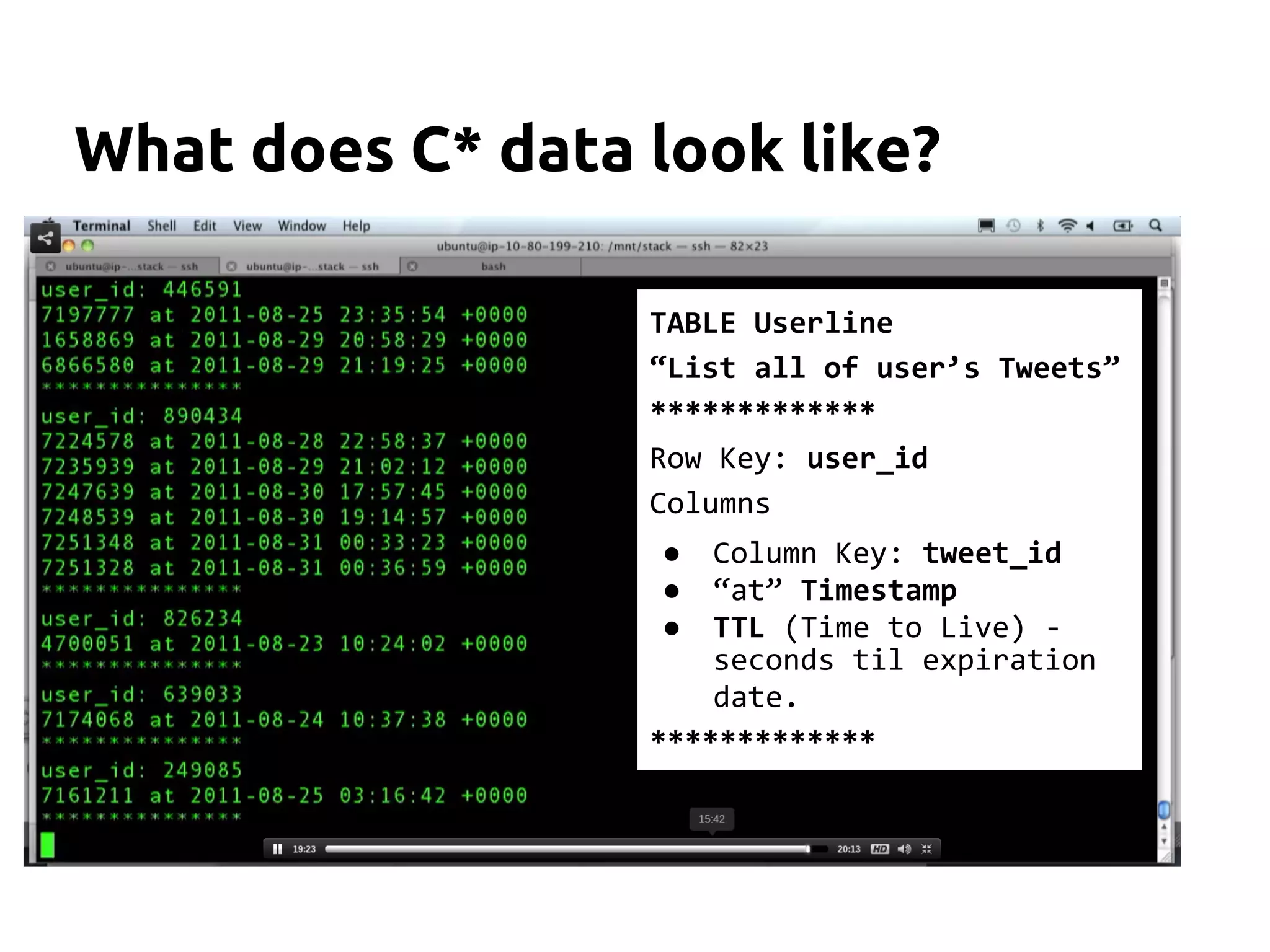
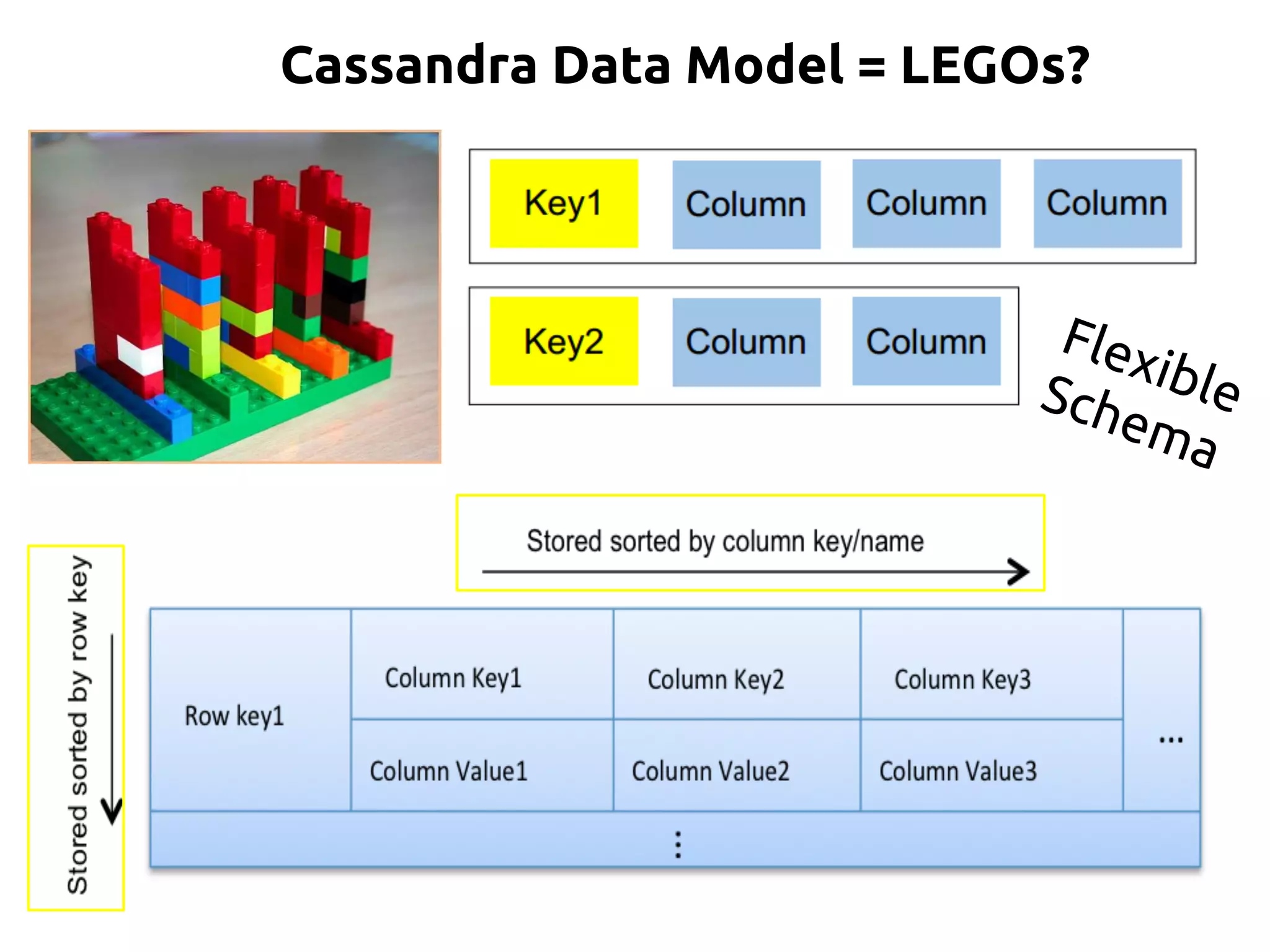
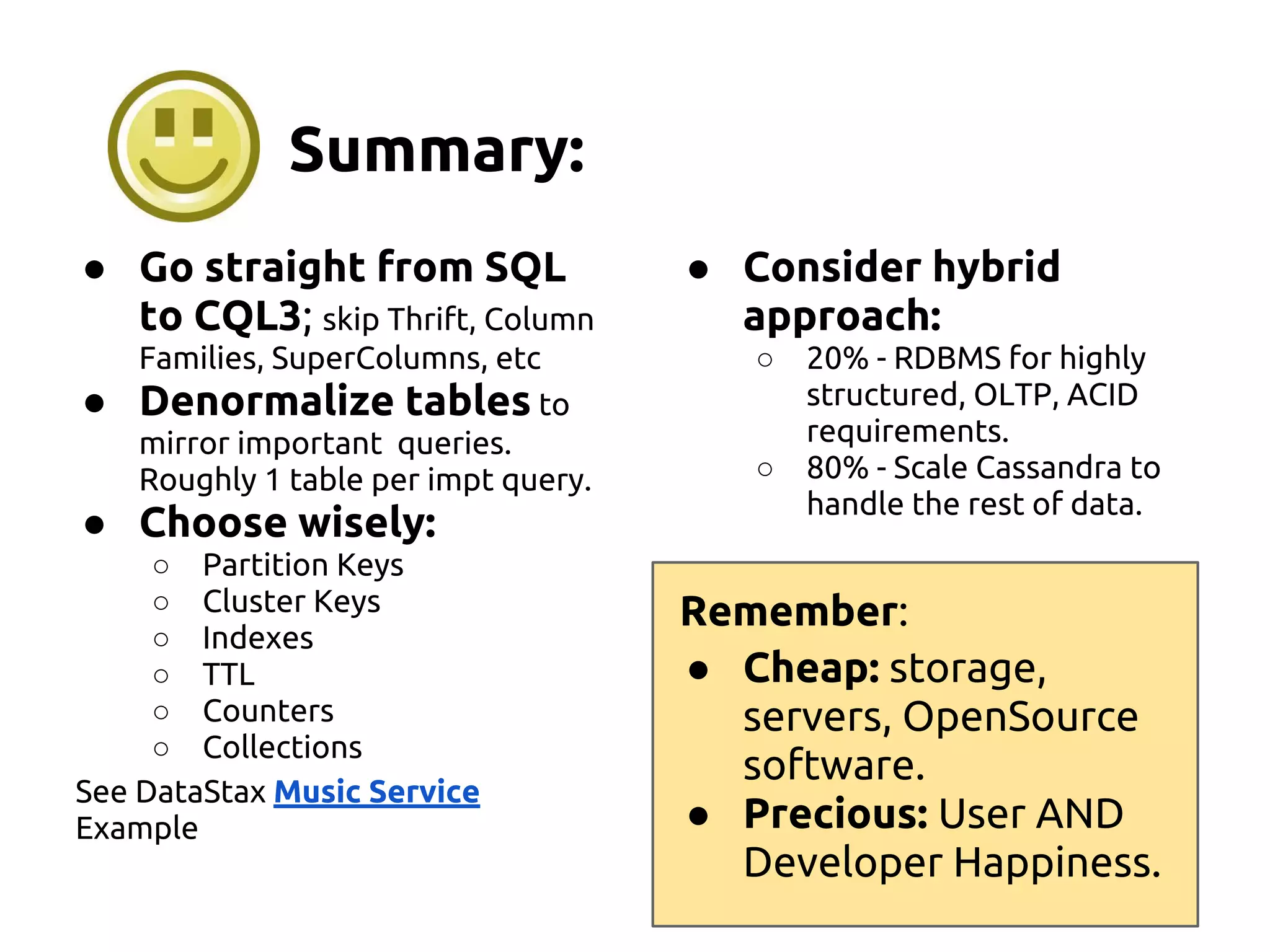
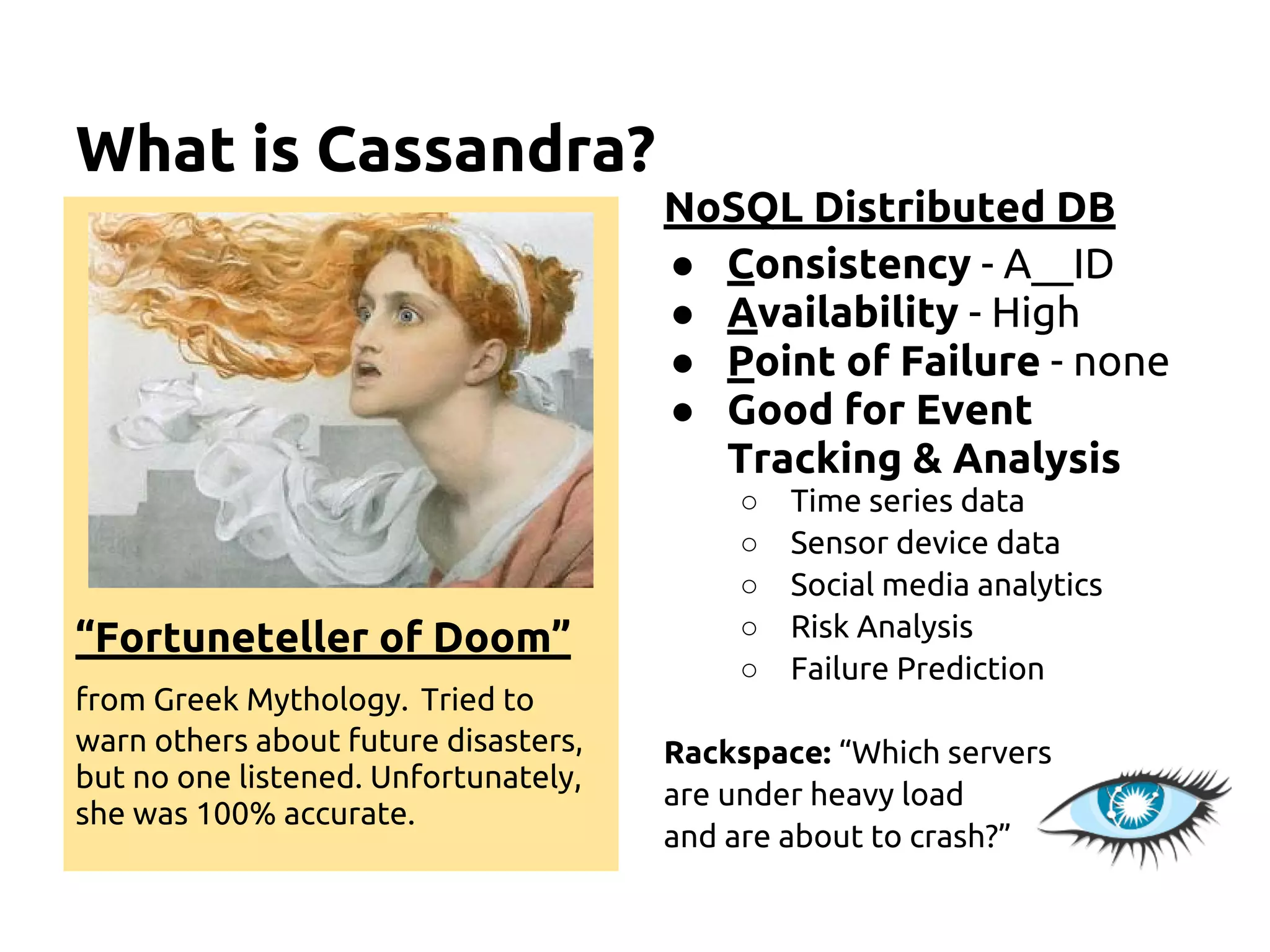
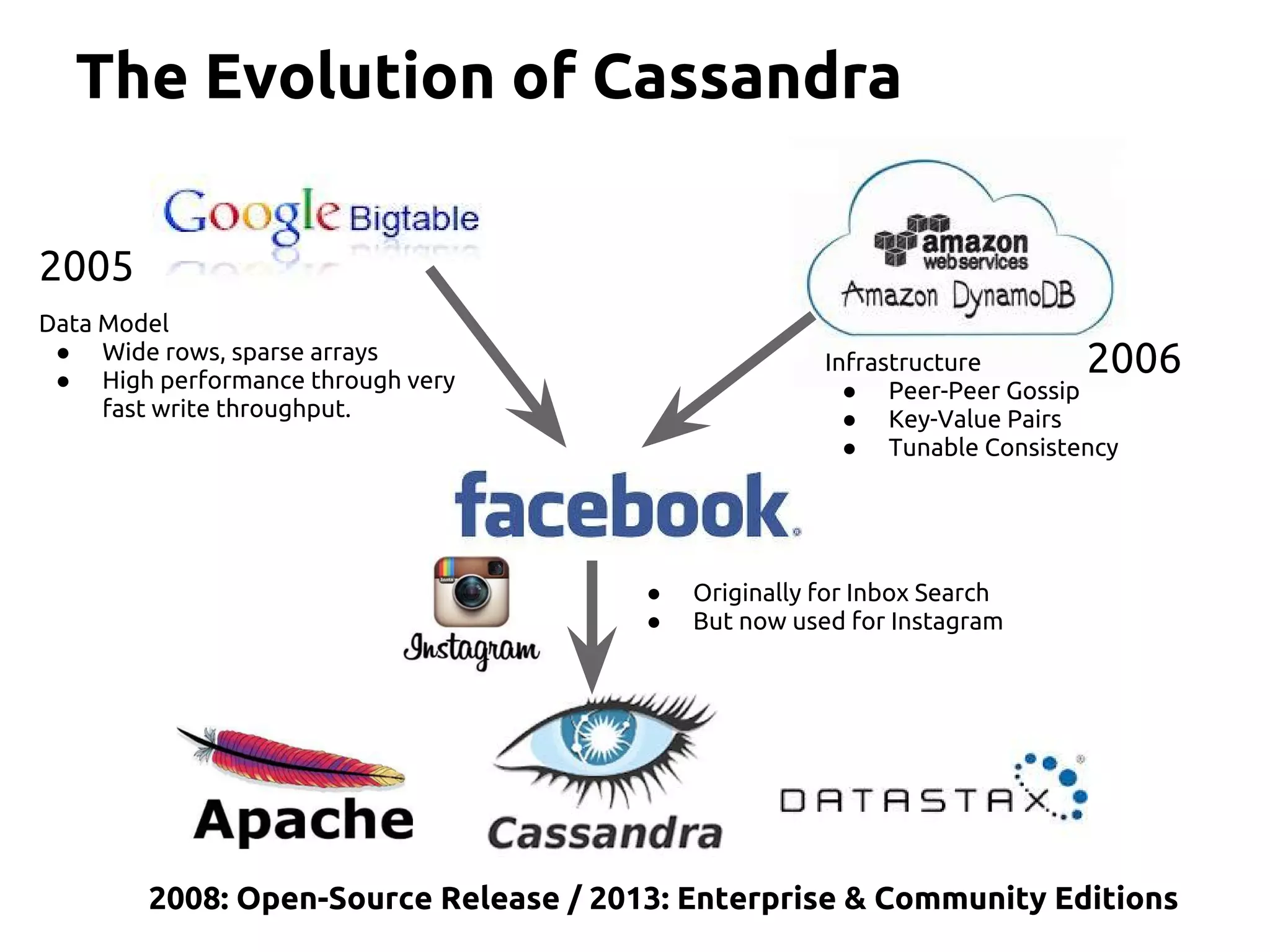
