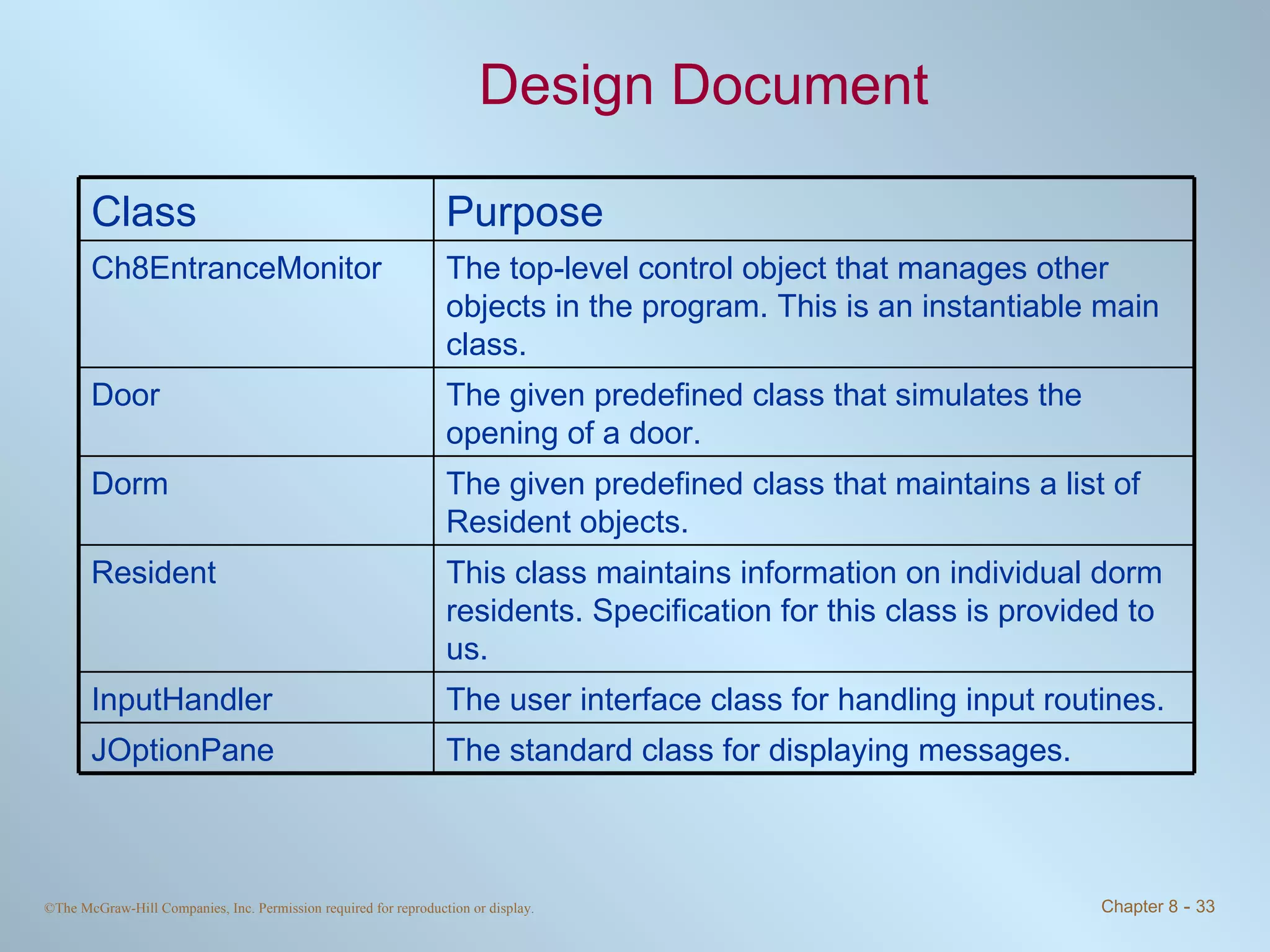
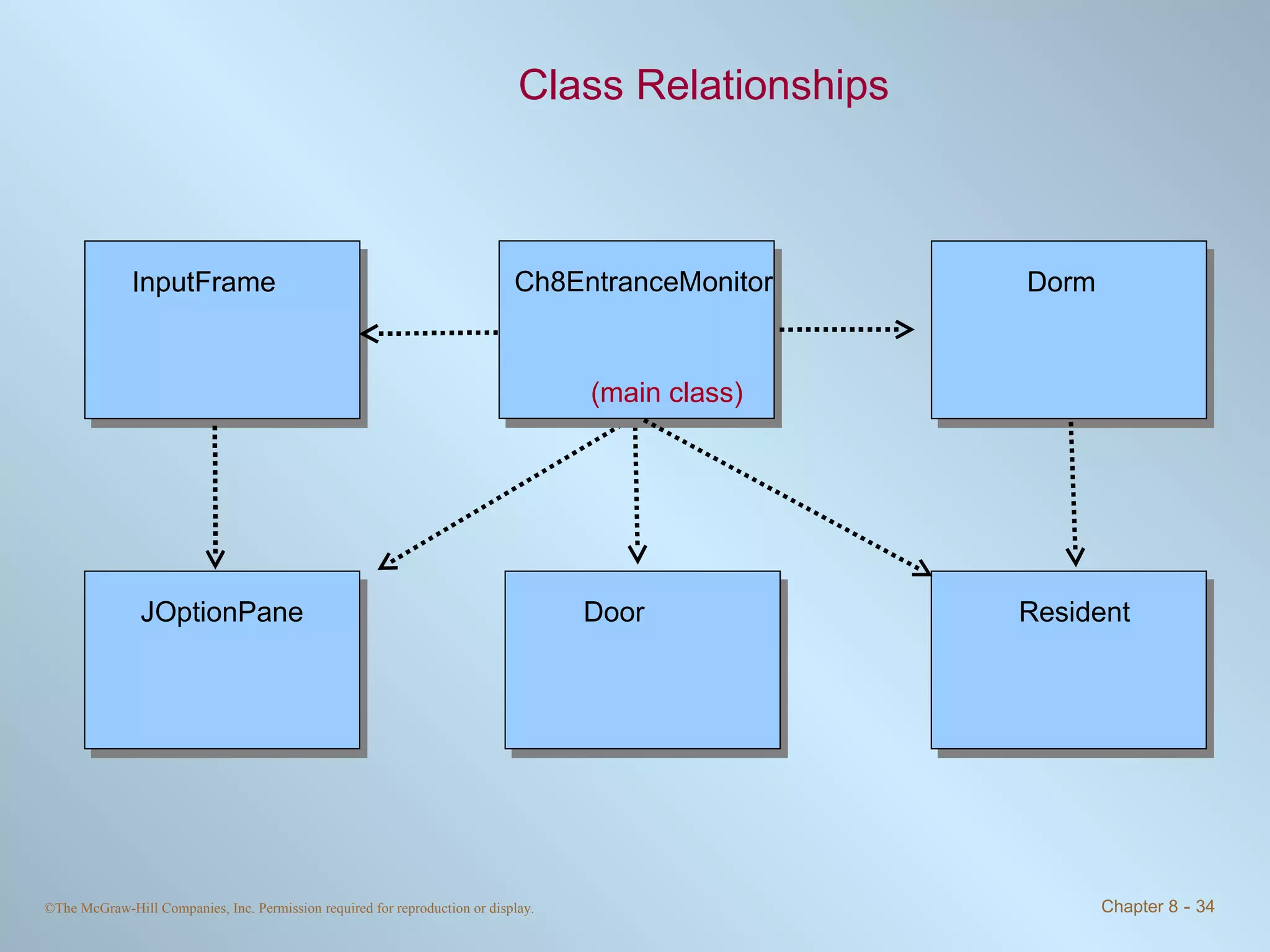
