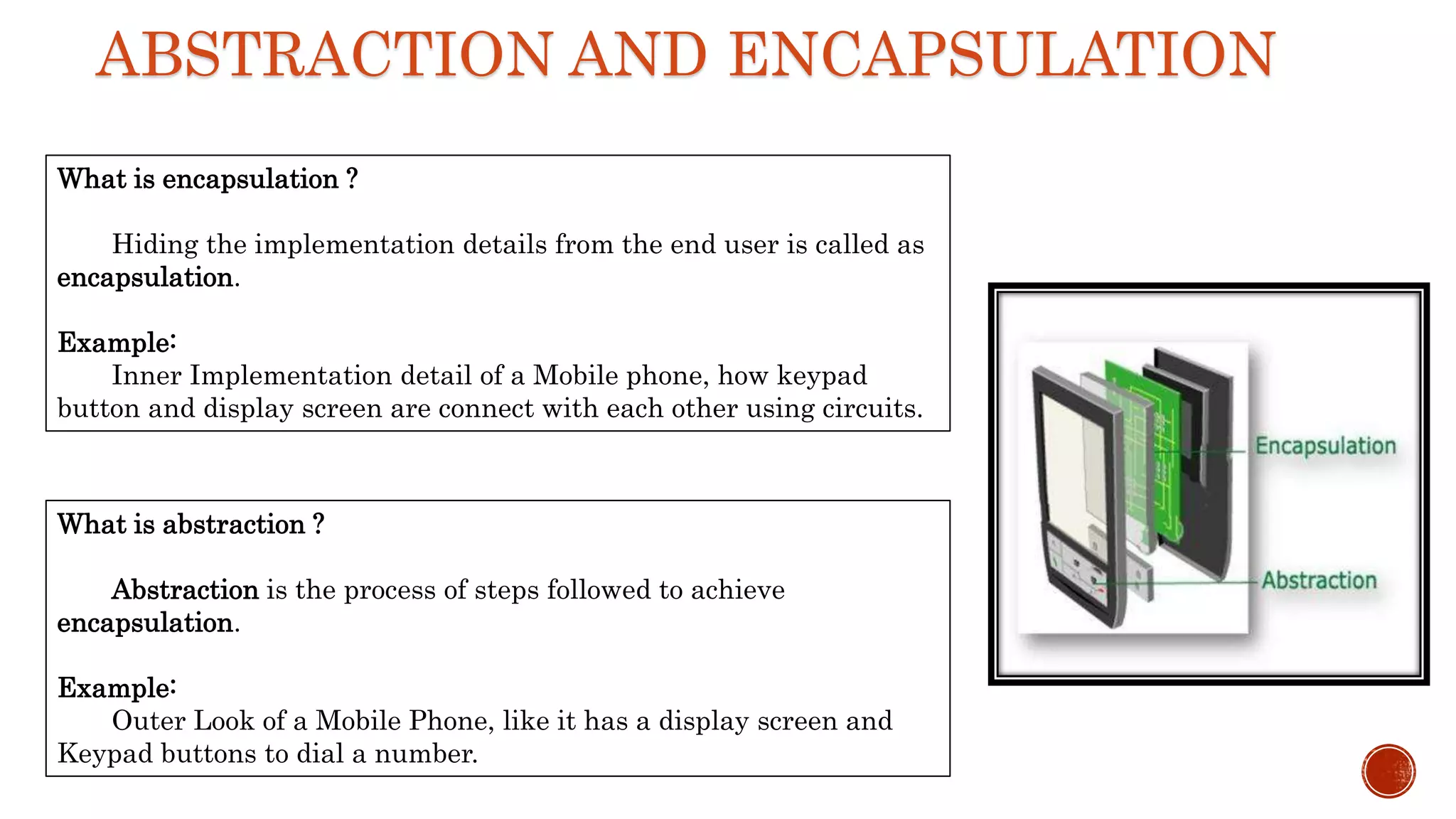
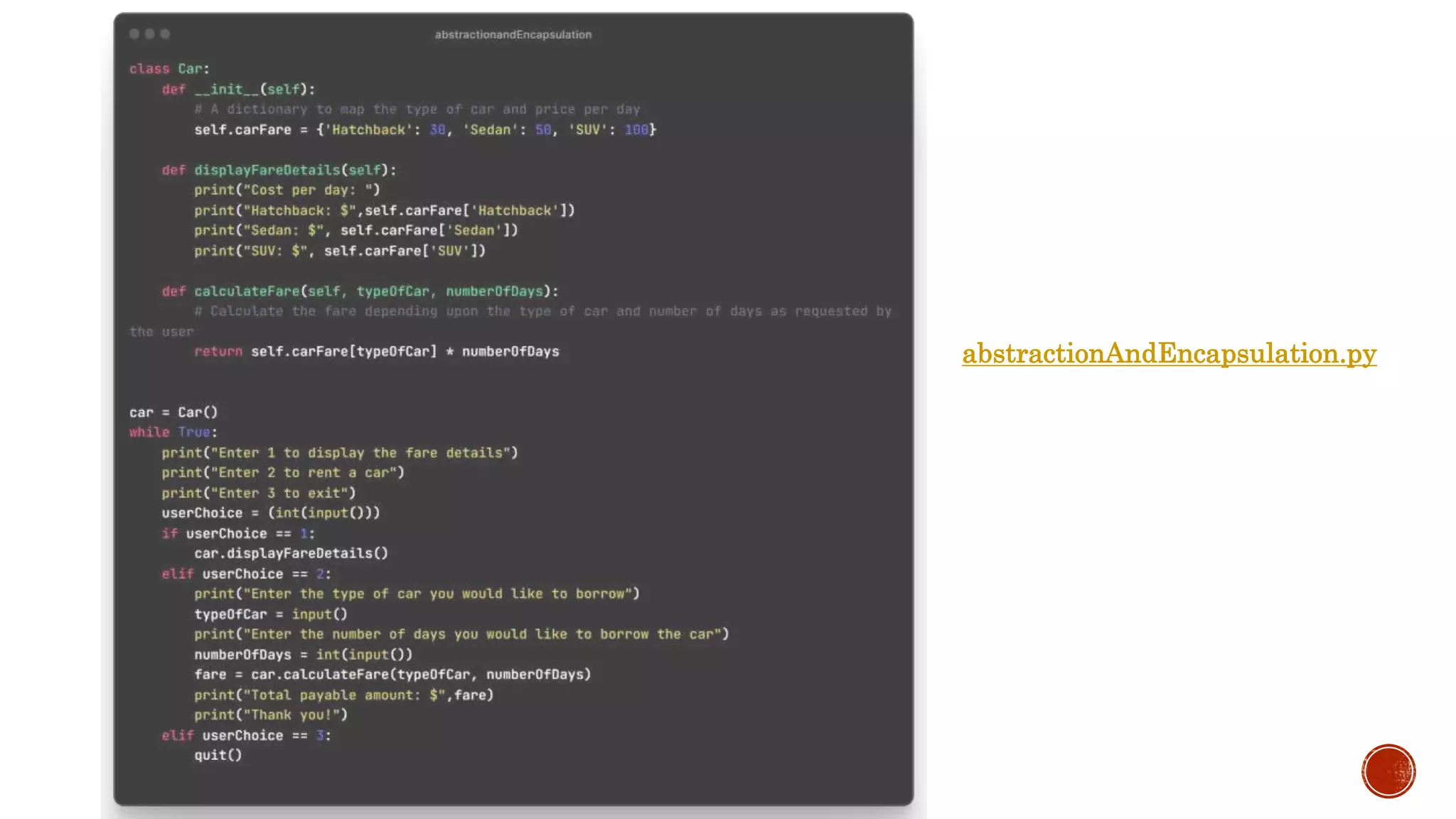
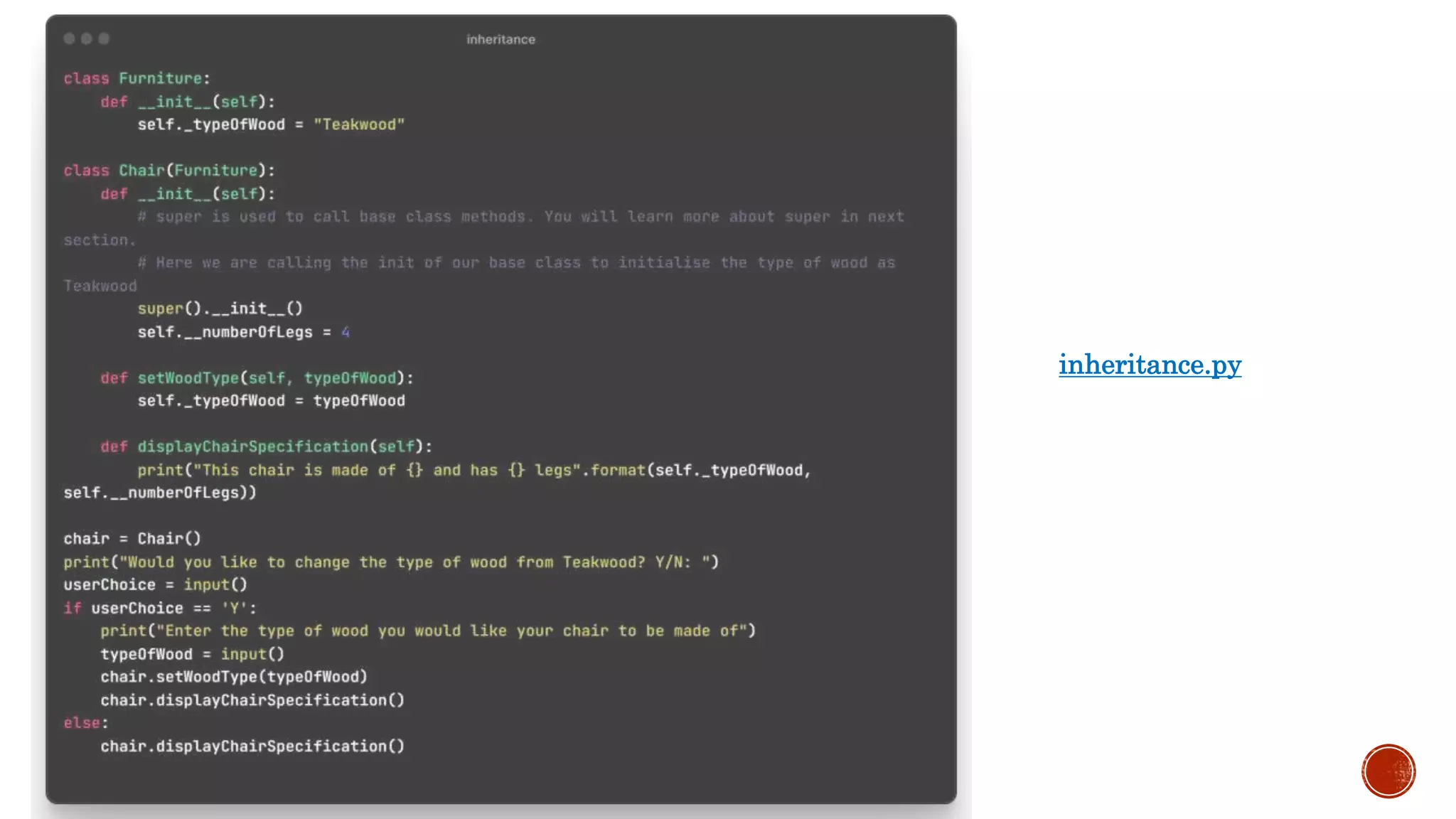