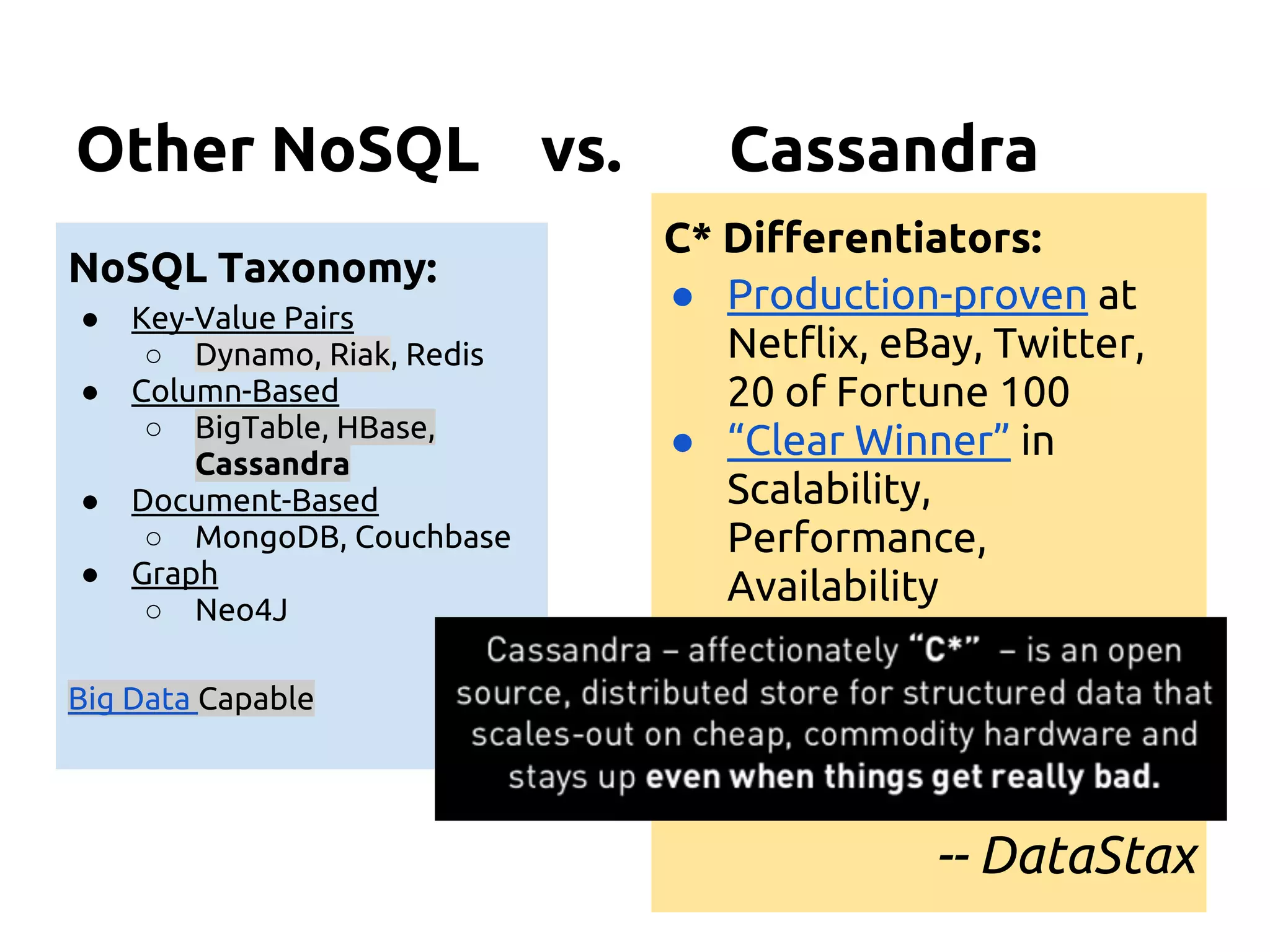
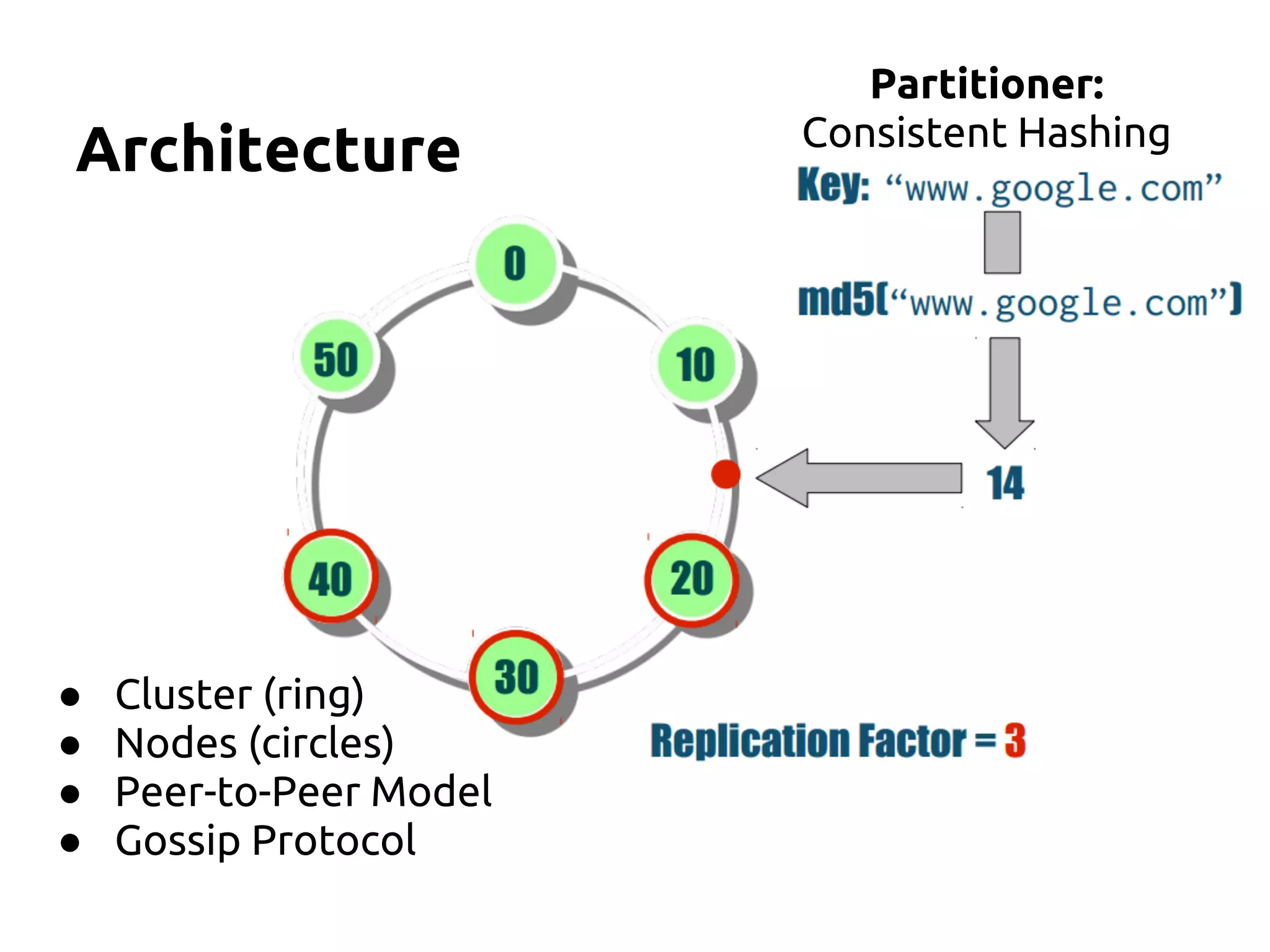
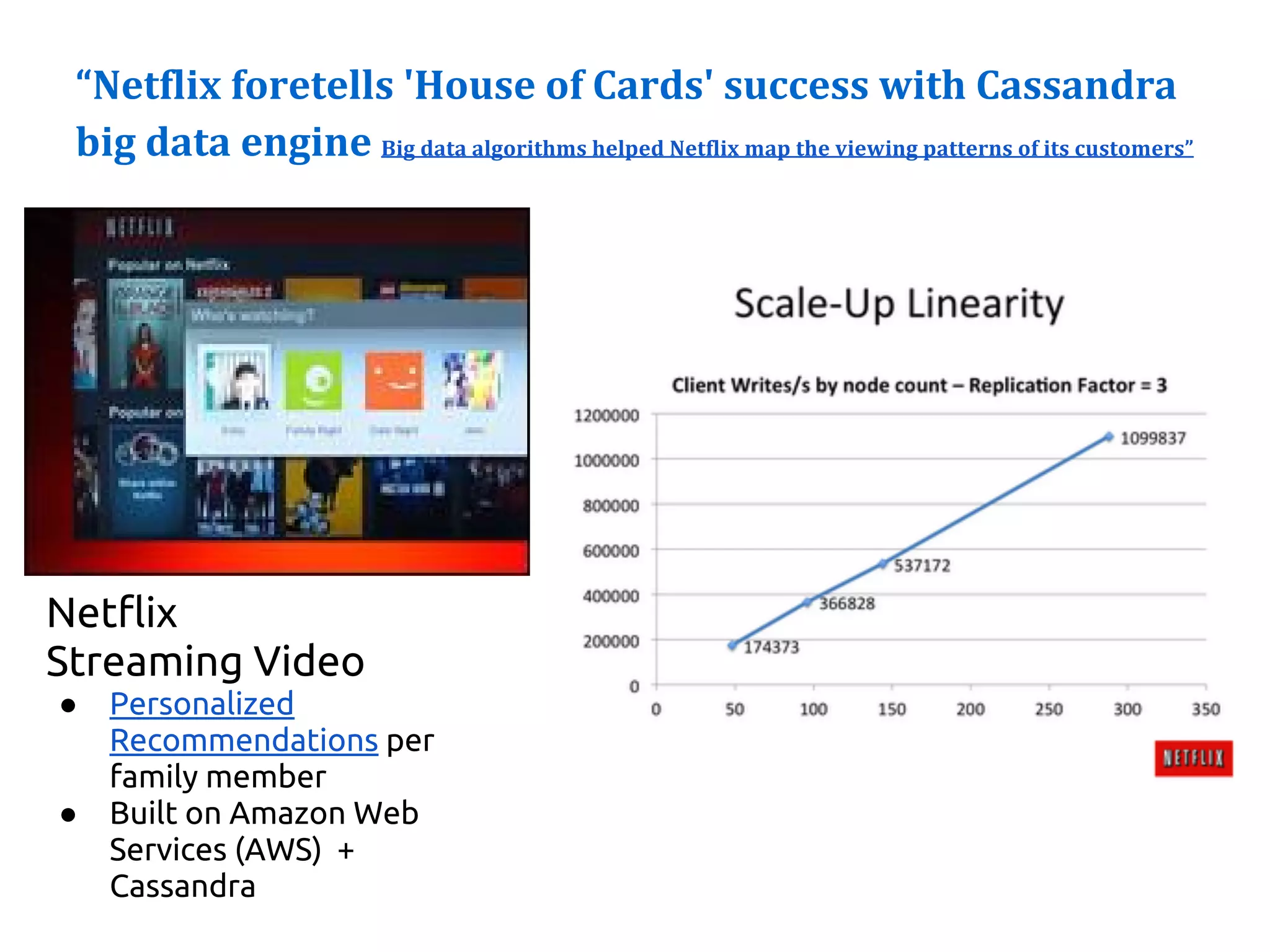
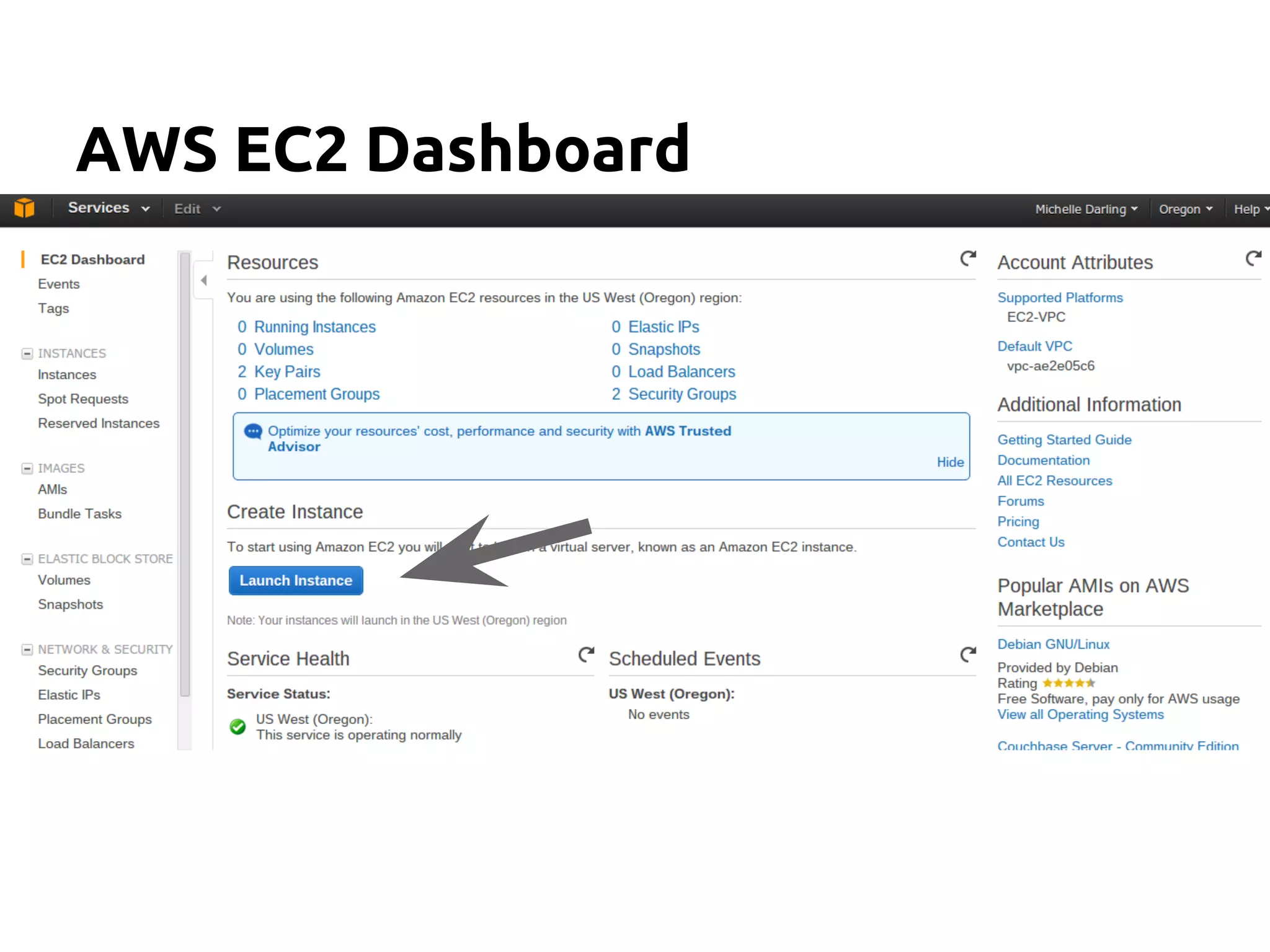
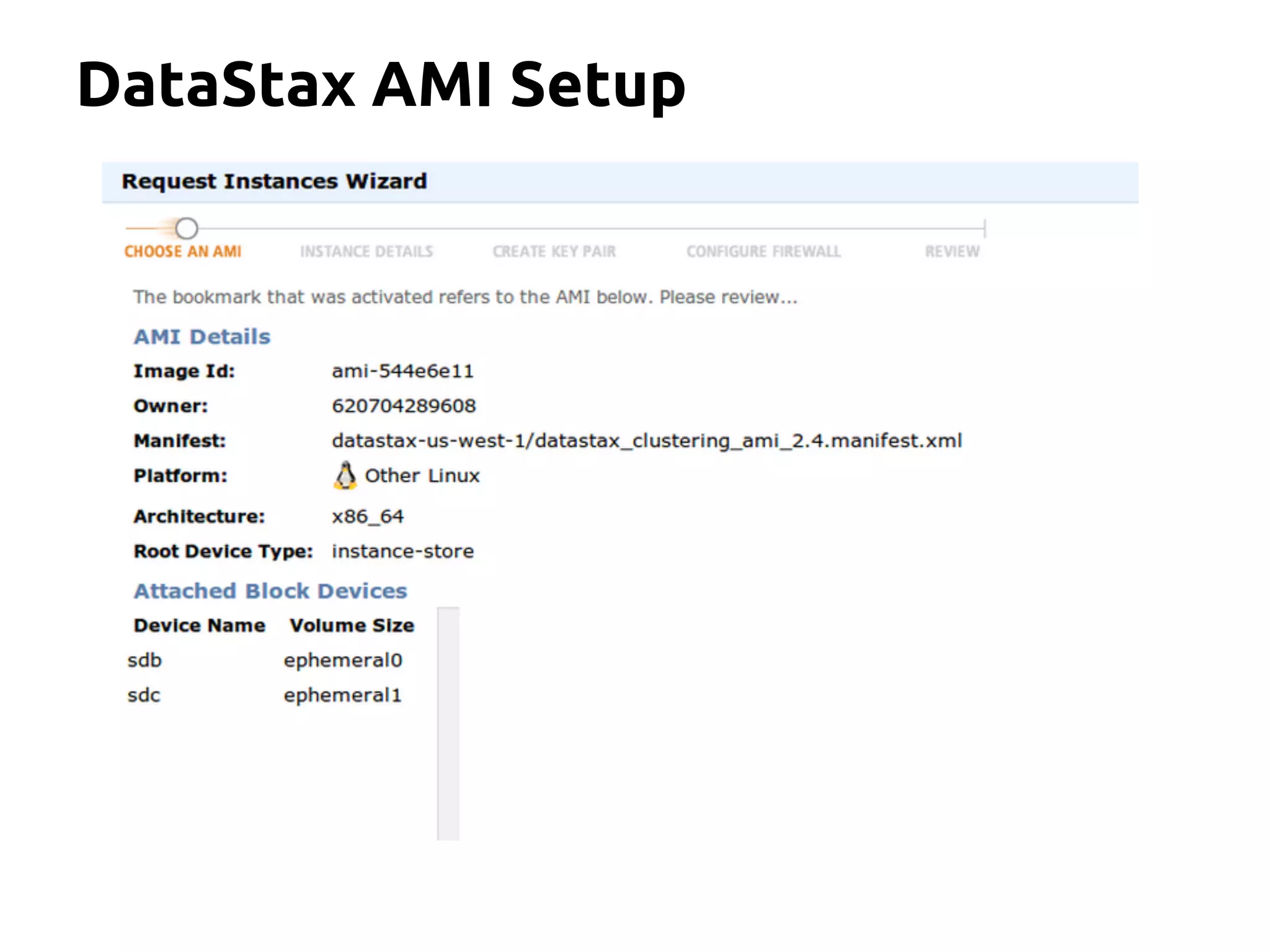
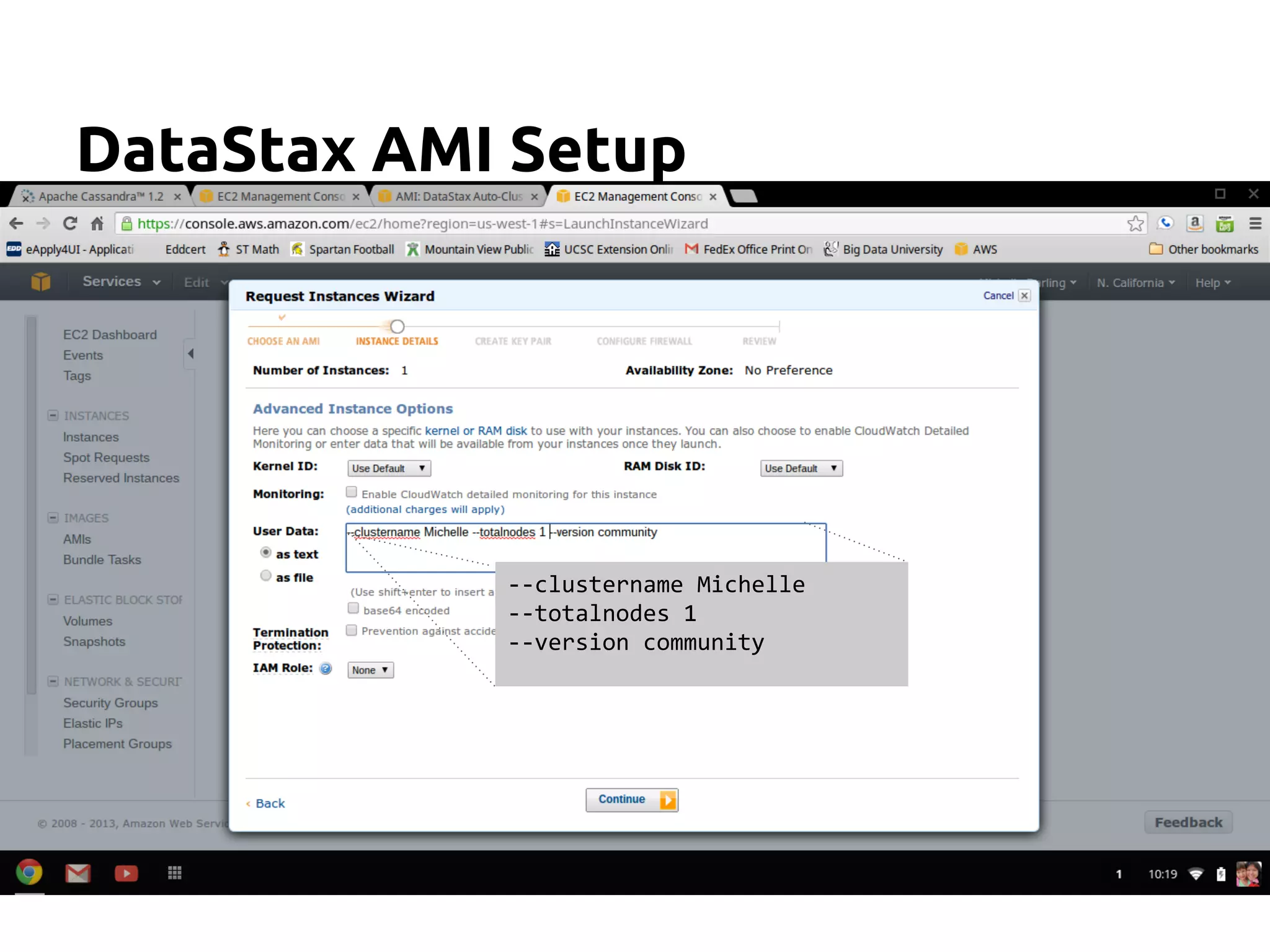
