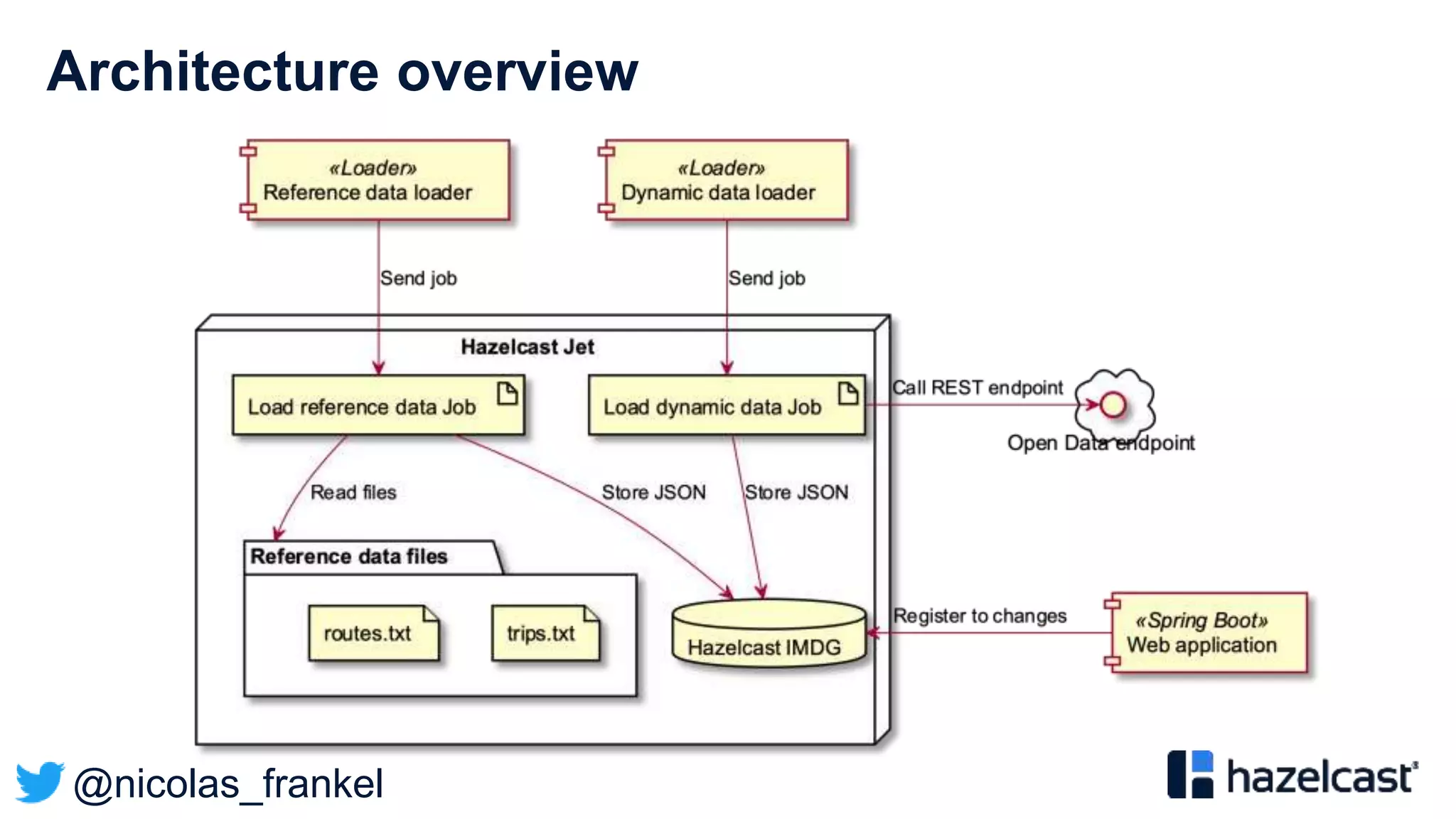
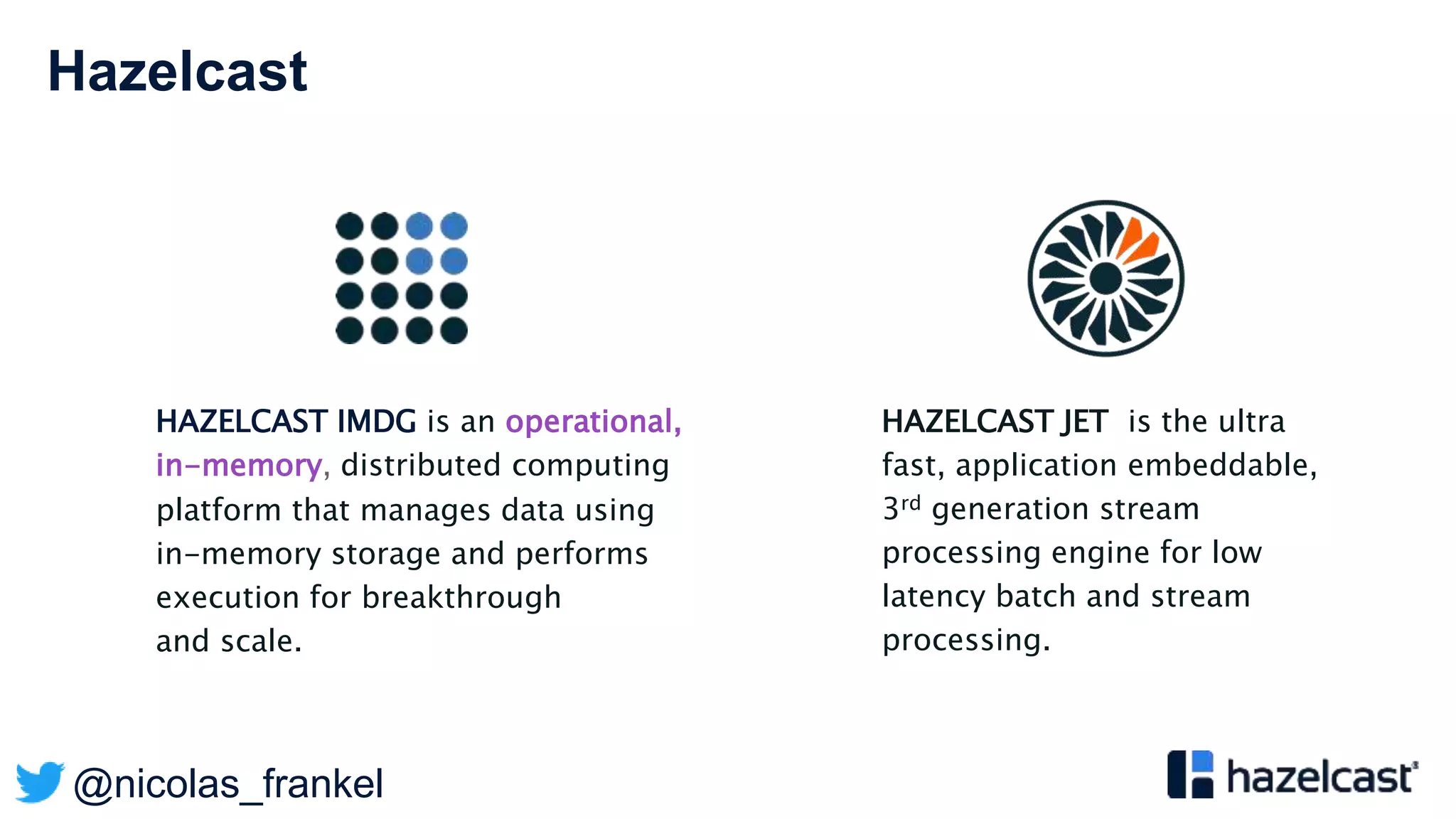
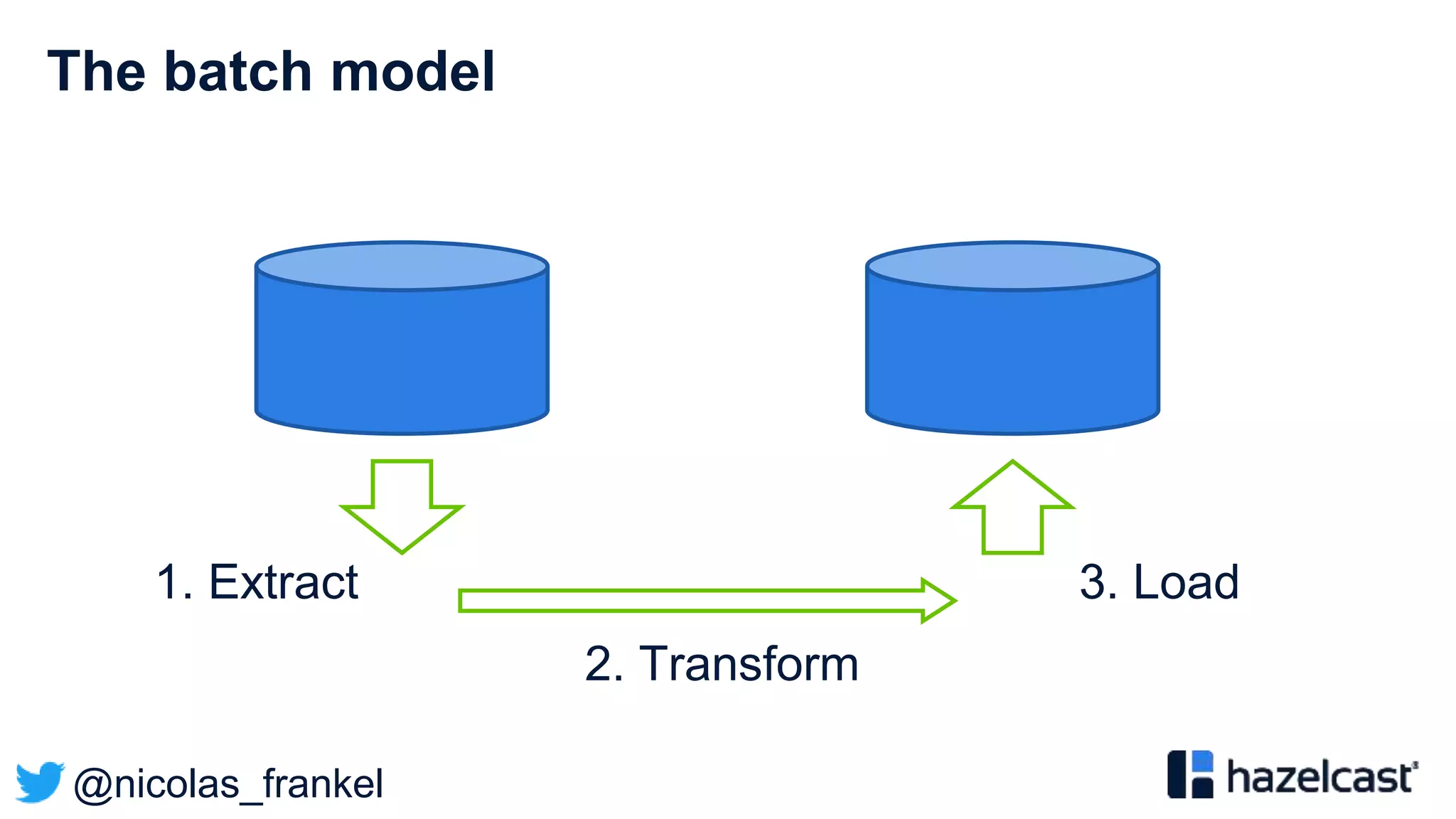
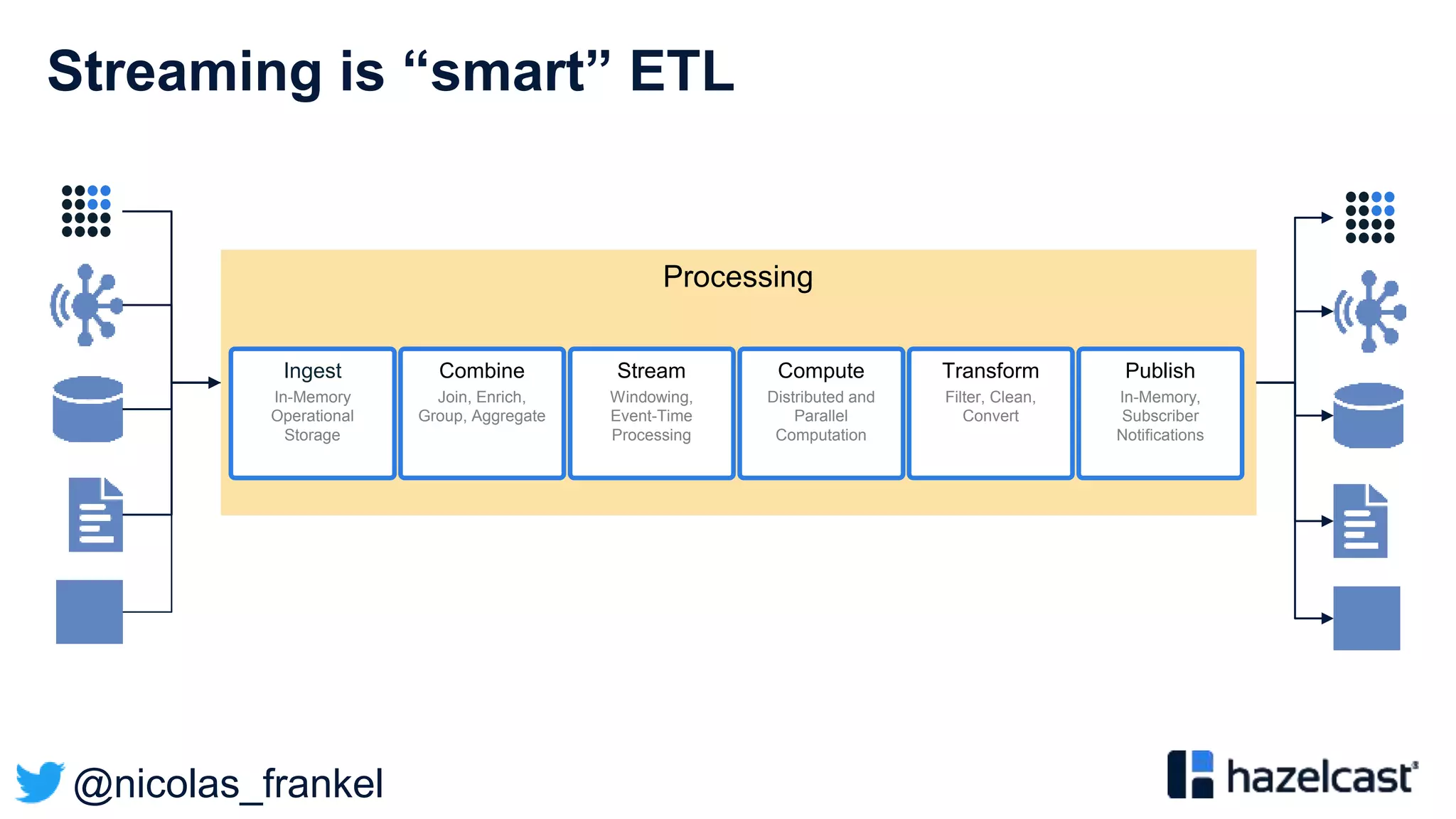
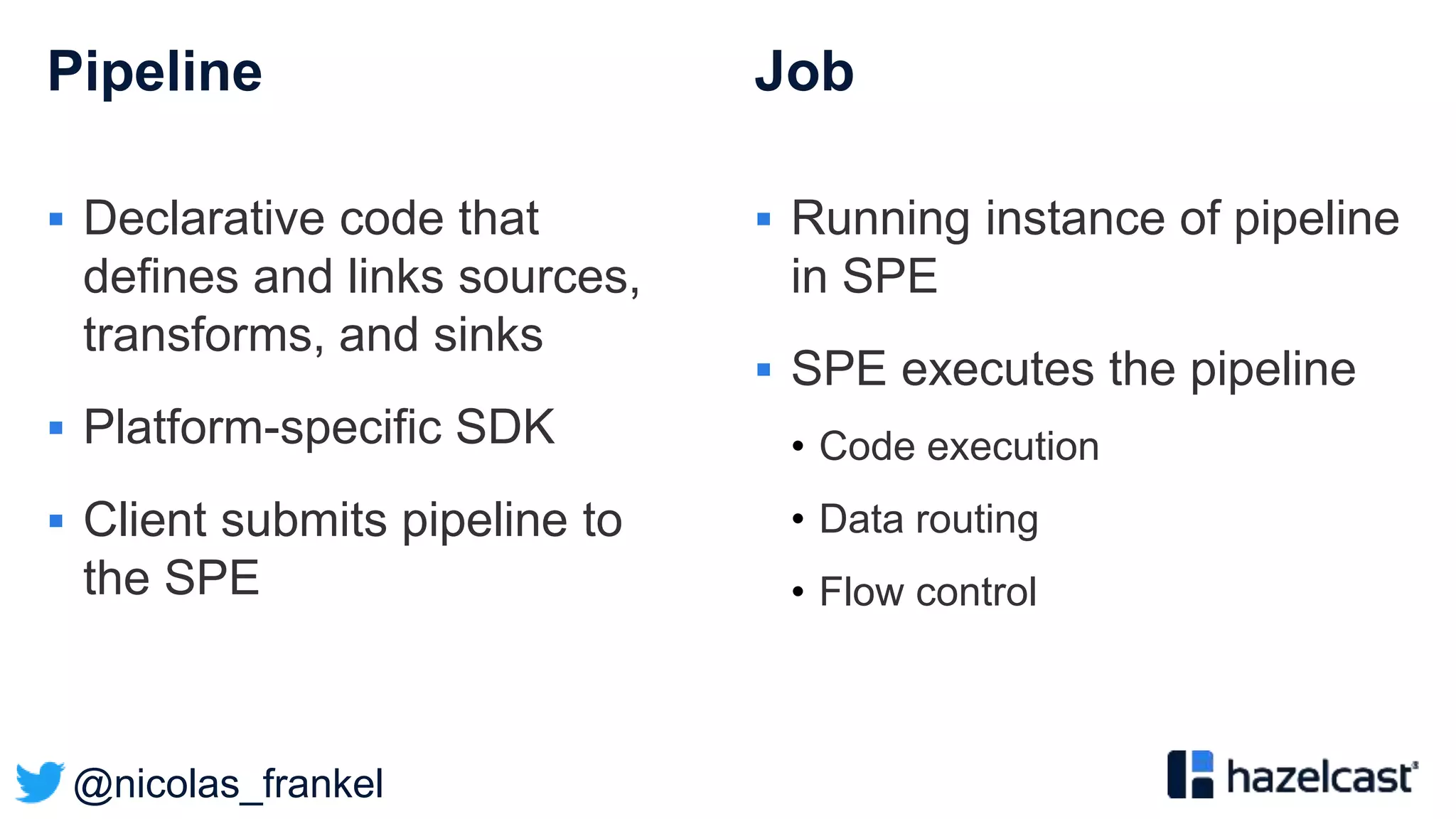
