This document discusses database system concepts and architecture. It covers several topics:
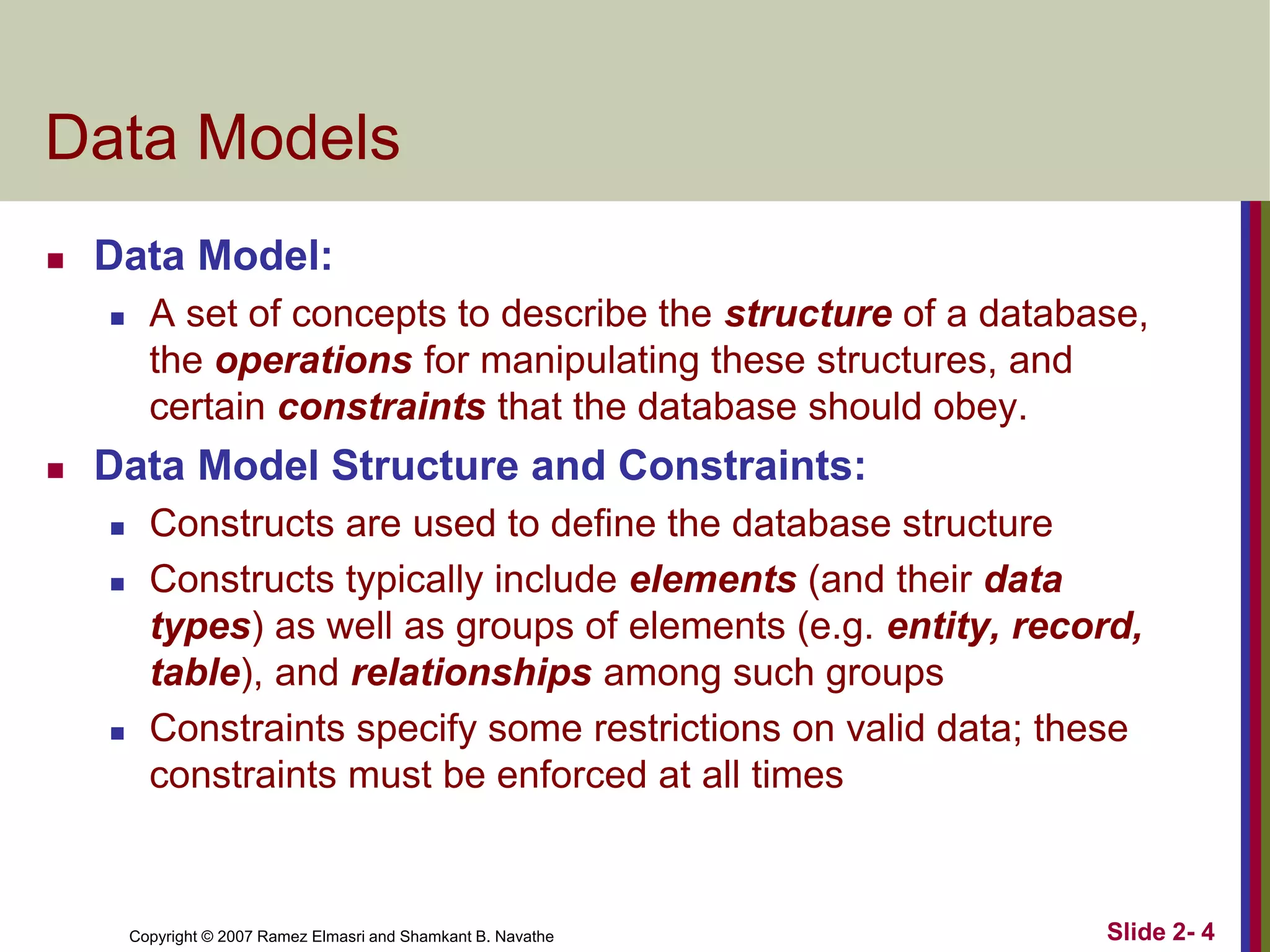
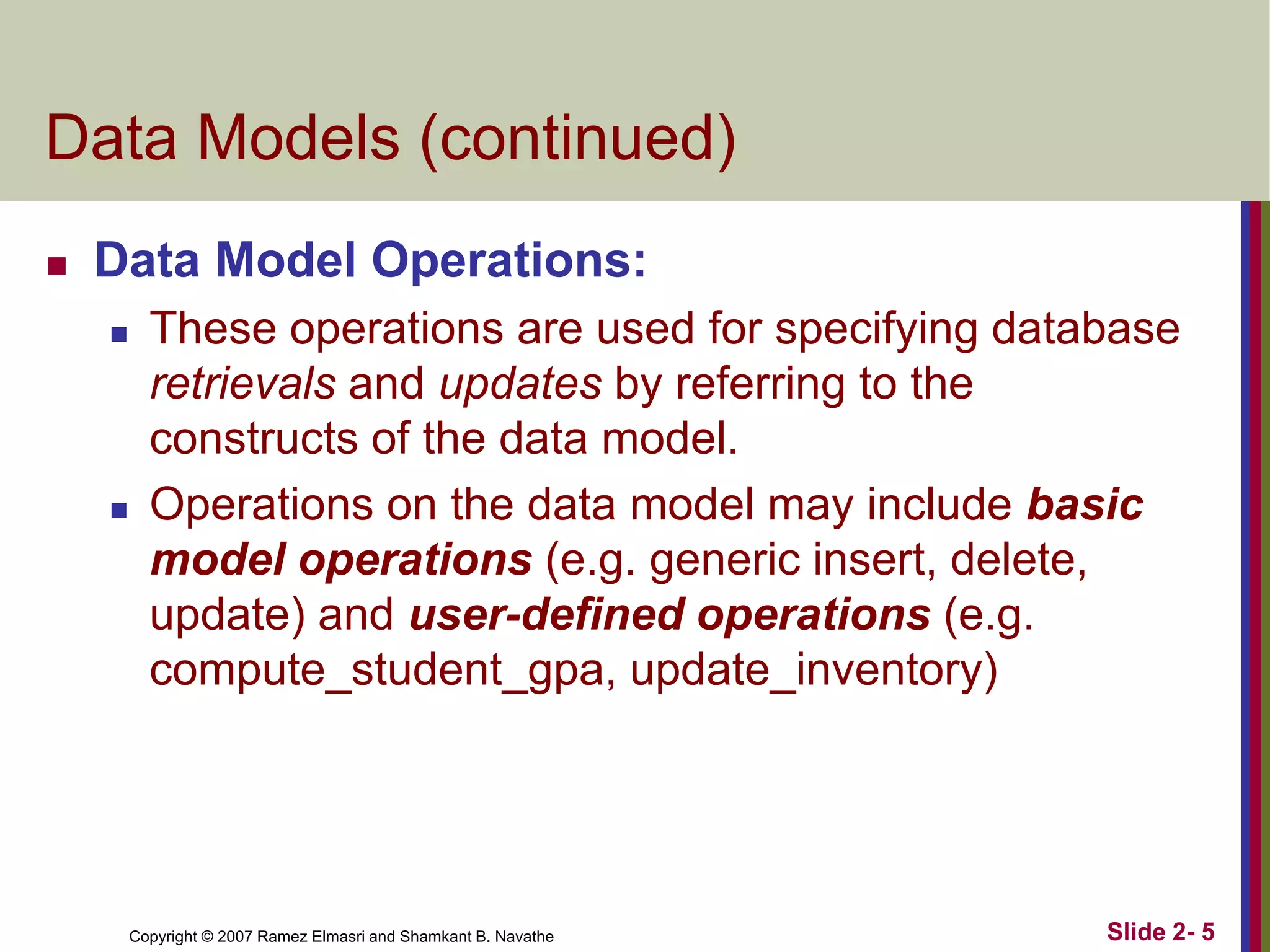
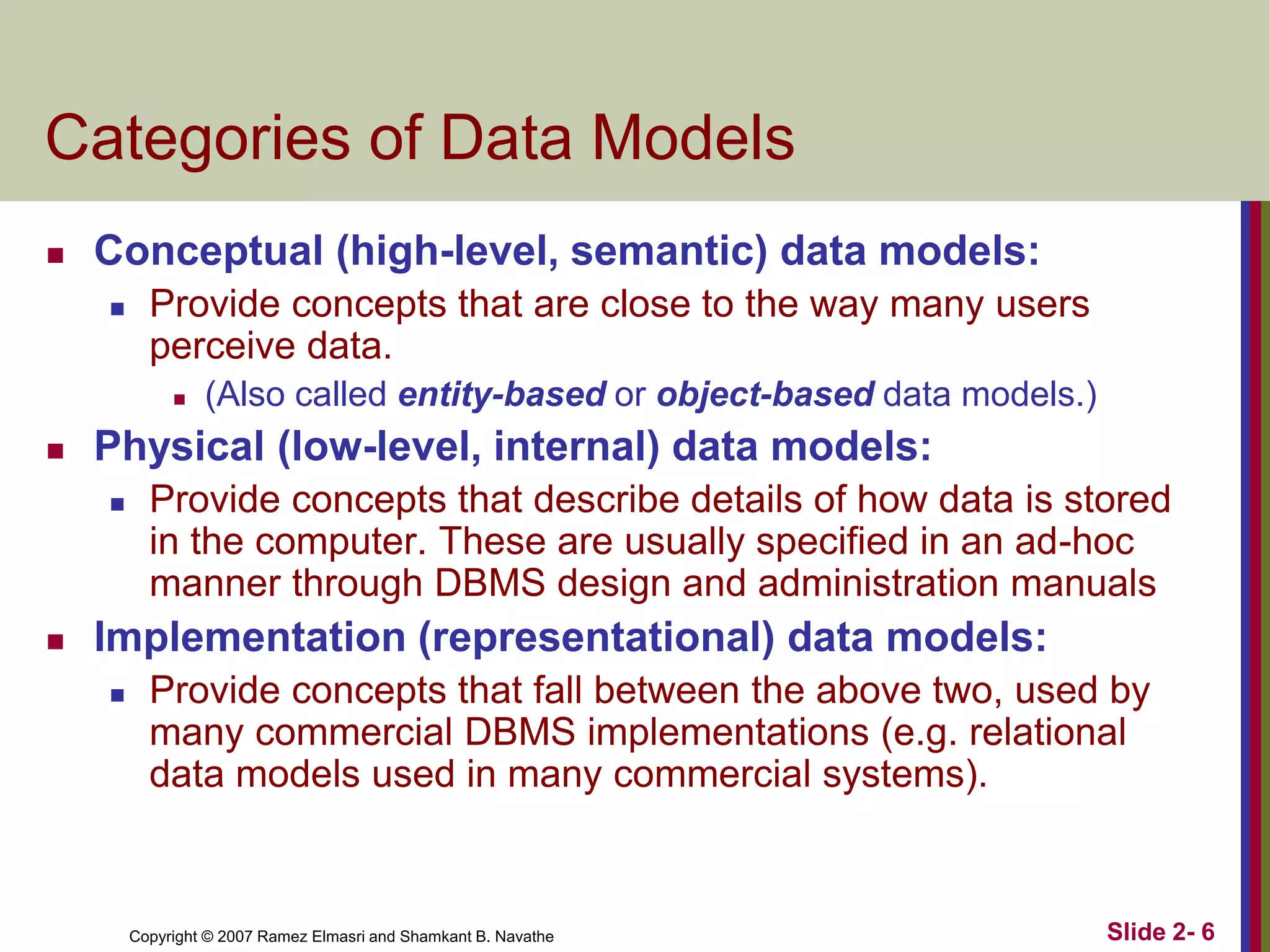
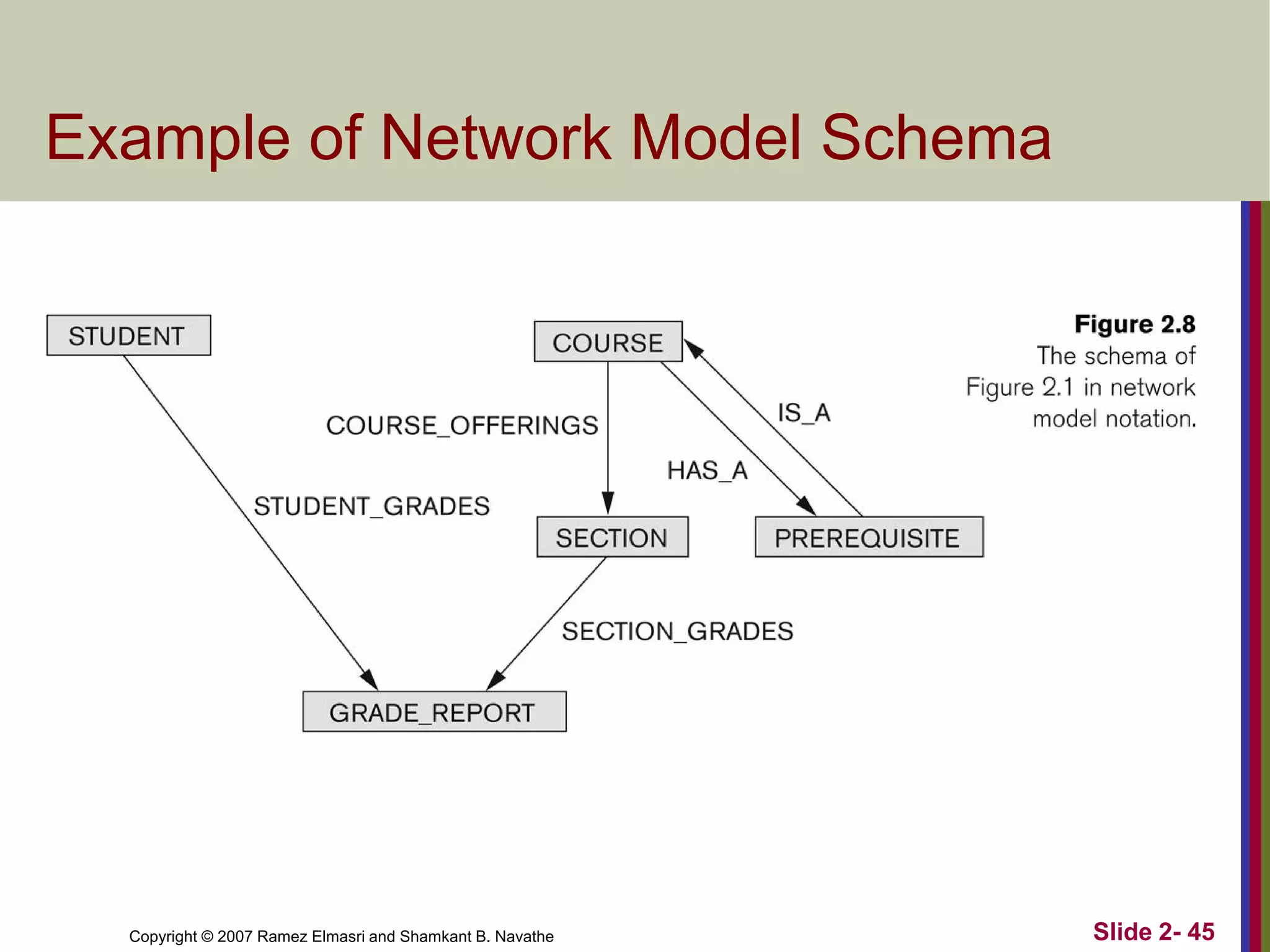
- Data models define database structure, operations, and constraints. Common categories are conceptual, physical, and implementation models.
