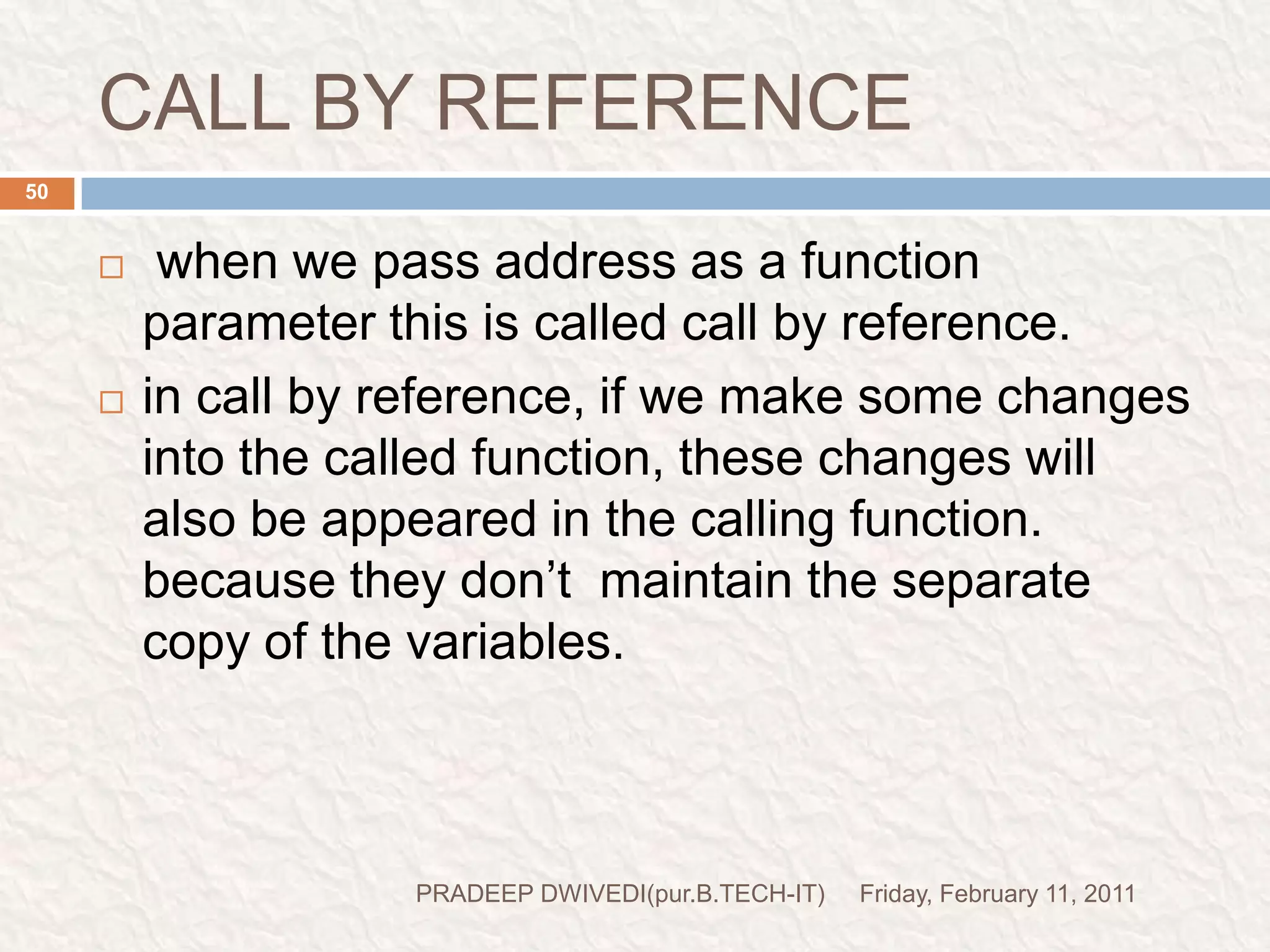
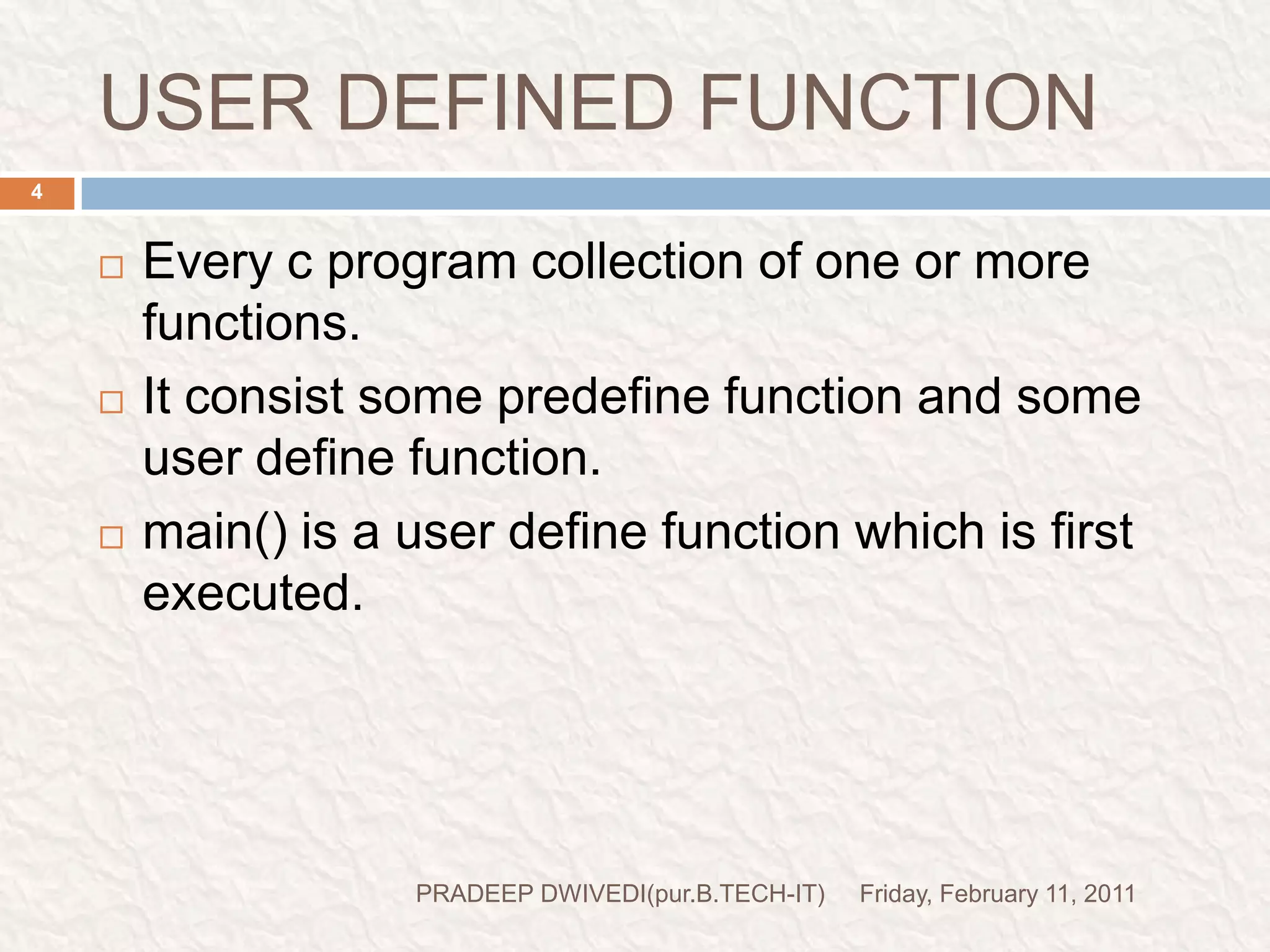
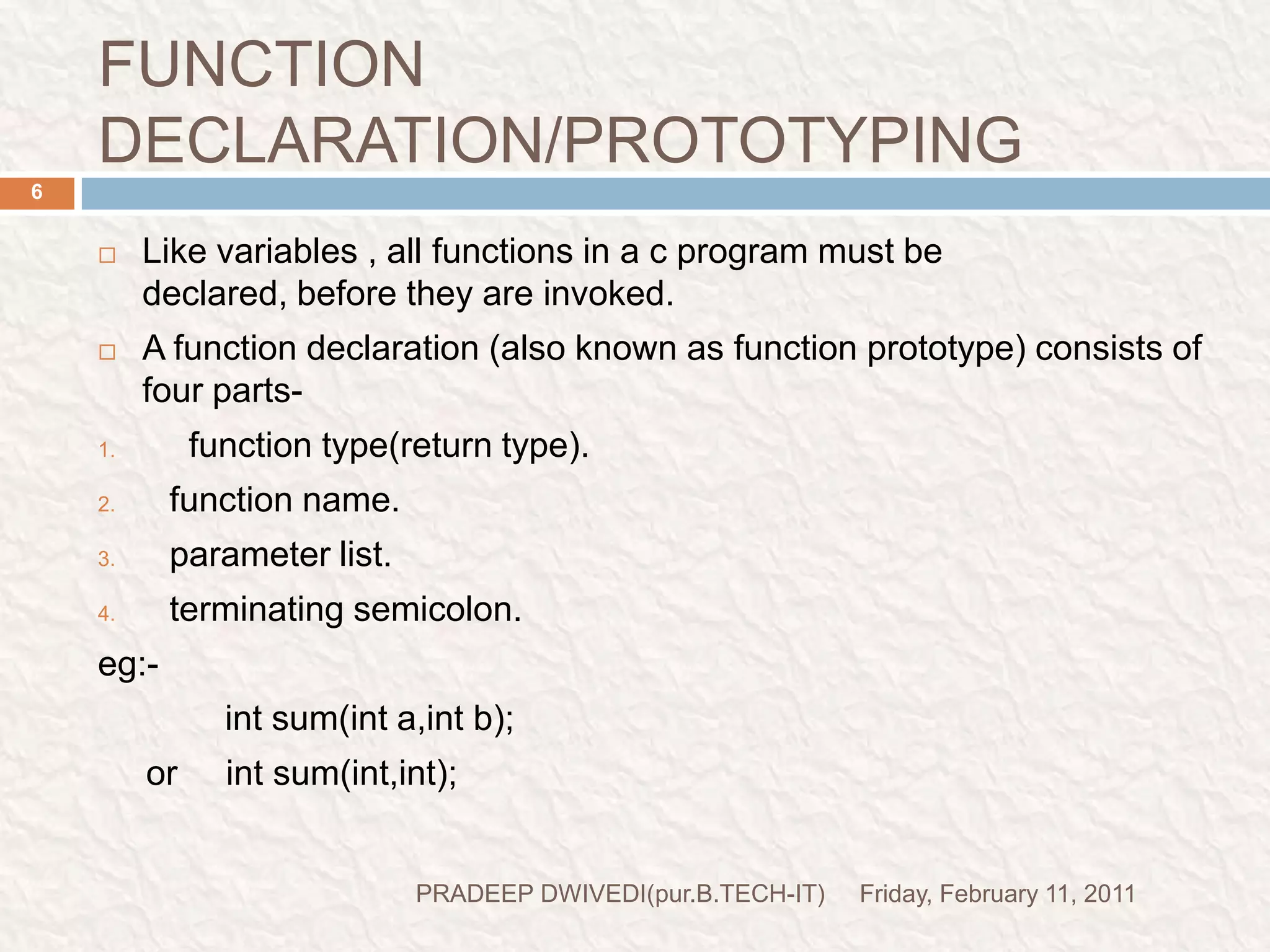
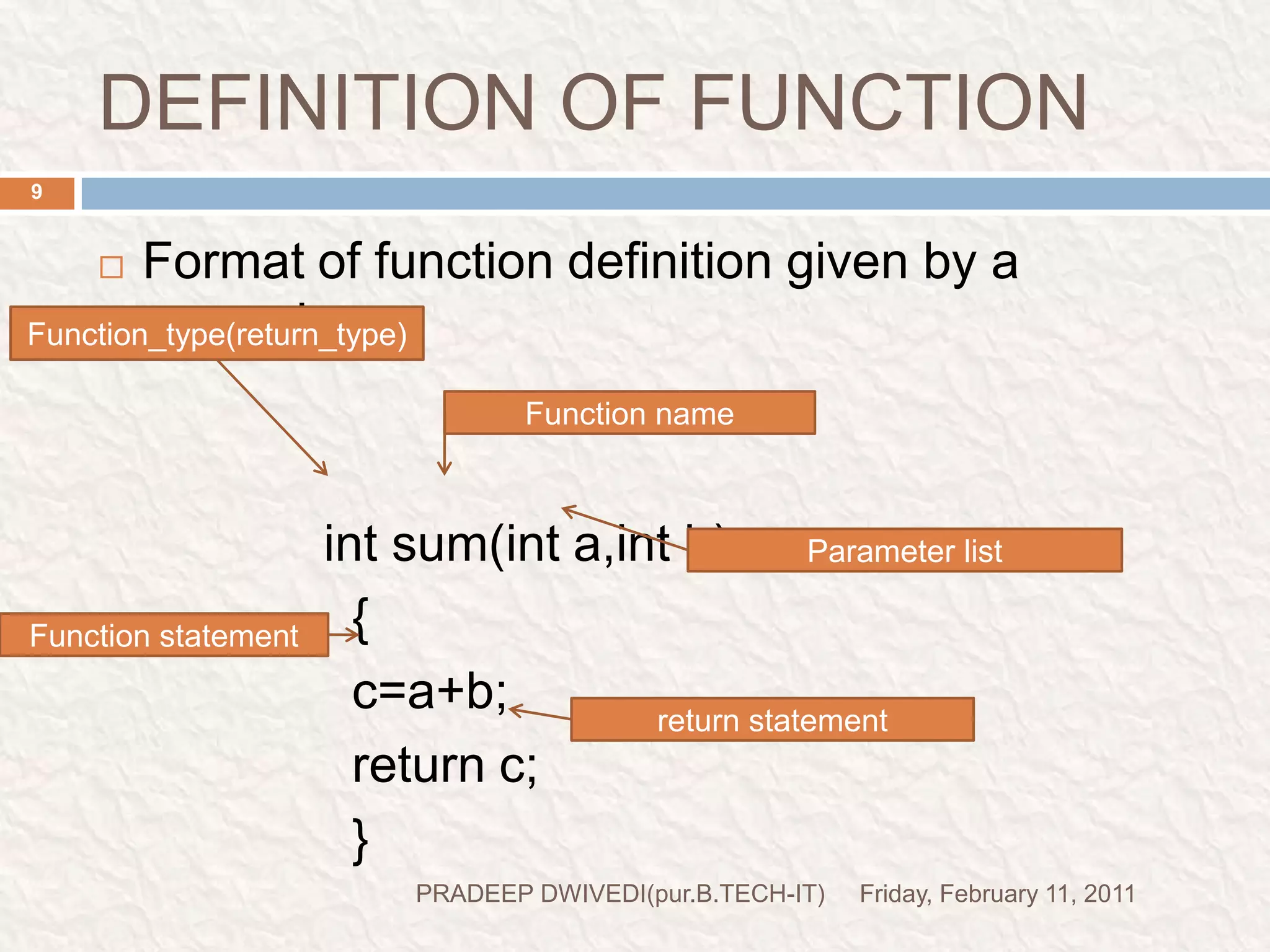
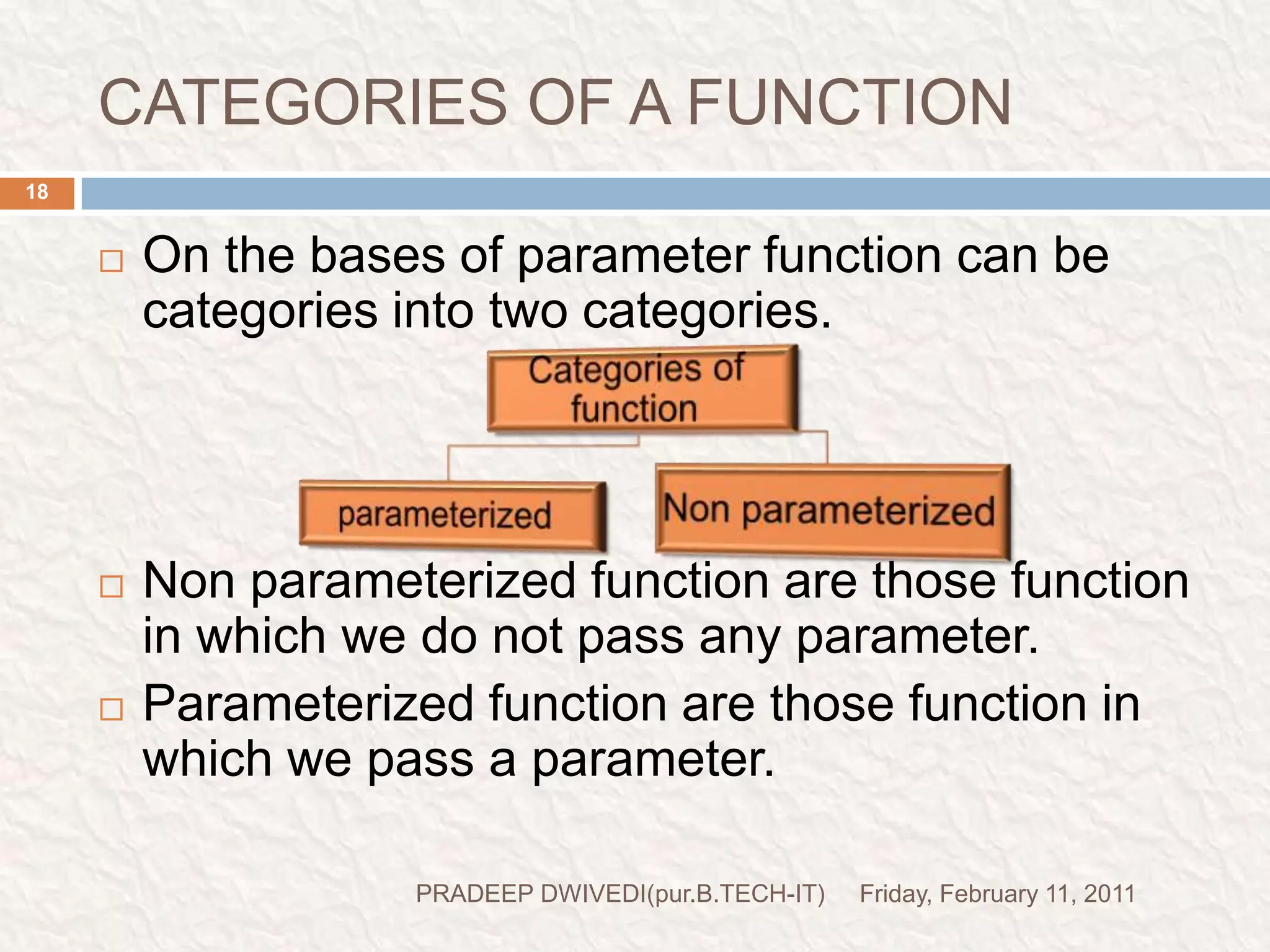
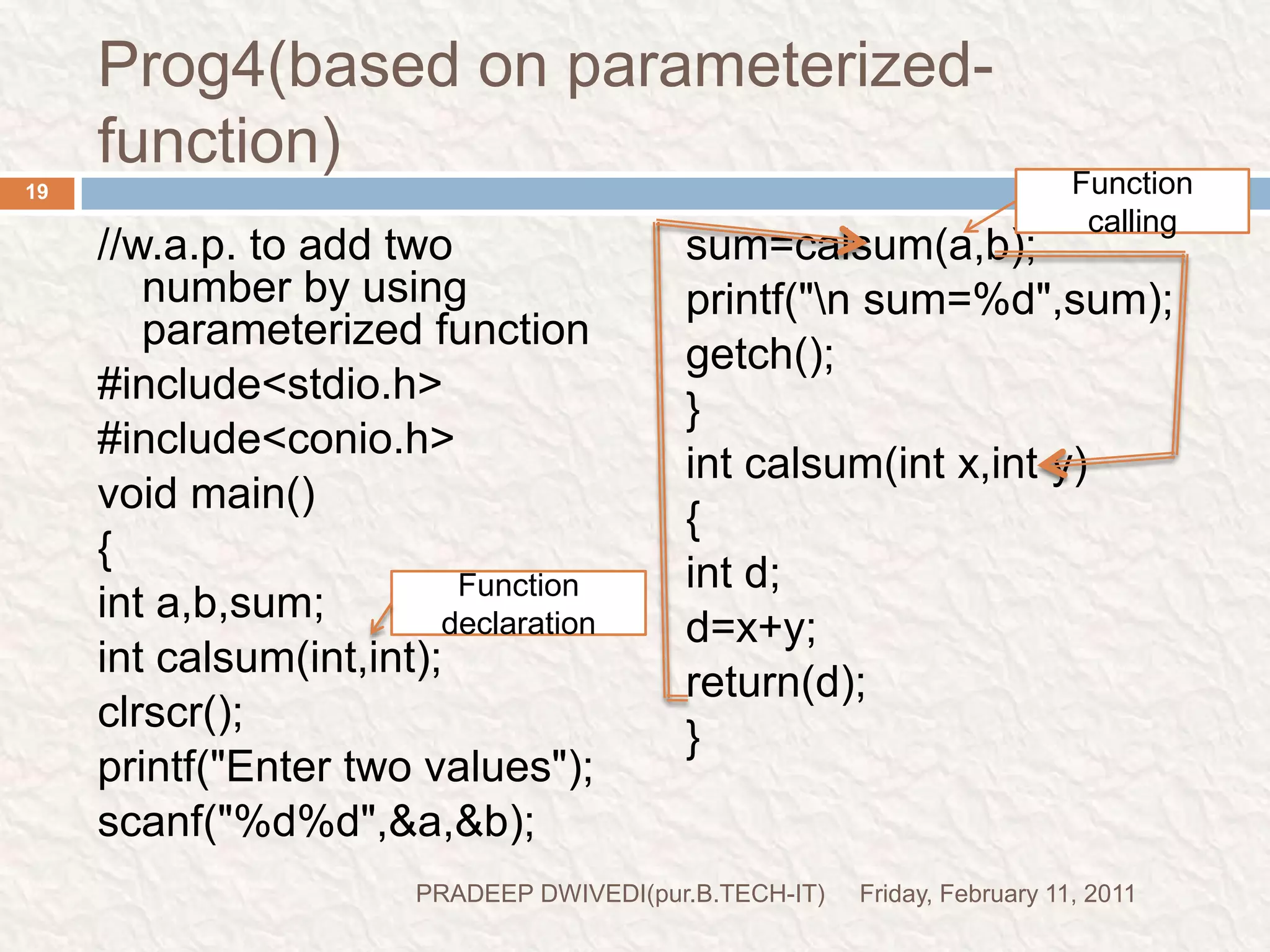
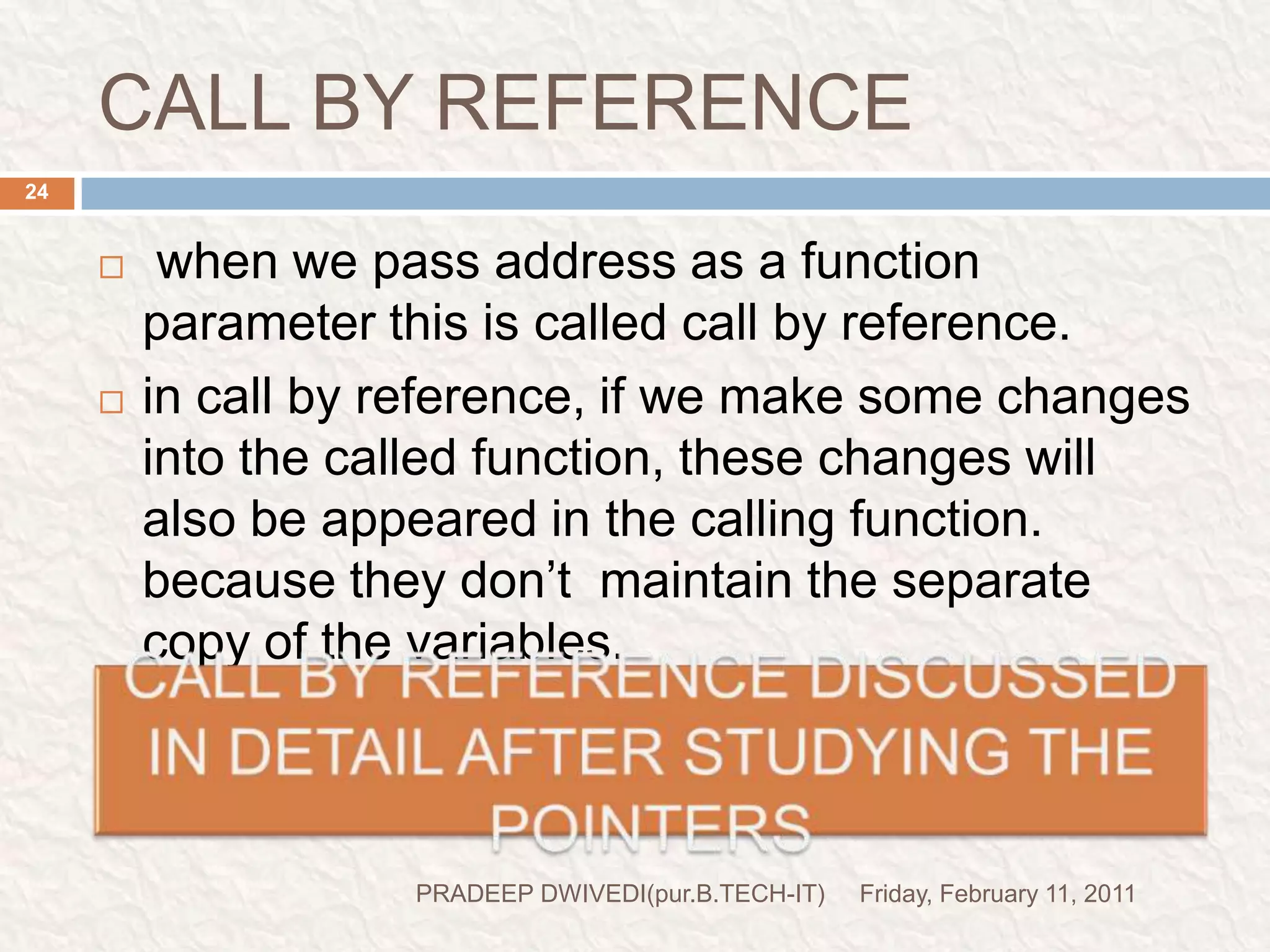
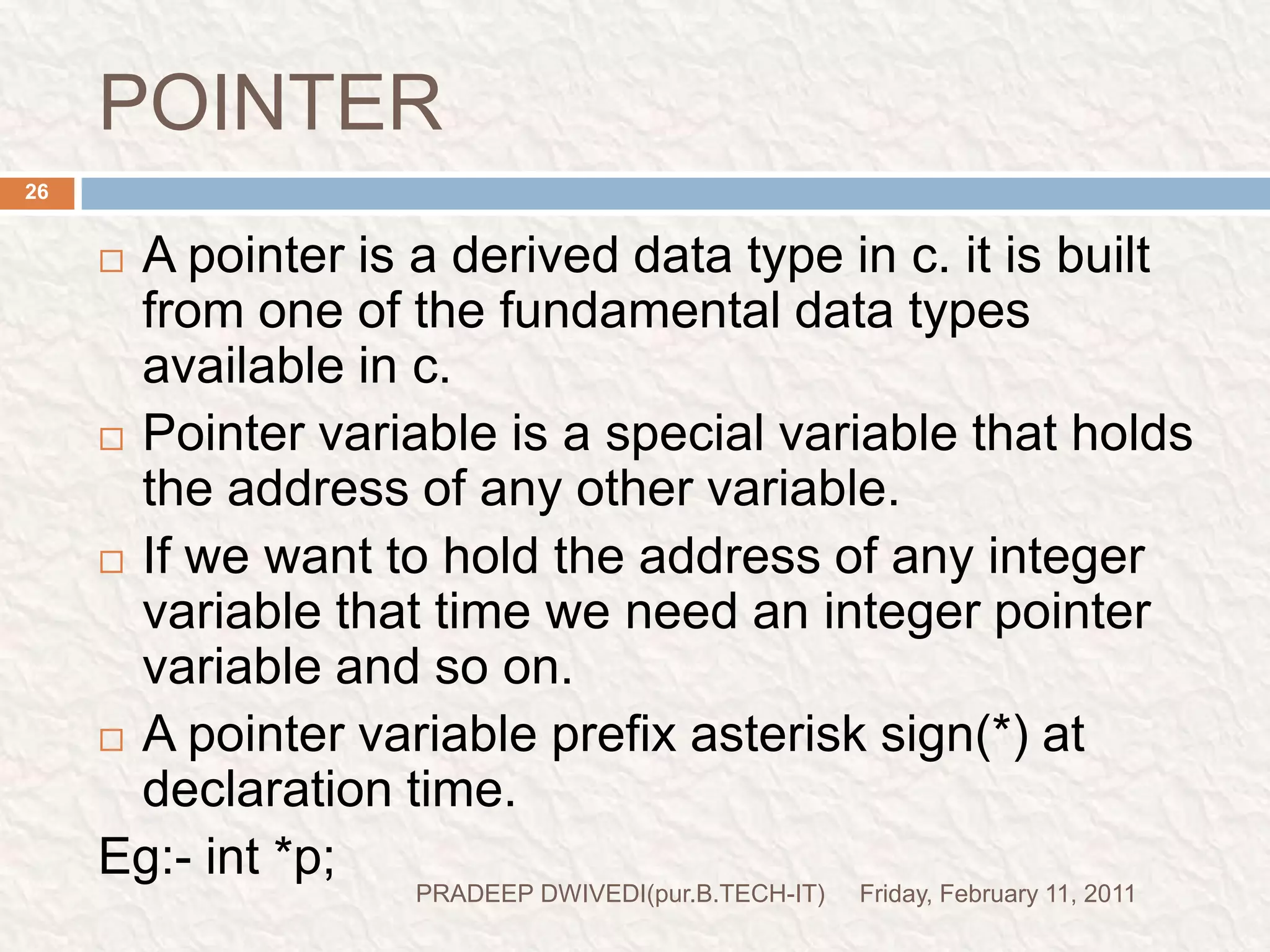
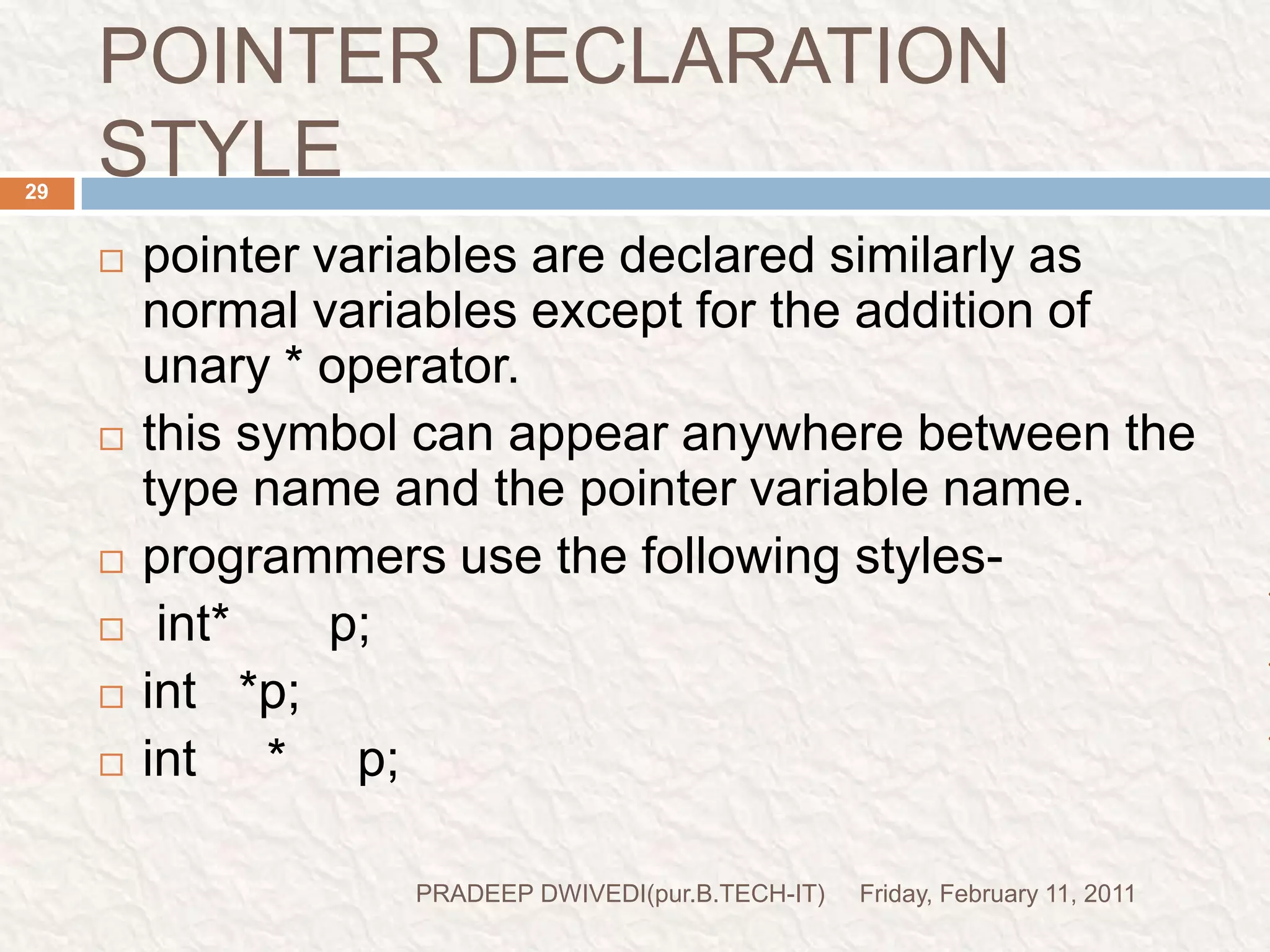
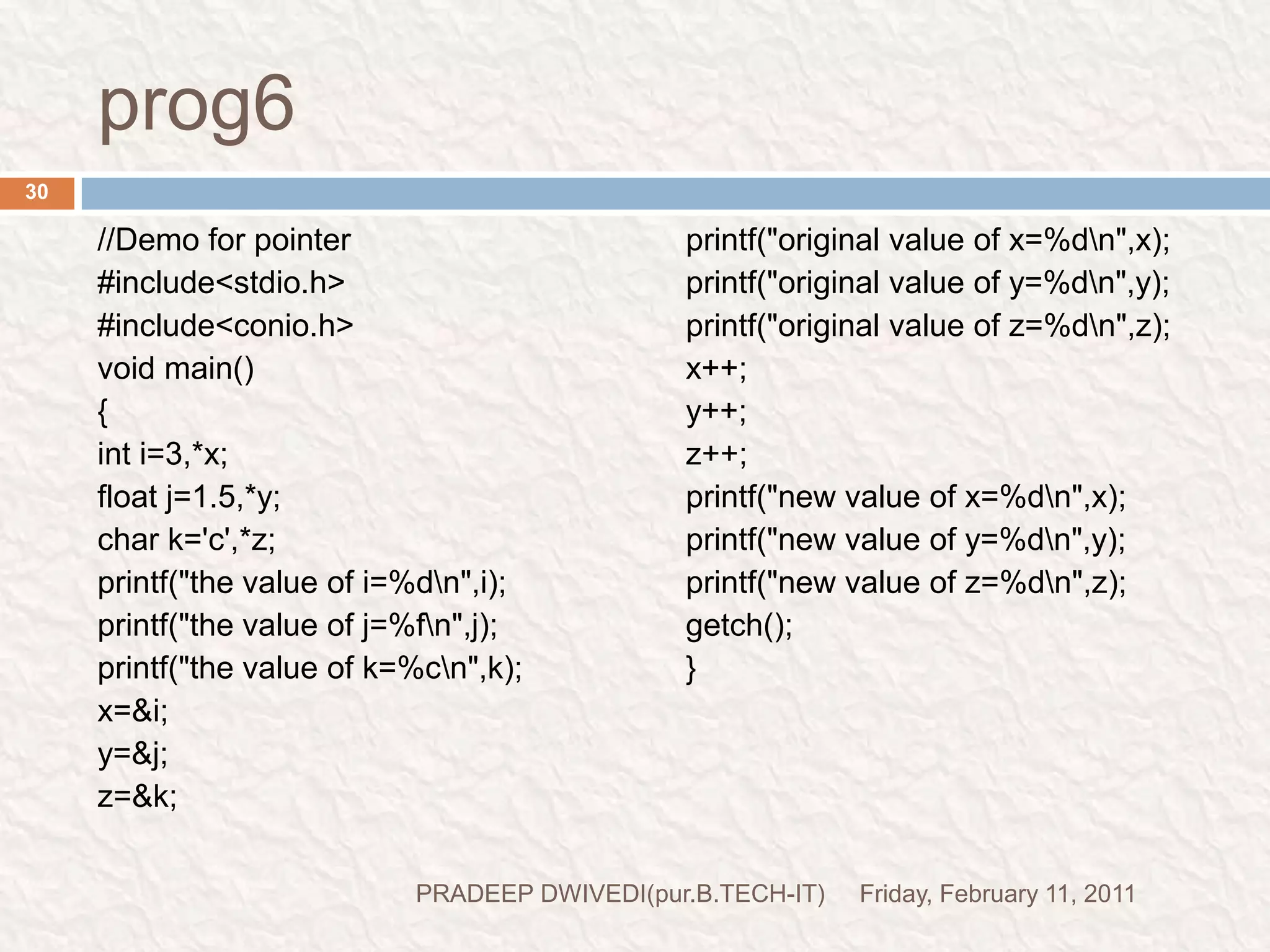
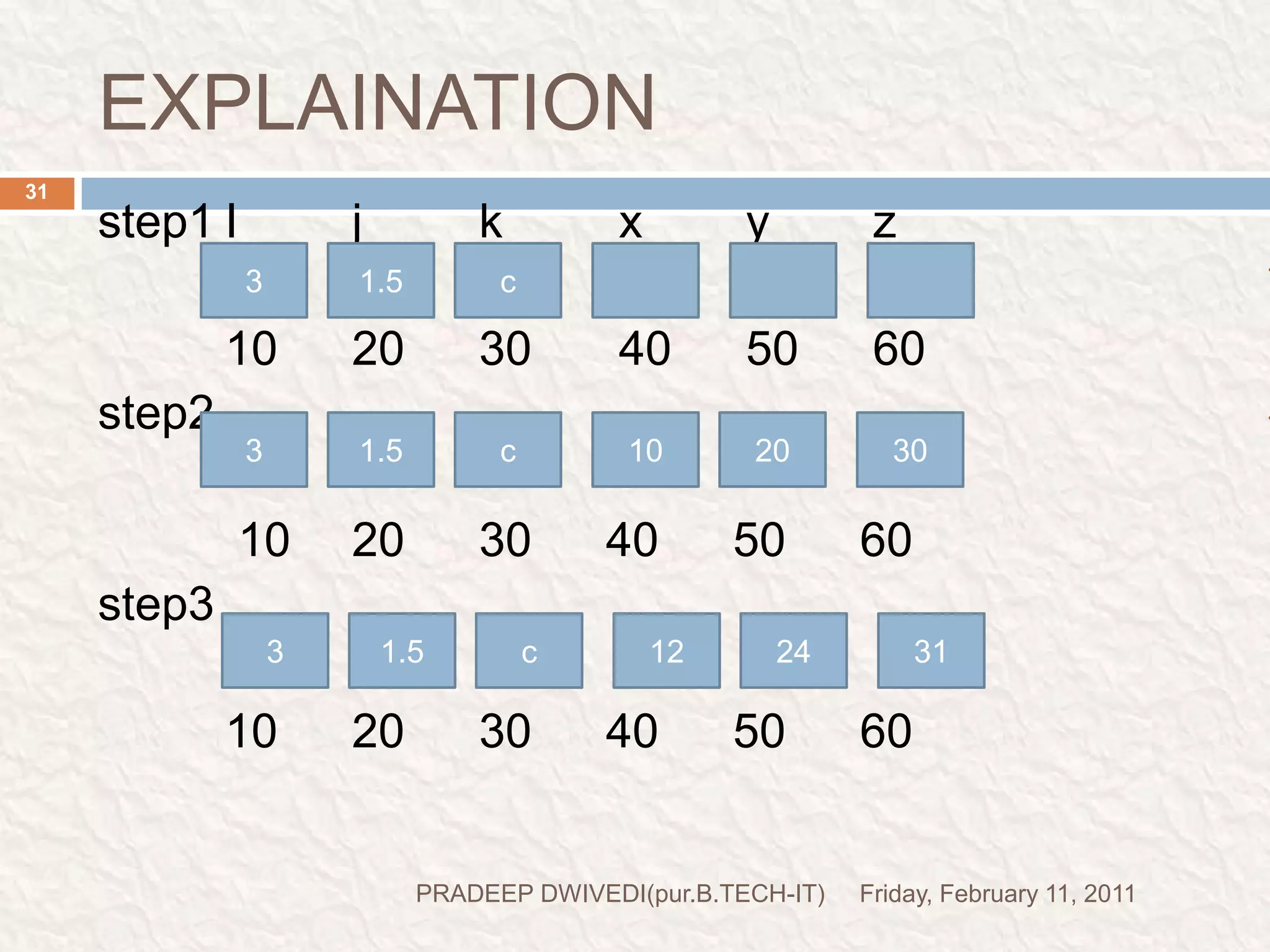
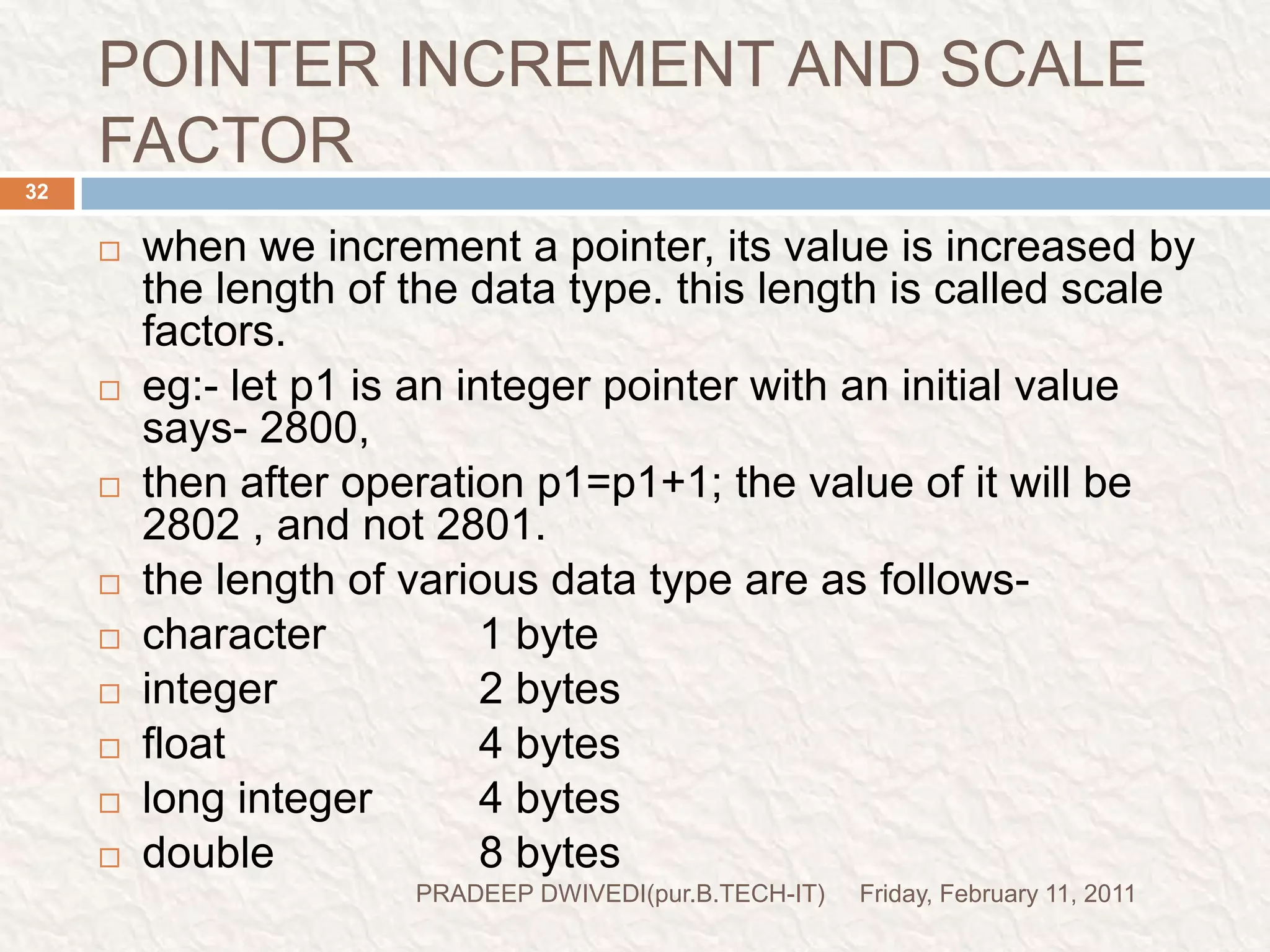
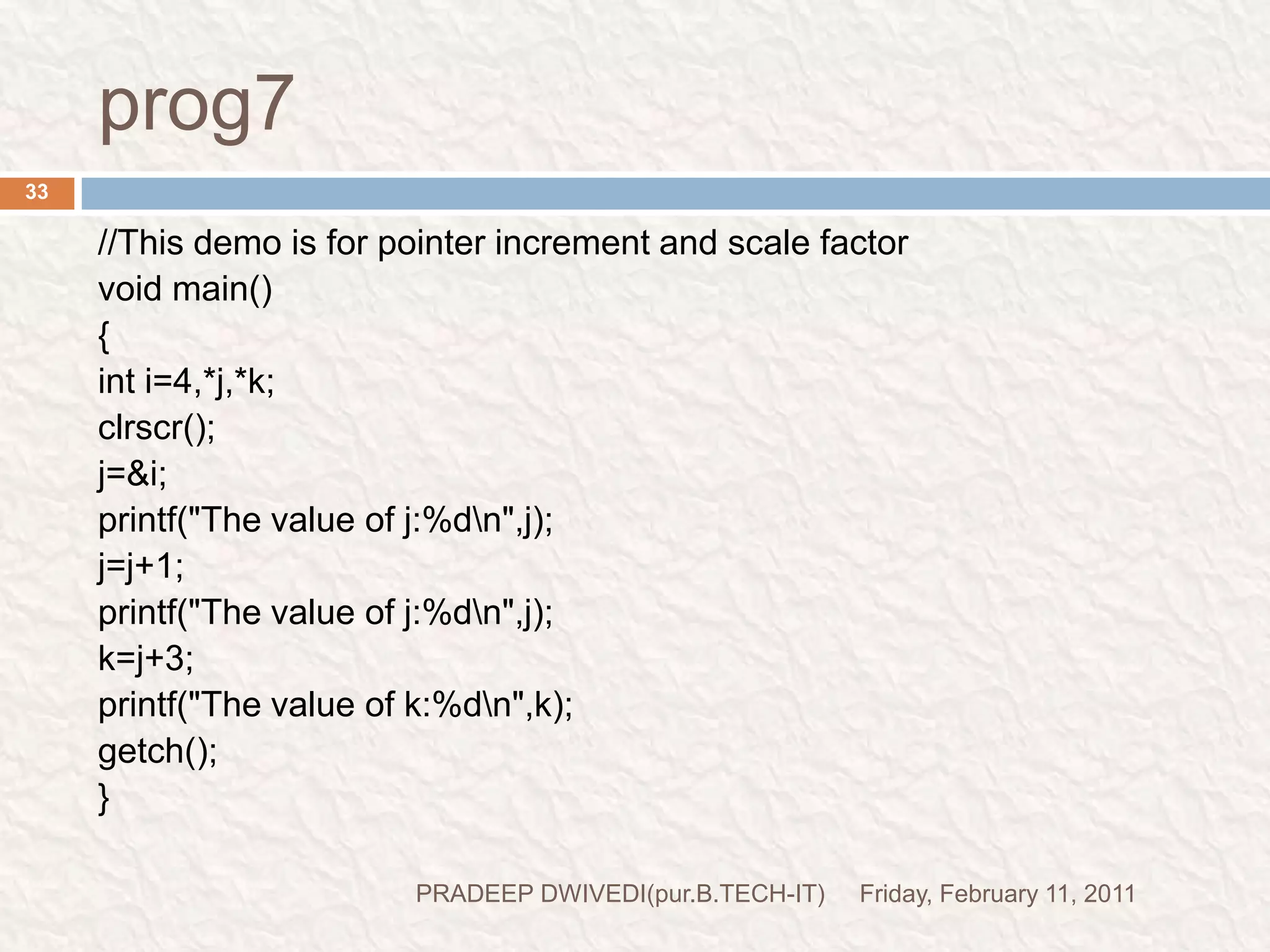
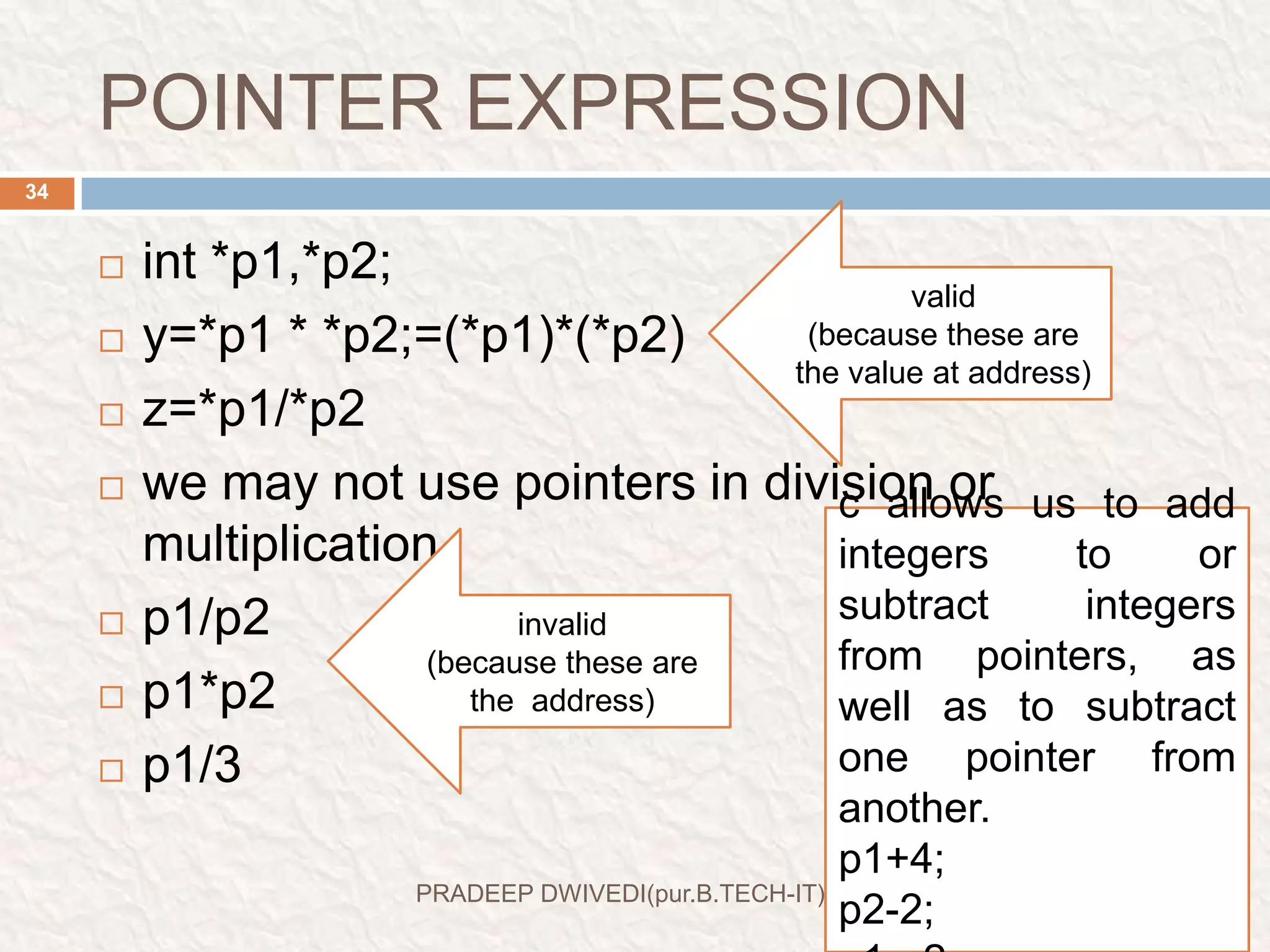
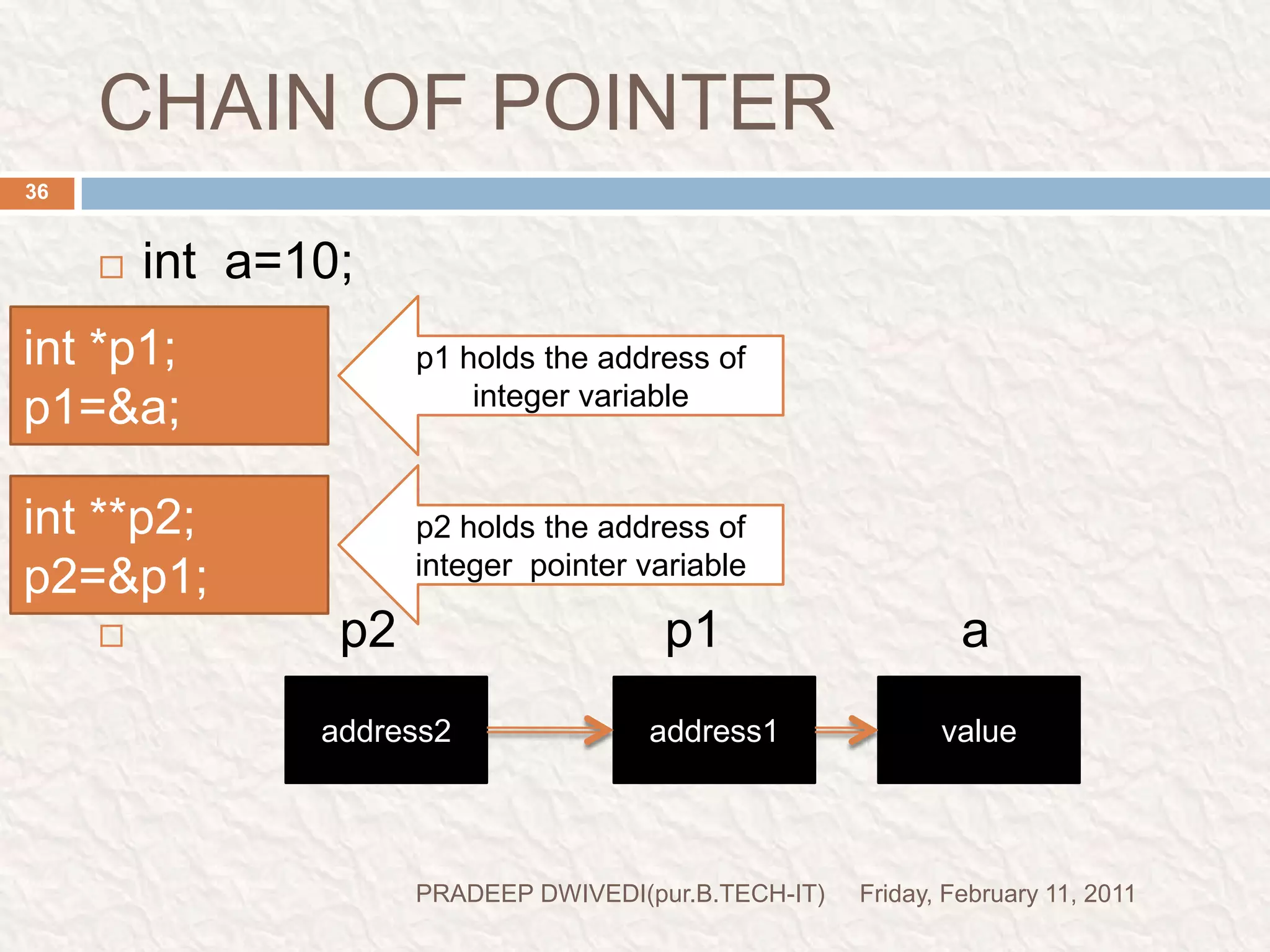