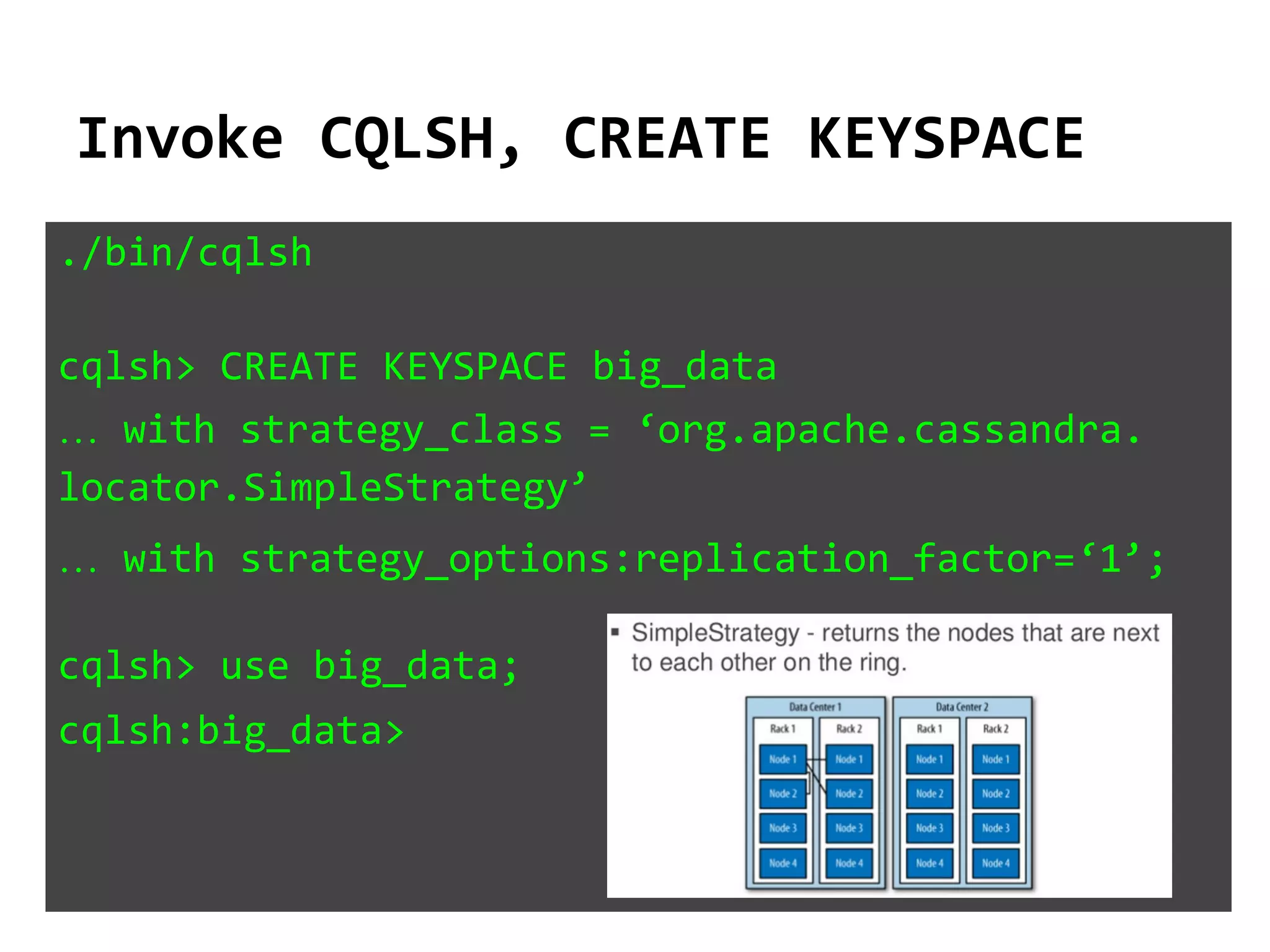
The document serves as an introduction to Apache Cassandra, covering its installation, data modeling, and unique features such as high availability, scalability, and performance. It