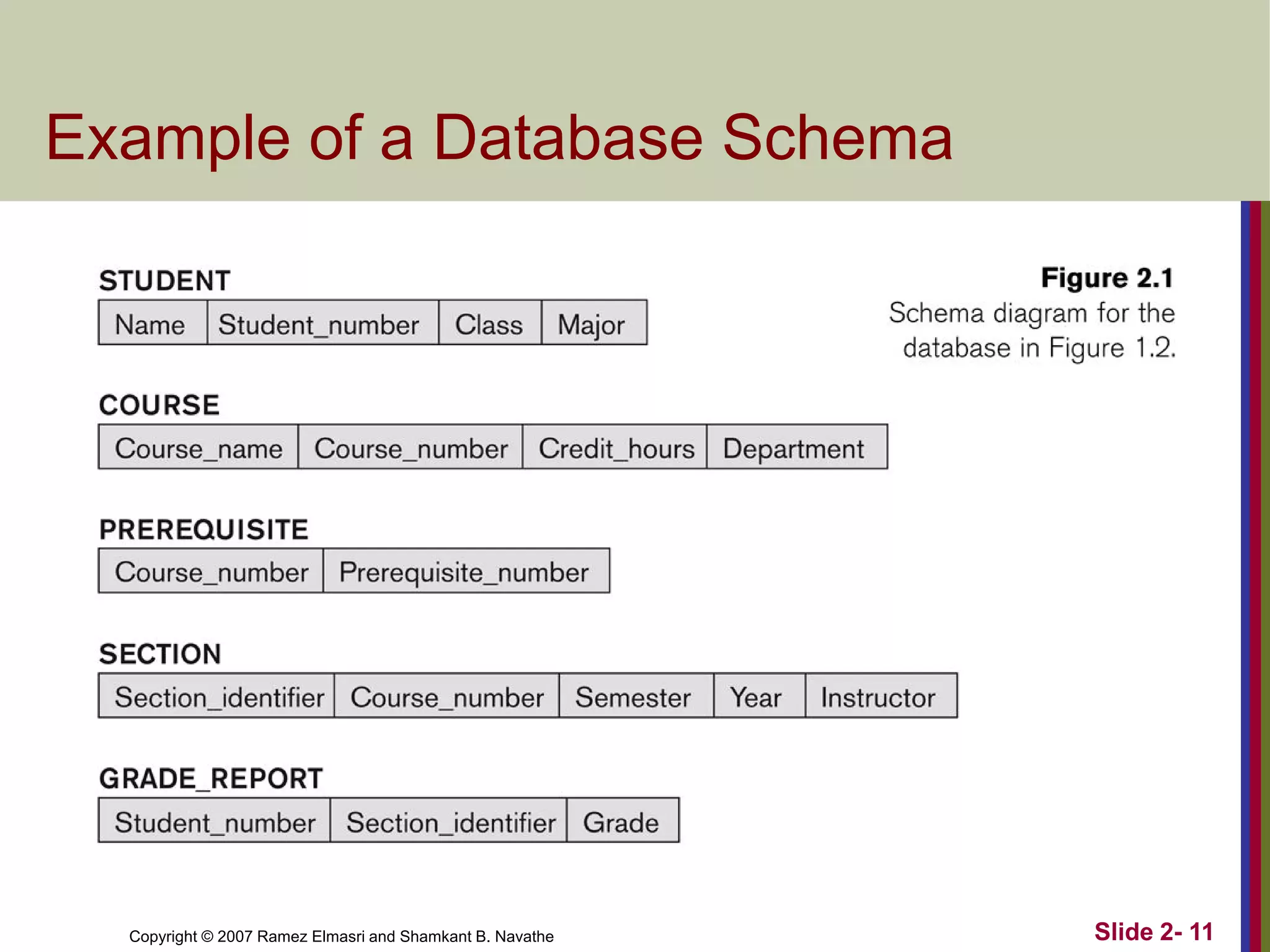
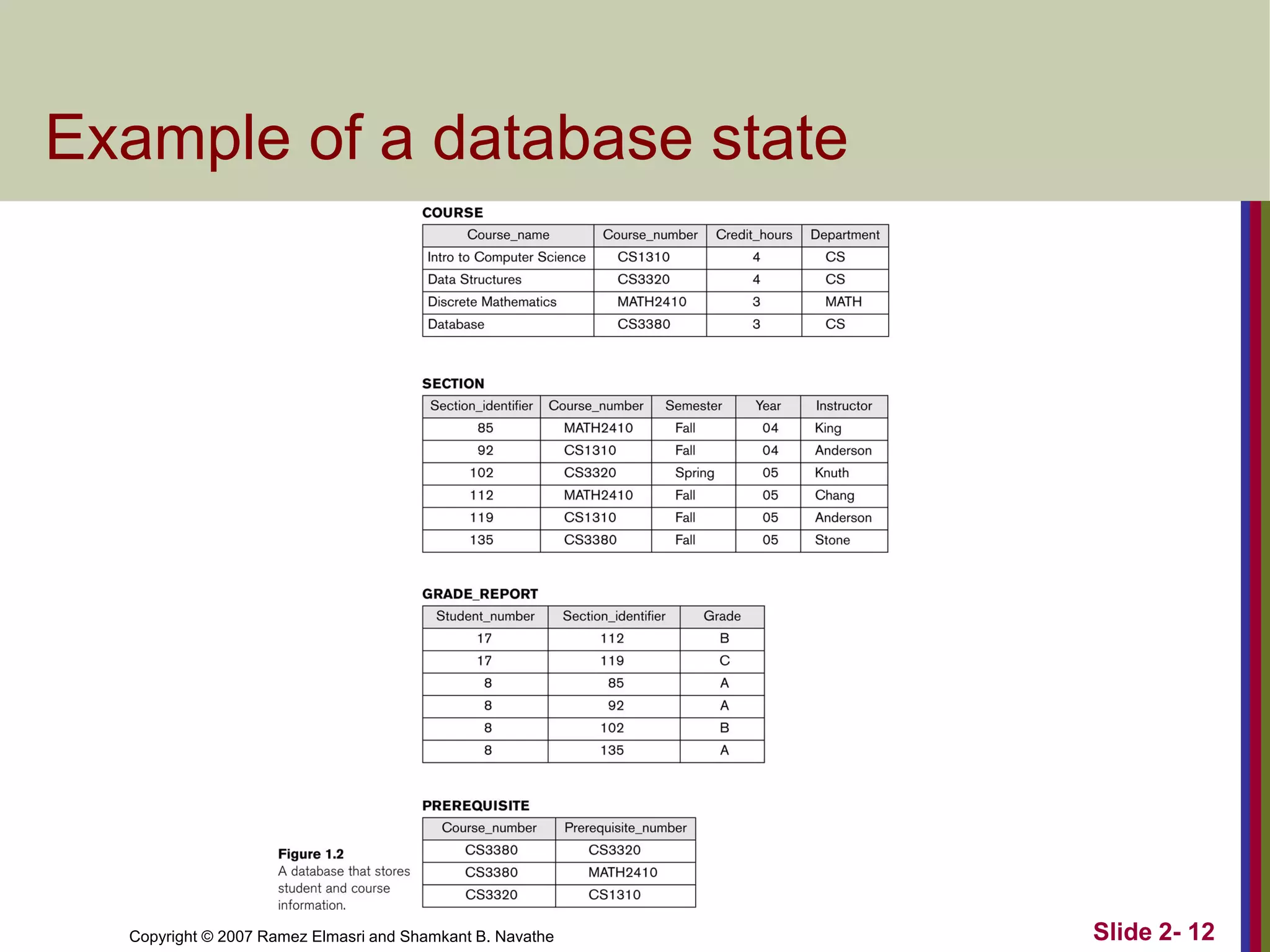
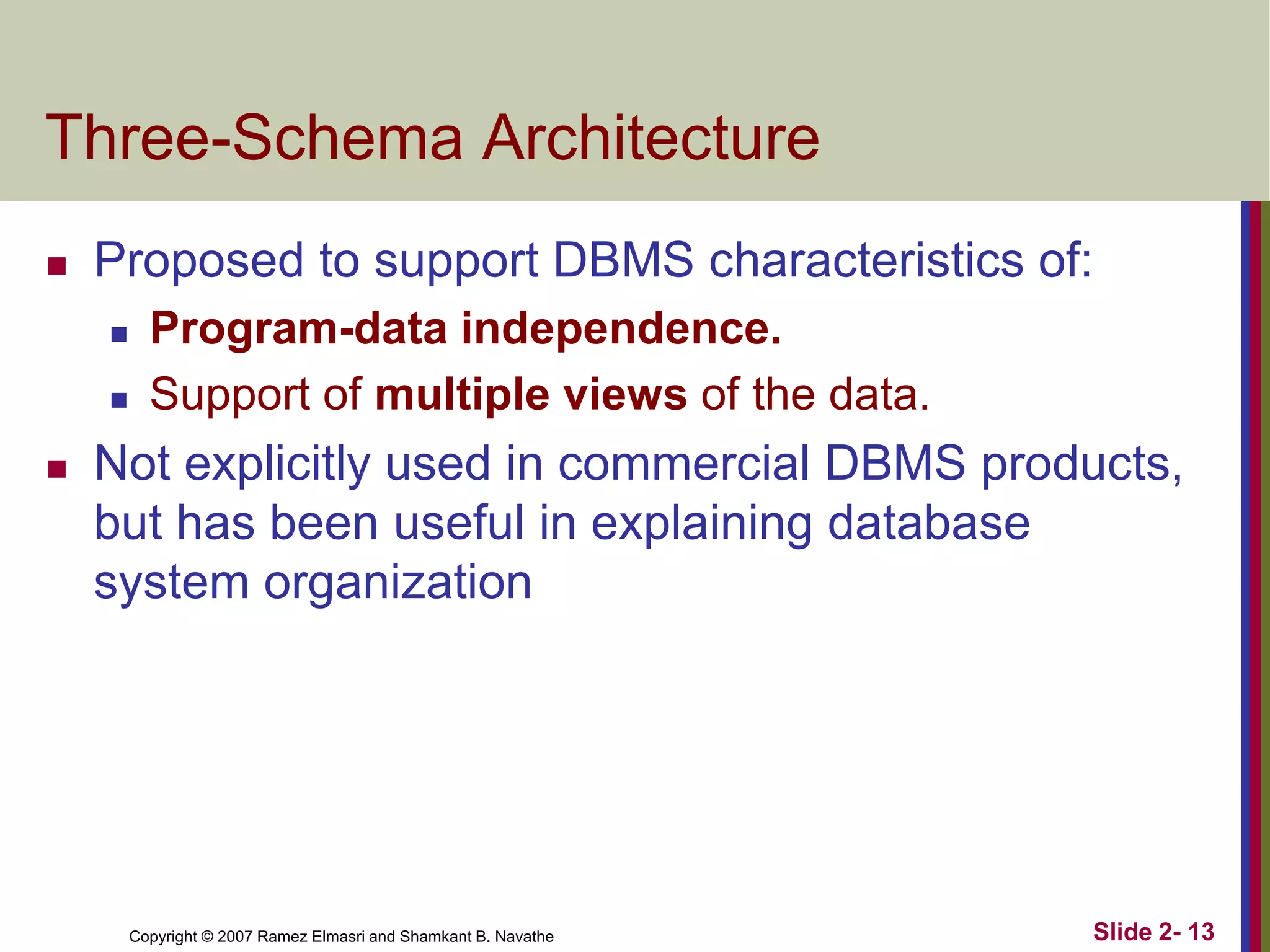
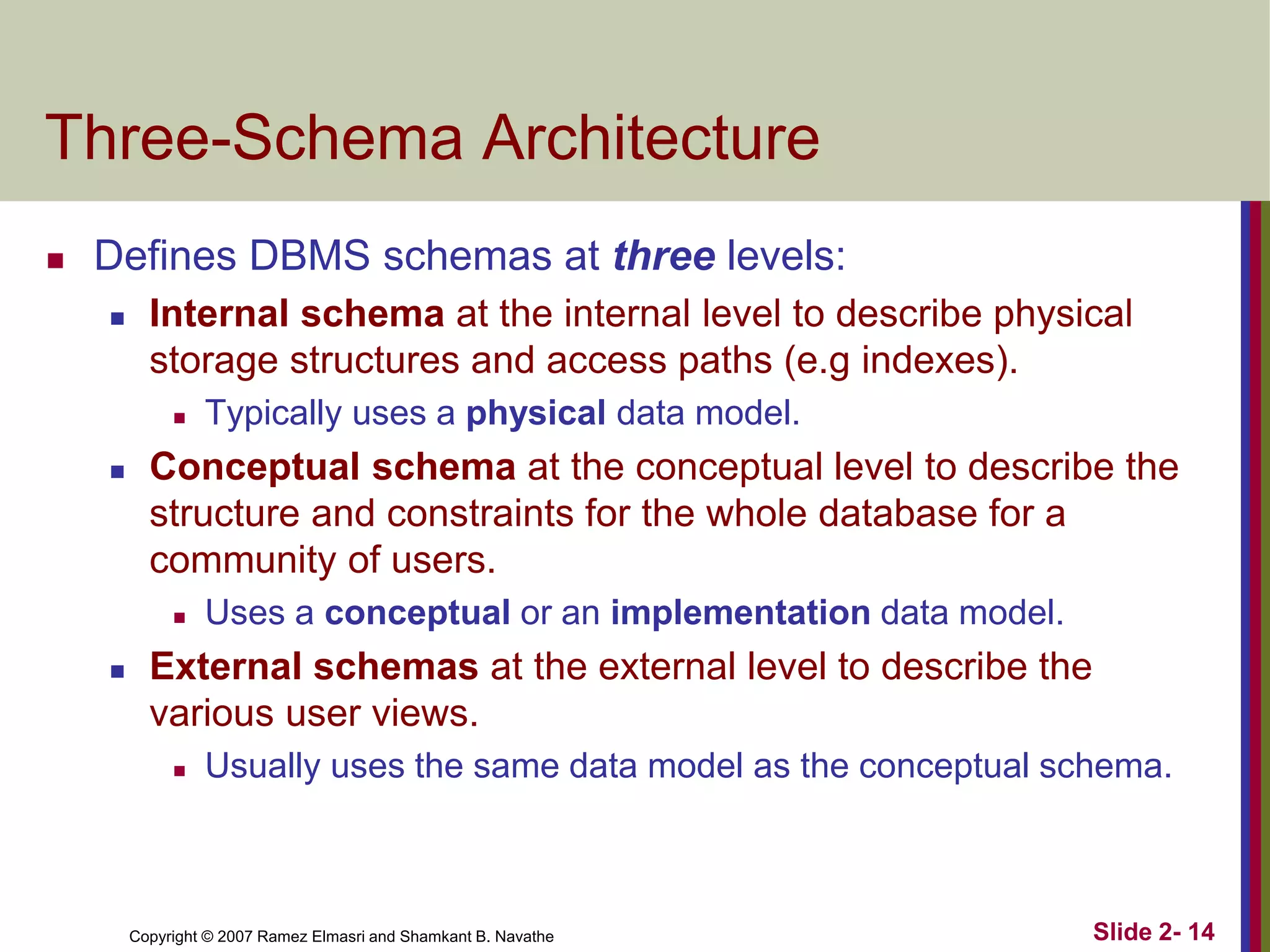
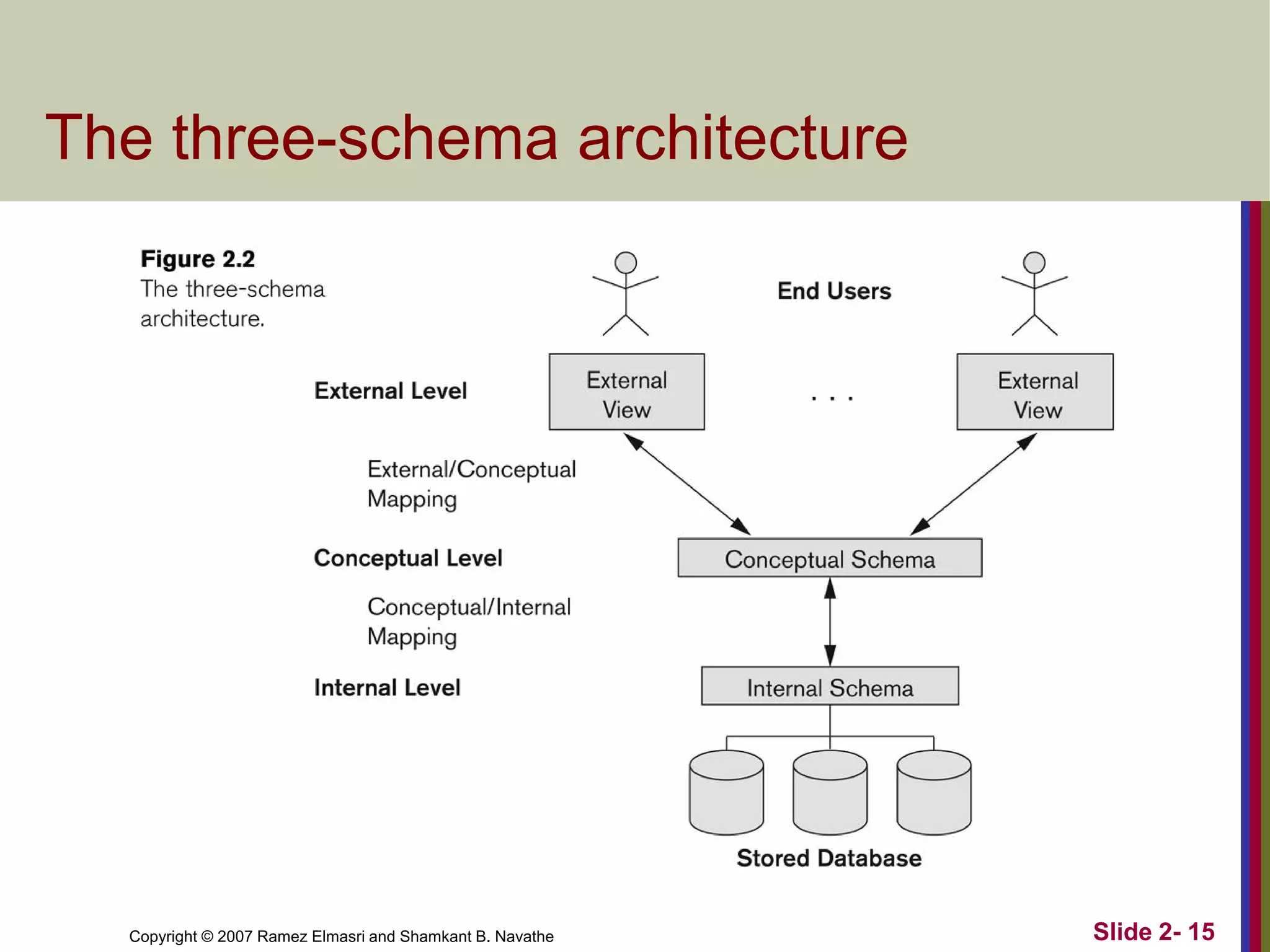