This chapter discusses exceptions and assertions in Java. The key points are:
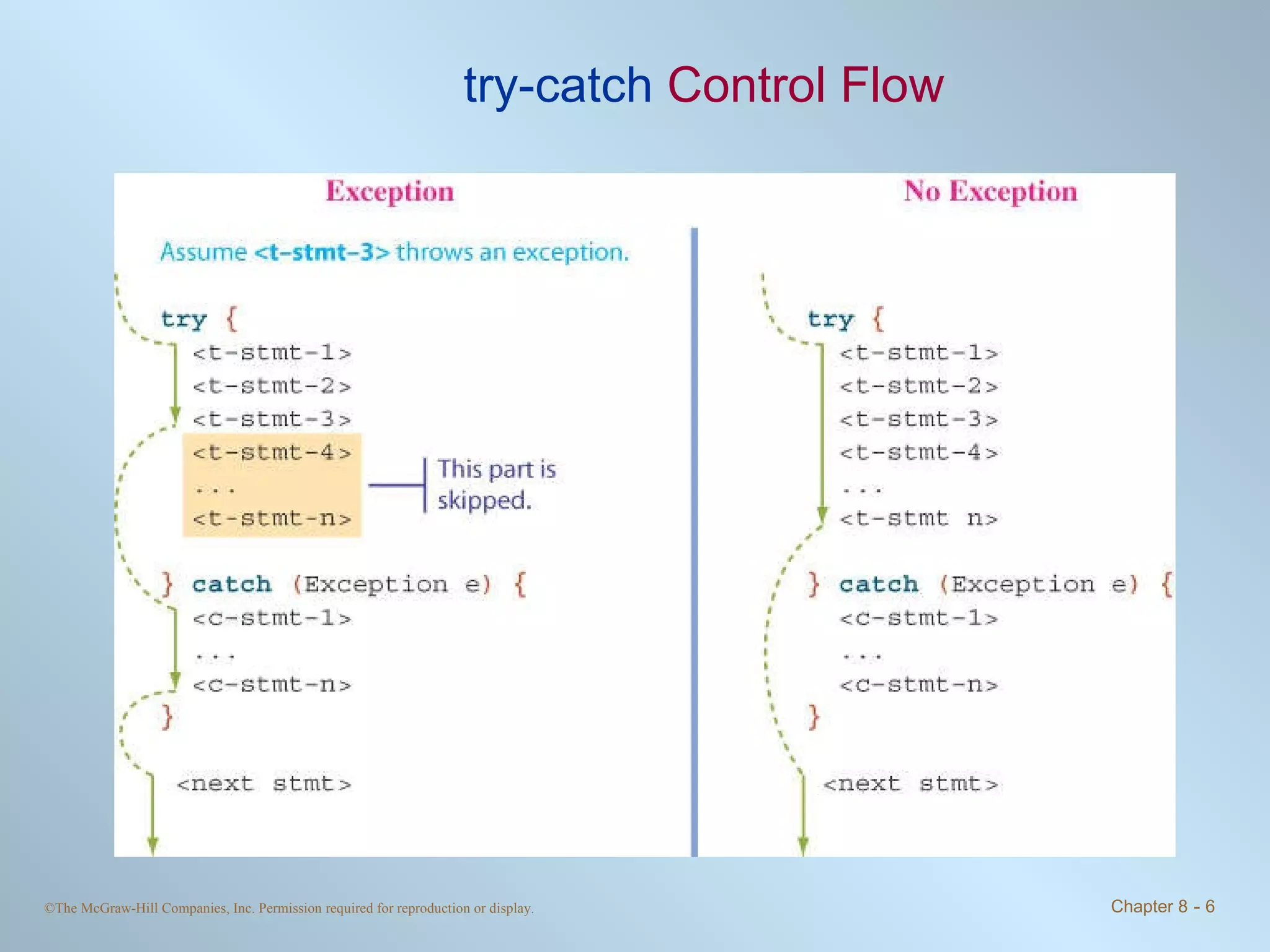
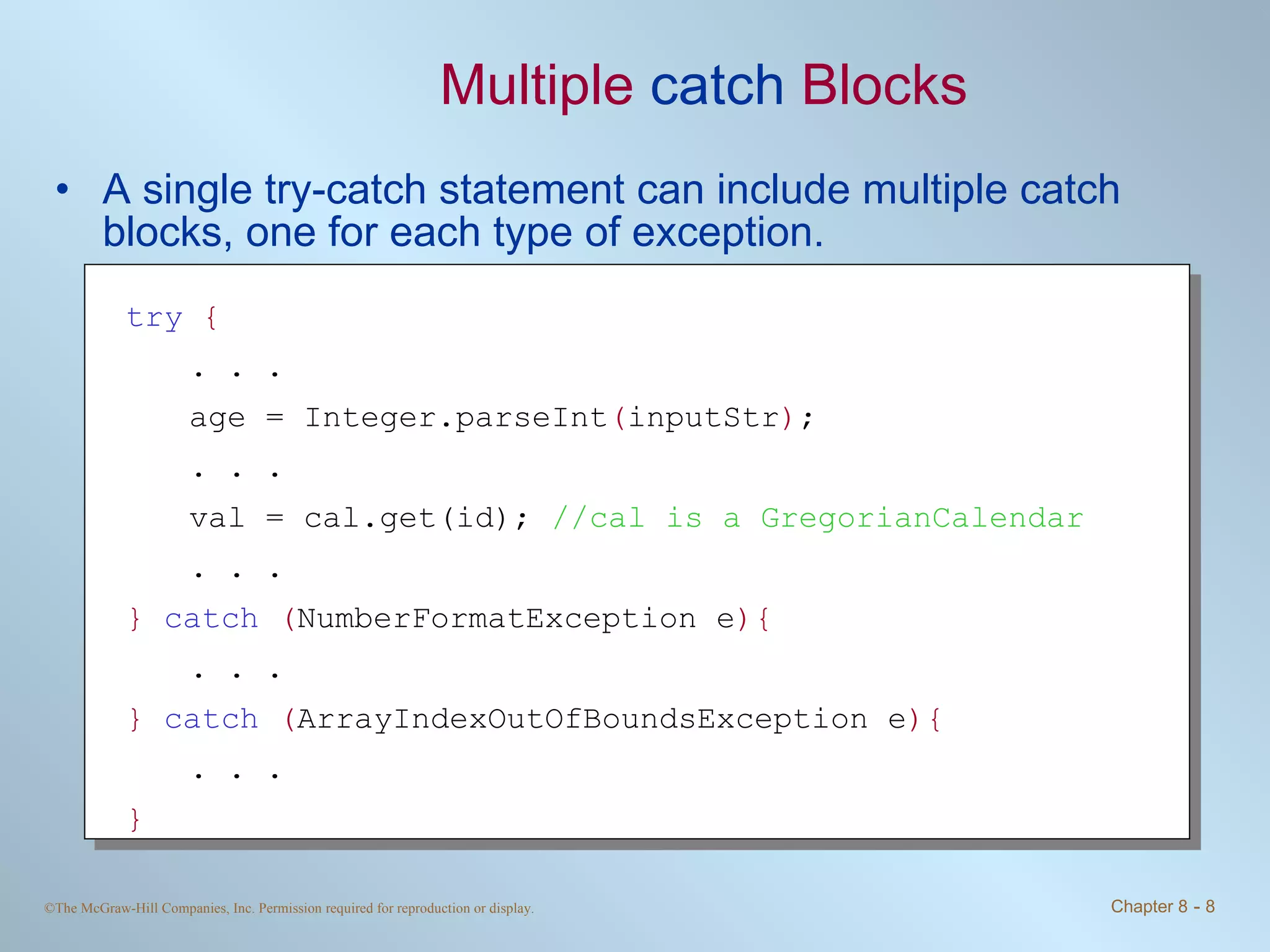
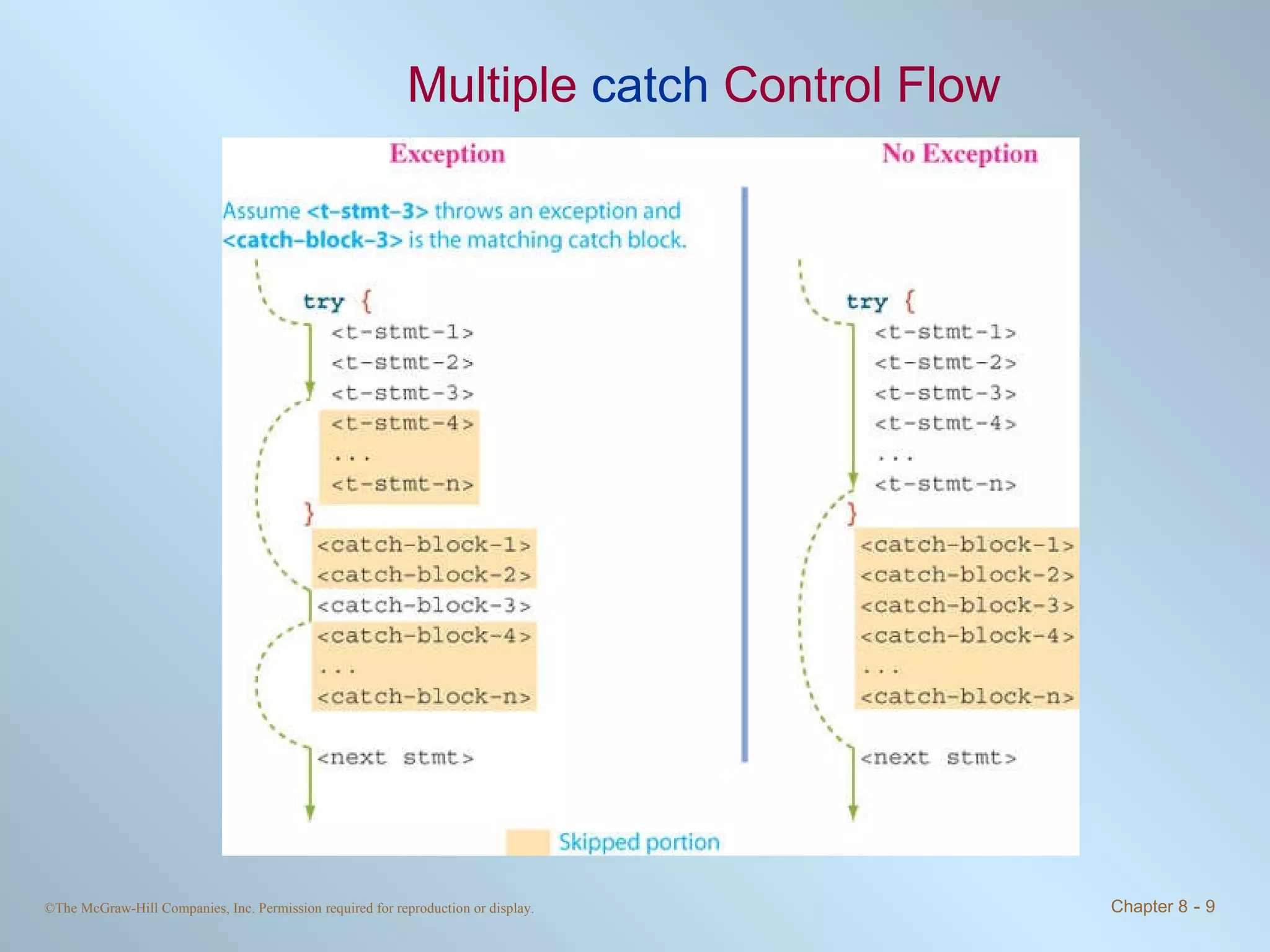
