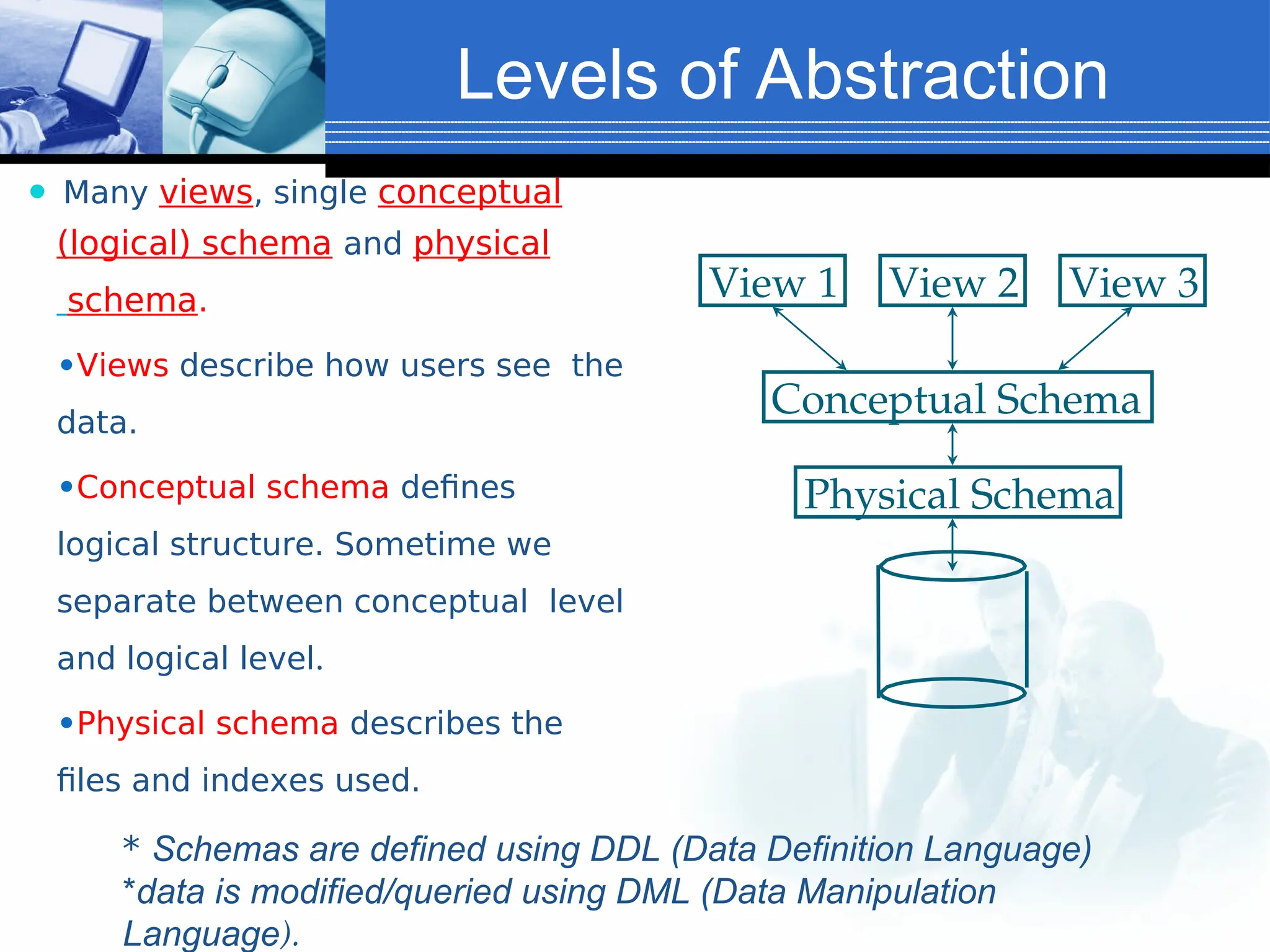
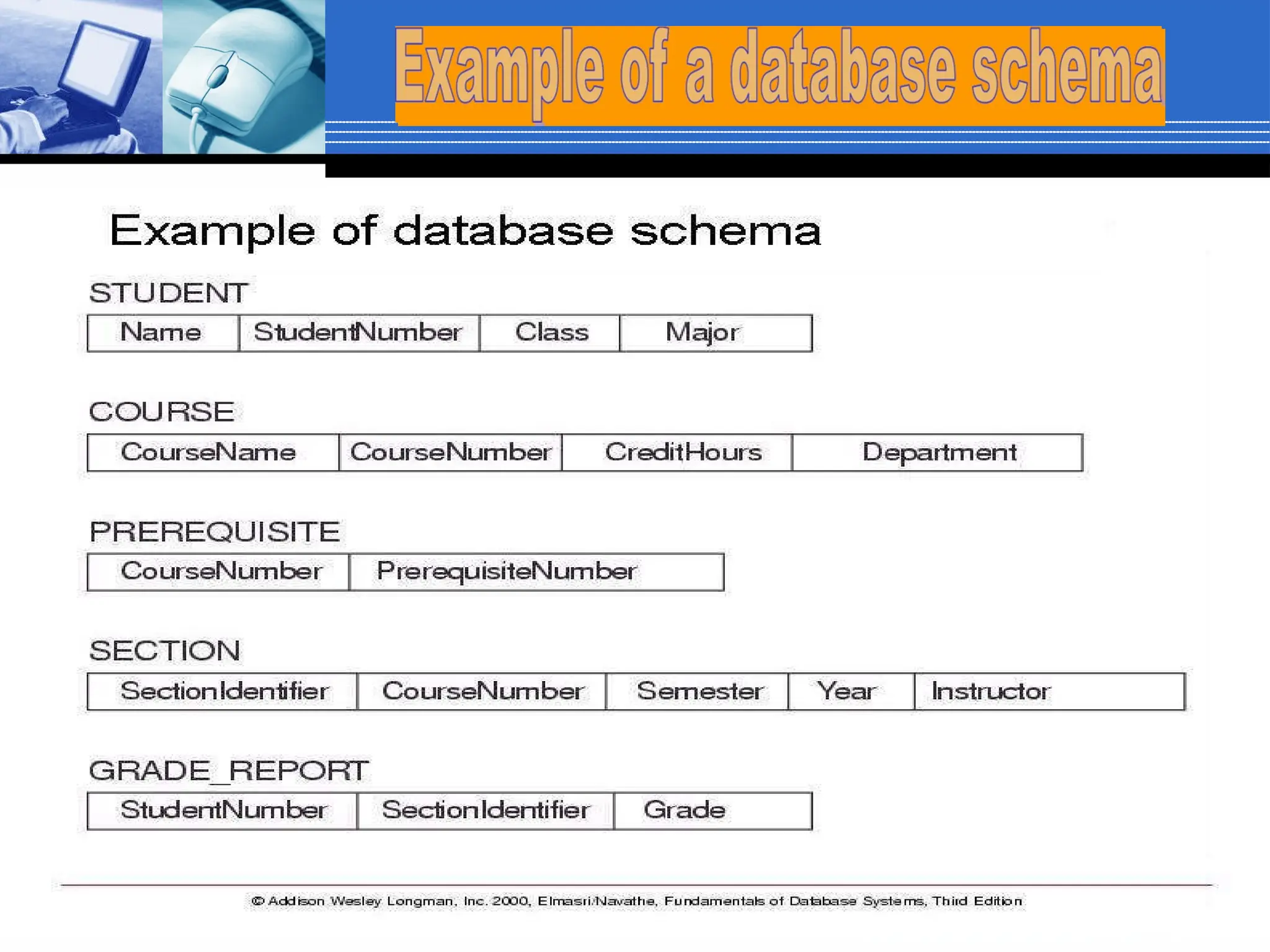
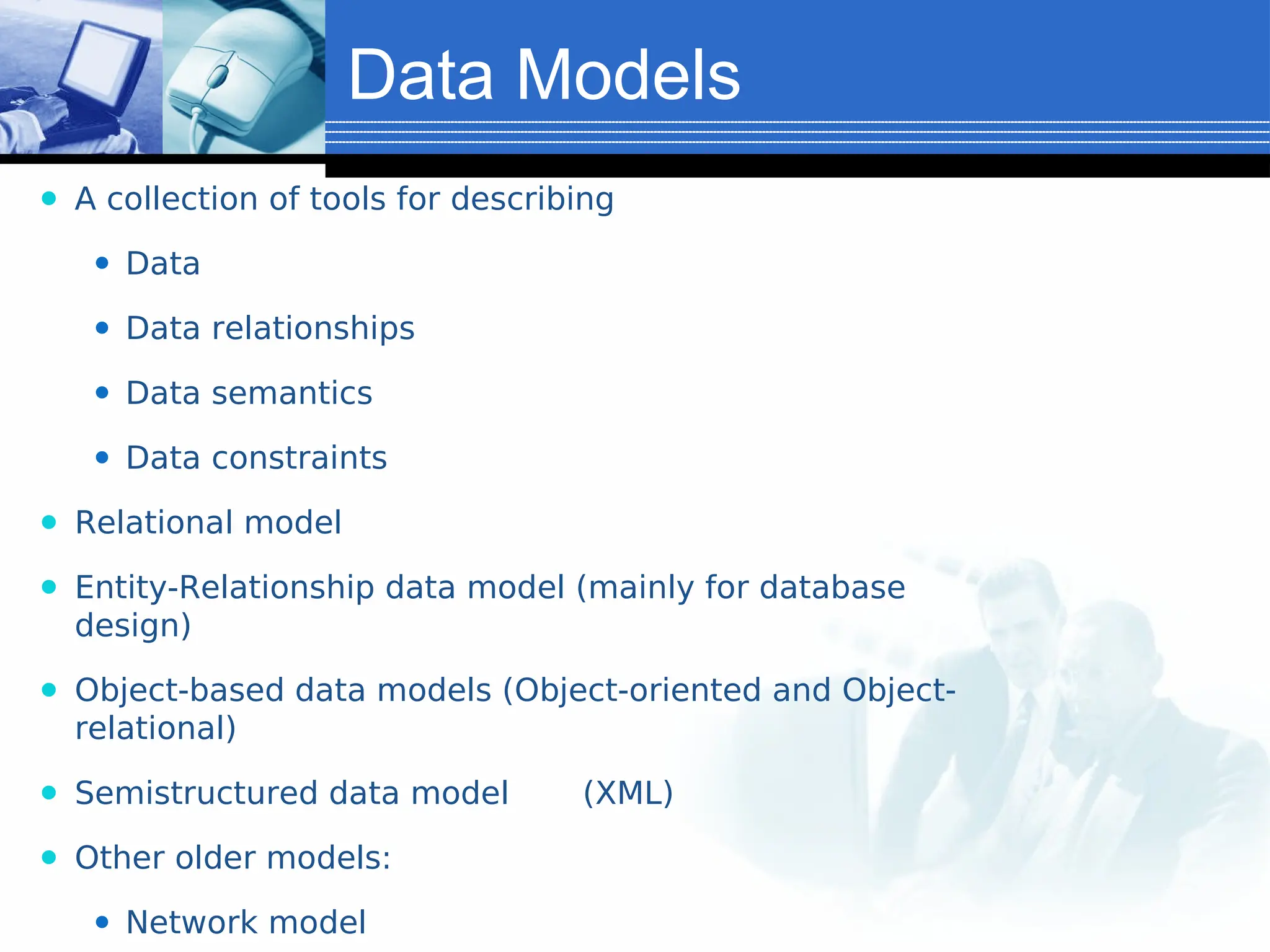