outlines the differences between Cassandra and other NoSQL databases and provides a brief overview of its architecture and data model. The session emphasizes adapting to Cassandra's flexible schema for data representation and encourages using CQL3 for user-friendly database interactions.





![DATA MODELING
A Major Paradigm Shift!
RDBMS Cassandra
Structured Data, Fixed Schema Unstructured Data, Flexible Schema
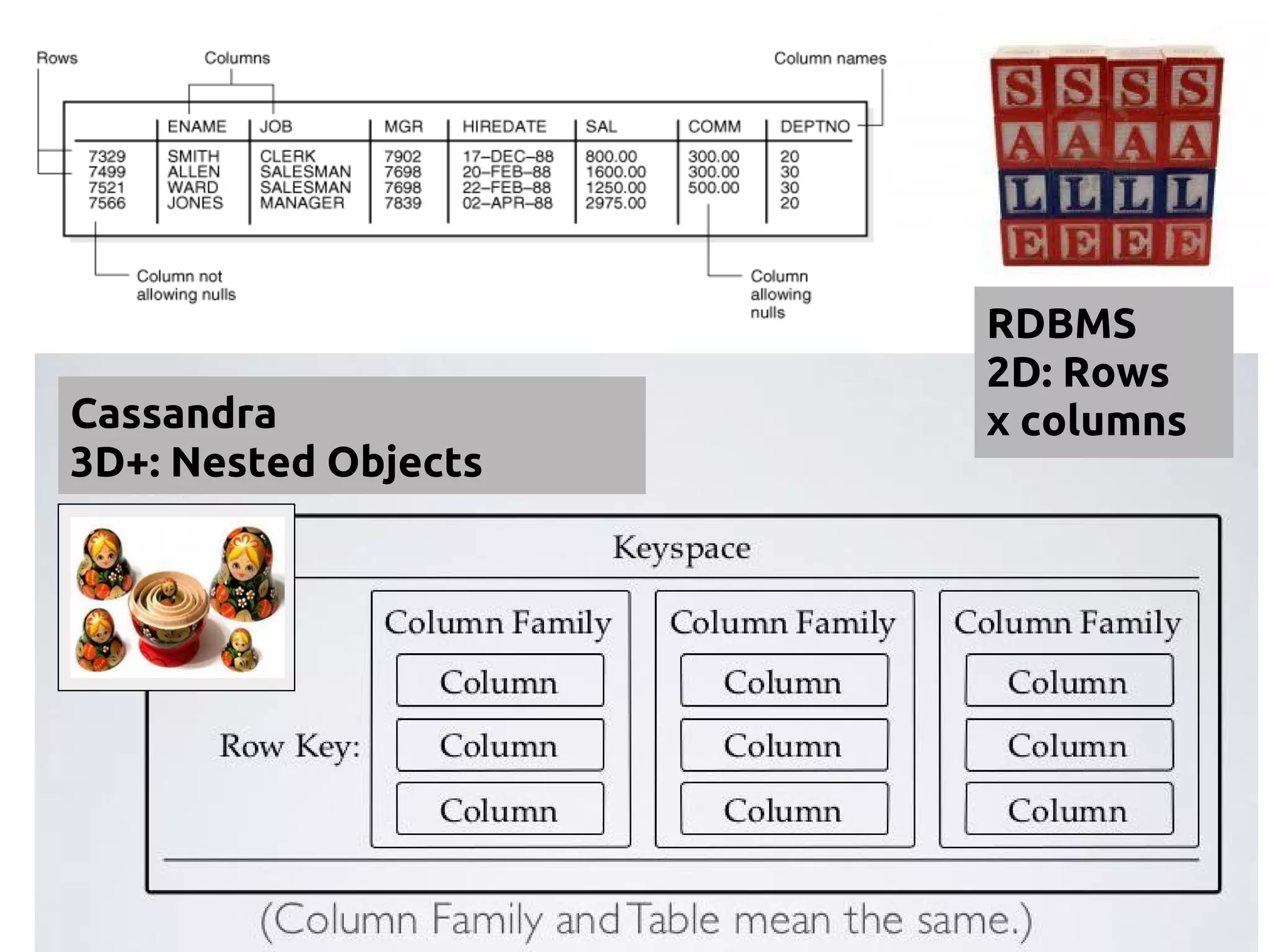
