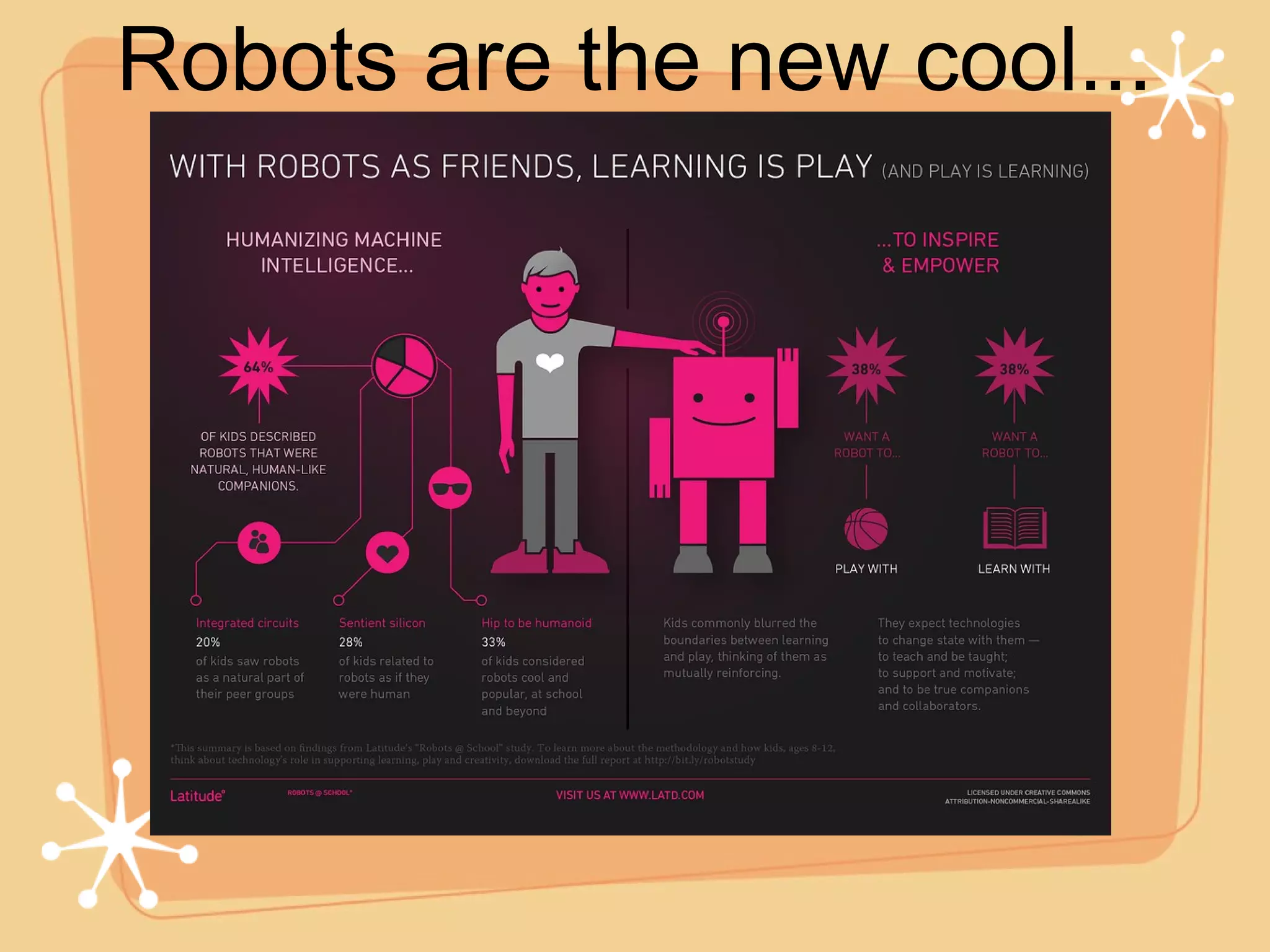
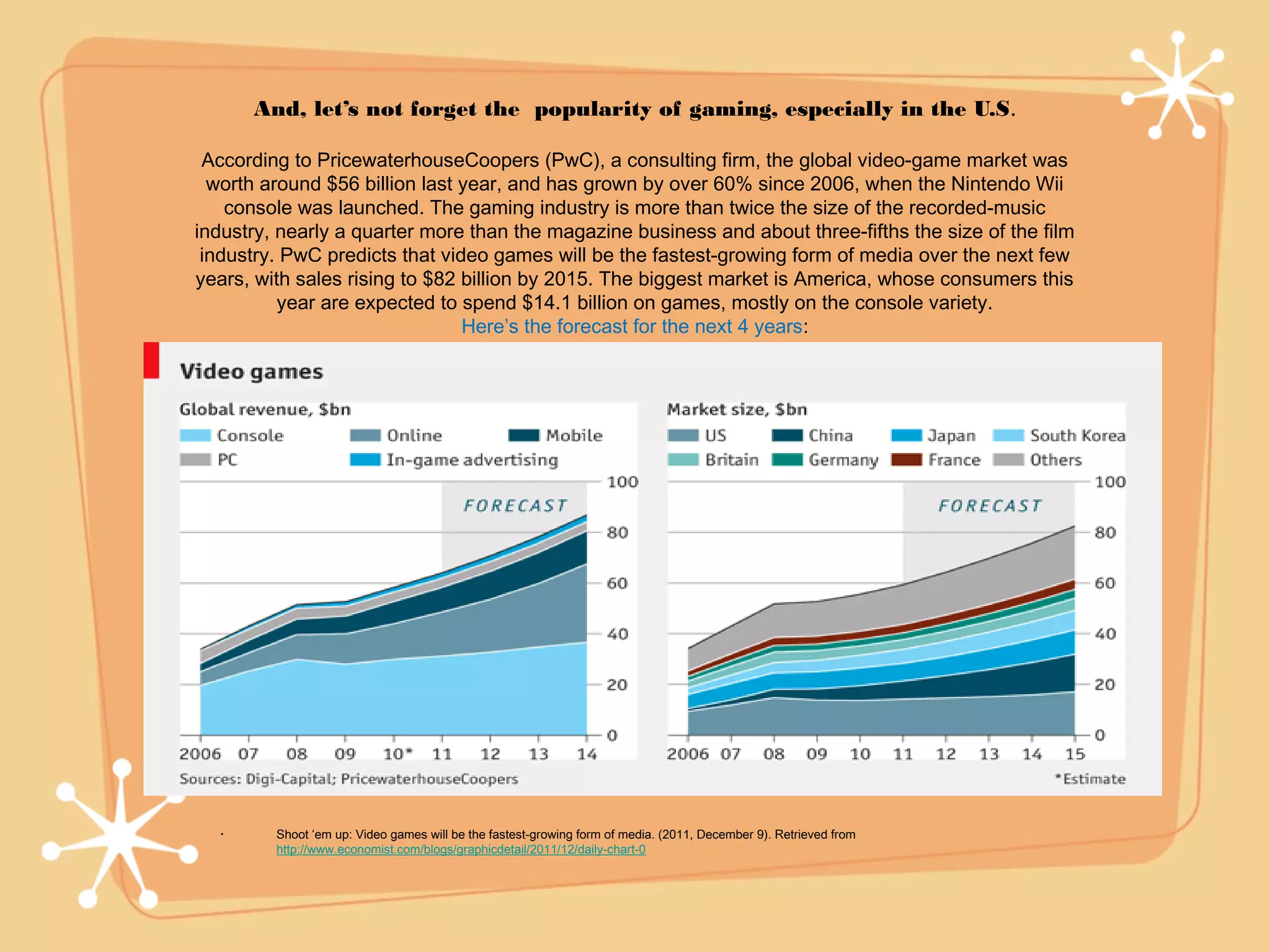
The document describes a camp that focuses on robotics, virtual reality, and gaming. Students will learn about robot design and programming, experience virtual reality to visit different places, and take their ideas to create video games. The camp aims to develop students' skills in areas like critical thinking, teamwork, and STEM learning in a fun, hands-on way through interactive projects and activities using different technologies.