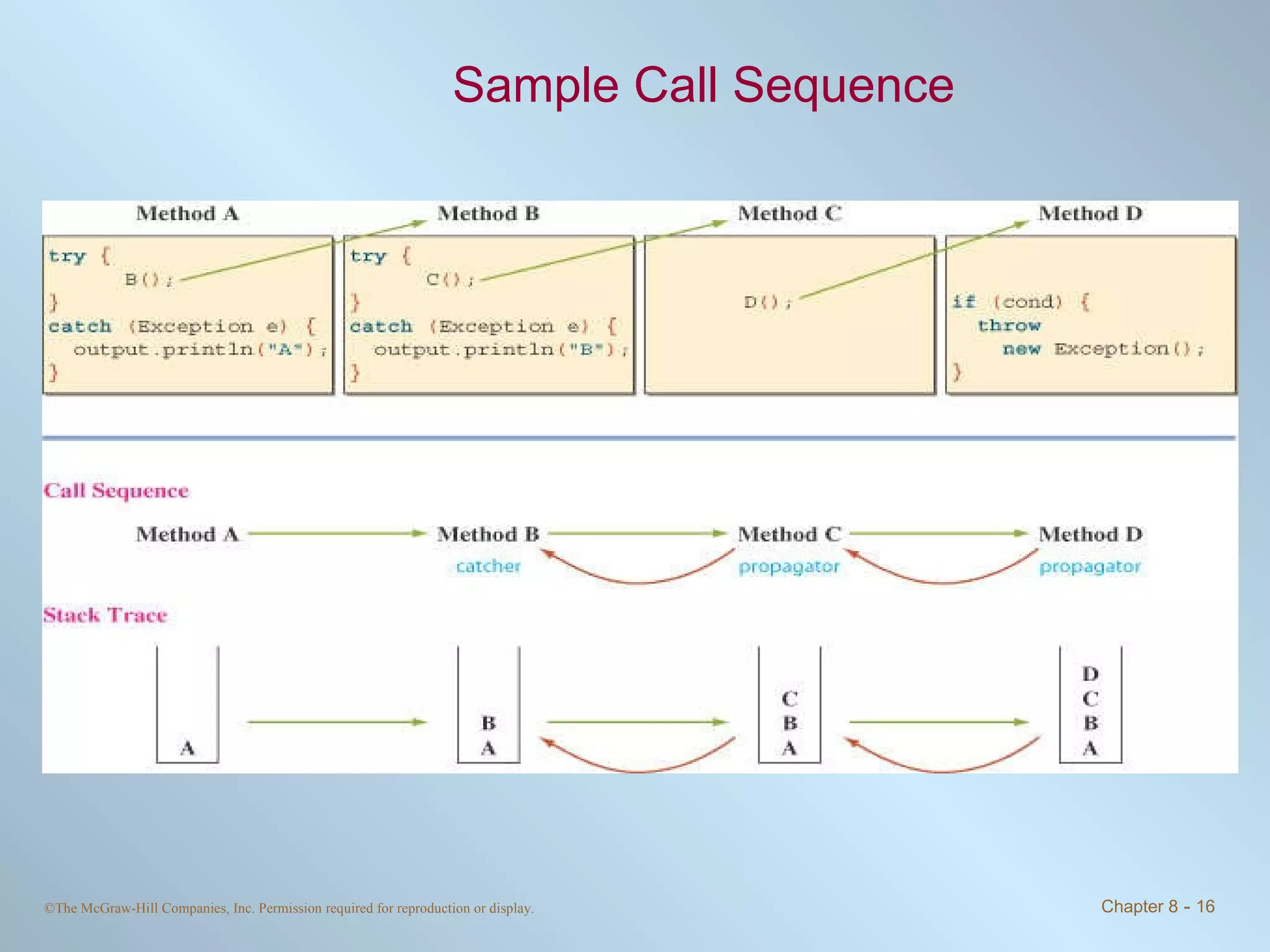
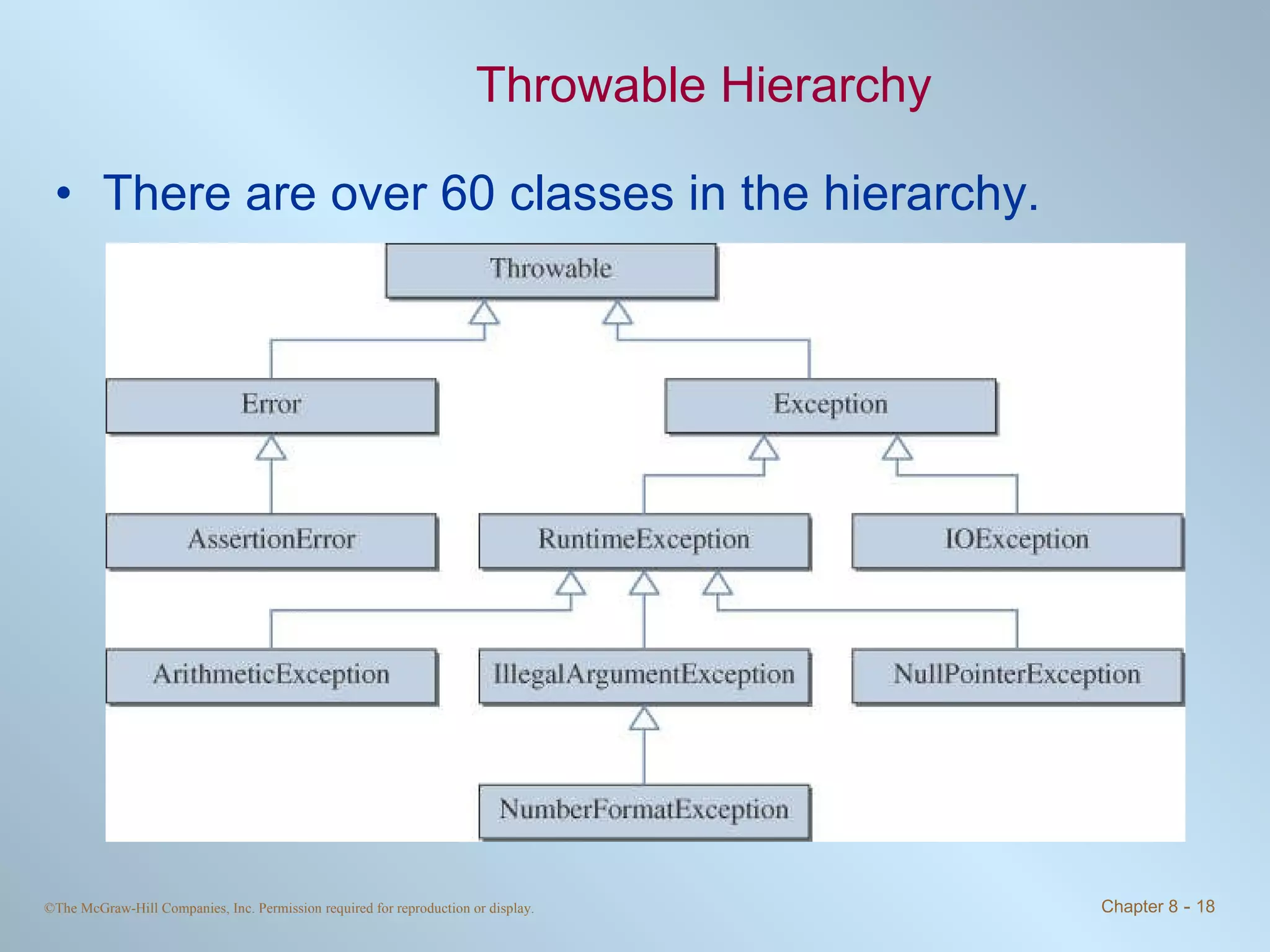