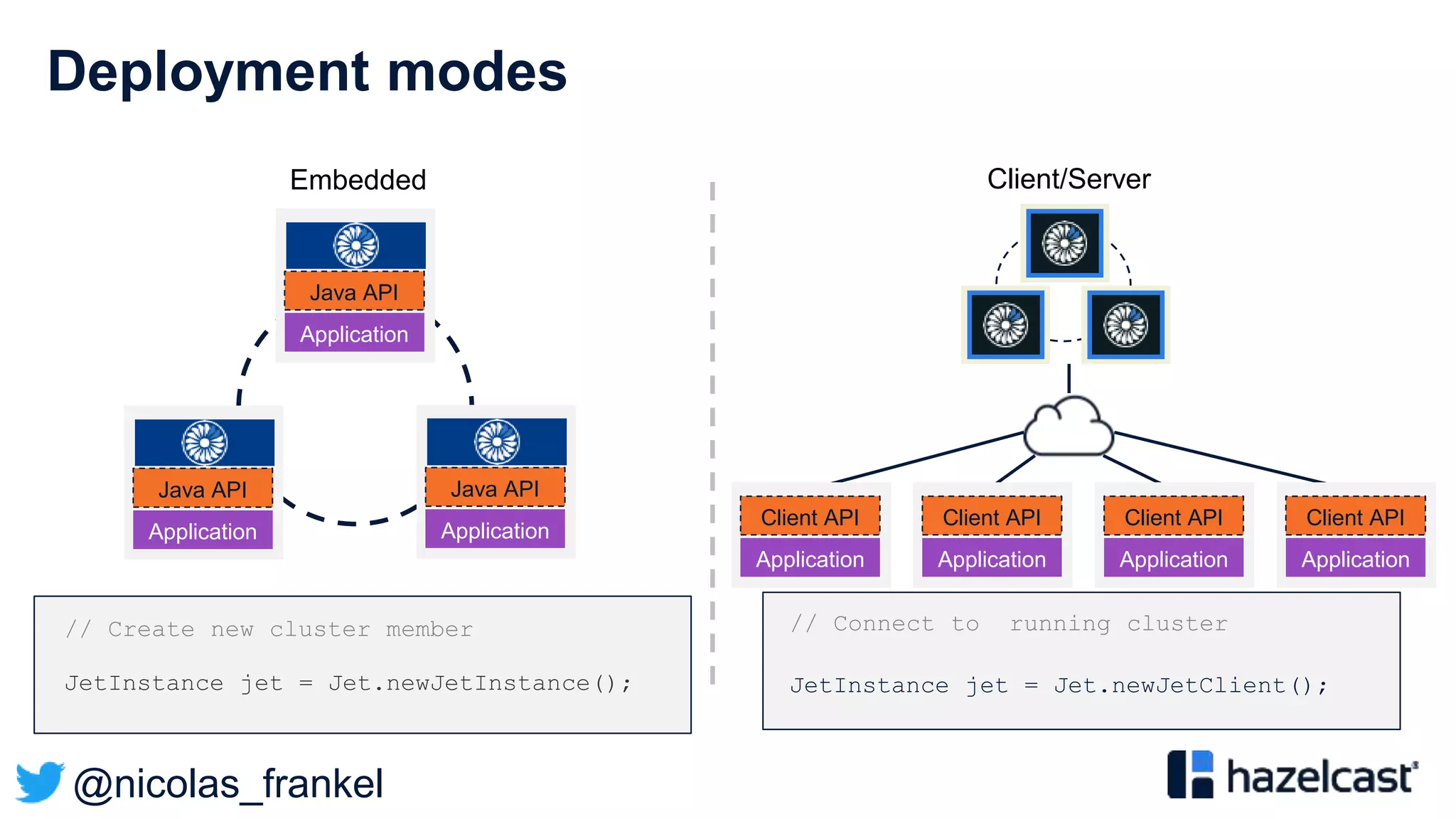
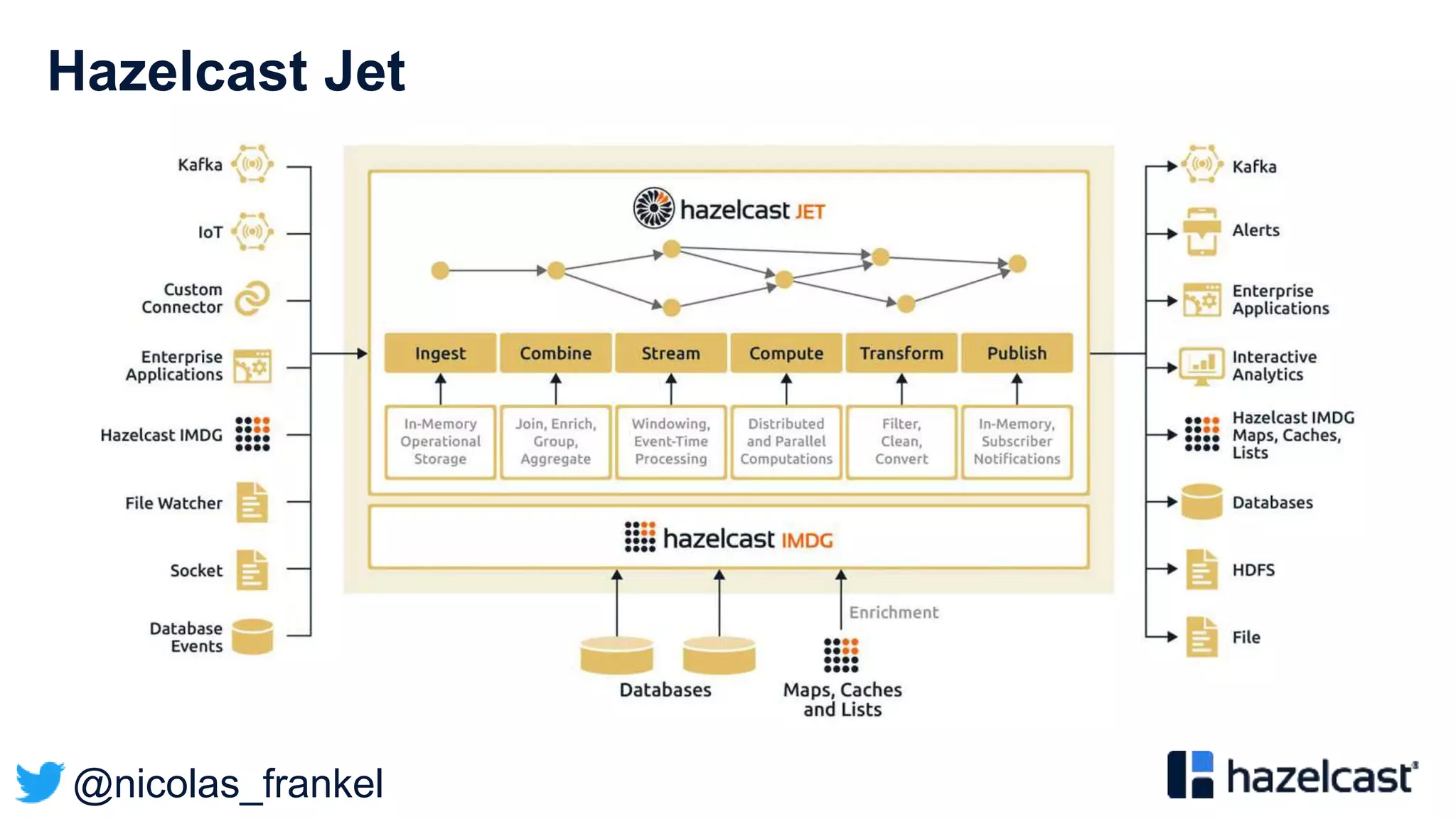
This document discusses stream processing and summarizes a presentation about the topic. It introduces Hazelcast