“Array of Arrays”
2D: ROW x COLUMN
“Nested Key-Value Pairs”
3D: ROW Key x COLUMN key x COLUMN values
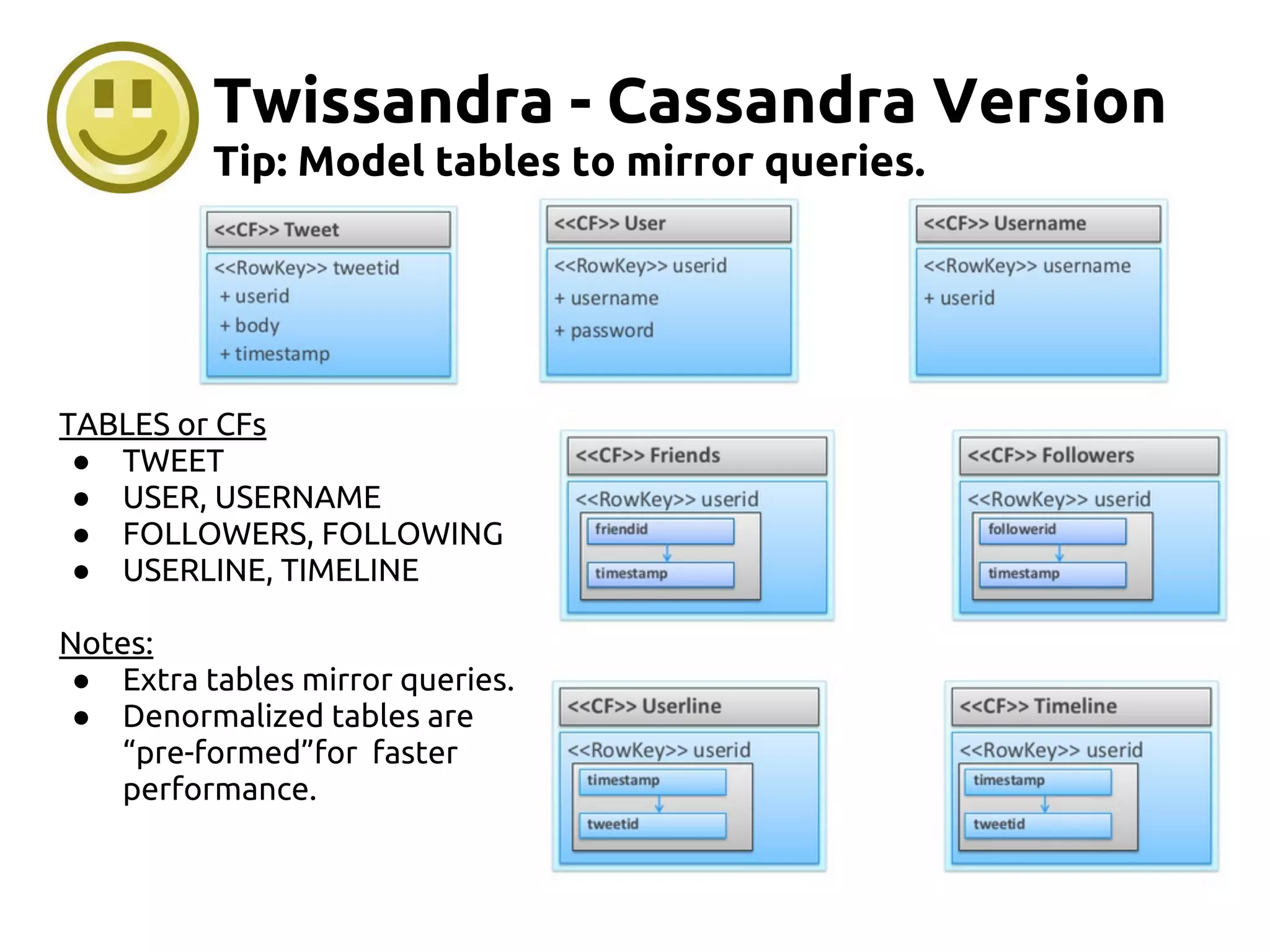
DATABASE KEYSPACE
TABLE TABLE a.k.a COLUMN FAMILY
