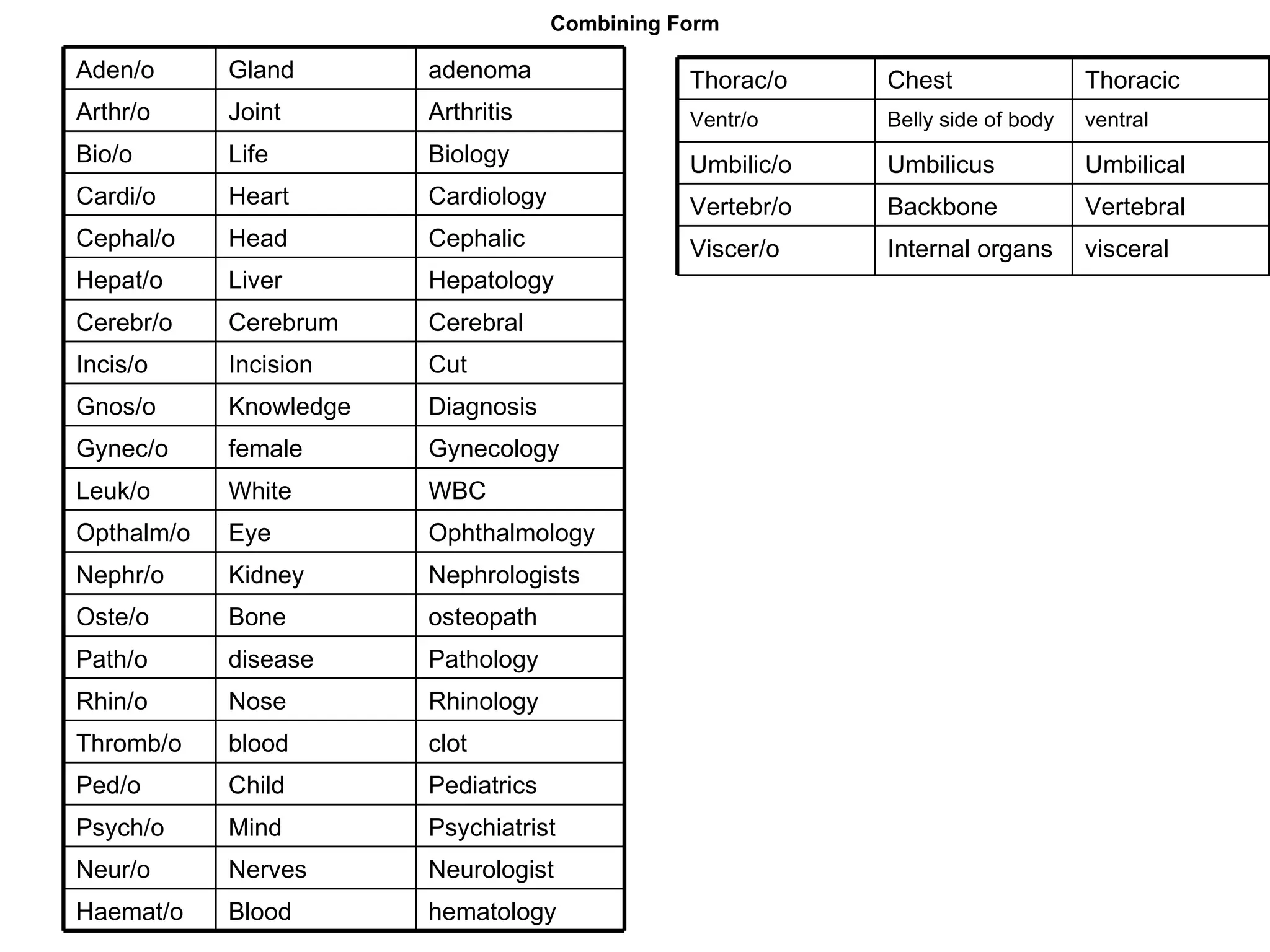
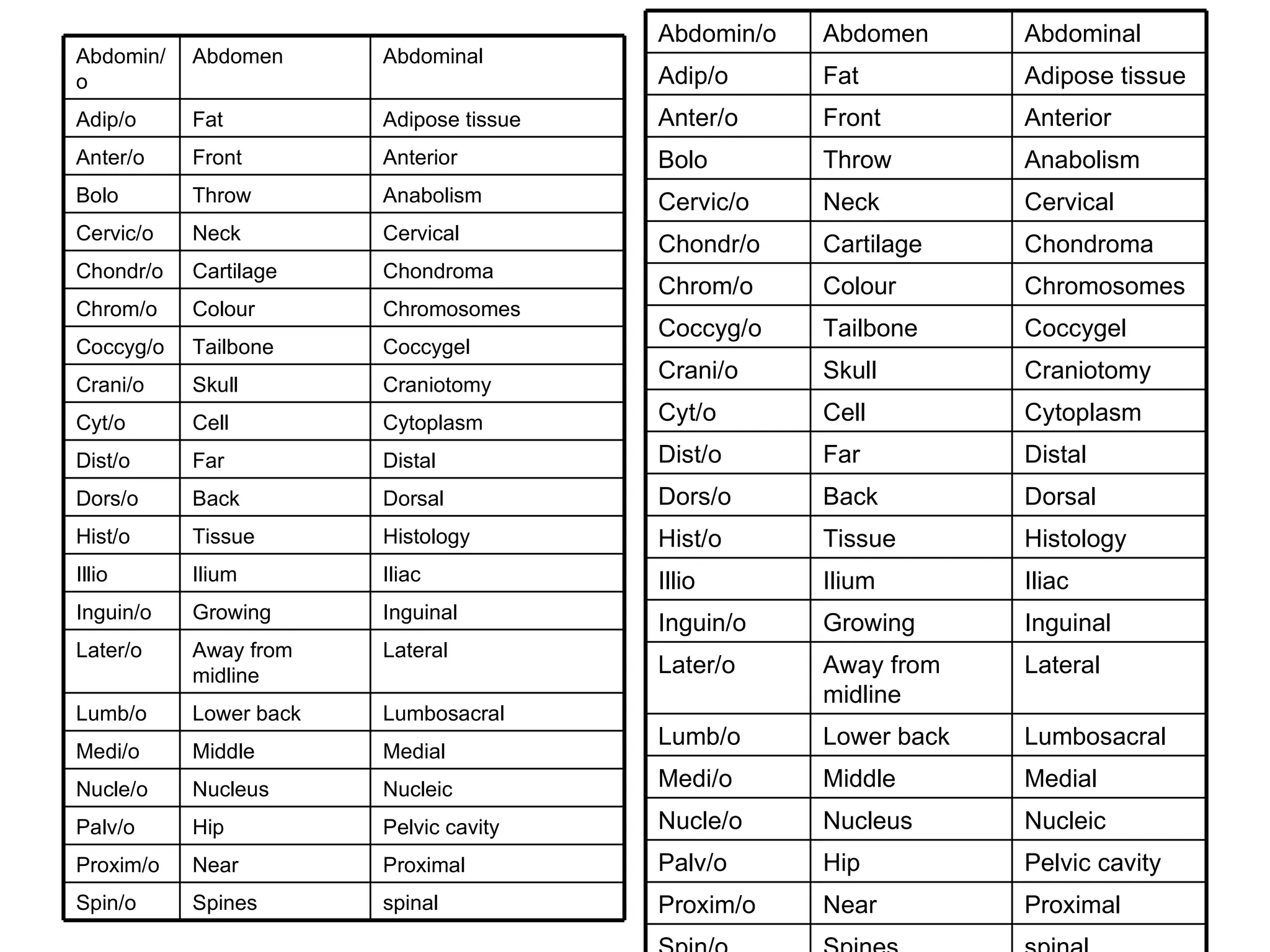
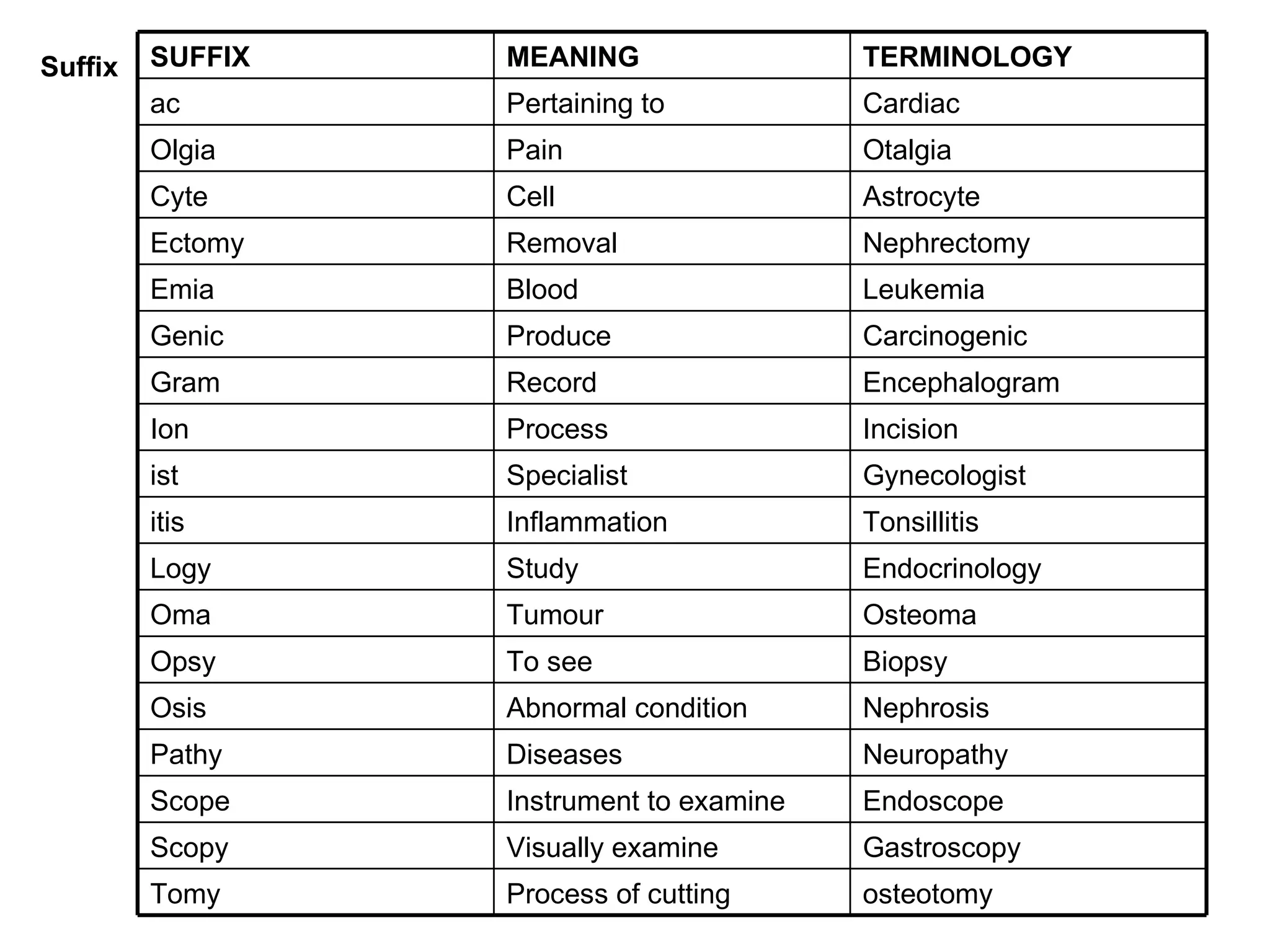