The document discusses user defined functions in C programming. It covers the key elements of a function including declaration, definition, parameters, return type, calling functions, and categories of functions. Examples are provided to demonstrate function declaration, definition, calling, parameterized functions, and call by value vs call by reference. Pointers are also introduced, including pointer declaration, incrementing pointers, and scale factors.















![POINTER vs ARRAYFriday, February 11, 2011PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)39Array is also used to hold the address but, array variable used to holds the base address of an array.The term base address means address of very first element in the array.Suppose we declare an array-int x[5]={1,2,3,4,5};](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-programmingslide-6-110211112544-phpapp02/75/C-programming-slide-6-38-2048.jpg)
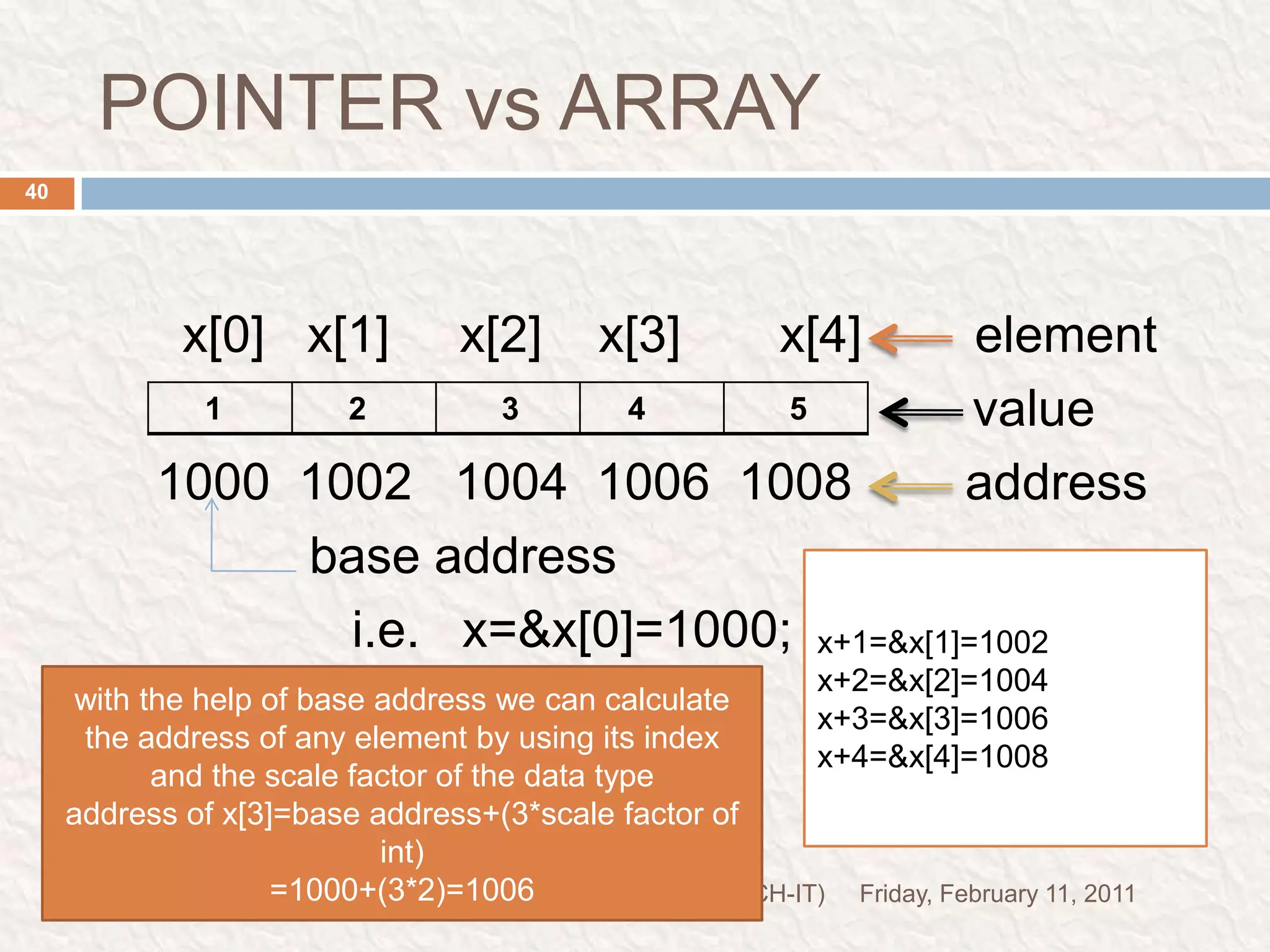
![POINTER vs ARRAYFriday, February 11, 2011PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)40 x[0] x[1] x[2] x[3] x[4] element value 1000 1002 1004 1006 1008 address base address i.e. x=&x[0]=1000;x+1=&x[1]=1002x+2=&x[2]=1004x+3=&x[3]=1006x+4=&x[4]=1008with the help of base address we can calculate the address of any element by using its index and the scale factor of the data typeaddress of x[3]=base address+(3*scale factor of