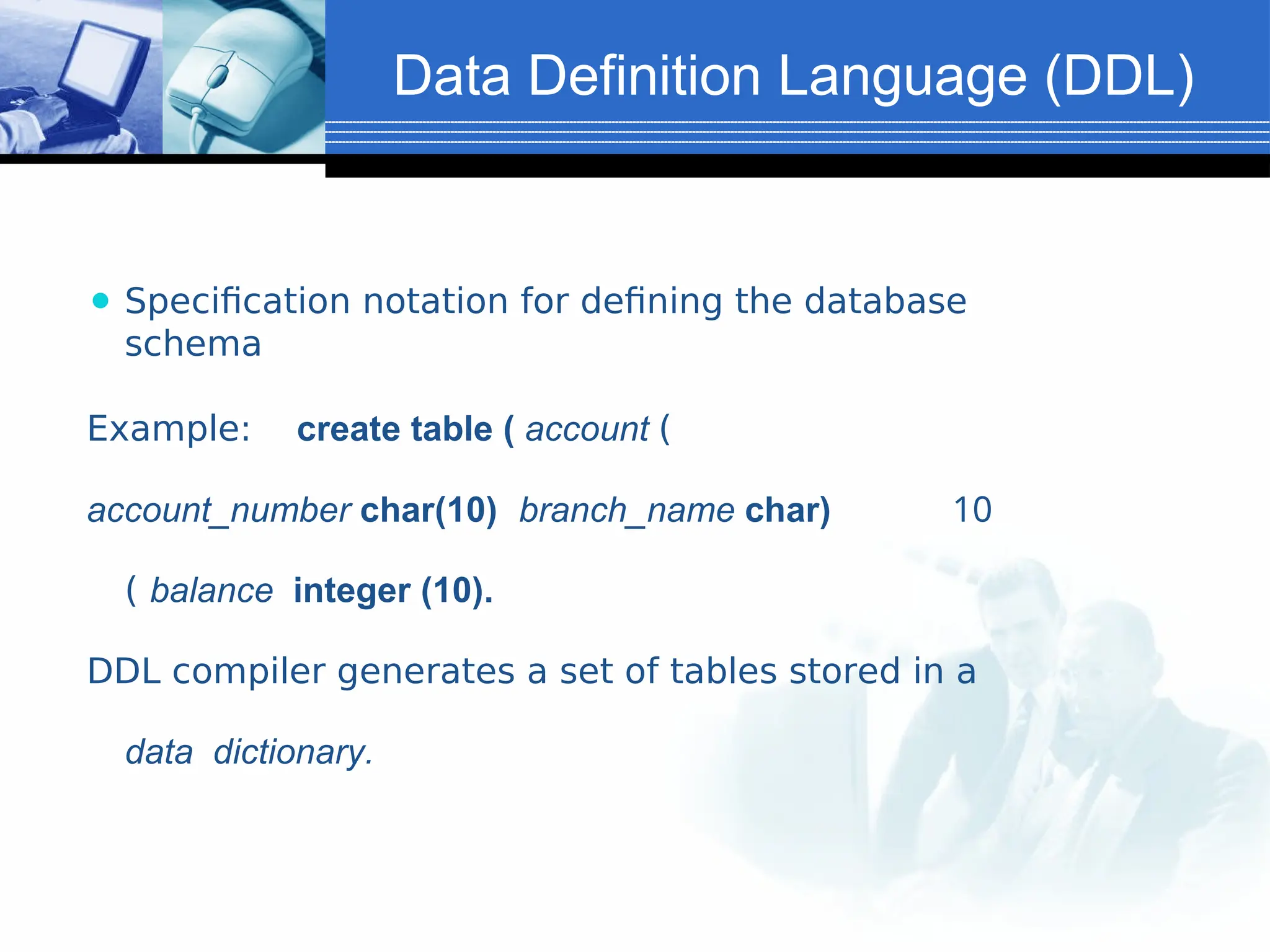
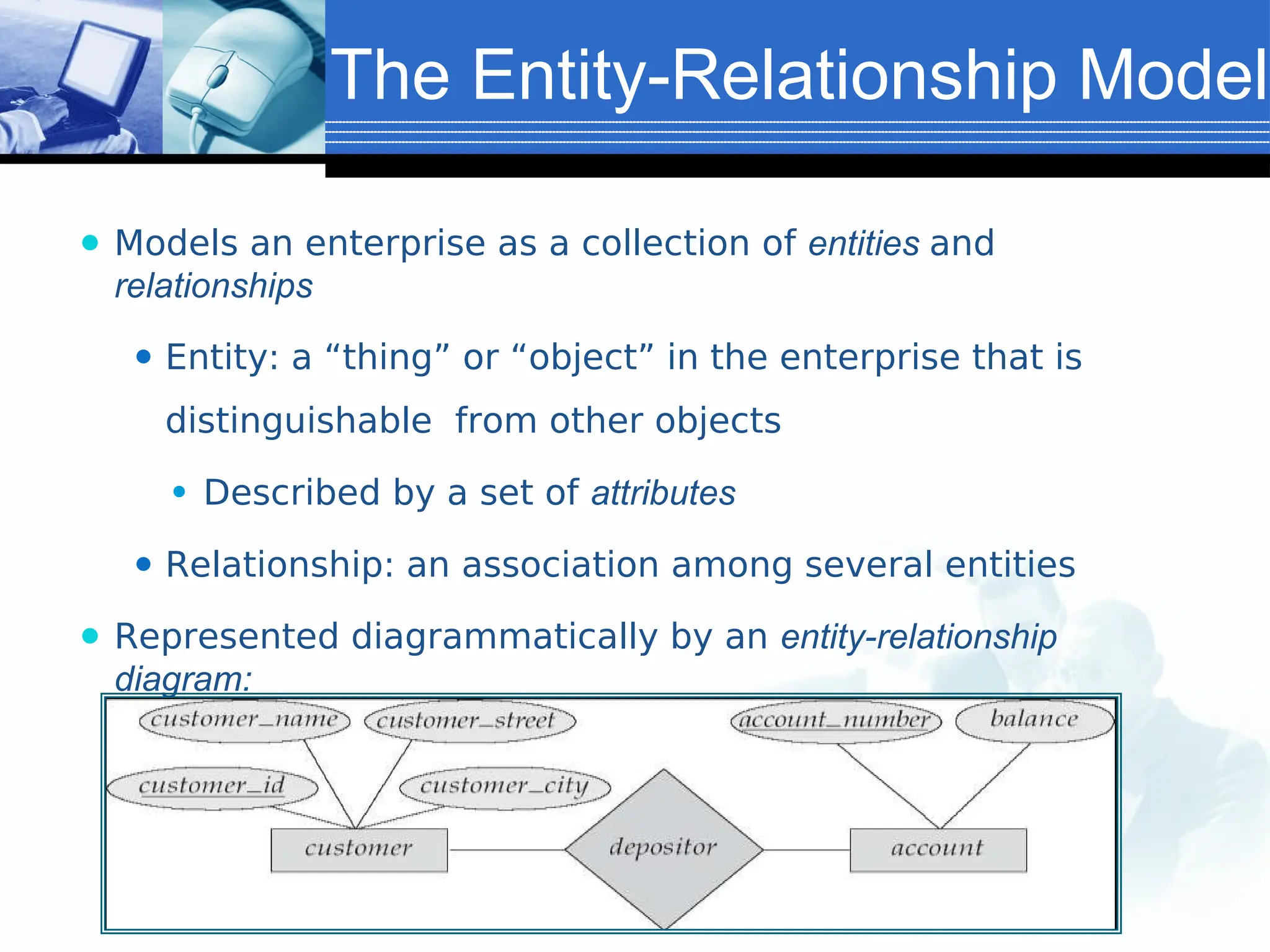
The document provides an introduction to database systems, including definitions of databases and database management systems (DBMS). It highlights the advantages of DBMS over file-based systems, such as improved data integrity, security, and reduced redundancy. Additionally, it discusses the levels of abstraction in database design, data manipulation languages, and the importance of data models.