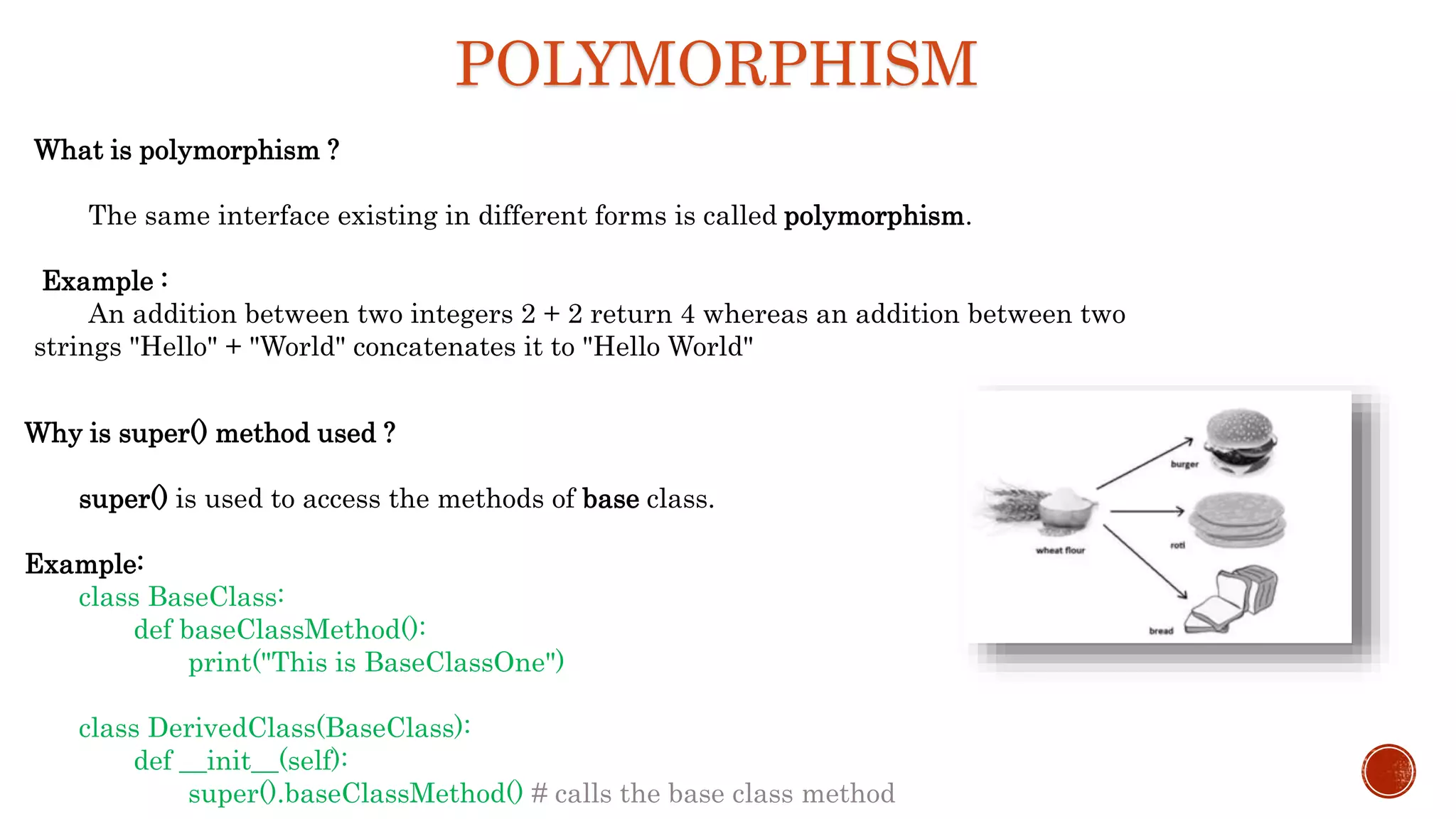
The document defines key object-oriented programming concepts like classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, encapsulation and abstraction.