int)=1000+(3*2)=1006](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-programmingslide-6-110211112544-phpapp02/75/C-programming-slide-6-39-2048.jpg)
![prog9//prog- pointer vs array#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>void main(){intarr[]={10,20,36,72,45,36};int *j,*k;clrscr();j=&arr[4];k=(arr+4);if(j==k)printf("Two pointers point two the same location");elseprintf("Two pointers do not point to the same location");getch();} Friday, February 11, 201142PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)address of arr[4]=&arr[4](arr+4) arr[0]+4=&arr[4]true](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-programmingslide-6-110211112544-phpapp02/75/C-programming-slide-6-41-2048.jpg)
![prog10//wap to sibtract a pointer from anoter pointer#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>void main(){intarr[]={10,20,30,40,60,57,56};int *i,*j;clrscr();i=&arr[1];j=&arr[5];printf("value of i:%d\n",i);printf("value of j:%d\n",j);printf("The value at address i:%d\n",*i);printf("The value at address j:%d\n",*j);printf("The difference between address: %d\n",j-i);printf("The difference between values is %d\n",*j-*i);getch();}Friday, February 11, 201143PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)I THINK THERE IS NO NEED TO EXPLIAN THIS PROGRAM](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-programmingslide-6-110211112544-phpapp02/75/C-programming-slide-6-42-2048.jpg)

