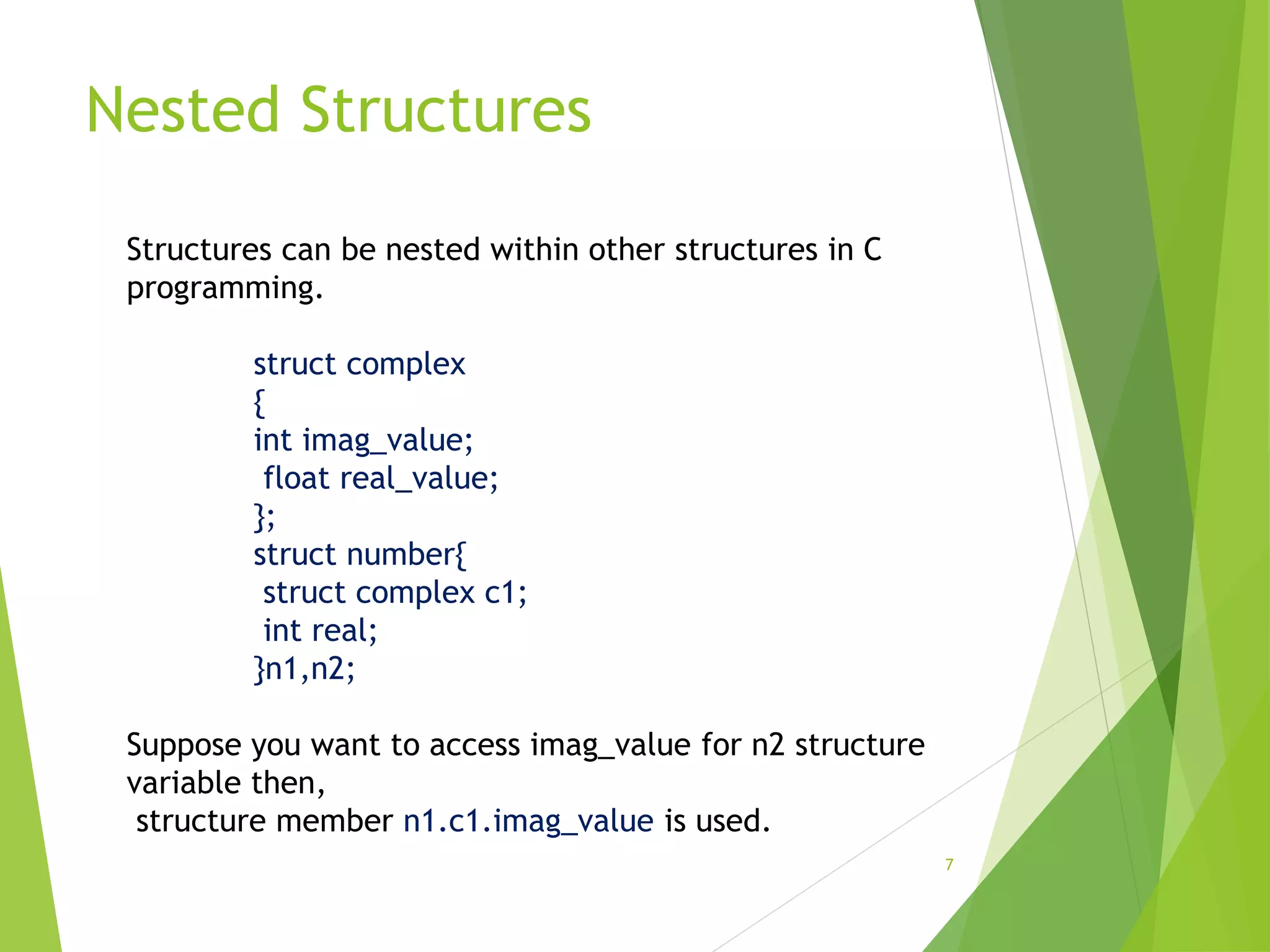
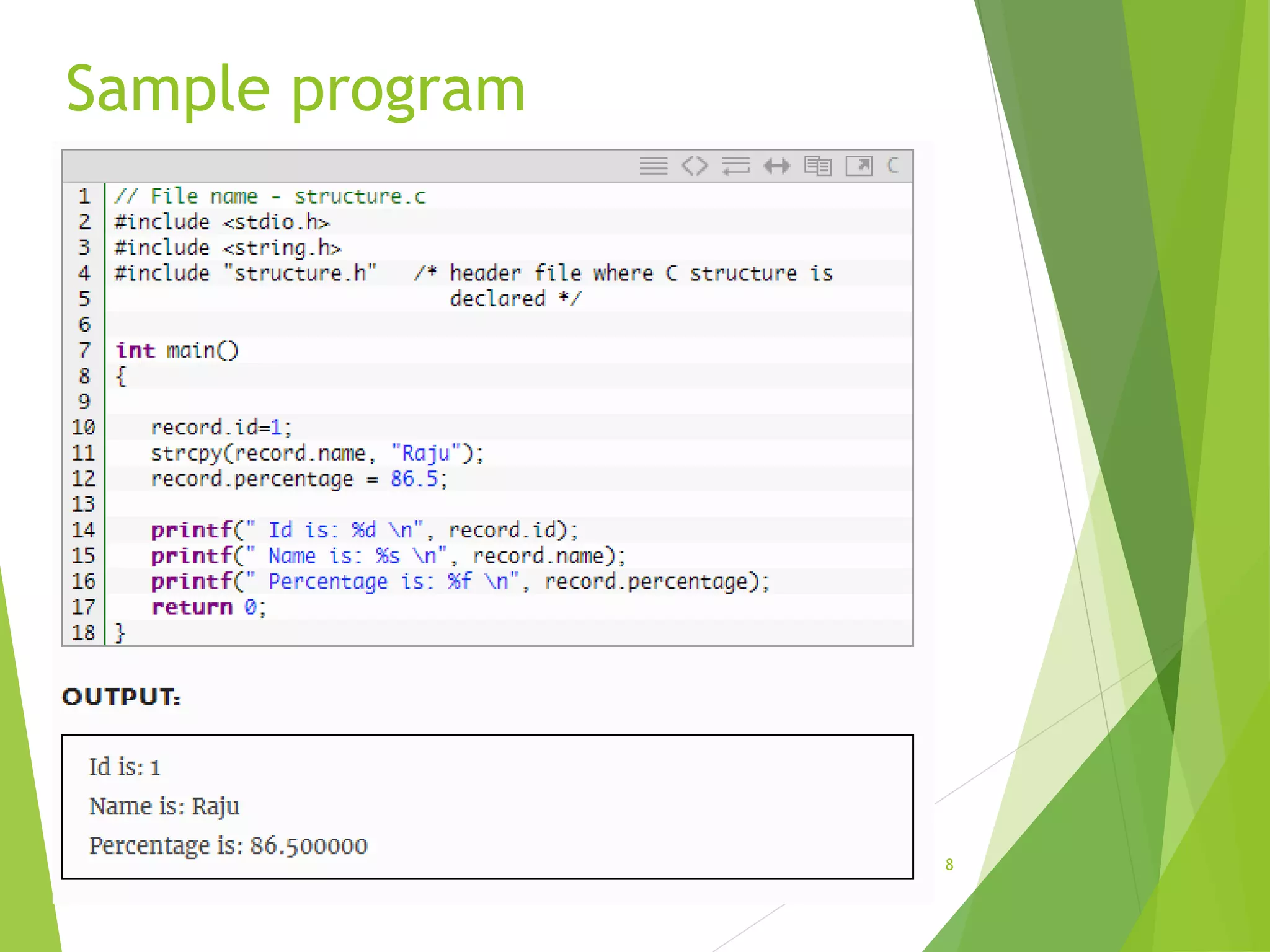
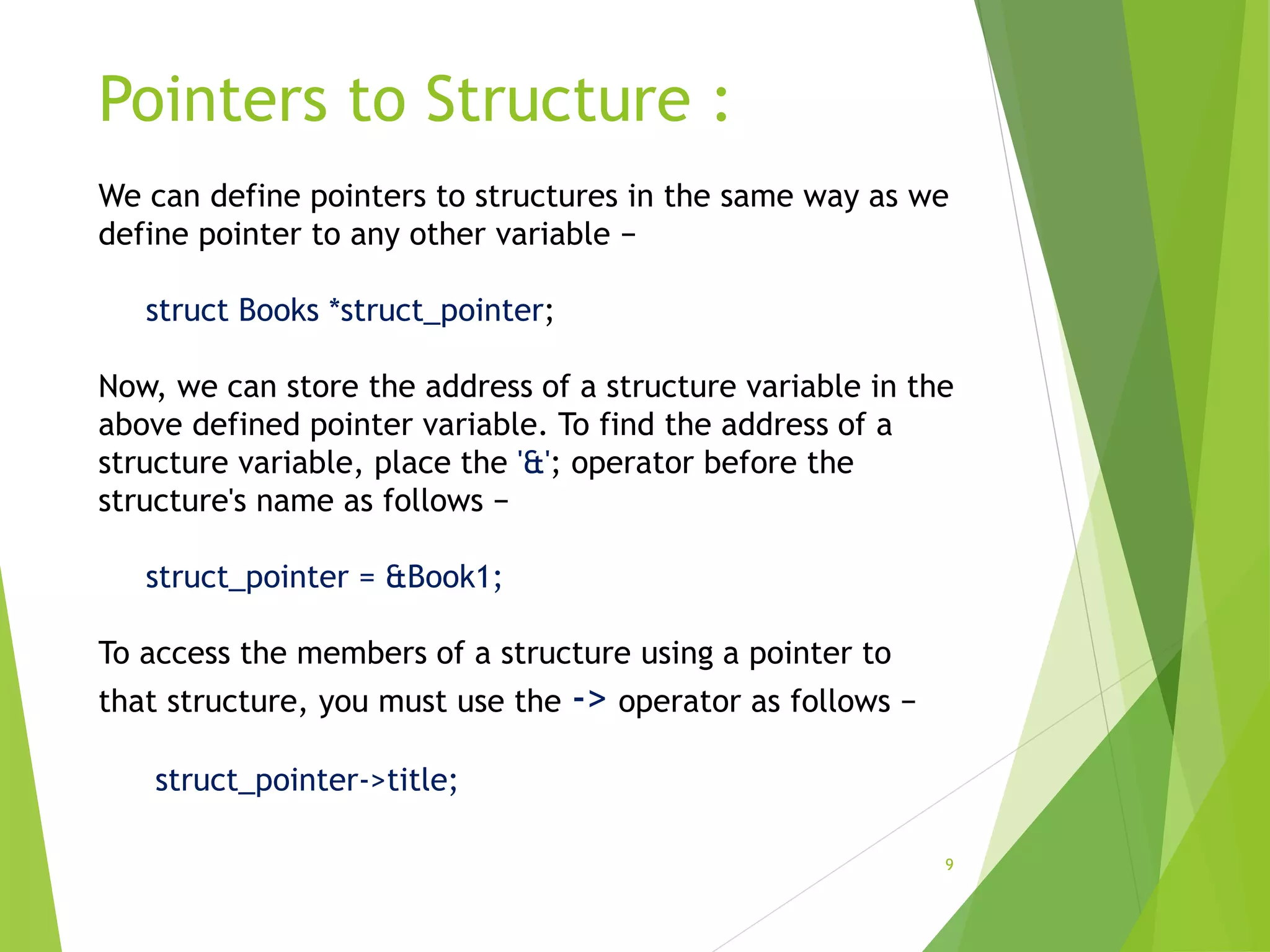
The document discusses structures in C programming. It defines a structure as a user-defined data type that allows combining different data types under a single name. Structures are used to represent records with multiple attributes. The document explains how to declare and define structures with tags, and access structure members using dot and pointer operators. It provides an example of a nested structure and a program demonstrating the use of functions and pointers with structures.



![Structure declarations
4
To define a structure, you must use the struct statement. The struct statement
defines a new data type, with more than one member. The format of the struct
statement is as follows −
struct [structure tag] {
