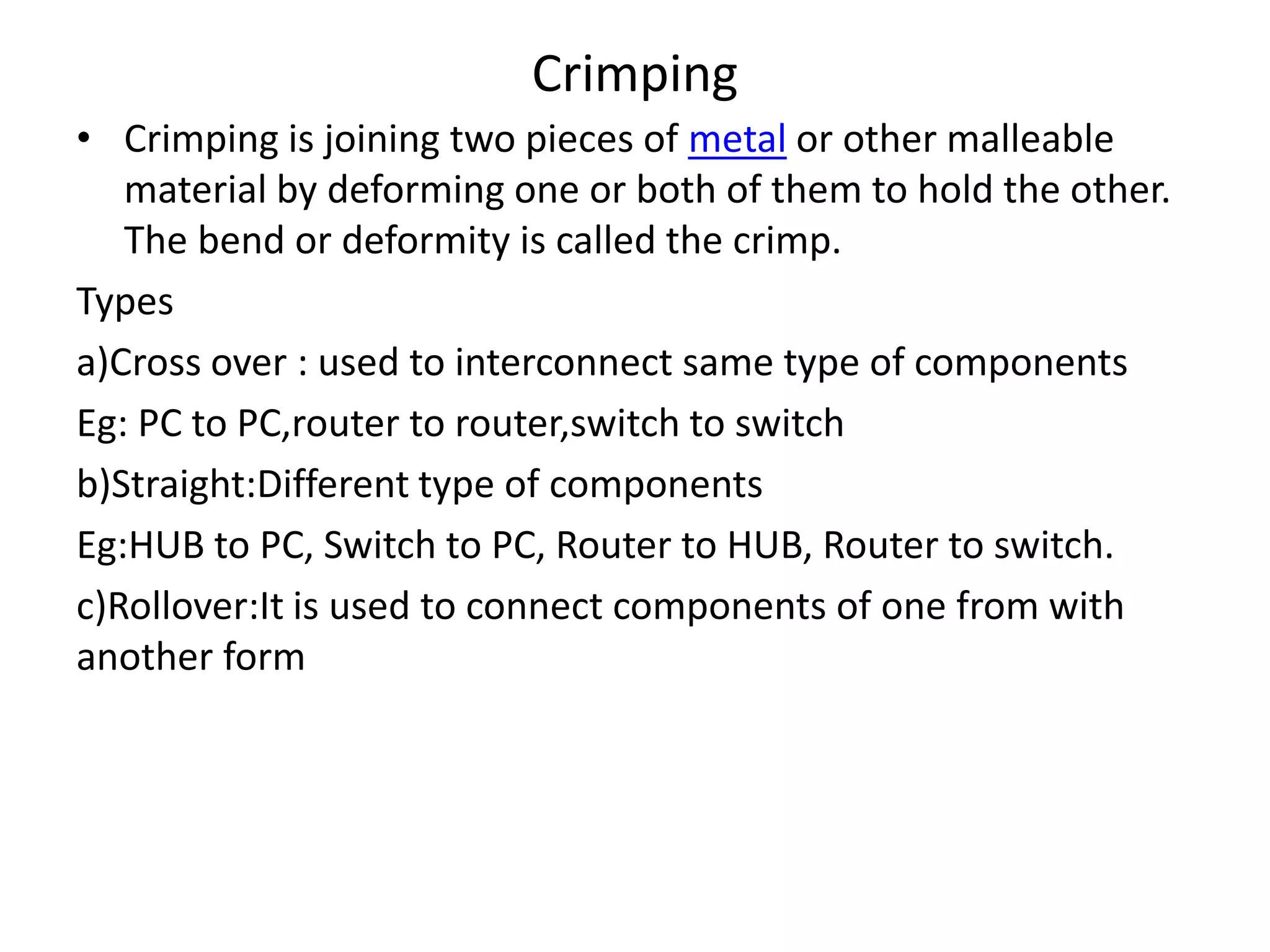
A network consists of two or more connected computers that can share resources. There are different types of networks including LAN, MAN, and WAN depending on the geographical area covered. Basic hardware components of a network include network interface cards, transmission media, repeaters, hubs, bridges, switches, routers, and firewalls. Network interface cards allow computers to physically connect to a network and have MAC addresses to provide low-level addressing. Wired transmission media include twisted-pair cables, coaxial cables, and fiber-optic cables while wireless includes radio waves, satellites, and infrared. Common networking terminology includes protocols like Telnet, ARP, SNMP, and DHCP.