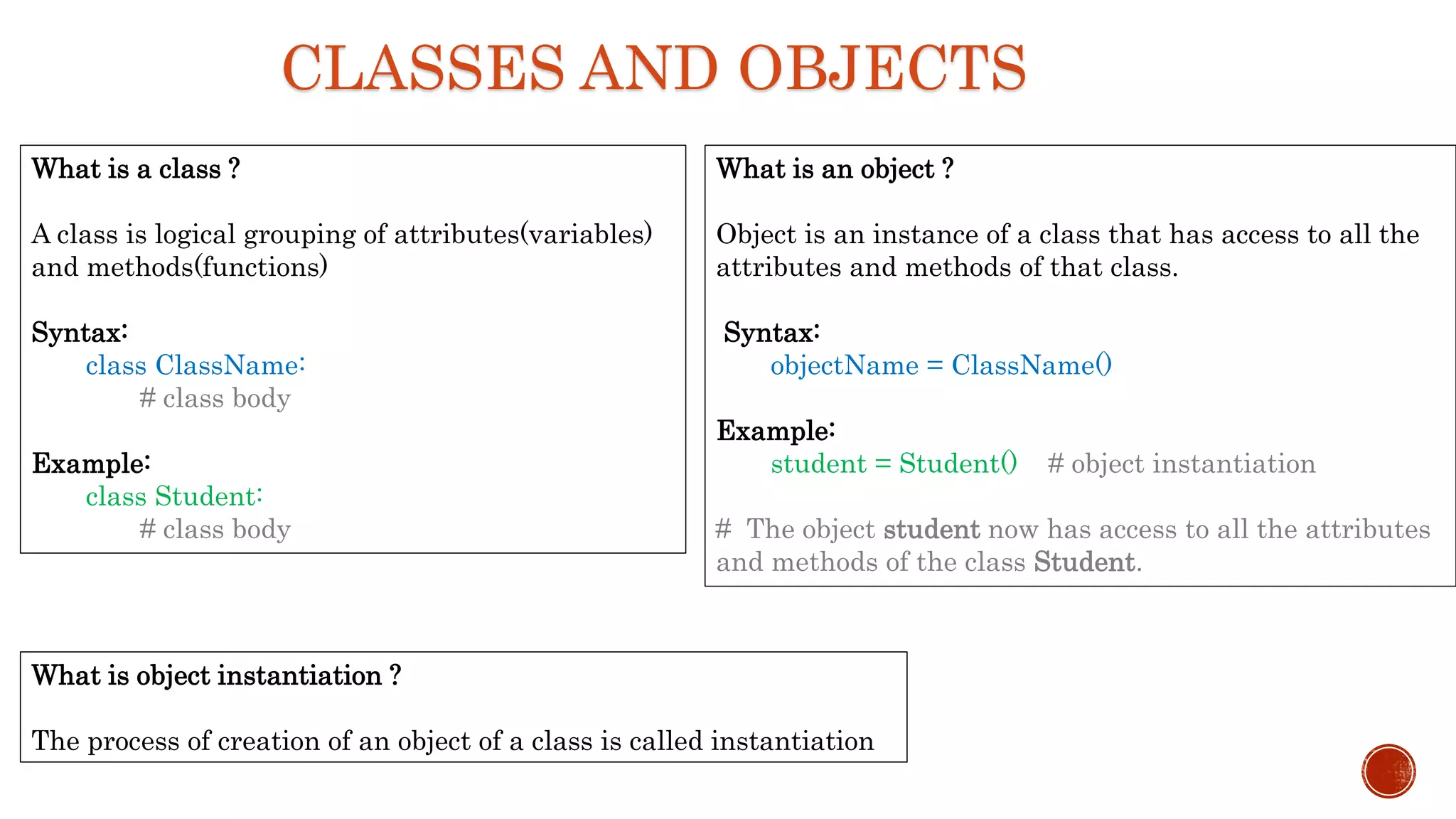
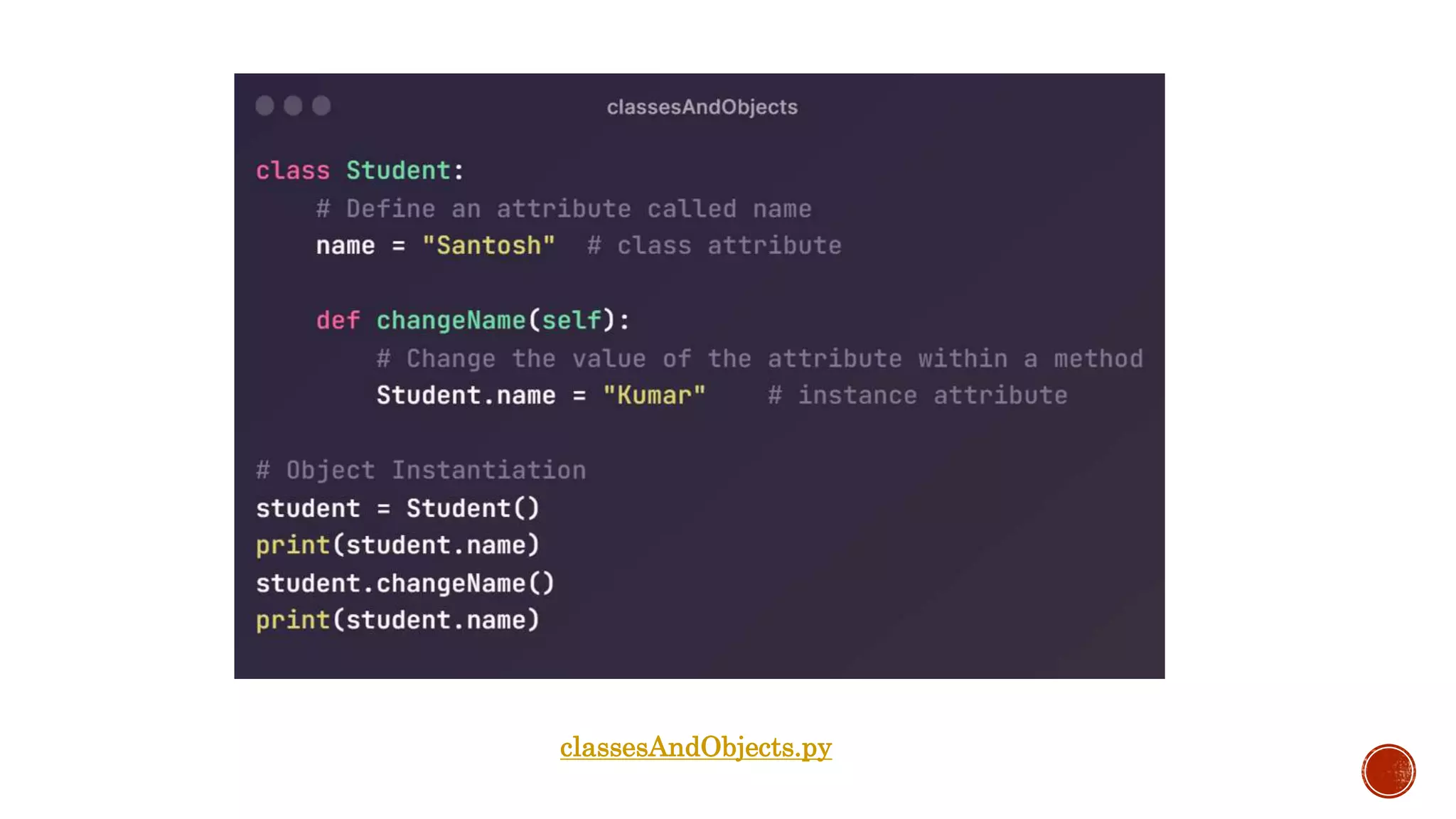
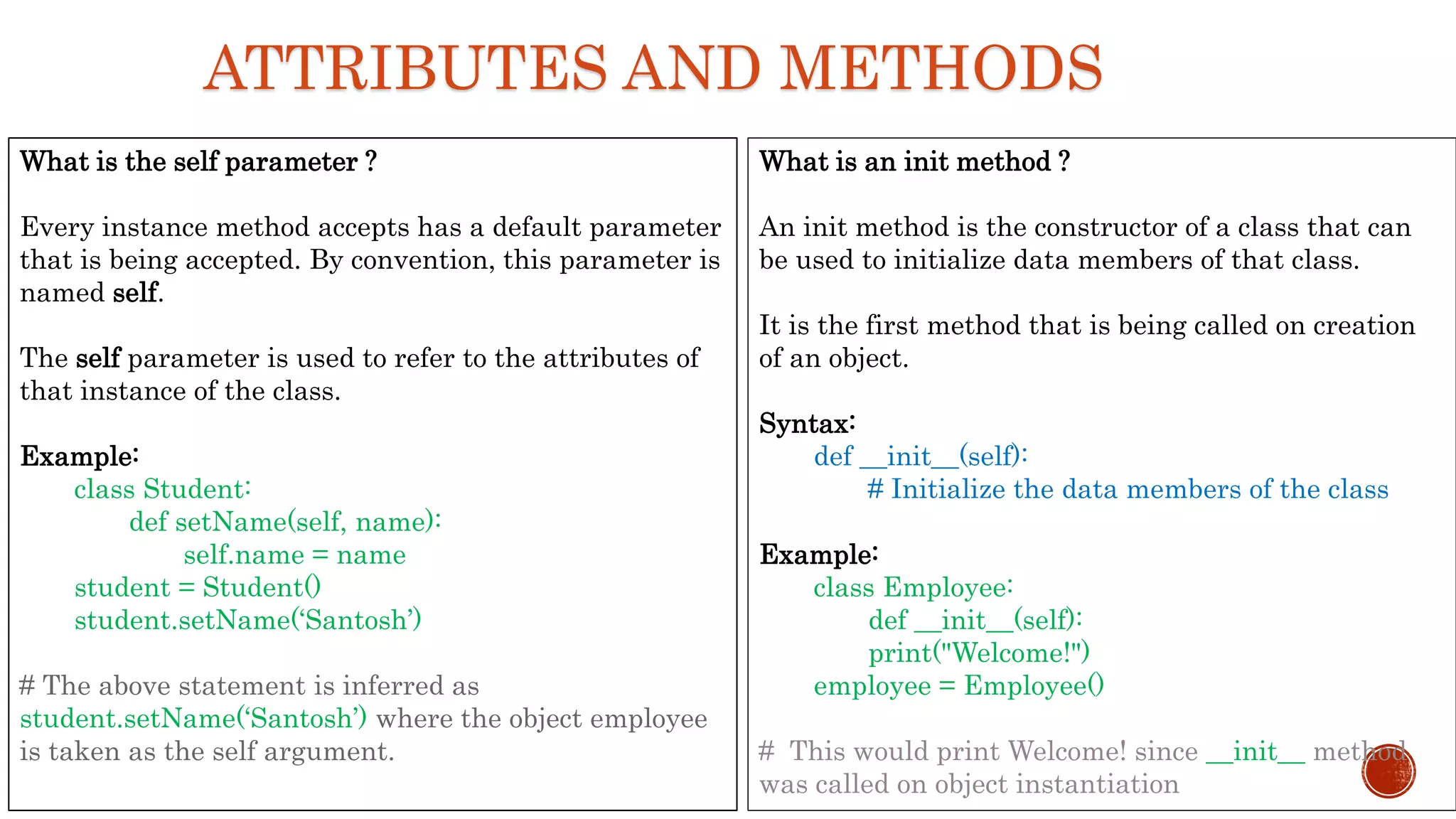
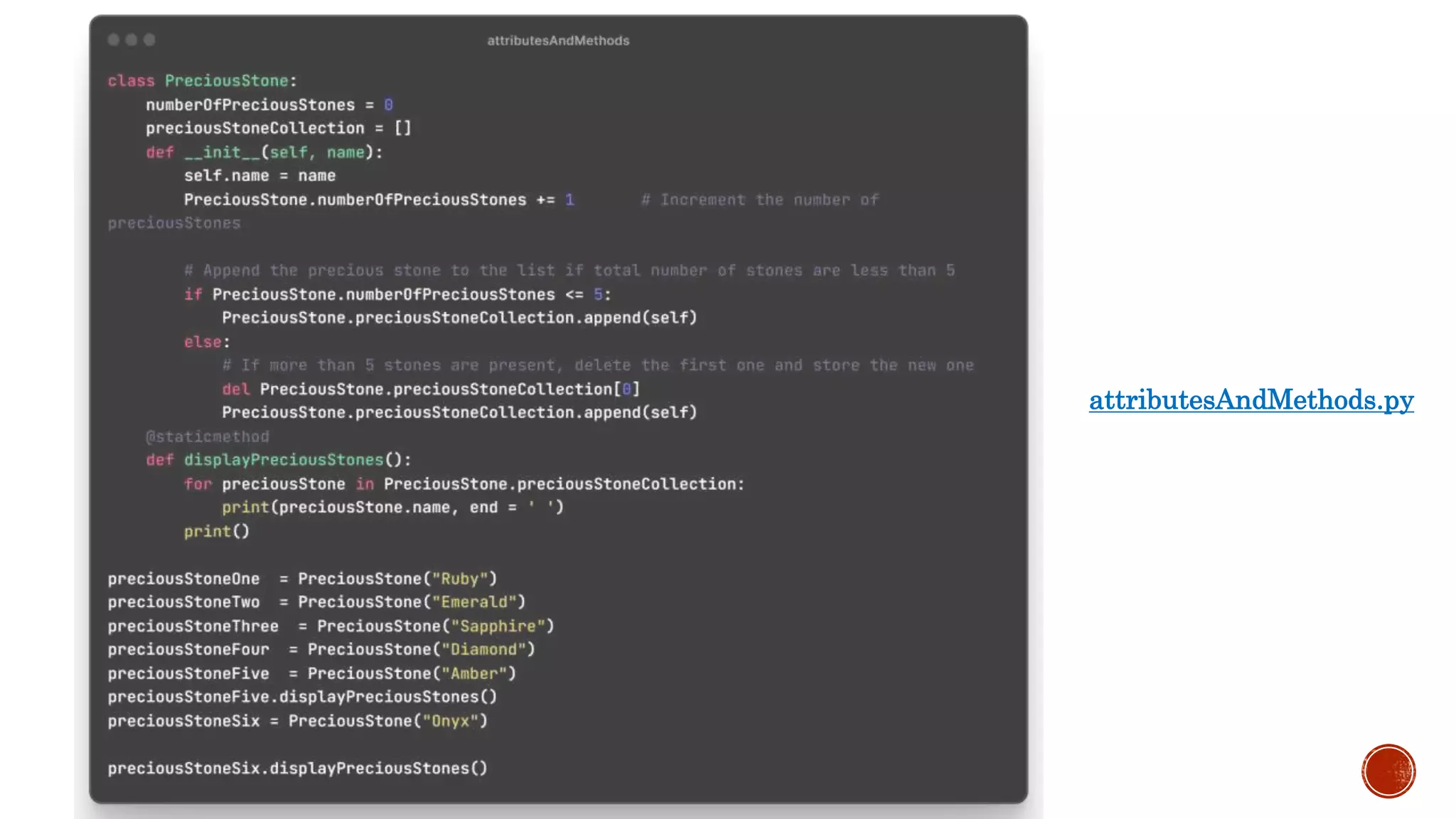
It explains that a class is a logical grouping of attributes and methods, an object is an instance of a class, and object instantiation is the process of creating an object. It discusses self parameter, init methods, class attributes, instance attributes, static and instance methods.
