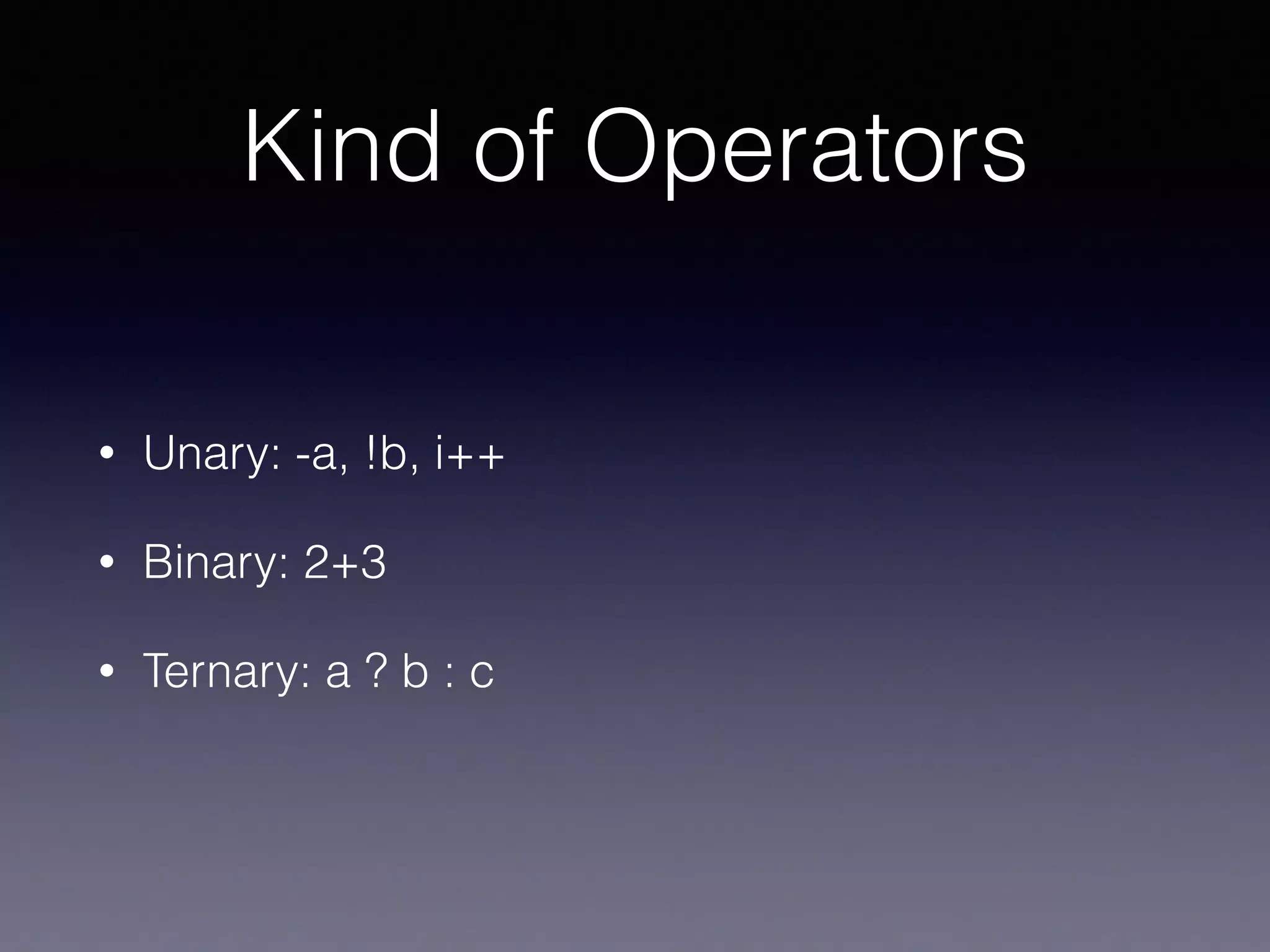
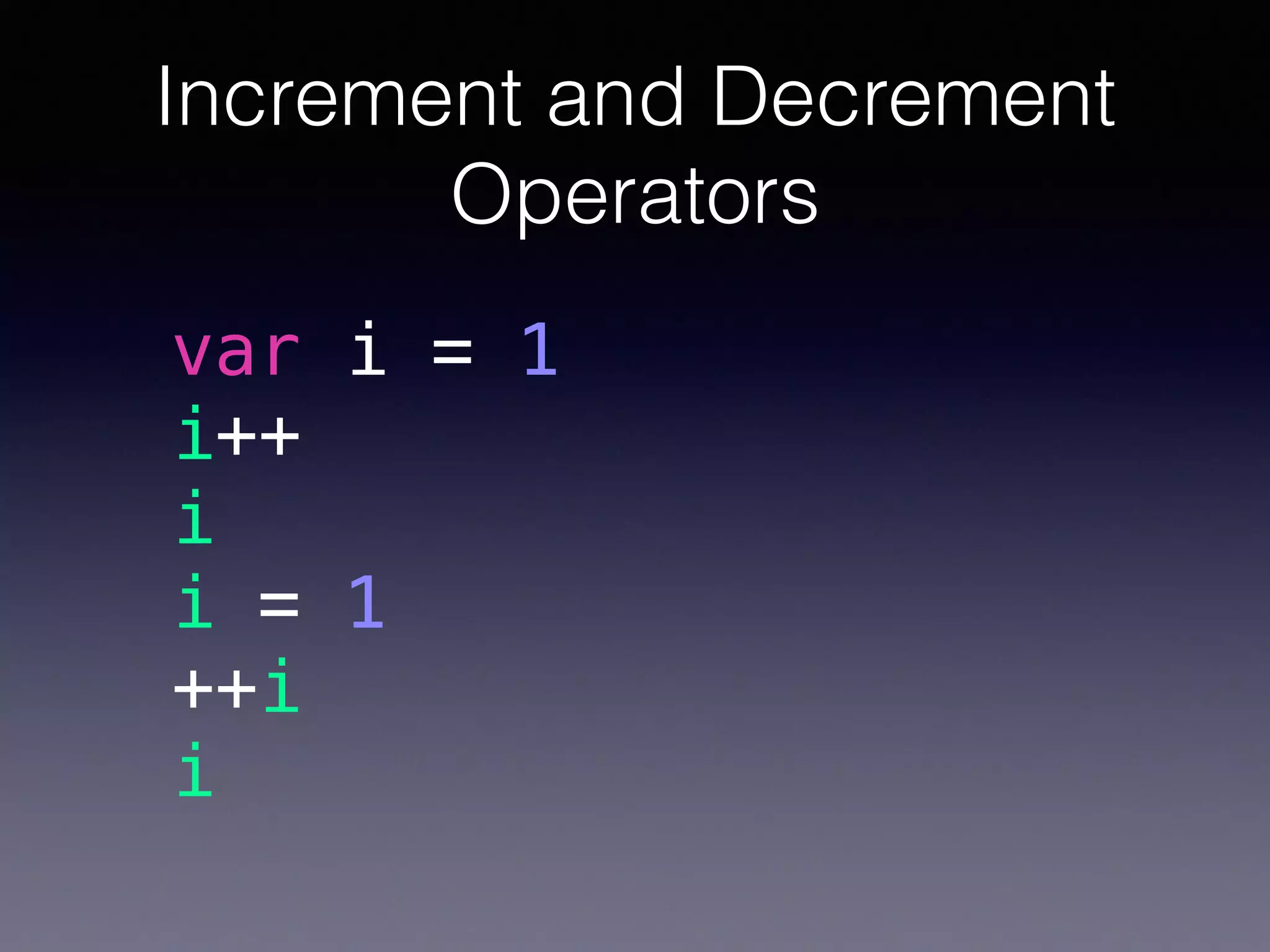
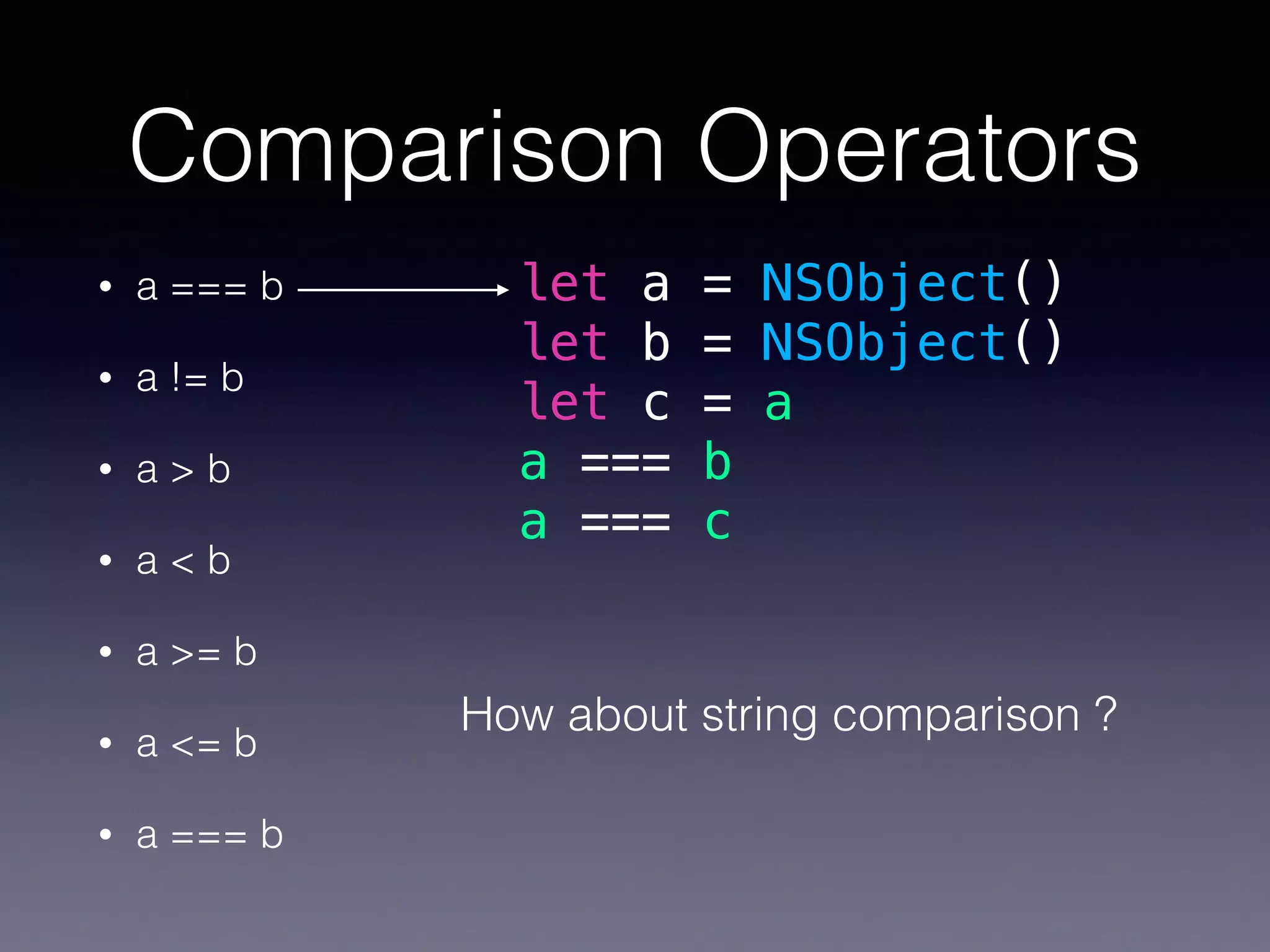
This document summarizes basic Swift operators, strings, and characters. It covers unary, binary, ternary, assignment, arithmetic, comparison, increment/decrement, and special operators. It also discusses strings as collections of characters, string interpolation, accessing and modifying strings, counting characters, and Unicode representations. The document is intended as part of a Swift study group on these basic Swift concepts.