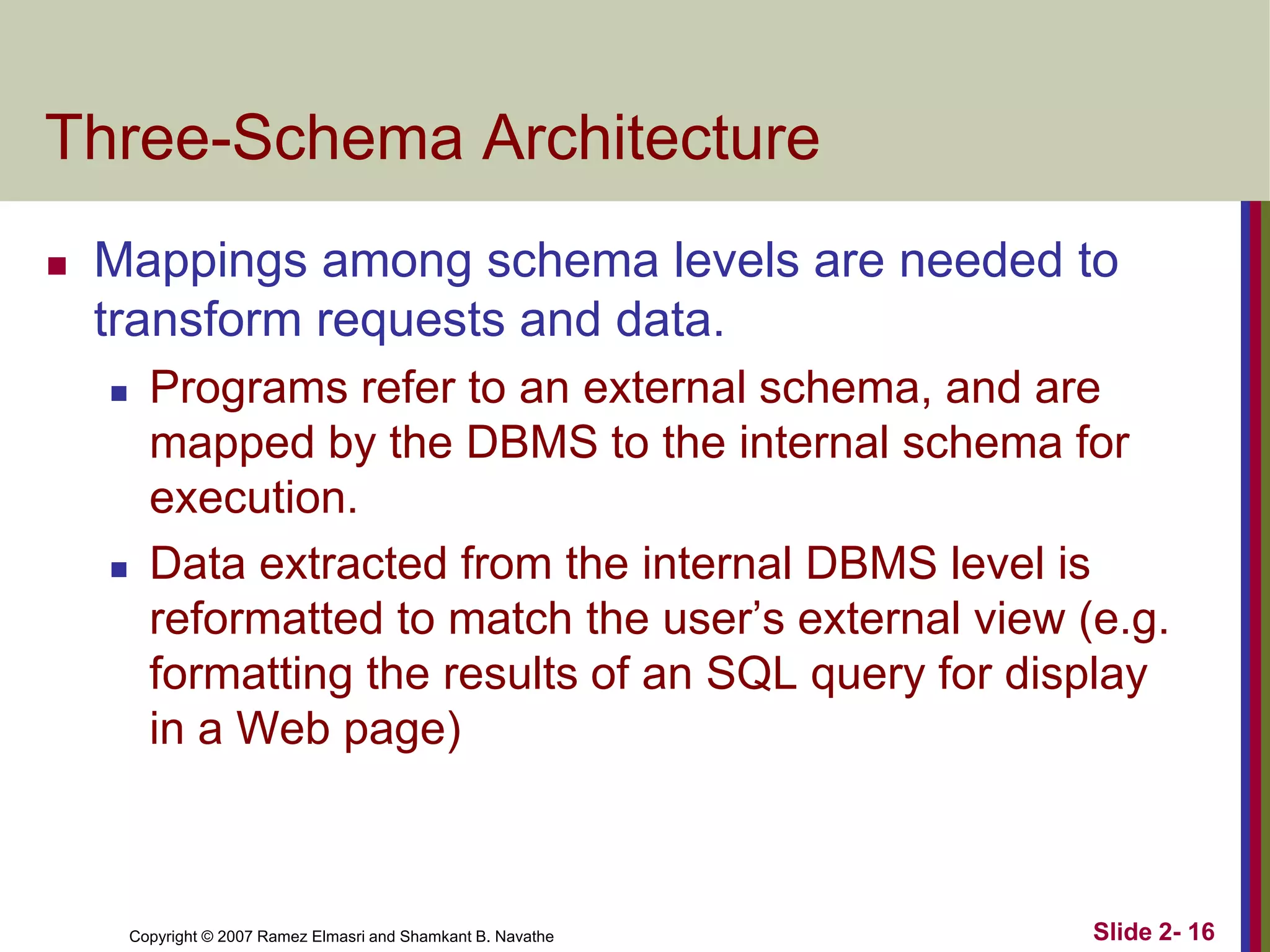
- Schemas describe database structure and constraints, while instances represent actual stored data. The three-schema architecture separates conceptual, internal, and external schemas.
