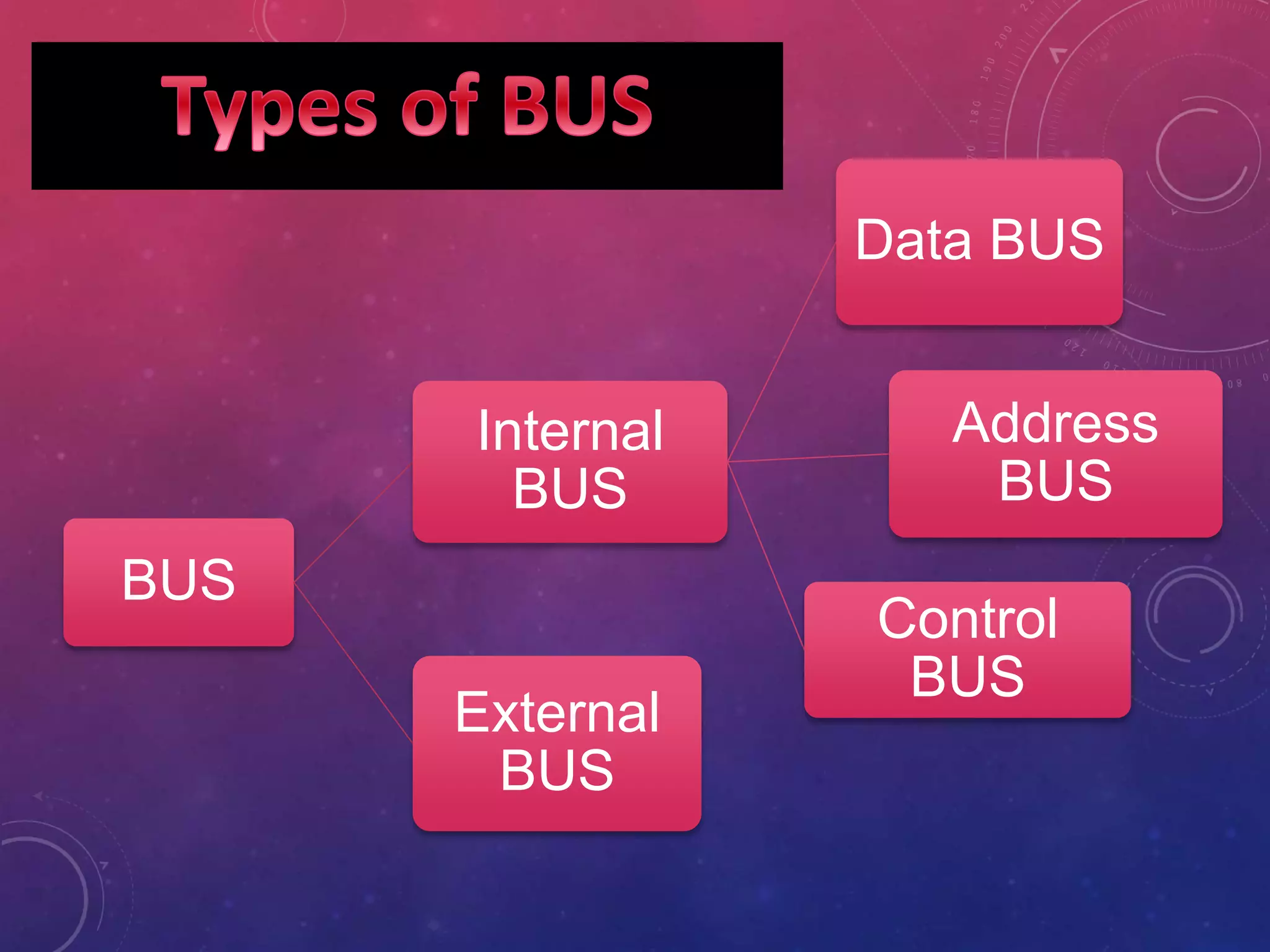
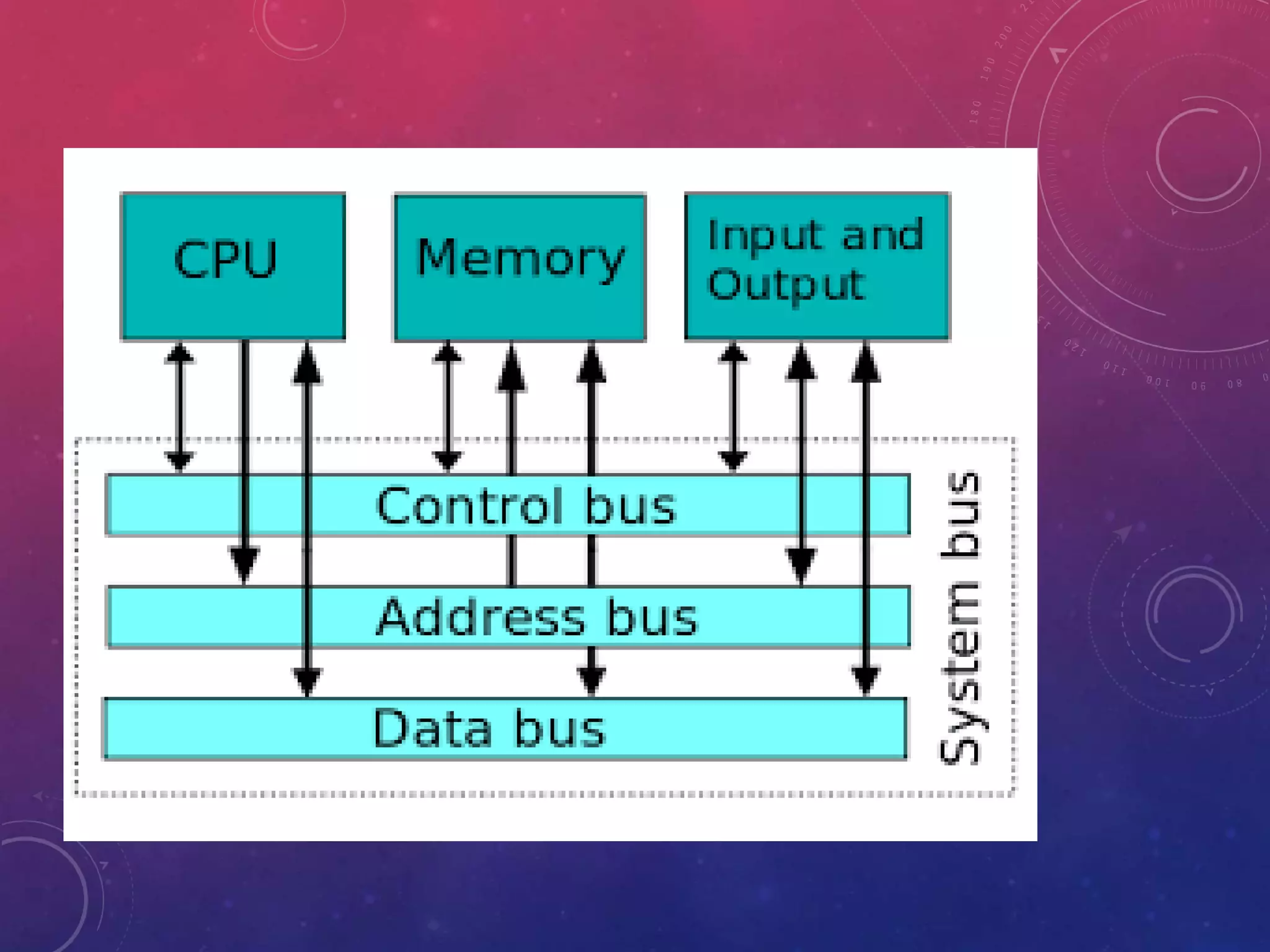
This document discusses different types of computer buses. It defines a bus as a communication channel that connects various computer components using cables. It describes the functions of buses in transferring data, addressing memory locations, and supplying power. It then discusses internal buses that connect internal computer components to the motherboard and carry data, addresses, and control signals. It provides examples of different internal buses like the data bus, address bus, and control bus. It also defines external buses that connect internal components to external devices like USB ports.