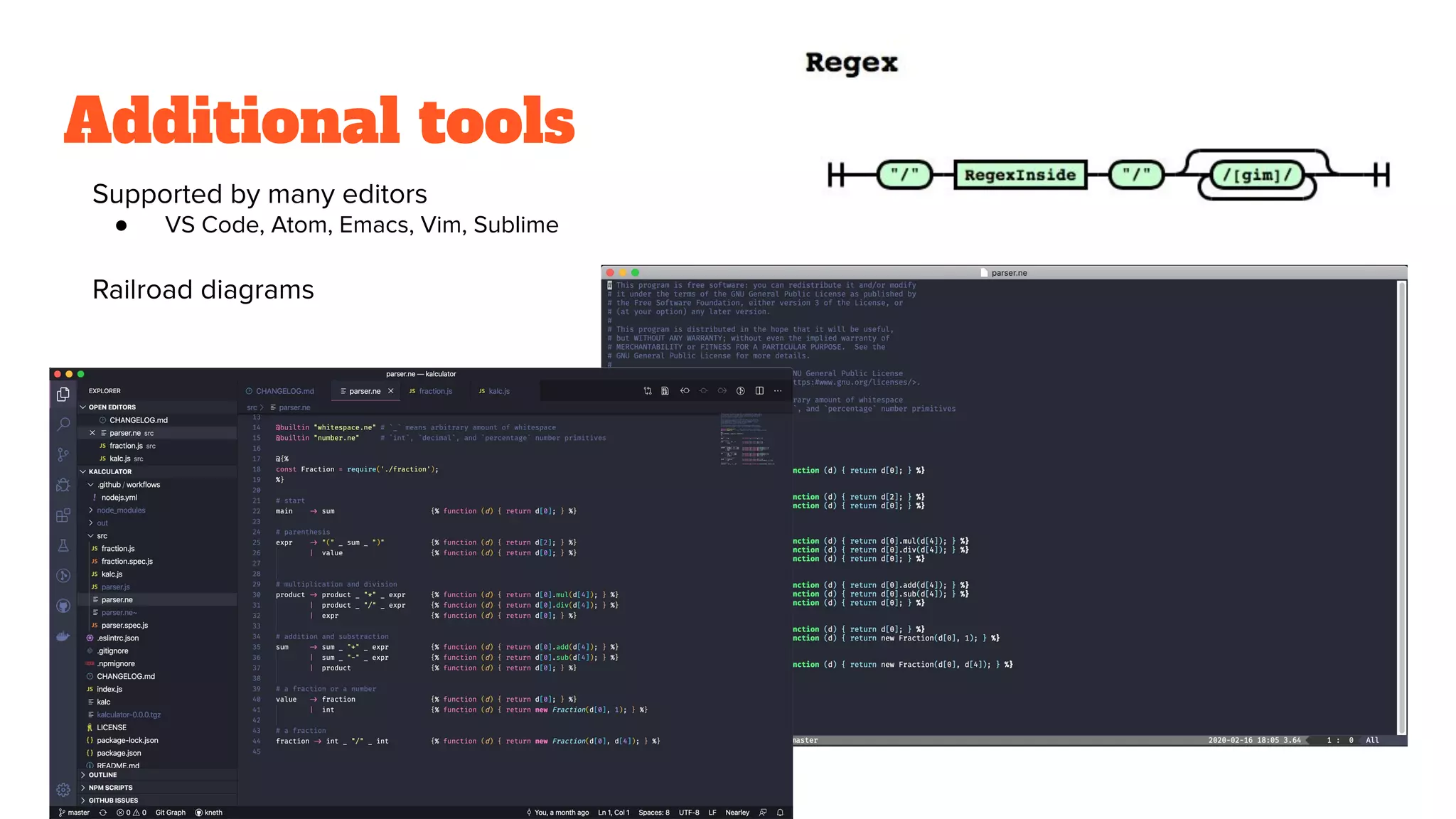
This document discusses building parsers in JavaScript. It begins with an overview of parsing and grammar. Nearley is introduced as a parser generator that implements Earley's parsing algorithm. Nearley allows defining grammars and generating JavaScript parsers from them. The document then provides an example of building a fraction calculator parser using Nearley. It presents the grammar and source code for the parser and fraction calculation logic. Key advantages of Nearley for JavaScript parsing are its support for left-recursive grammars and ability to generate parsers with semantic actions.











![How to use
● Easy installation: npm install nearley --save-dev
● Generate a parser: npx nearleyc -o parser.js parser.ne
○ Add to scripts in package.json
● The .ne files contains rules, terminals, non-terminals, and actions
expr -> "(" _ sum _ ")" {% function (d) { return d[2]; }
%}
| value {% function (d) { return d[0]; }
%}
Non-terminal Terminal Whitespace Action The return value
from the sum rule](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/buildingparsersinjavascript-200221073752/75/Building-parsers-in-JavaScript-12-2048.jpg)