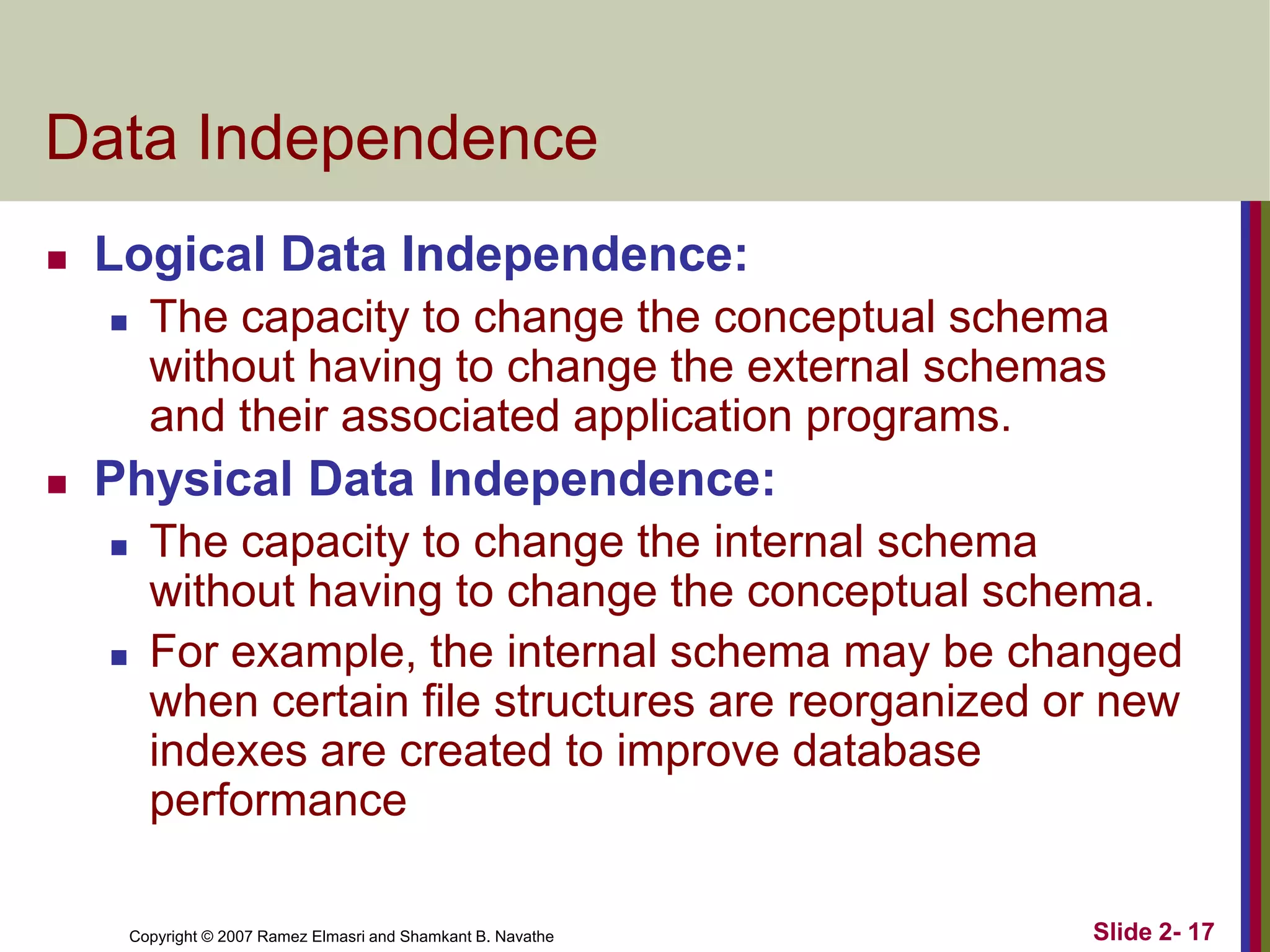
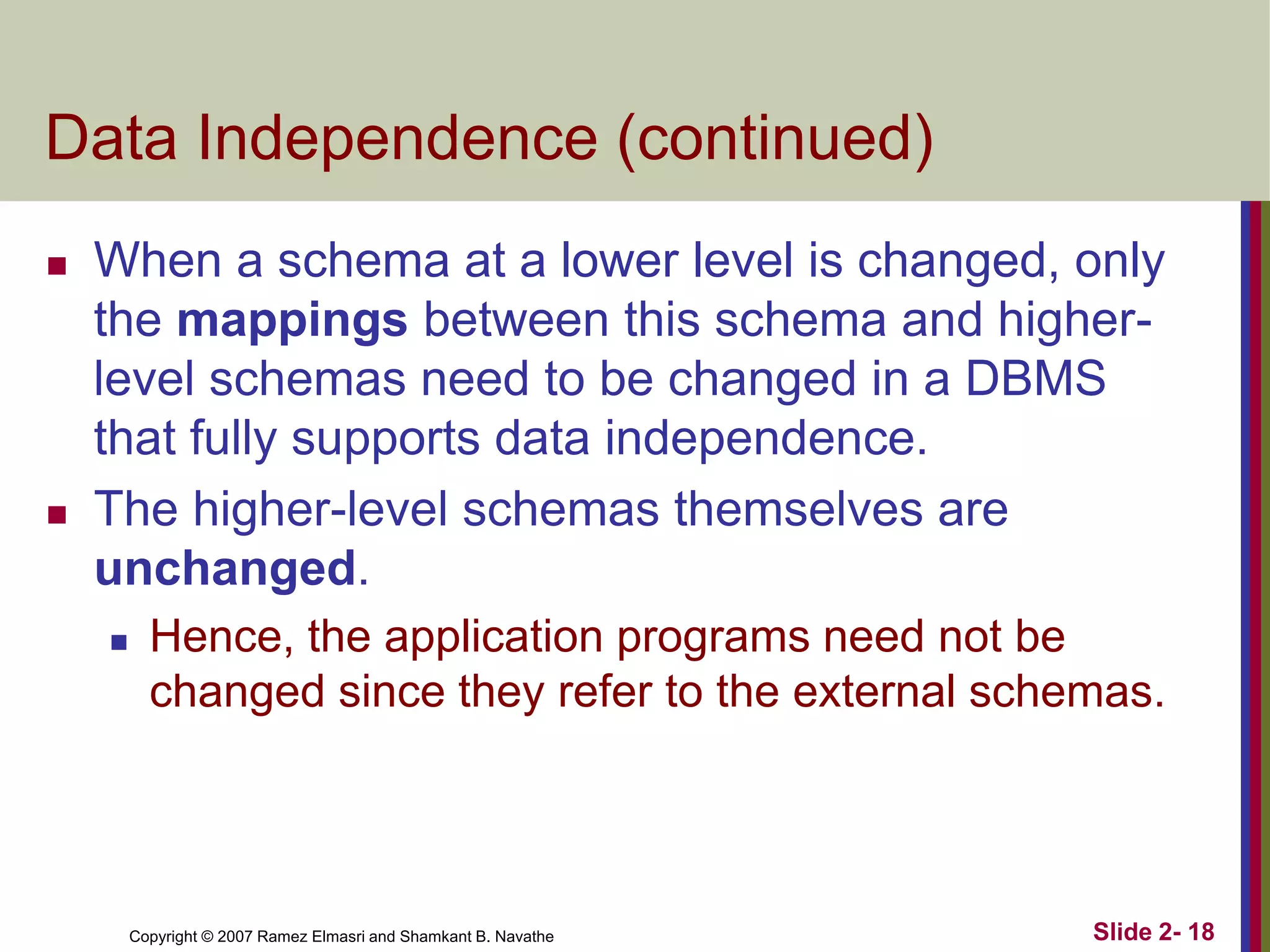
- Data independence allows changes to lower-level schemas without affecting higher levels.