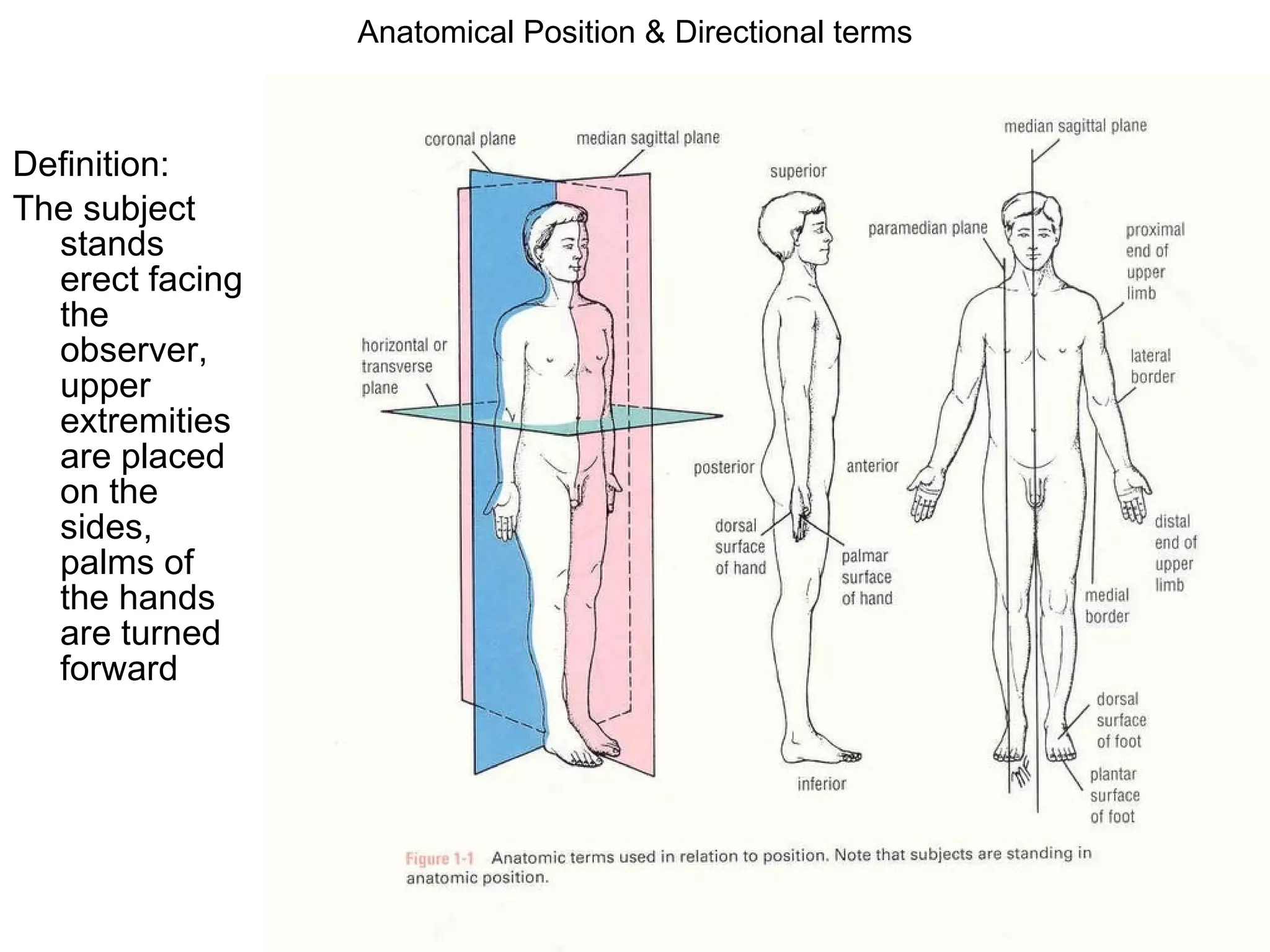
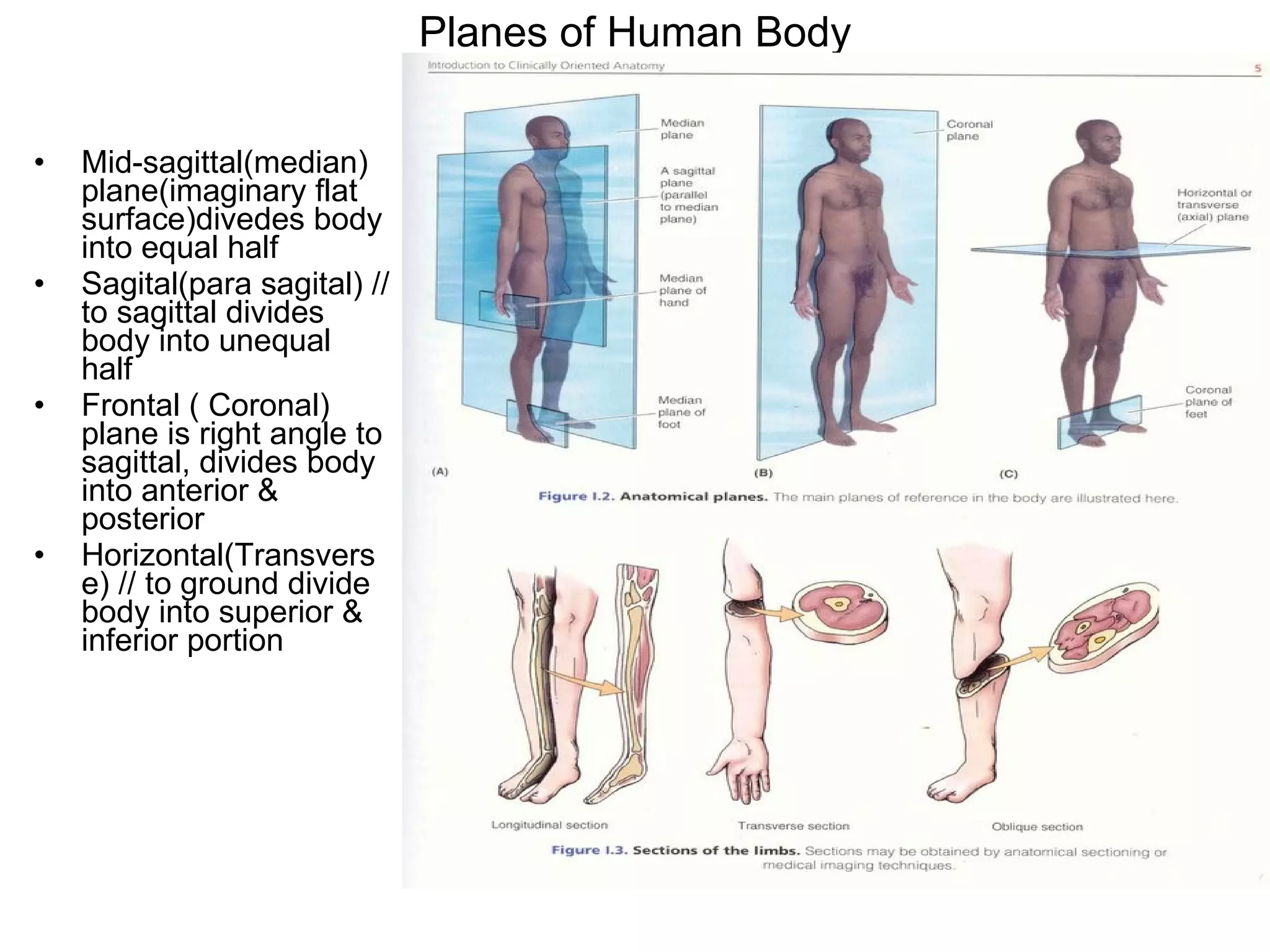