member definition;
member definition;
...
member definition;
} [one or more structure variables];
struct person
{
char name[50];
int cit_no;
float salary;
};
We can create the structure for a
person as mentioned above as:](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mine-170227205159/75/C-programing-Structure-4-2048.jpg)
![Structure variable declaration
5
When a structure is defined, it creates a user-defined type
but, no storage is allocated. For the above structure of person,
variable can be declared as:
struct person
{
char name[50];
int cit_no;
float salary;
};
Inside main function:
struct person p1, p2, p[20];
Another way of creating sturcture variable
is: struct person
{
char name[50];
int cit_no;
float salary;
}p1 ,p2 ,p[20];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mine-170227205159/75/C-programing-Structure-5-2048.jpg)

![Example using function and pointer:
10
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
struct Books {
char title[50];
char author[50];
char subject[100];
int book_id;
};
/* function declaration */
void printBook( struct Books *book );
int main( ) {
struct Books Book1; /* Declare Book1 of type Book */
struct Books Book2; /* Declare Book2 of type Book */
/* book 1 specification */
strcpy( Book1.title, "C Programming");
strcpy( Book1.author, "Nuha Ali");
strcpy( Book1.subject, "C Programming Tutorial");
Book1.book_id = 6495407;
/* book 2 specification */
strcpy( Book2.title, "Telecom Billing");
strcpy( Book2.author, "Zara Ali");
strcpy( Book2.subject, "Telecom Billing Tutorial");
Book2.book_id = 6495700;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/mine-170227205159/75/C-programing-Structure-10-2048.jpg)