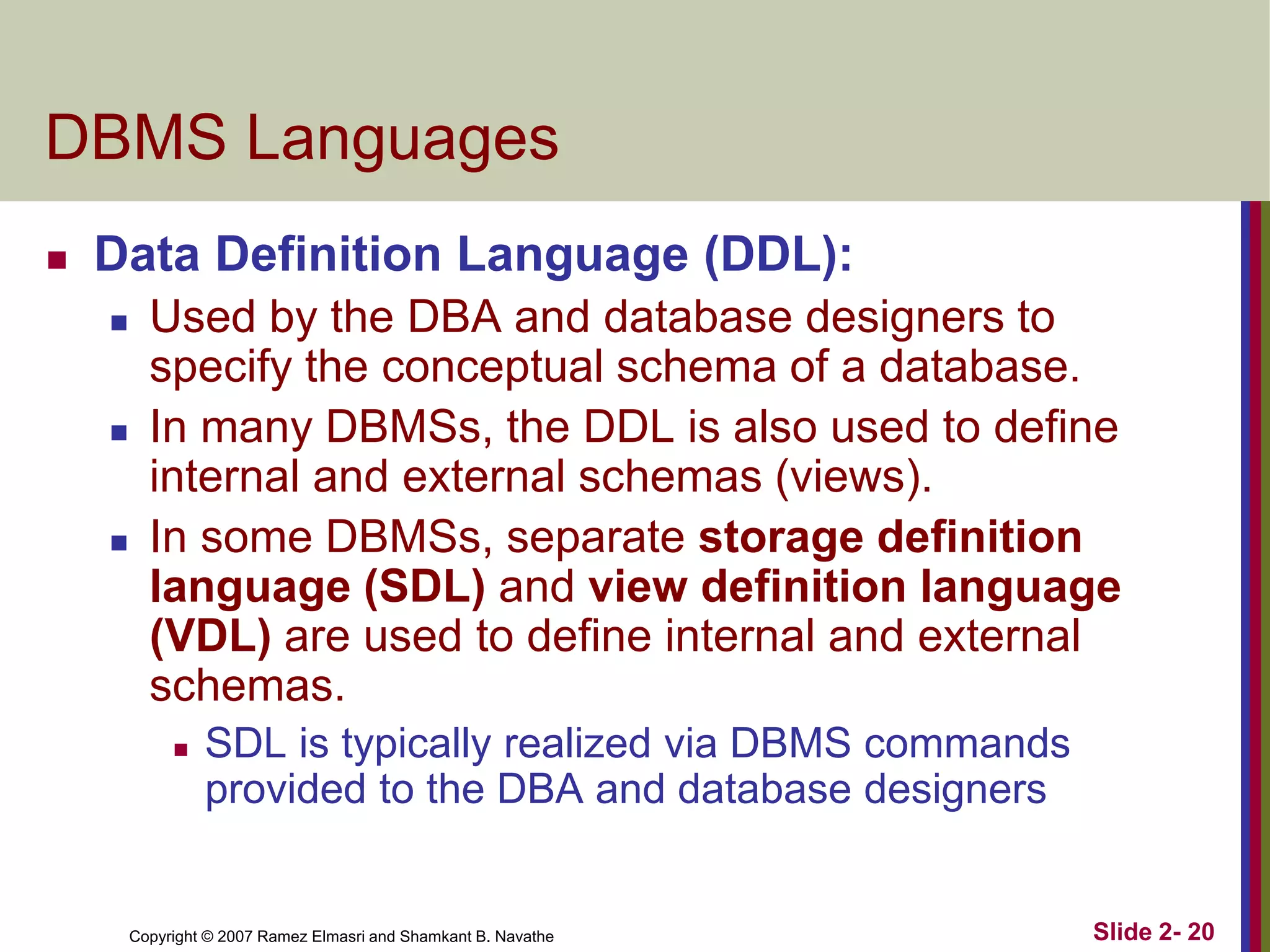
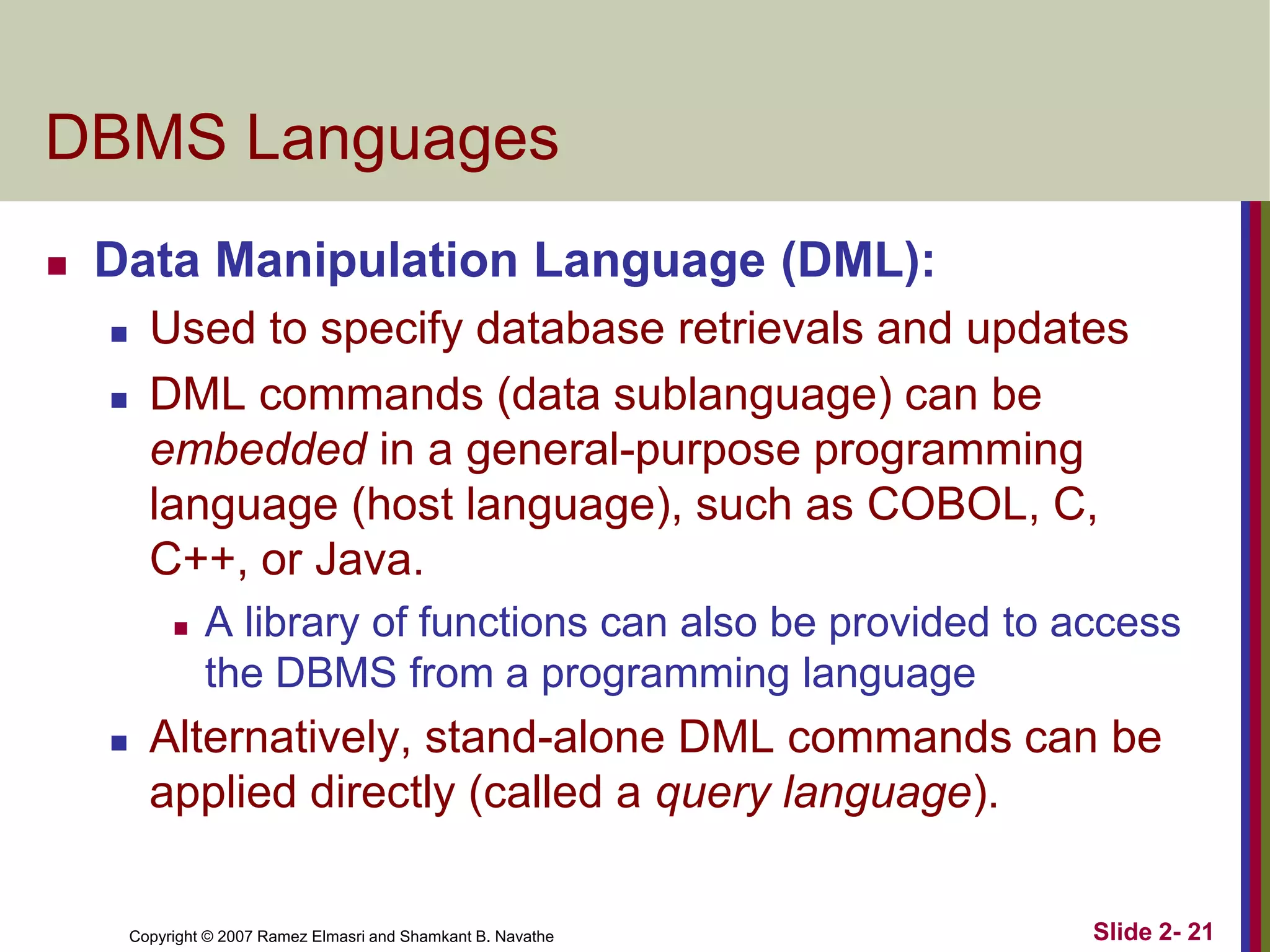
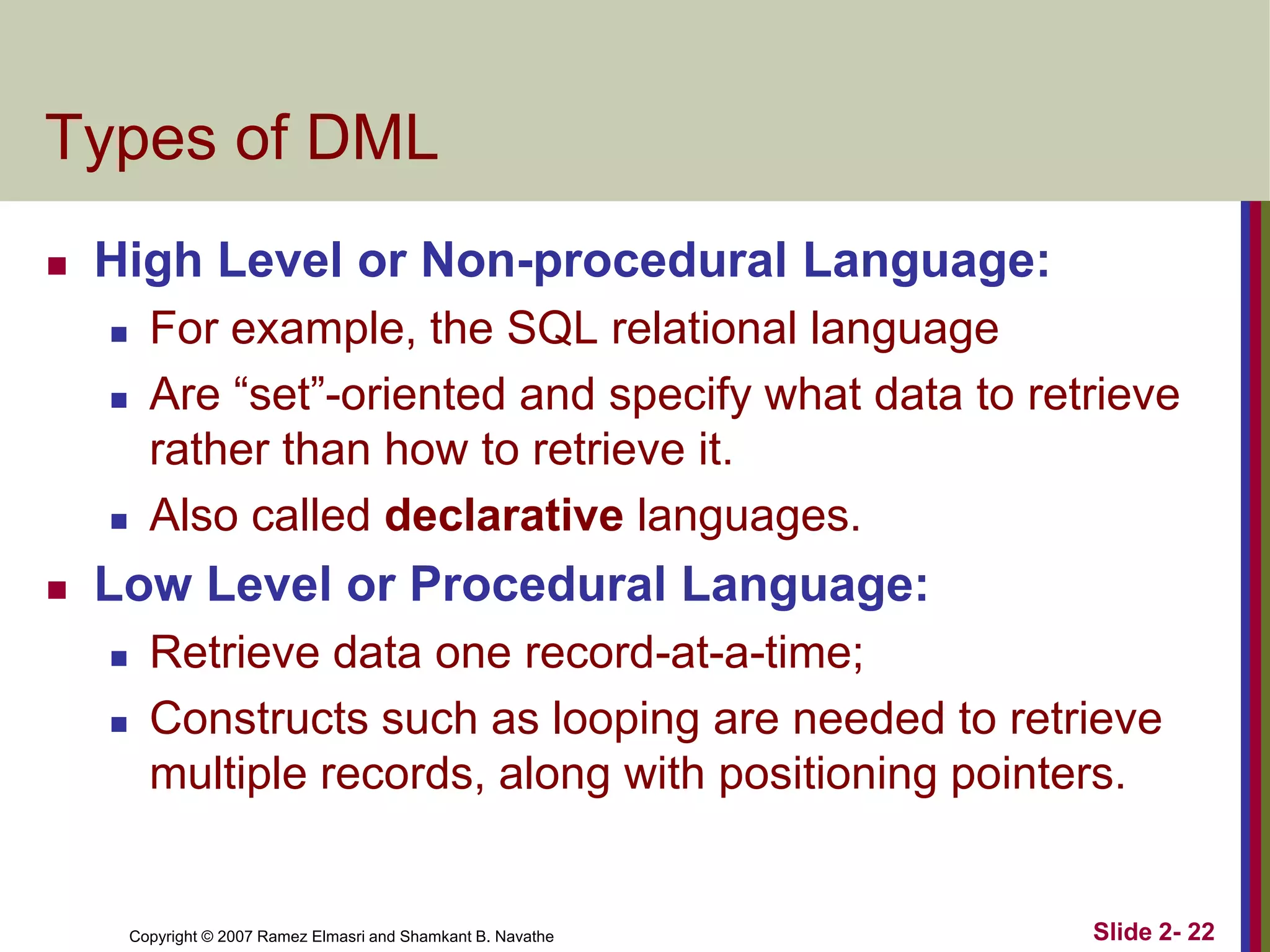
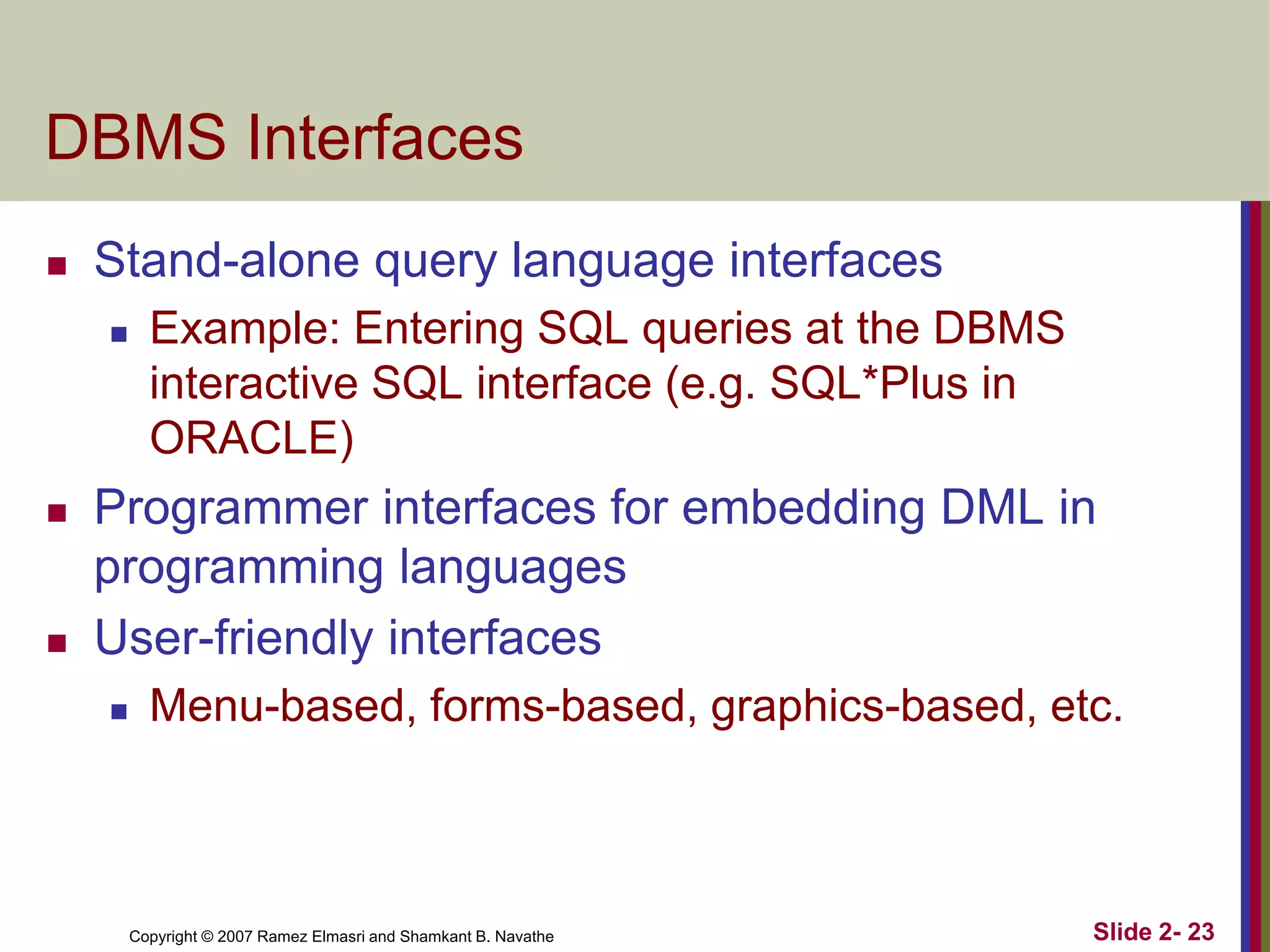
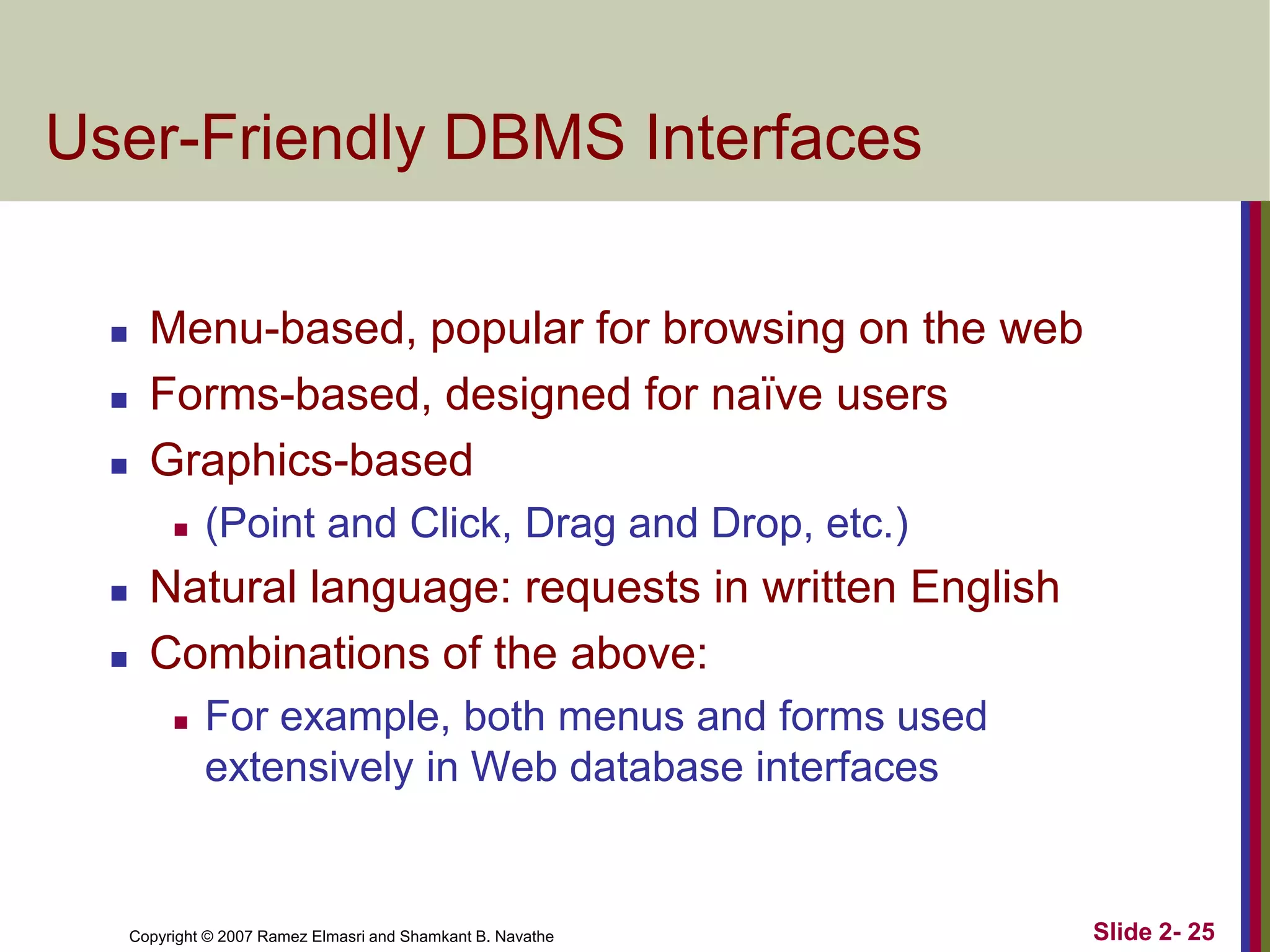