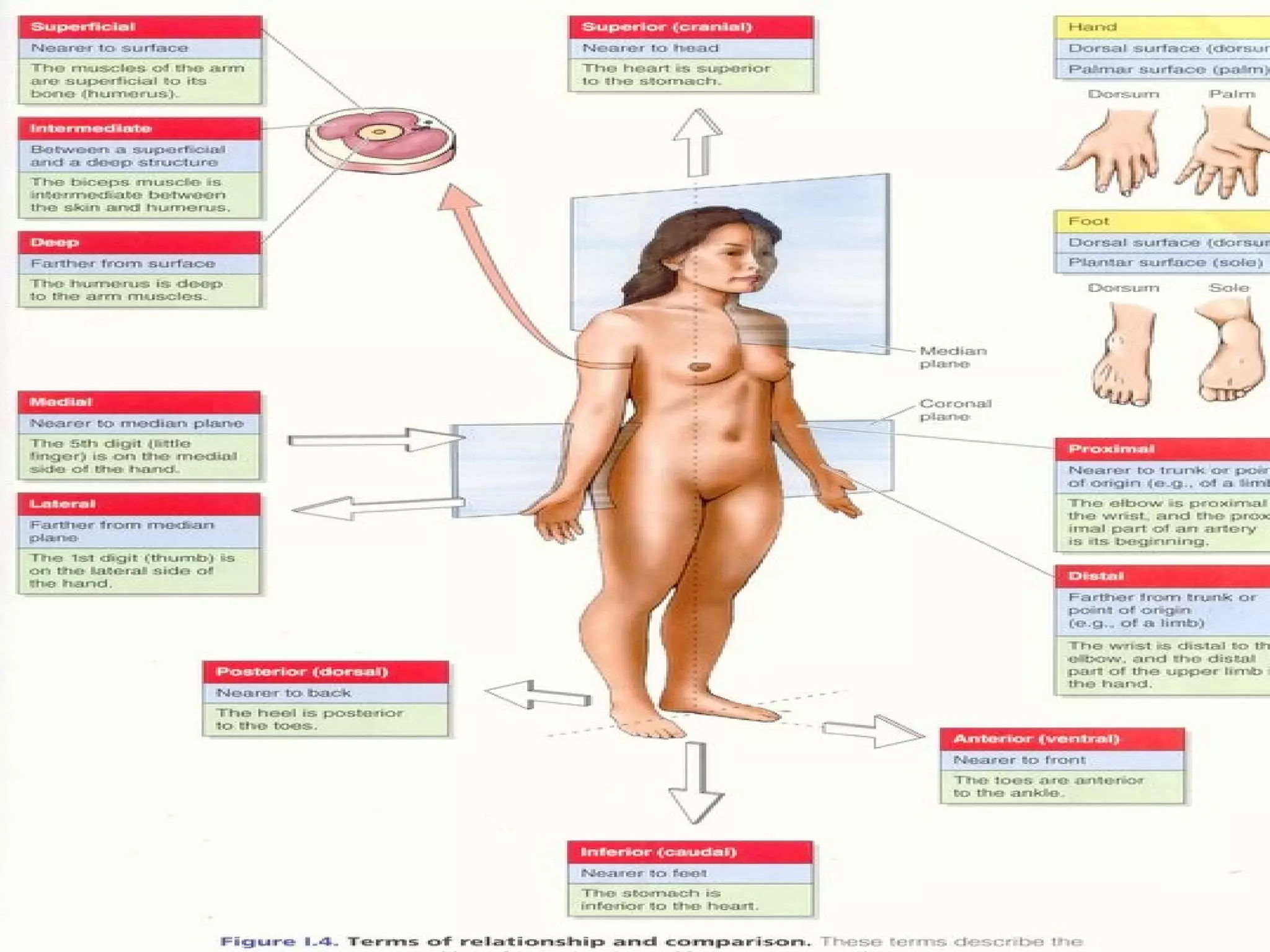
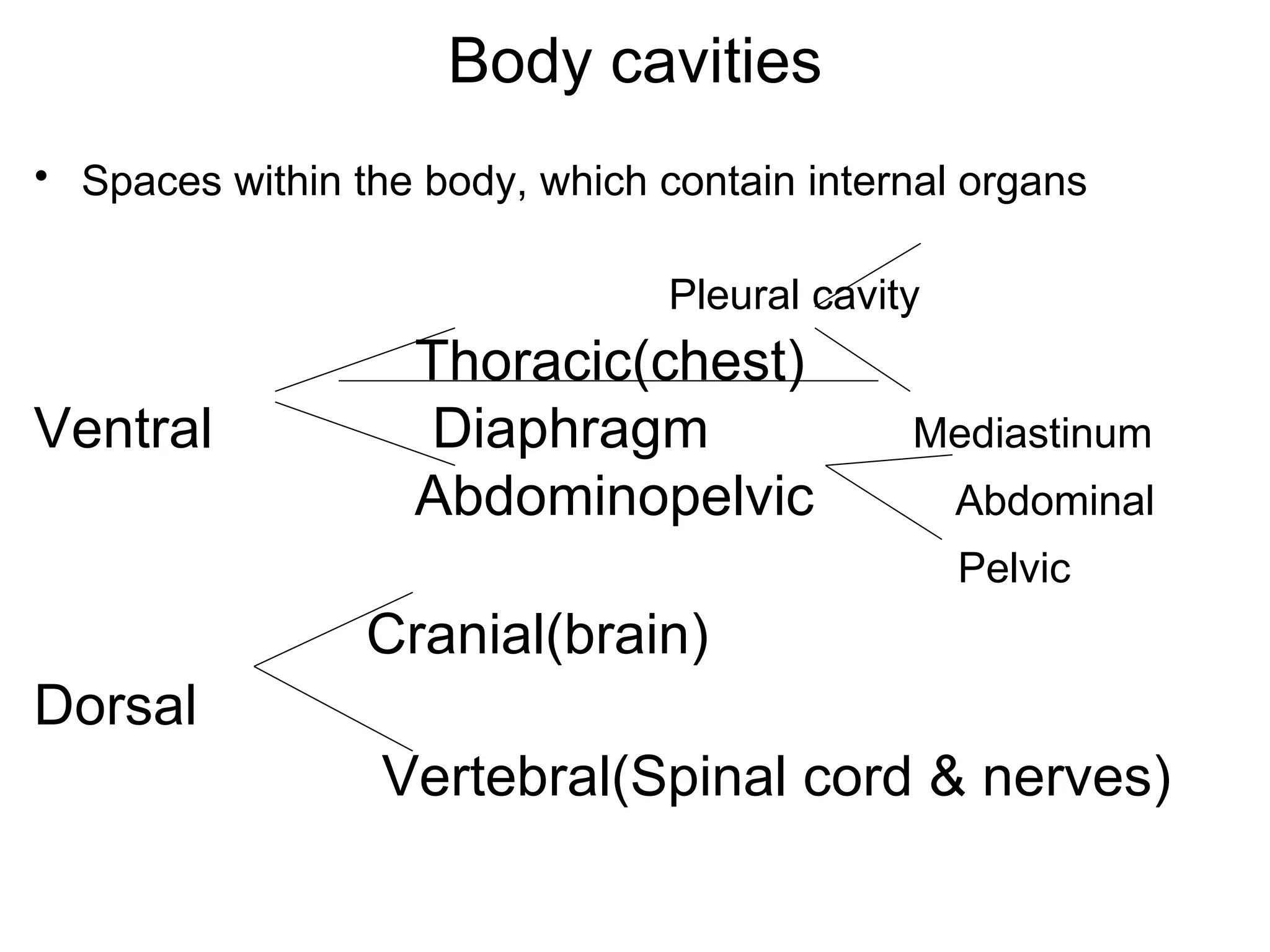
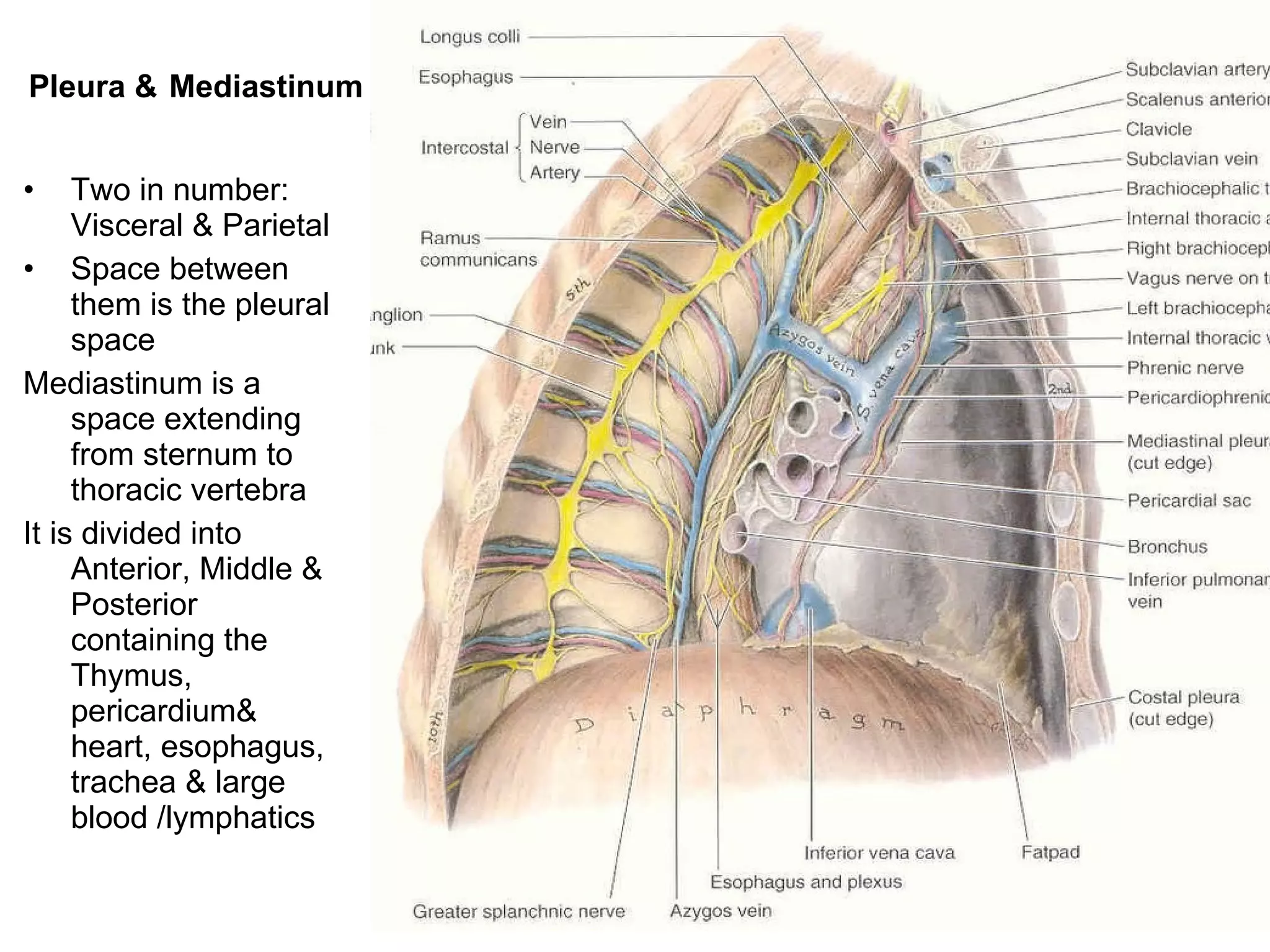