![POINTER AND CHARACTER STRINGSFriday, February 11, 2011PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)45The character arrays are declared and initialized as follows:- char str[5]=“good”;The compiler automatically inserts the null character ‘\0’ at the end of the string.C supports an alternative method to create string using pointer variable of type char.eg: char *str=“good”;Remember, although str is a pointer to the string, it is also the name of string .therefore, we don’t need to use indirection operator(*) here. NOTEFriday, February 11, 2011PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)46When we want to print the string, that time we use the format string (%s).and if we want to print the address of string that time we use format string (%d) or (%u)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-programmingslide-6-110211112544-phpapp02/75/C-programming-slide-6-44-2048.jpg)
![PROG11Friday, February 11, 2011PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)47//PROG POINTER VS CHARACTER ARRAY#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>void main(){char arr[]="PRADEEP DWIVEDI";char *s="HINDUSTAN COLLEGE OF SCIENCE AND TECHNOLOGY";clrscr();printf("%s\n",arr);printf("%s\n",s);printf("%d %d",arr,s);getch();}PRINT STRINGPRINT ADDRESSES](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-programmingslide-6-110211112544-phpapp02/75/C-programming-slide-6-45-2048.jpg)

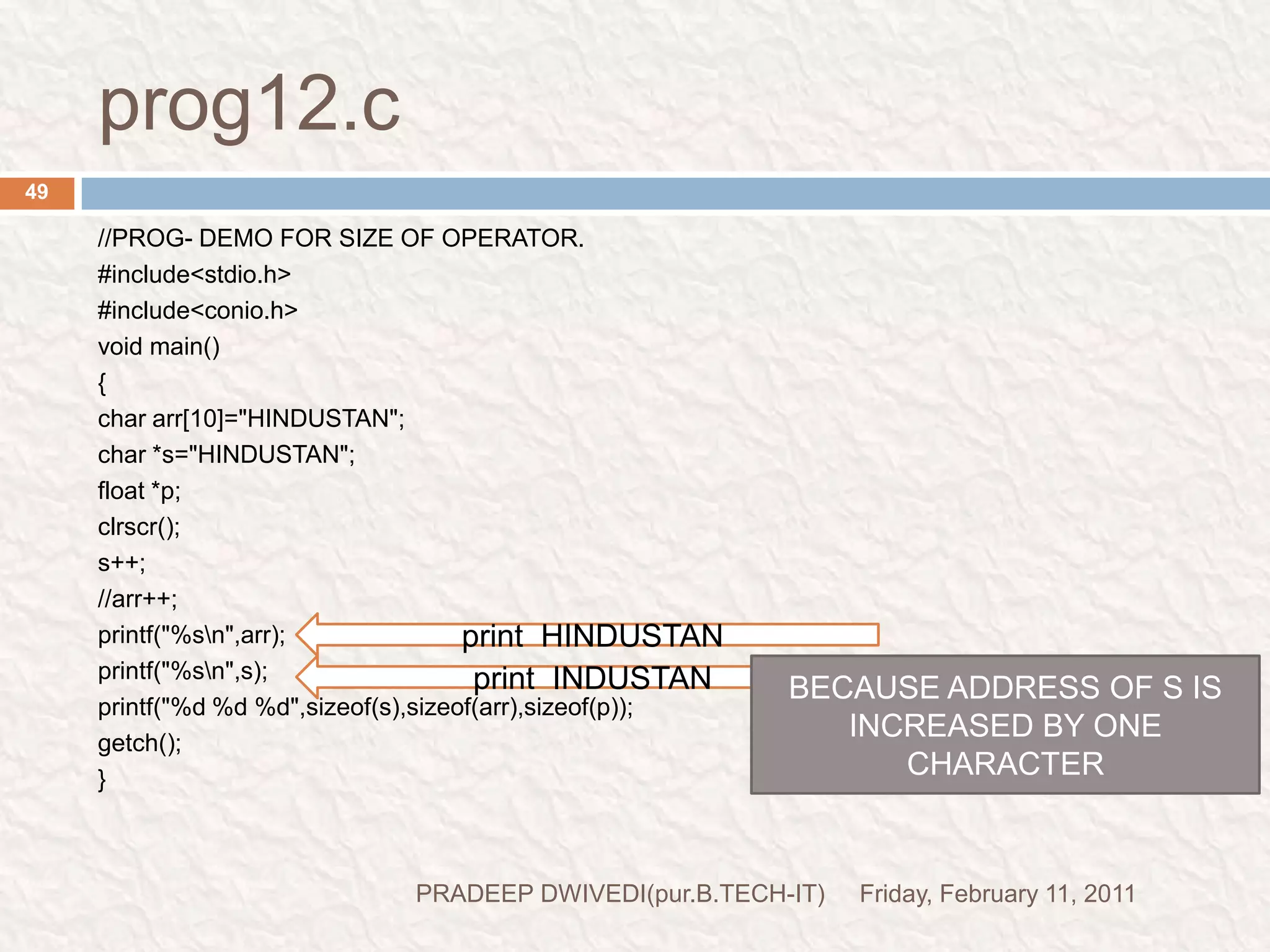
![prog12.cFriday, February 11, 2011PRADEEP DWIVEDI(pur.B.TECH-IT)49//PROG- DEMO FOR SIZE OF OPERATOR.#include<stdio.h>#include<conio.h>void main(){char arr[10]="HINDUSTAN";char *s="HINDUSTAN";float *p;clrscr();s++;//arr++;printf("%s\n",arr);printf("%s\n",s);printf("%d %d %d",sizeof(s),sizeof(arr),sizeof(p));getch();}print HINDUSTANprint INDUSTANBECAUSE ADDRESS OF S IS INCREASED BY ONE CHARACTERTHIS PRINT THE SIZE AS-2 10 2](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/c-programmingslide-6-110211112544-phpapp02/75/C-programming-slide-6-47-2048.jpg)