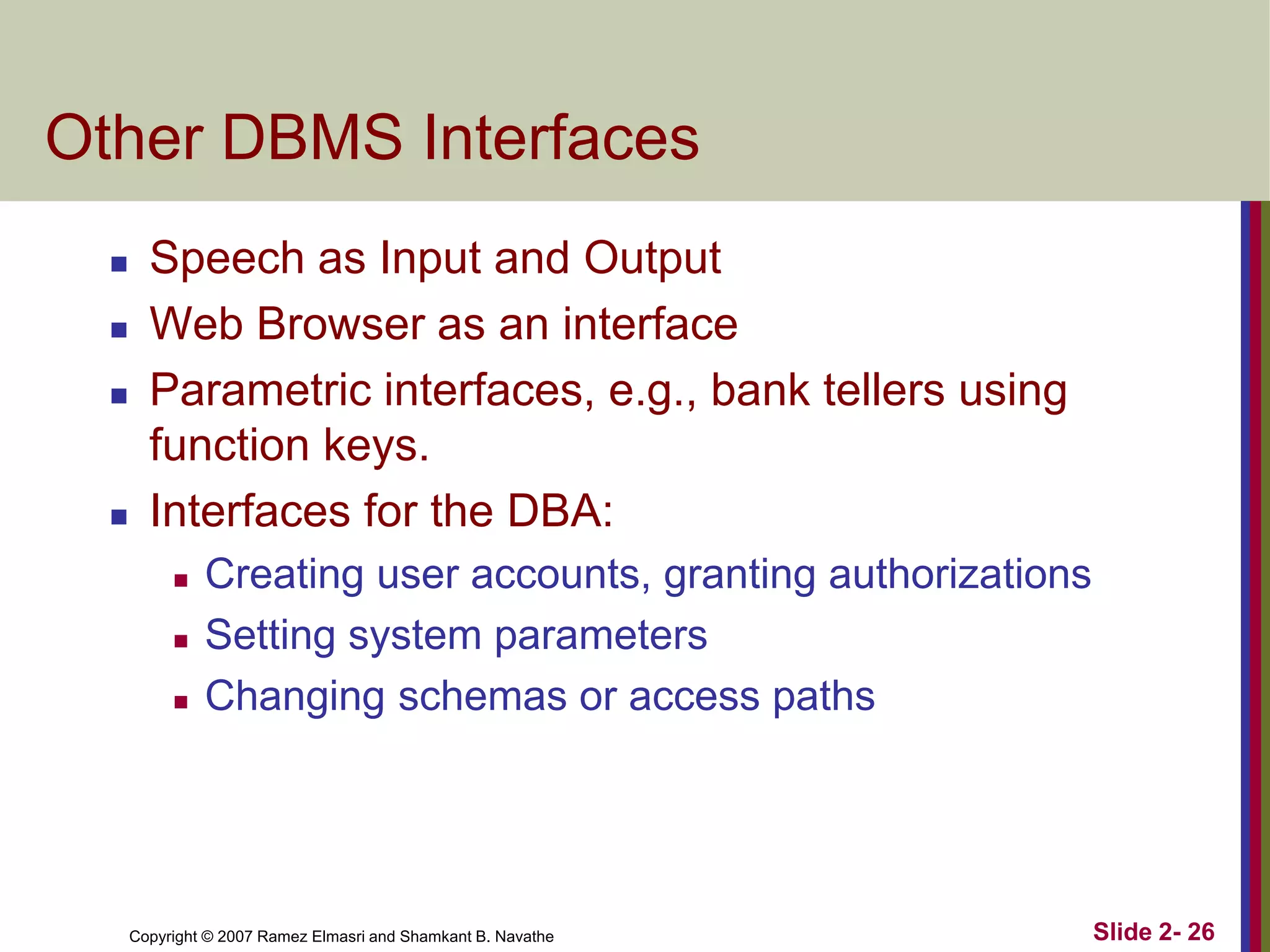
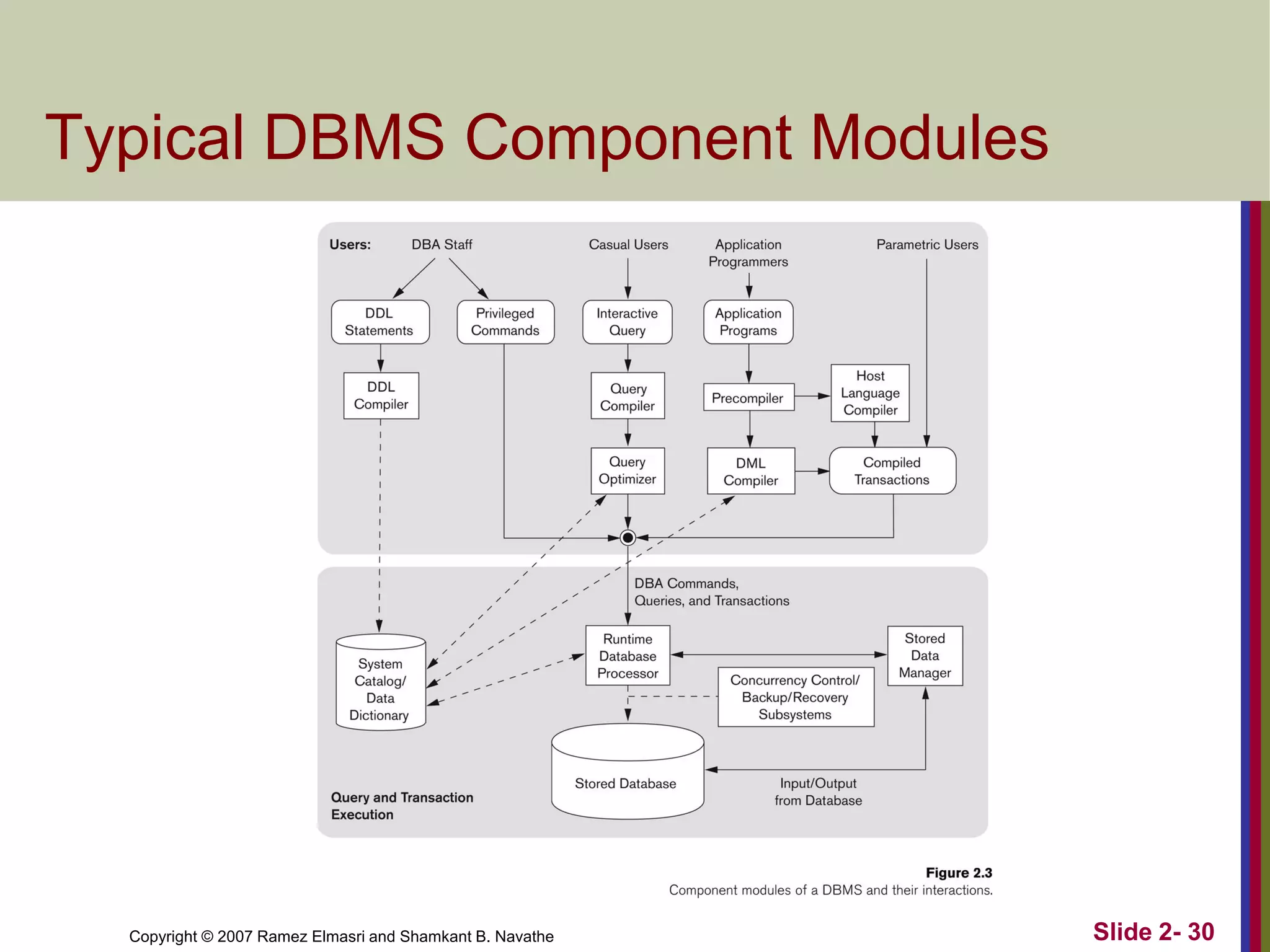
- DBMS languages include DDL for definition and DML for manipulation. Interfaces provide access for users, programmers, and administrators.