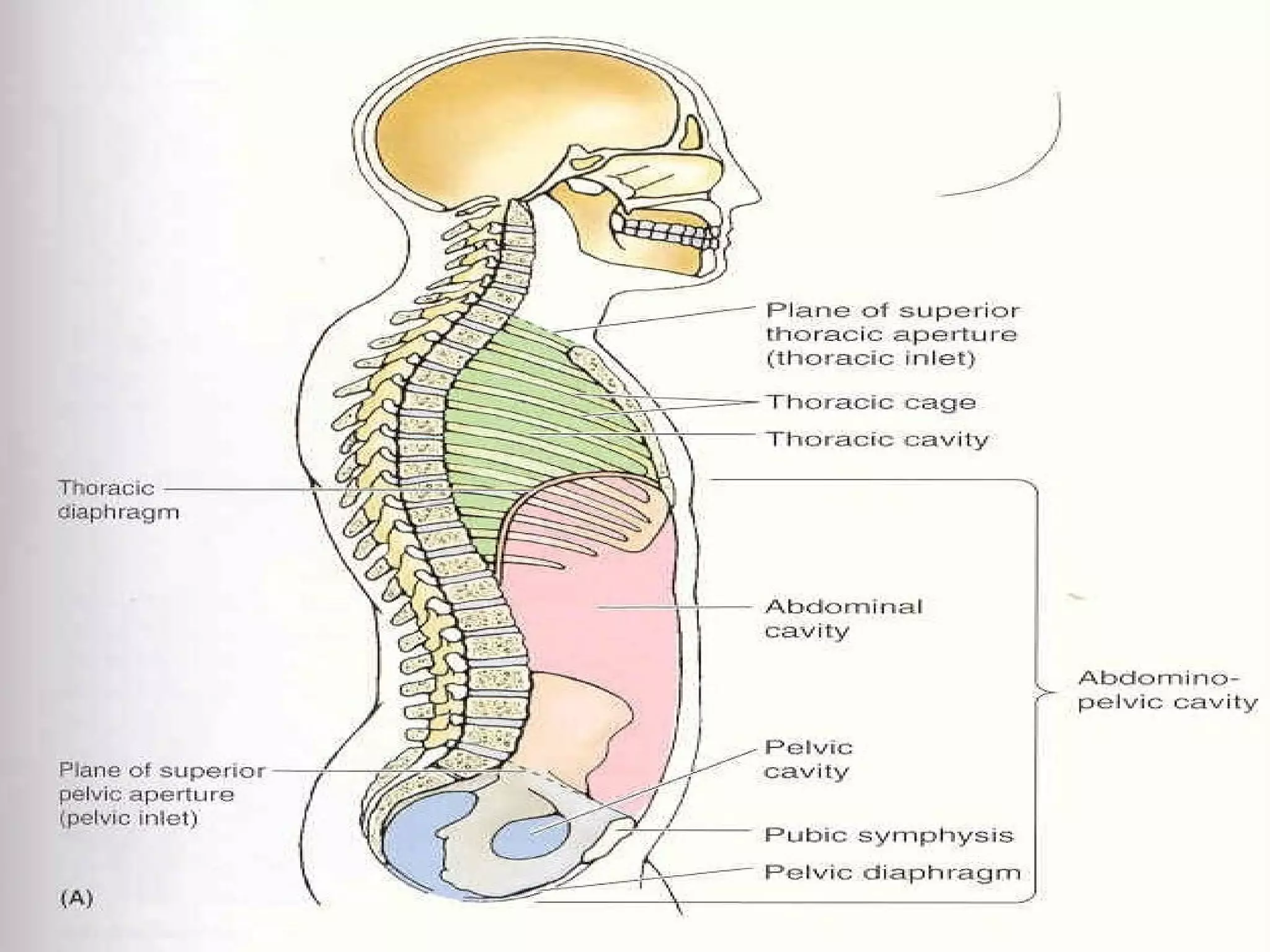
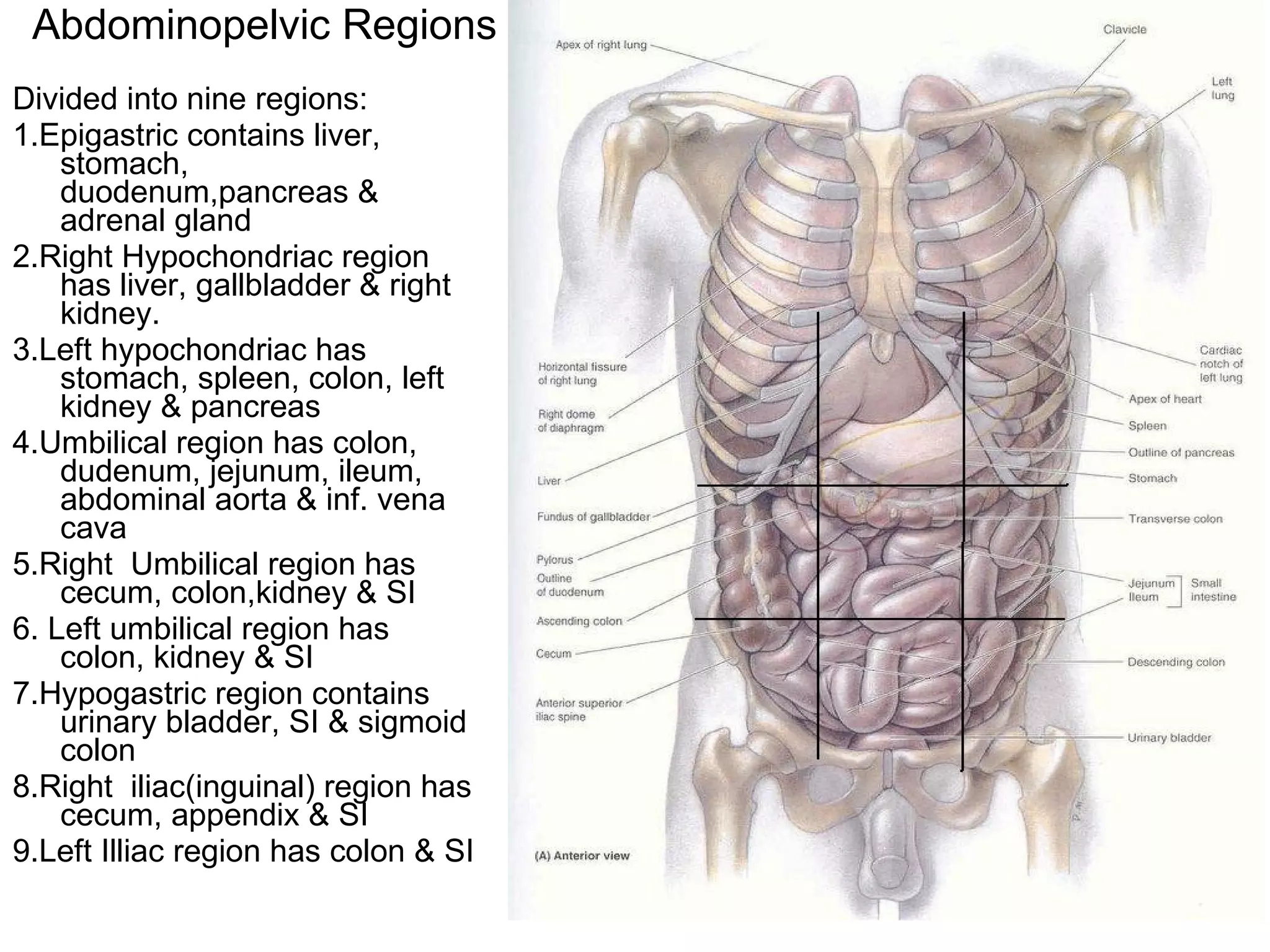
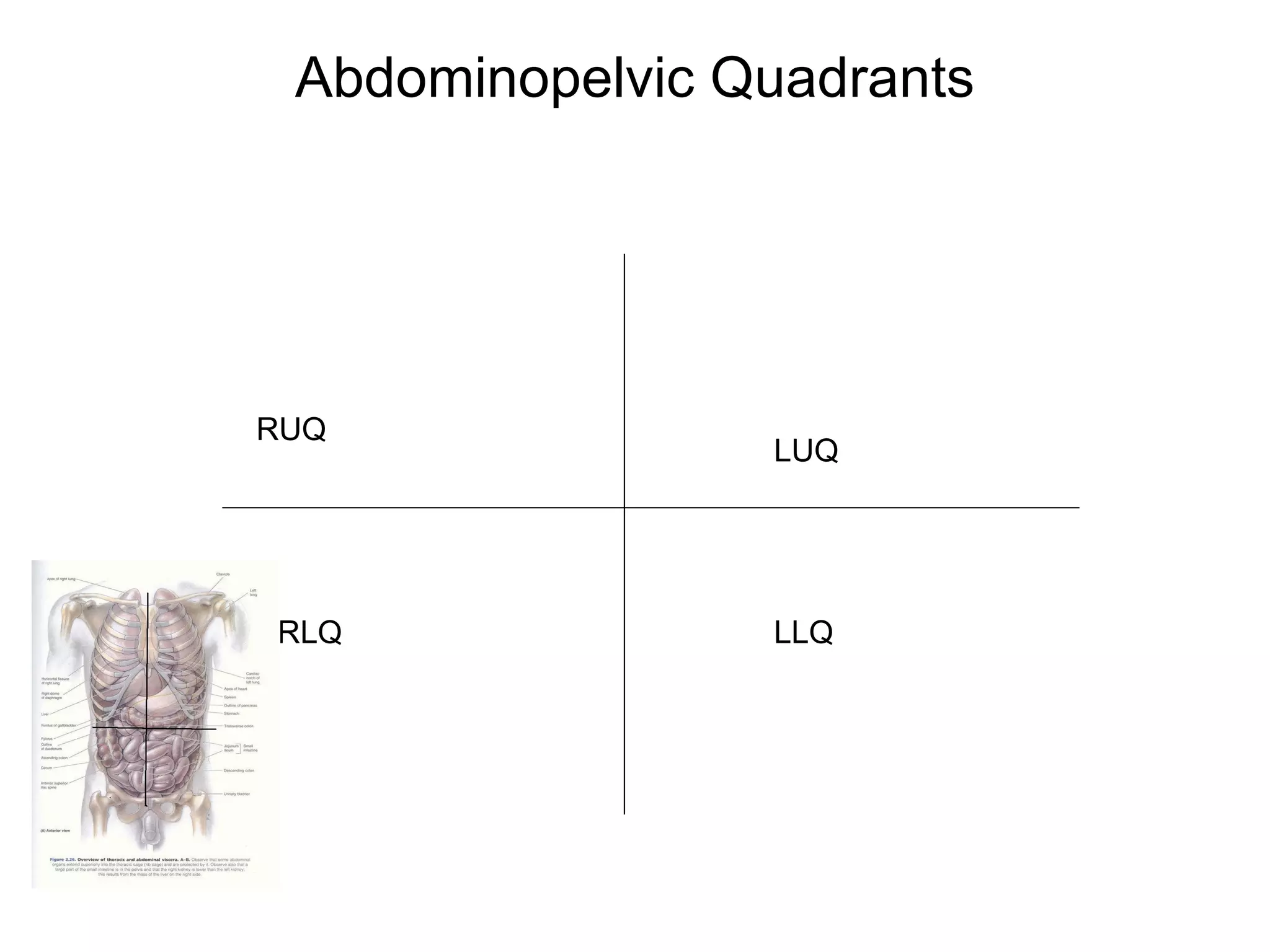