Jet as a stream processing engine and covers open data standards like GTFS. It also describes a demo that uses GTFS data to enrich public transit vehicle position updates in real-time using Hazelcast Jet. The presentation discusses streaming approaches, benefits over batch processing, and provides an overview of stream processing concepts.





























![@nicolas_frankel
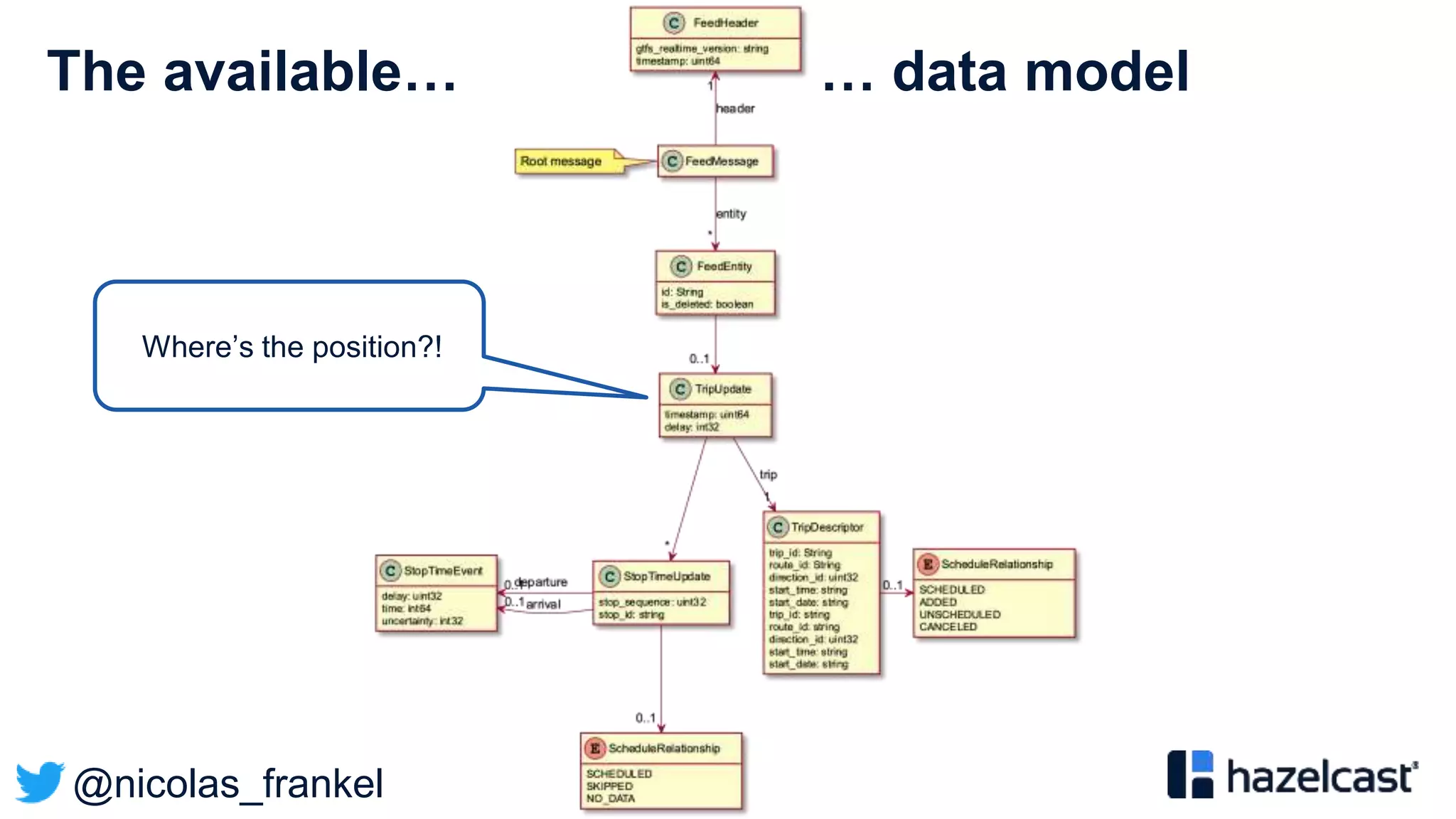
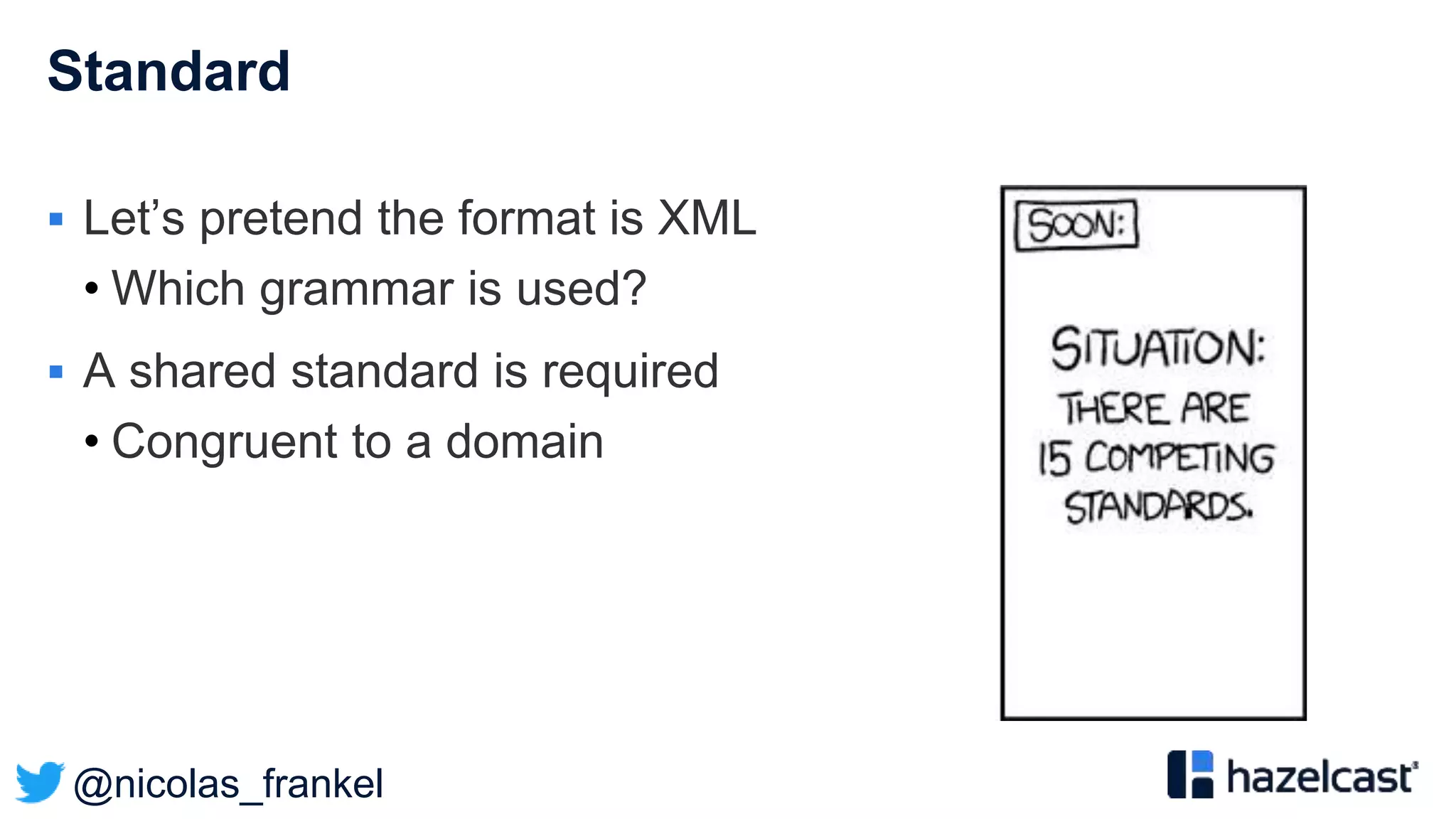
A standard for Public Transport
General Transit Feed Specification (GTFS)
” […] defines a common format for public transportation
schedules and associated geographic information. GTFS
feeds let public transit agencies publish their transit data and
developers write applications that consume that data in an
interoperable way.”