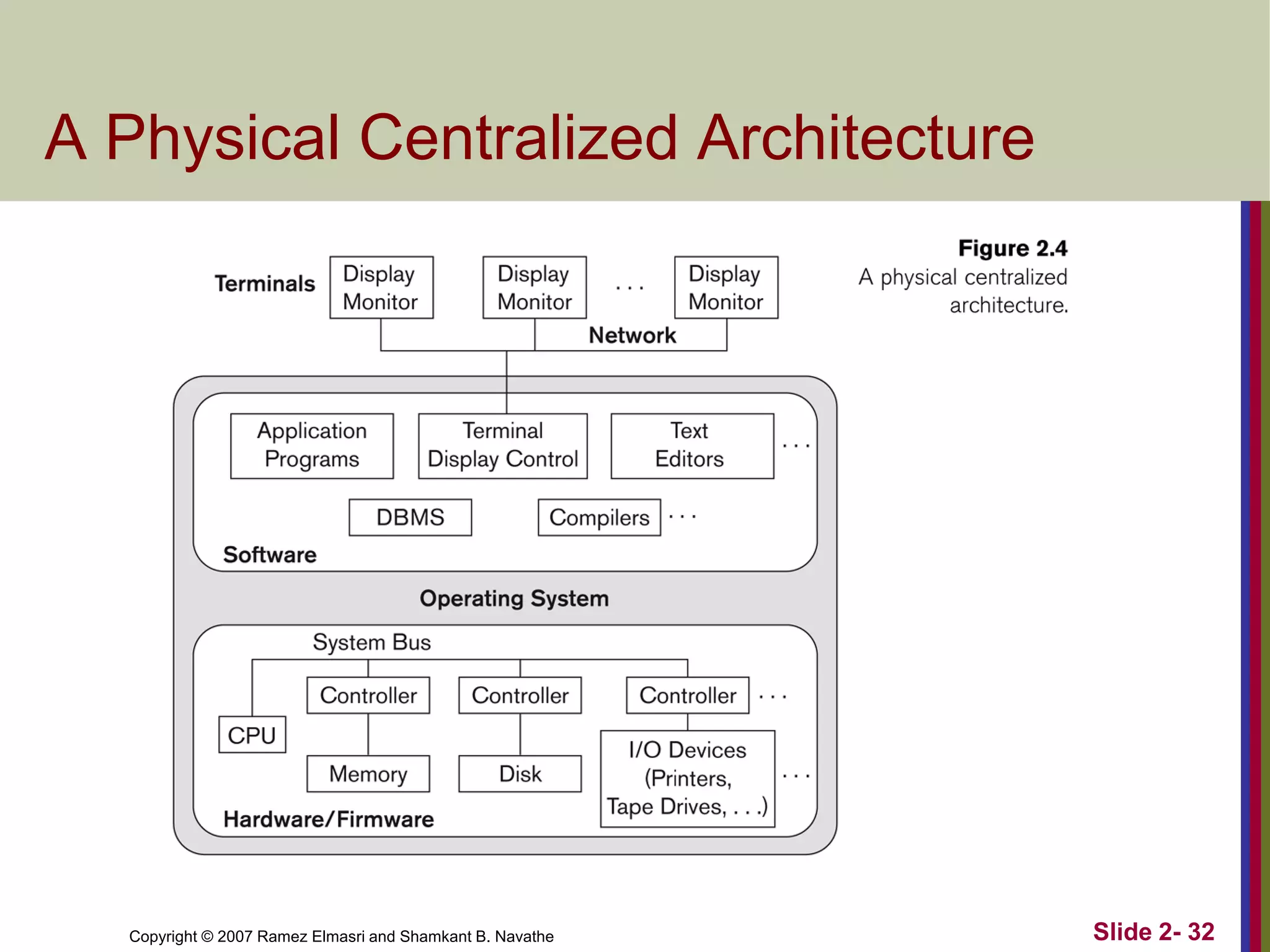
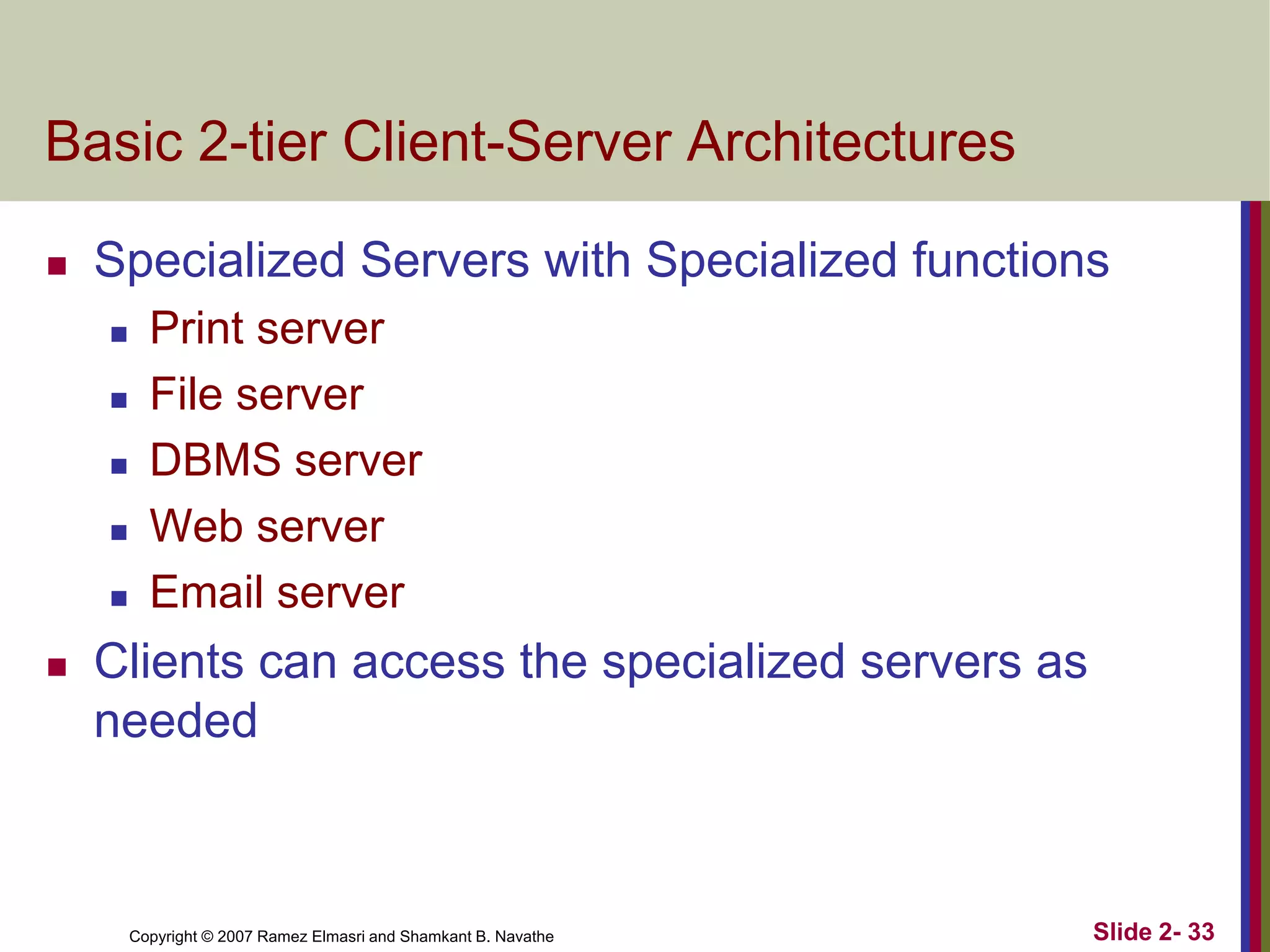
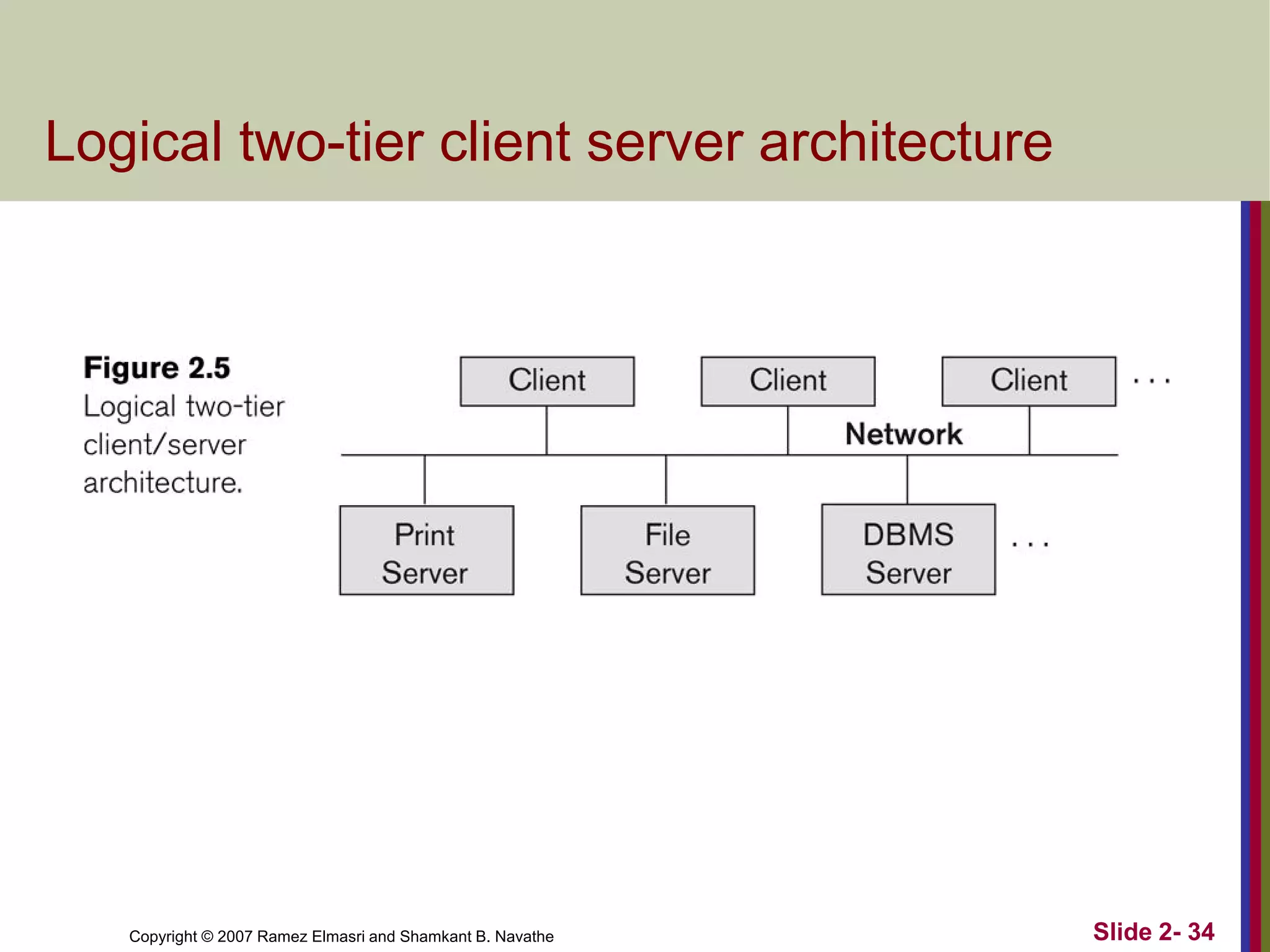
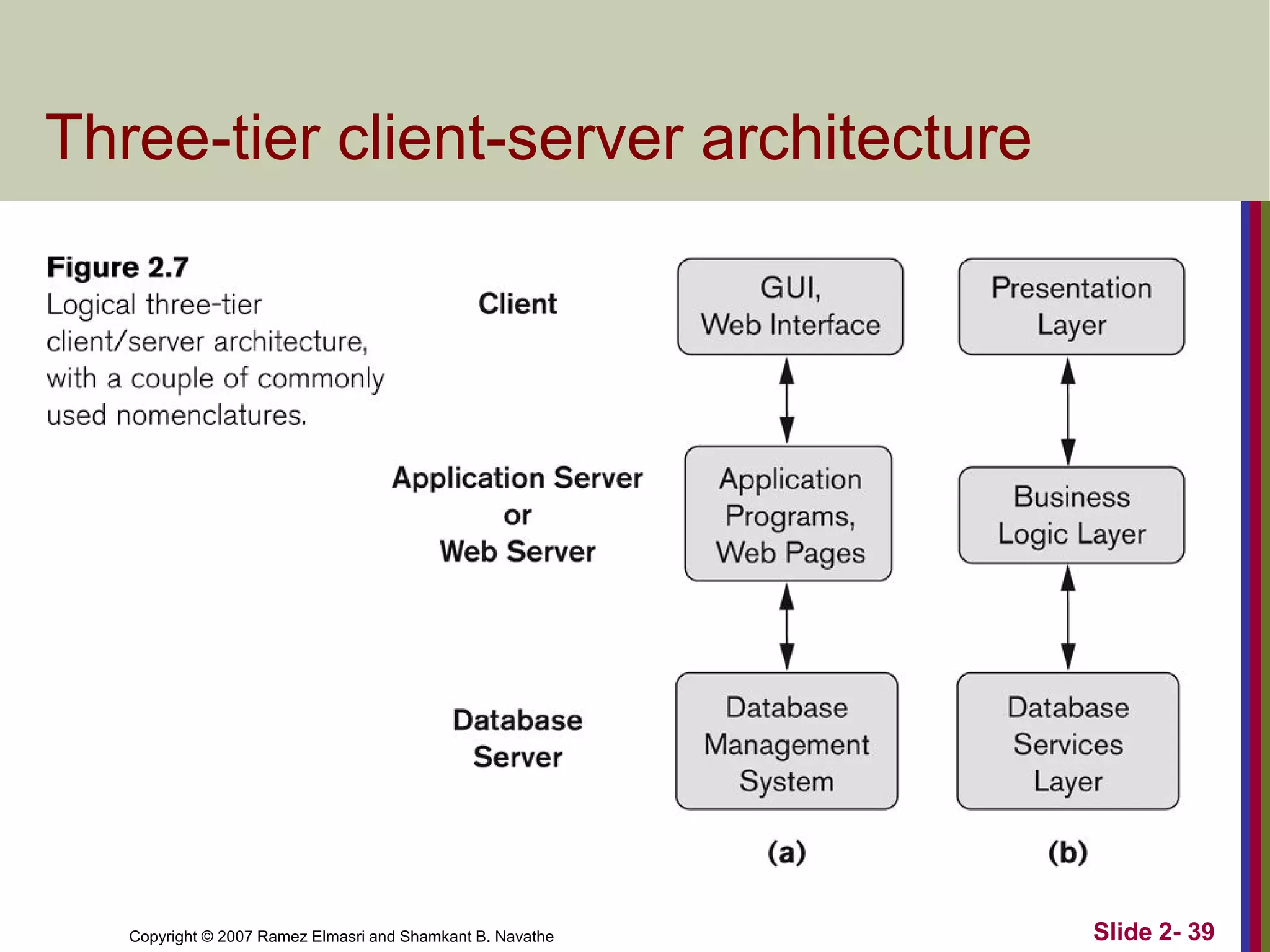
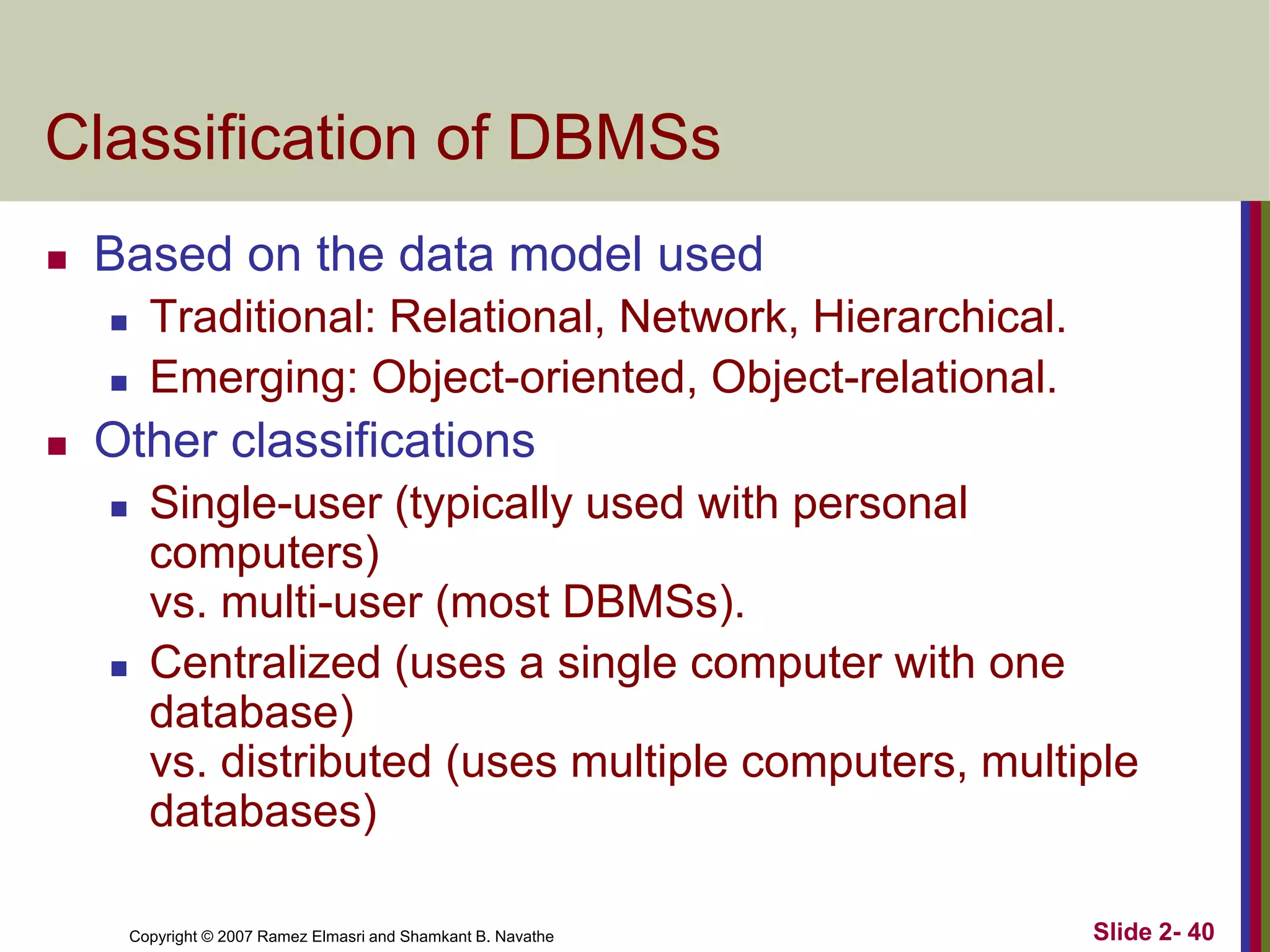