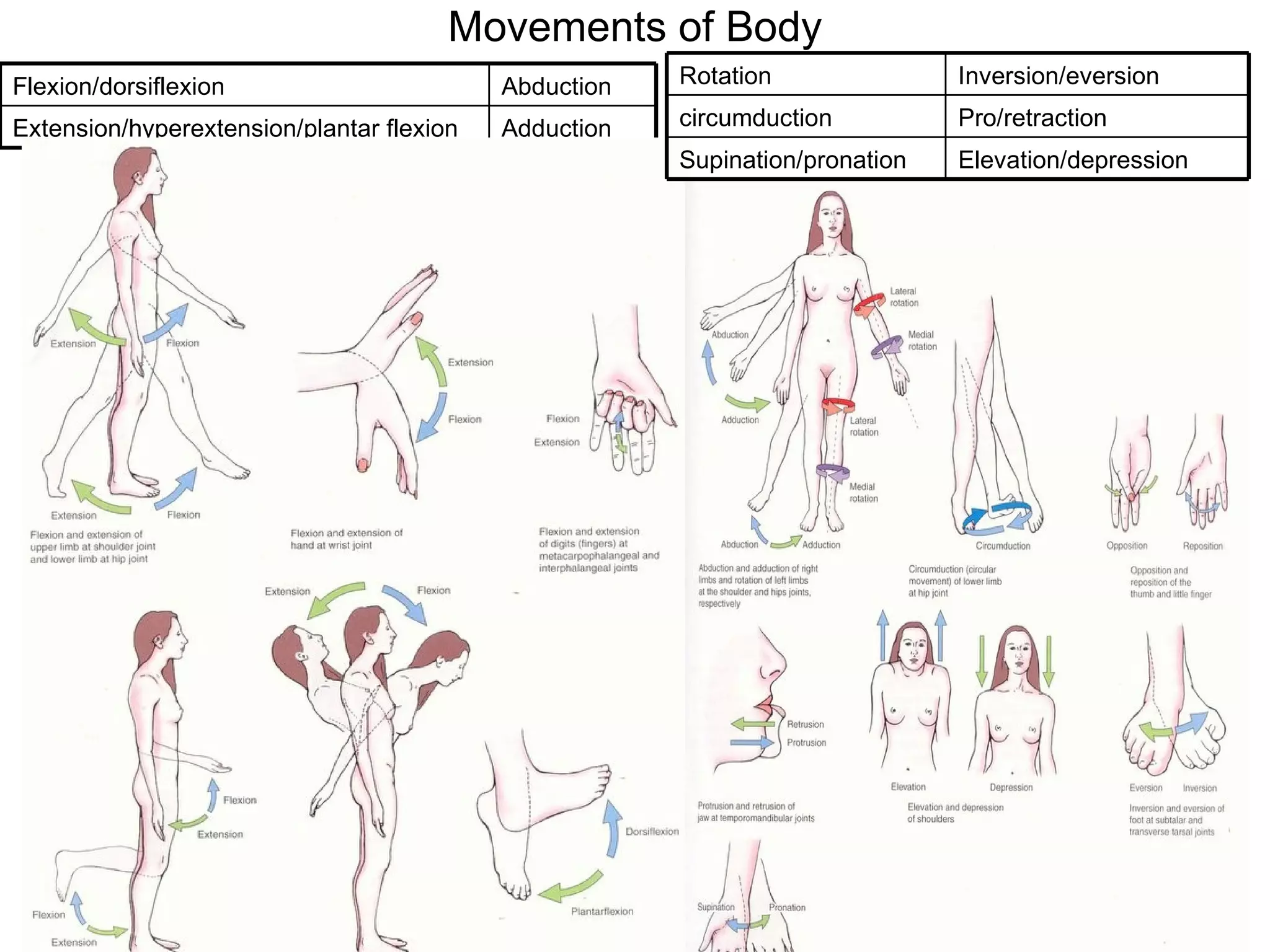
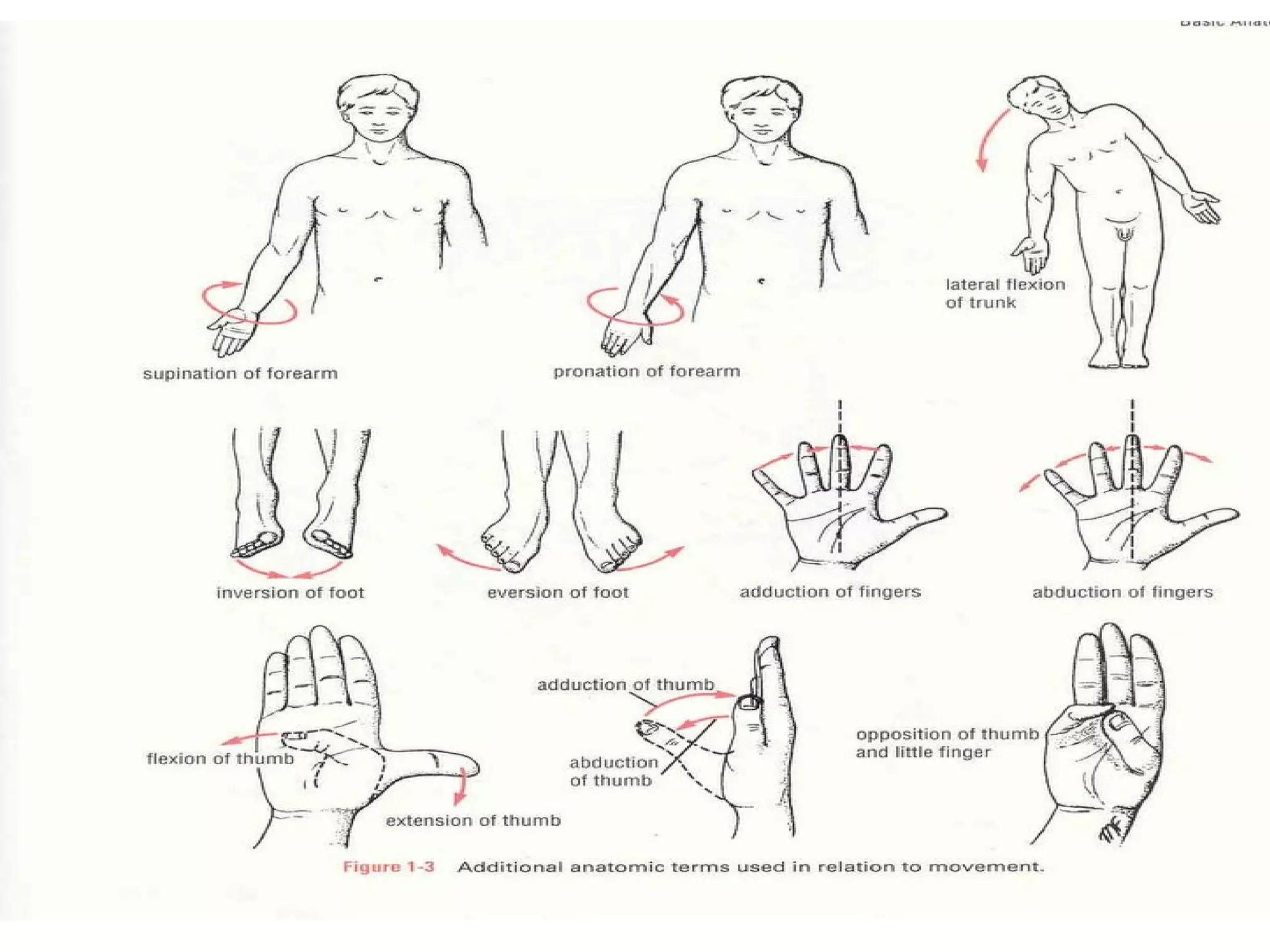