ROW ROW a.k.a PARTITION. Unit of replication.
COLUMN COLUMN [Name, Value, Timestamp]. a.k.a CLUSTER. Unit
of storage. Up to 2 billion columns per row.
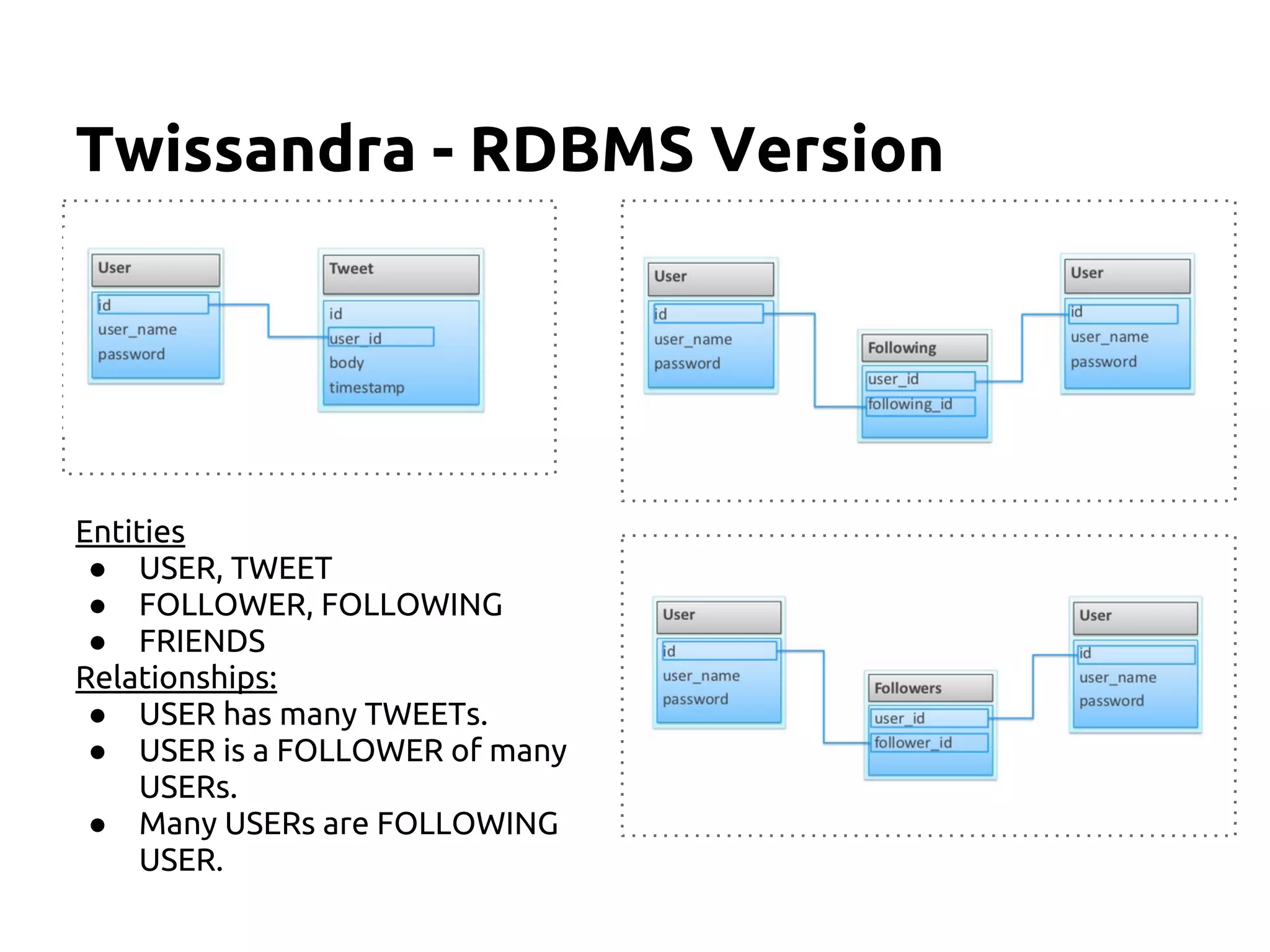
FOREIGN KEYS, JOINS,
ACID Consistency
Referential Integrity not enforced, so A_CID.
BUT relationships represented using COLLECTIONS.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/cassandratutorialfinalversion-130808130116-phpapp01/75/Cassandra-NoSQL-Tutorial-17-2048.jpg)