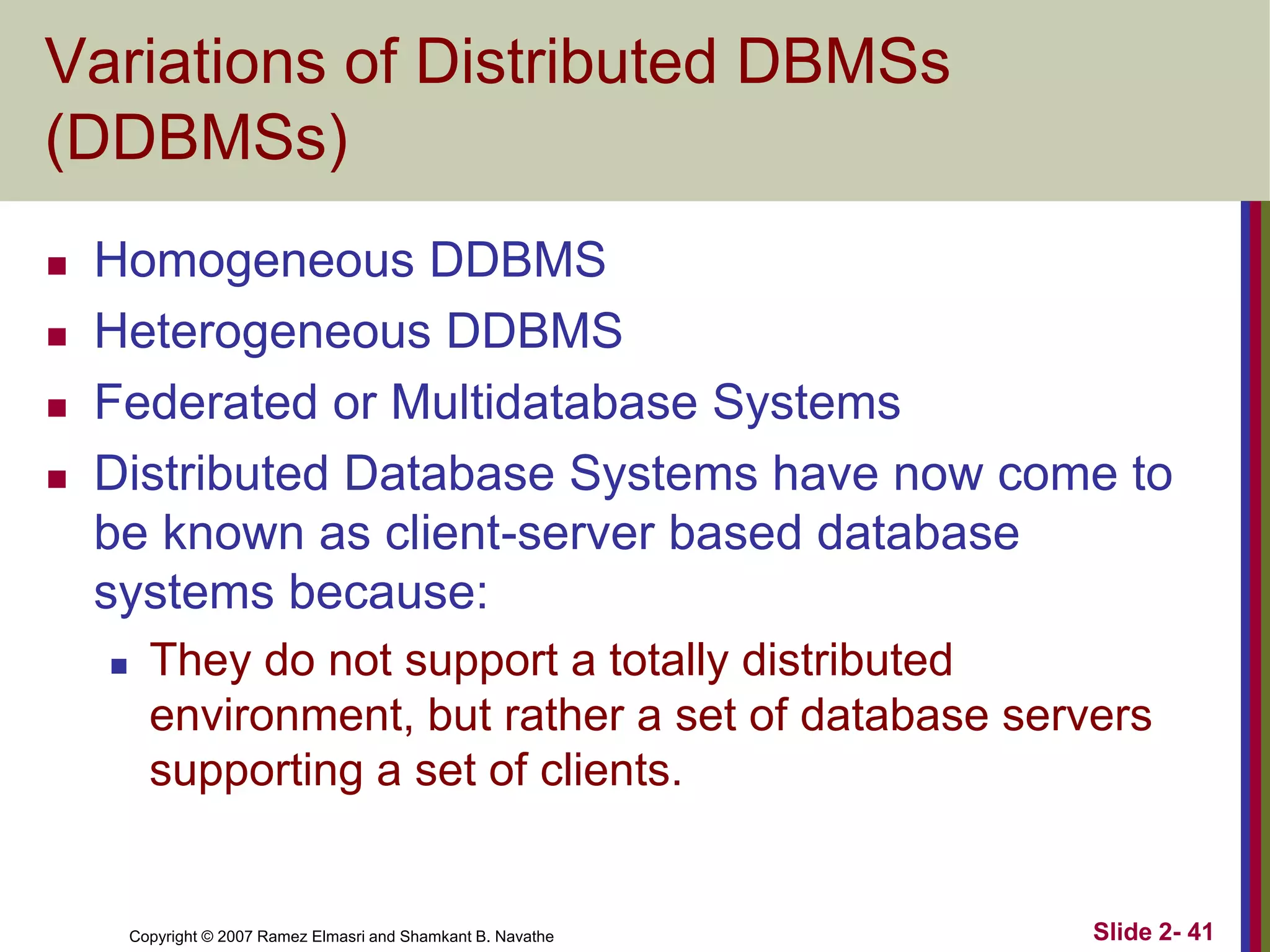
- Database architectures range from centralized to client-server. Client-server divides processing between client machines and centralized database servers.