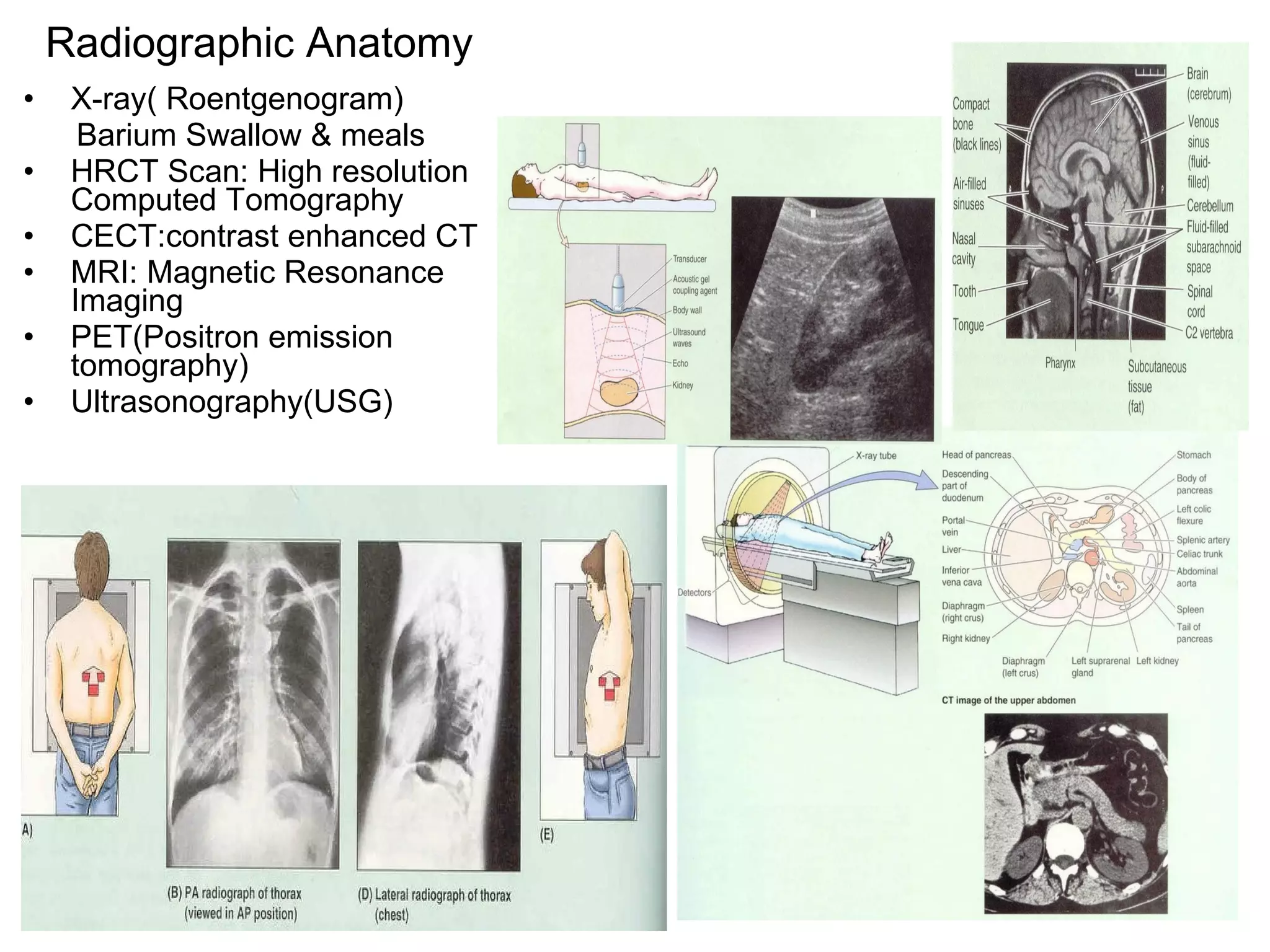
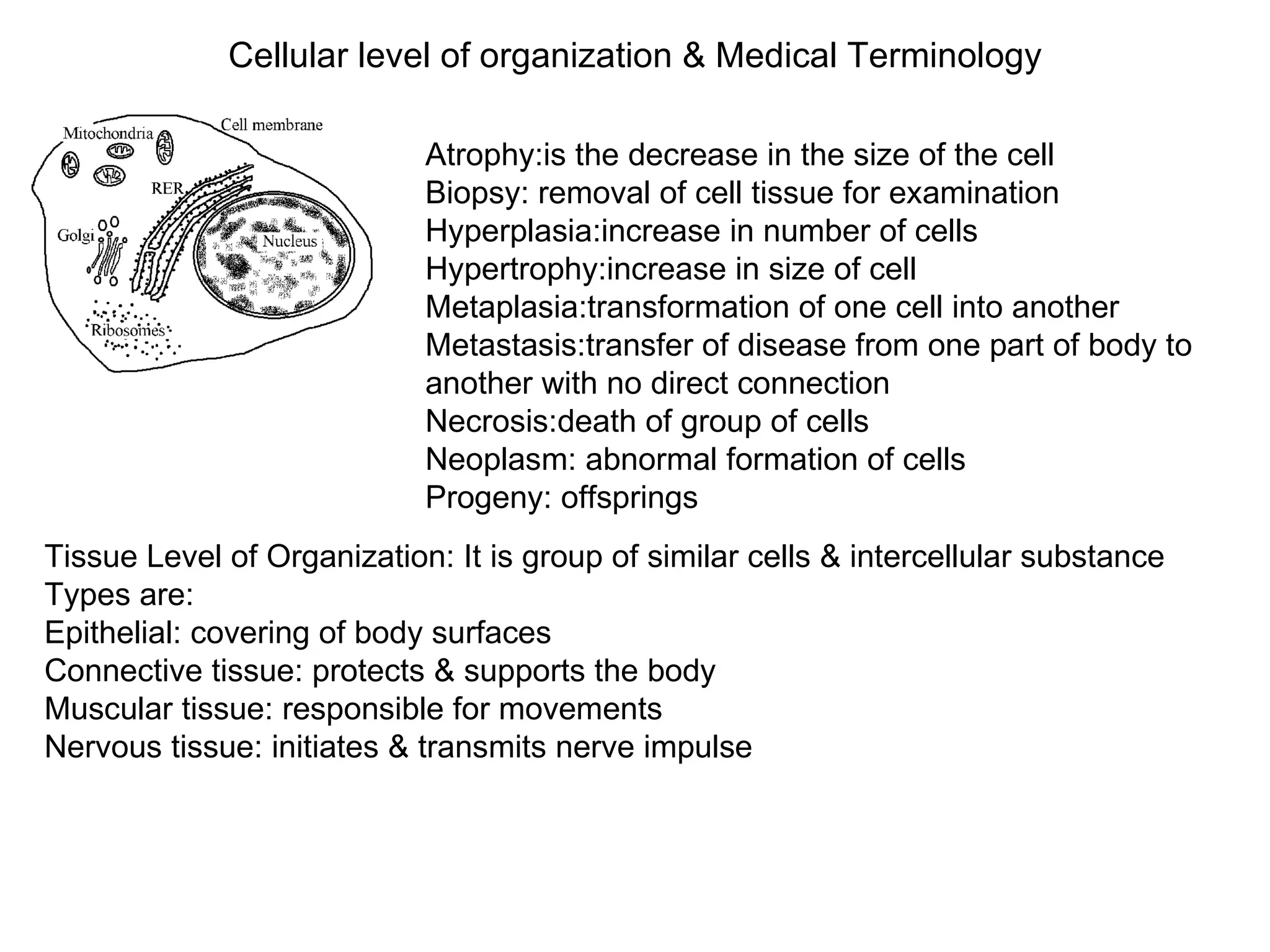
The document discusses the basic structure of medical terminology and provides examples of word roots, prefixes, and suffixes used in medical terms. It also summarizes several levels of human body organization from chemical to tissue and lists the major body systems.