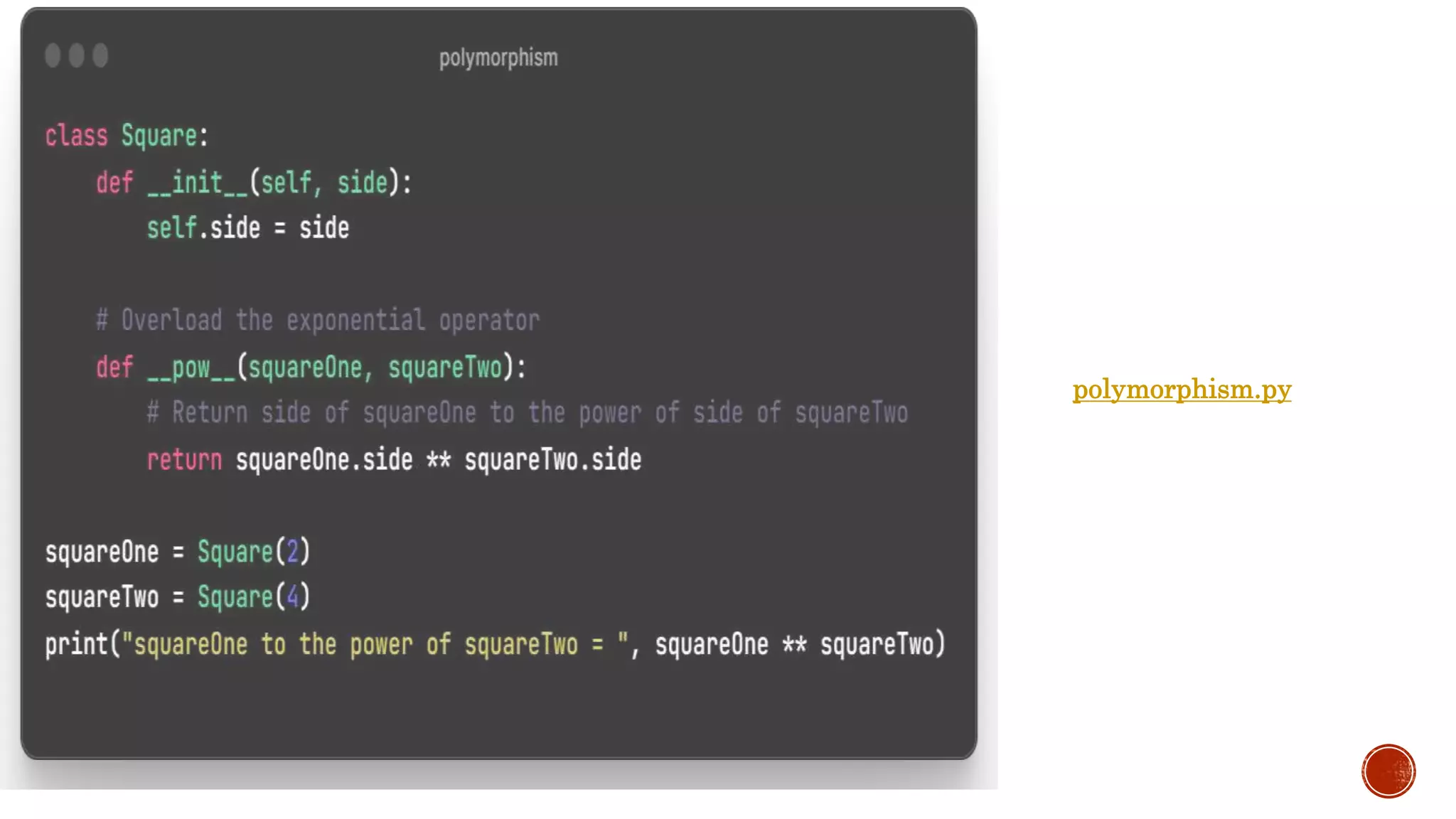
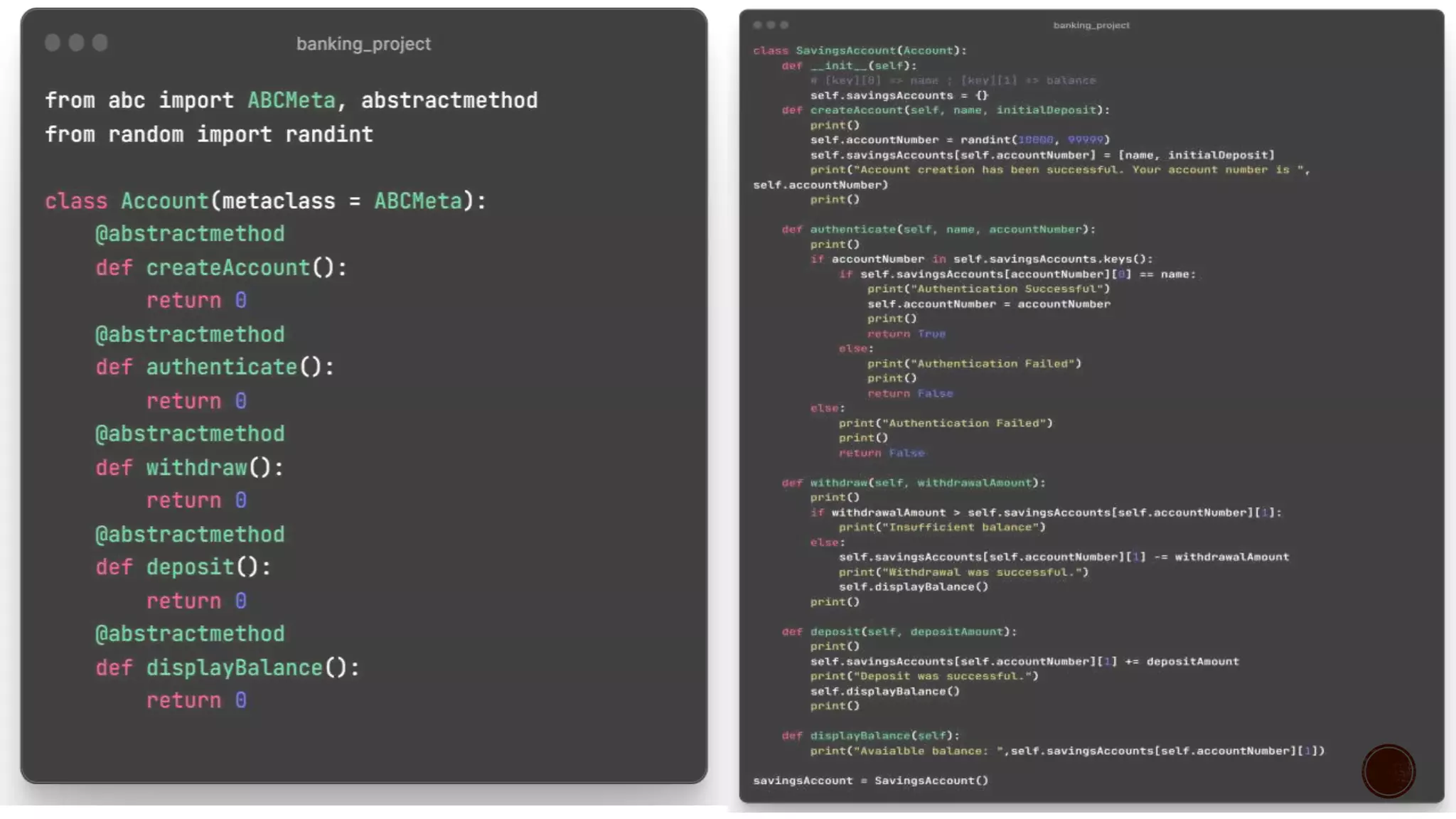
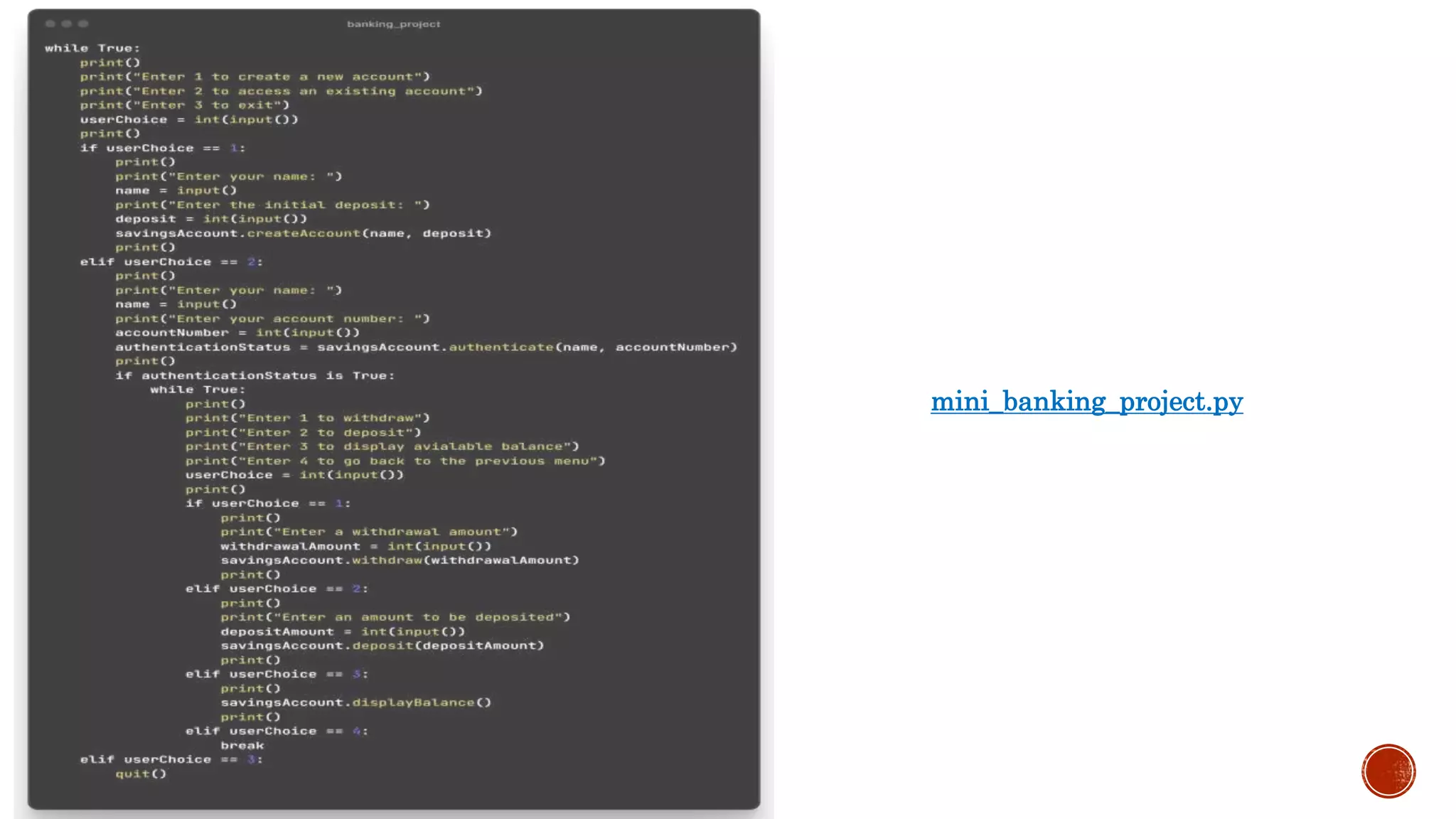
It describes inheritance, multiple and multilevel inheritance. It covers abstraction, encapsulation, polymorphism and operator overloading. It also discusses naming conventions, abstract base classes, overriding and the use of super().