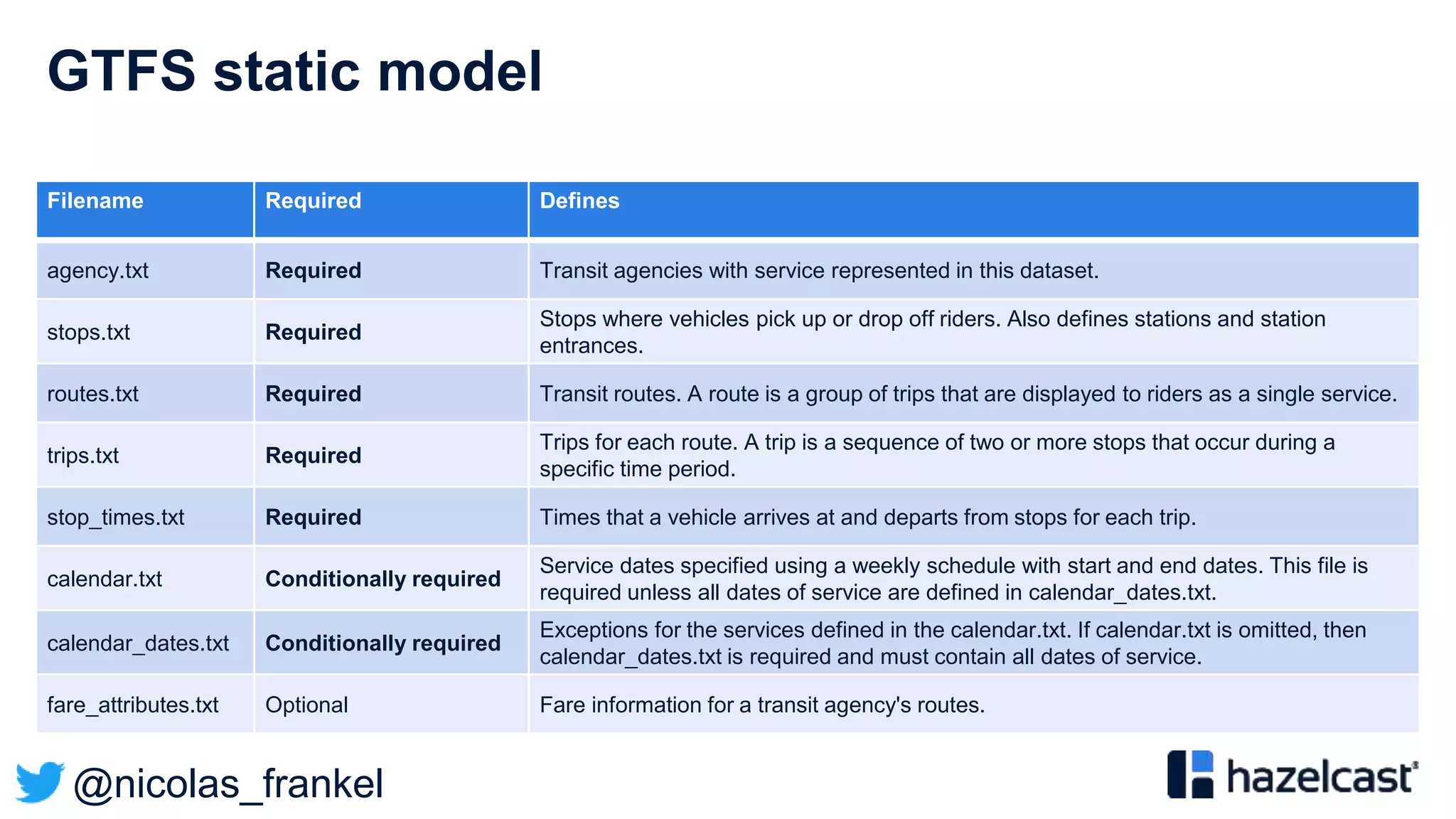
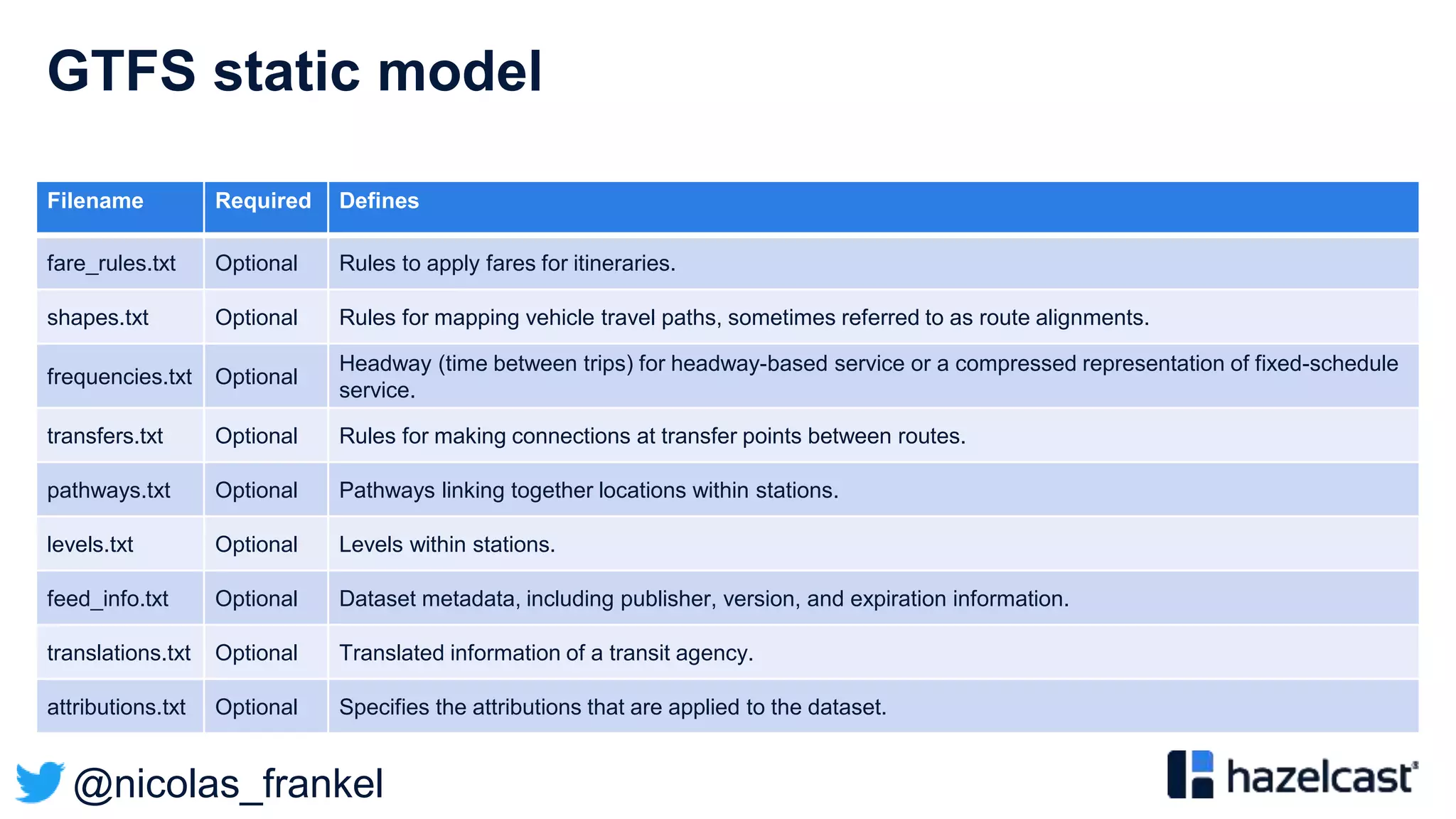
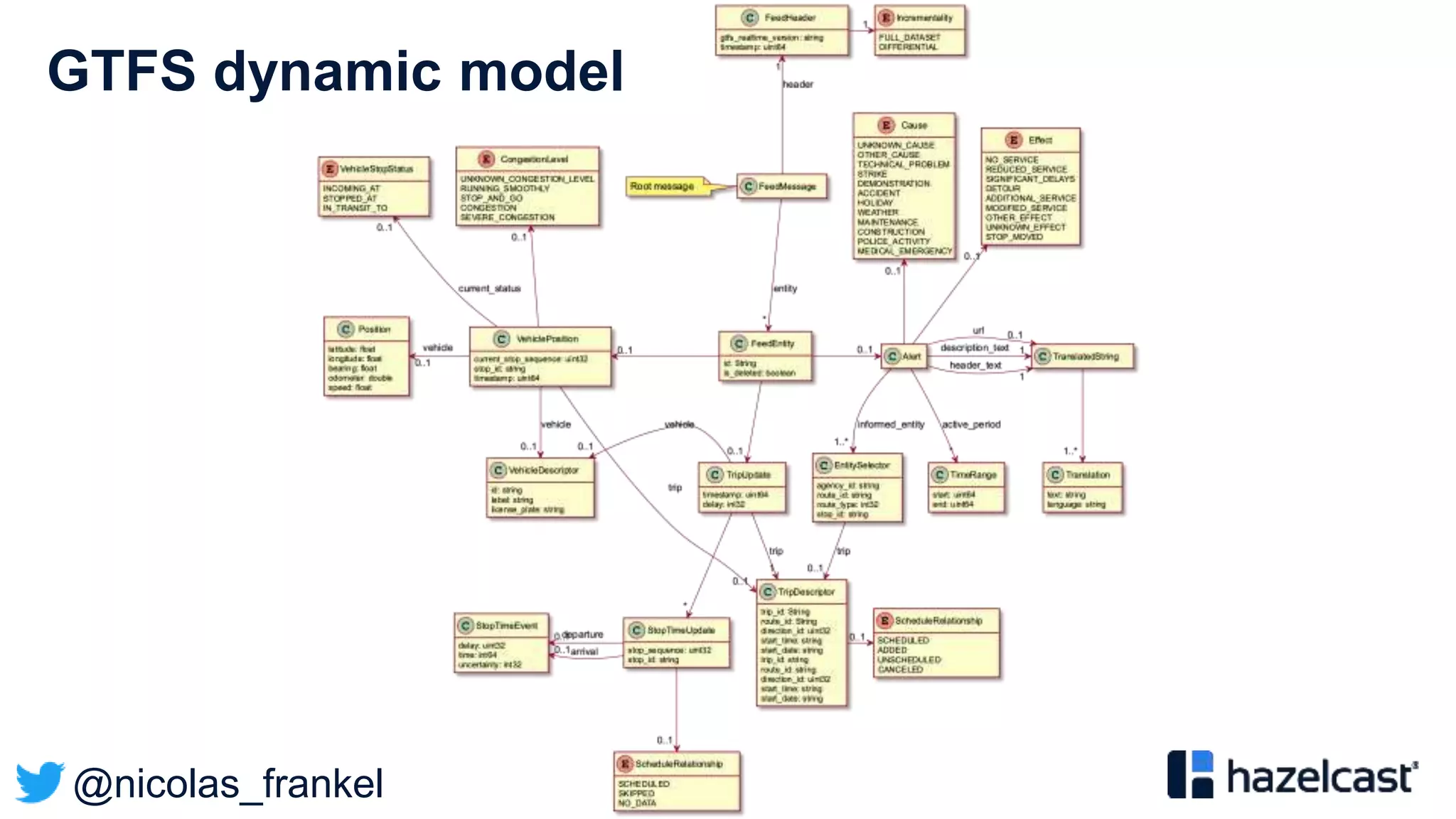
Based on two kinds of data:
• “Static” e.g. stops
• Dynamic e.g. position](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/bigdataconference-introductiontostreamprocessing-201126081513/75/BigData-conference-Introduction-to-stream-processing-37-2048.jpg)