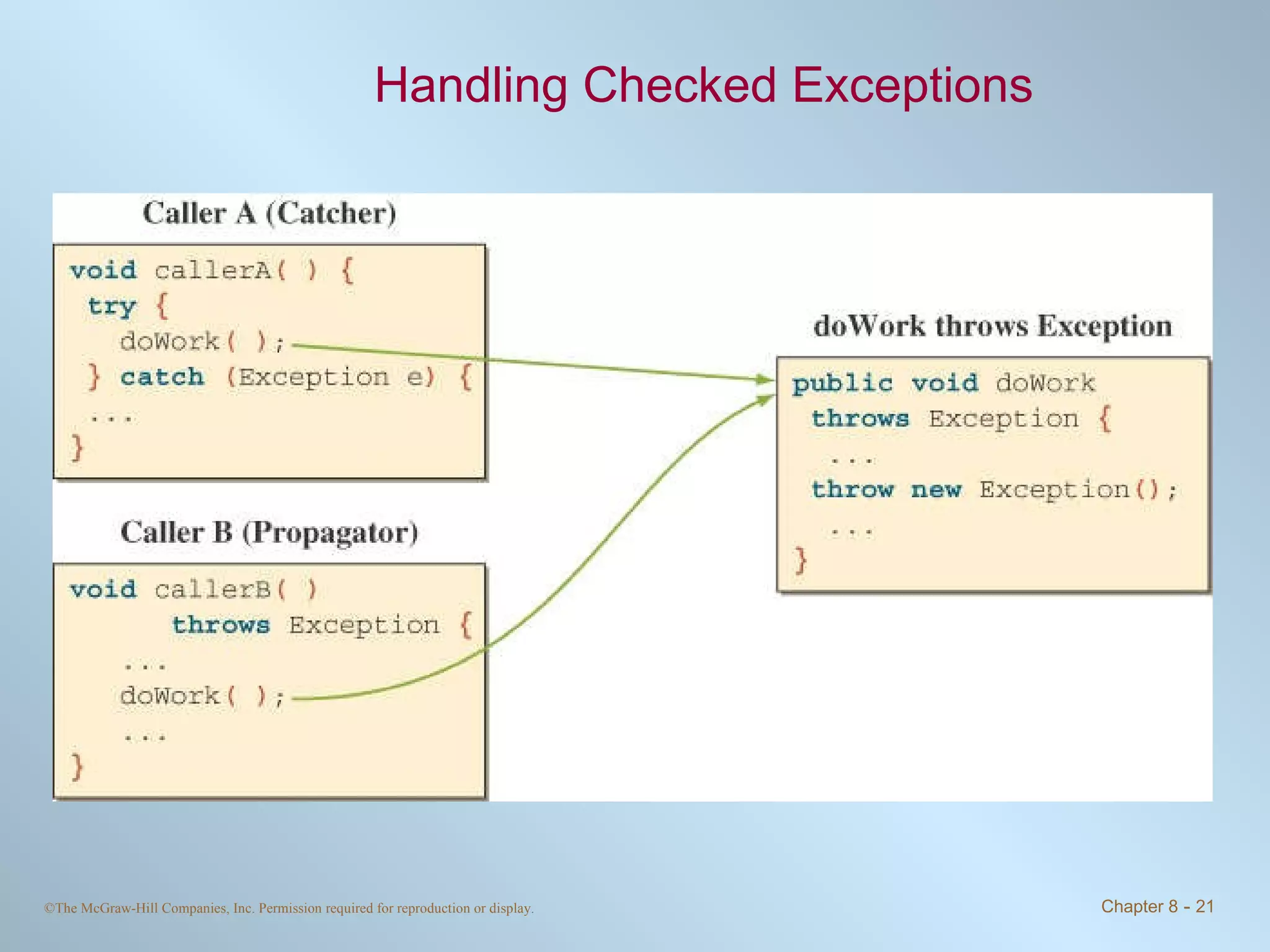
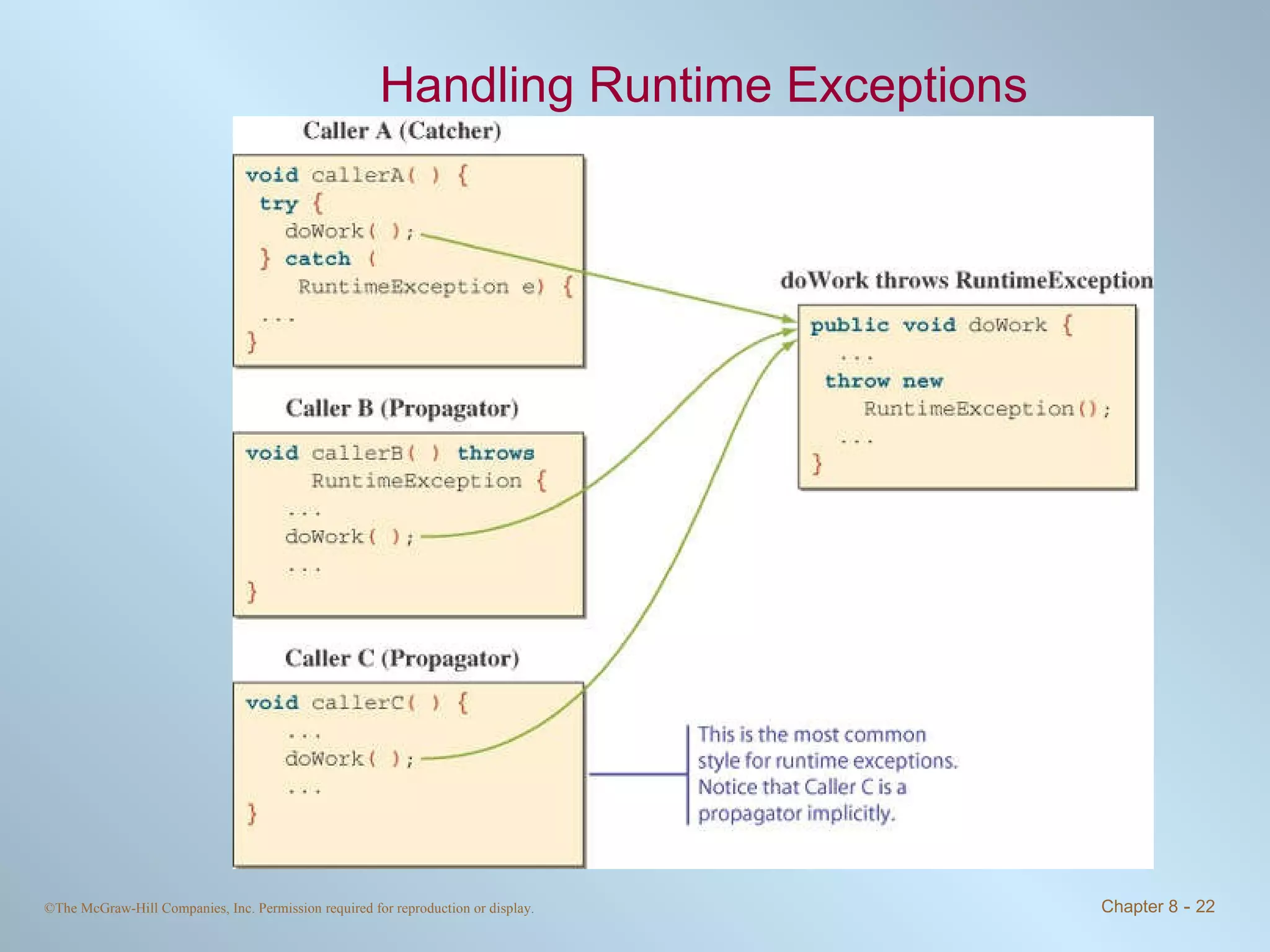
1. Exceptions represent error conditions and allow for graceful handling of errors rather than program crashes. Exceptions can be caught using try-catch blocks.
2. Checked exceptions must be caught or declared in a method, while unchecked exceptions do not require handling.
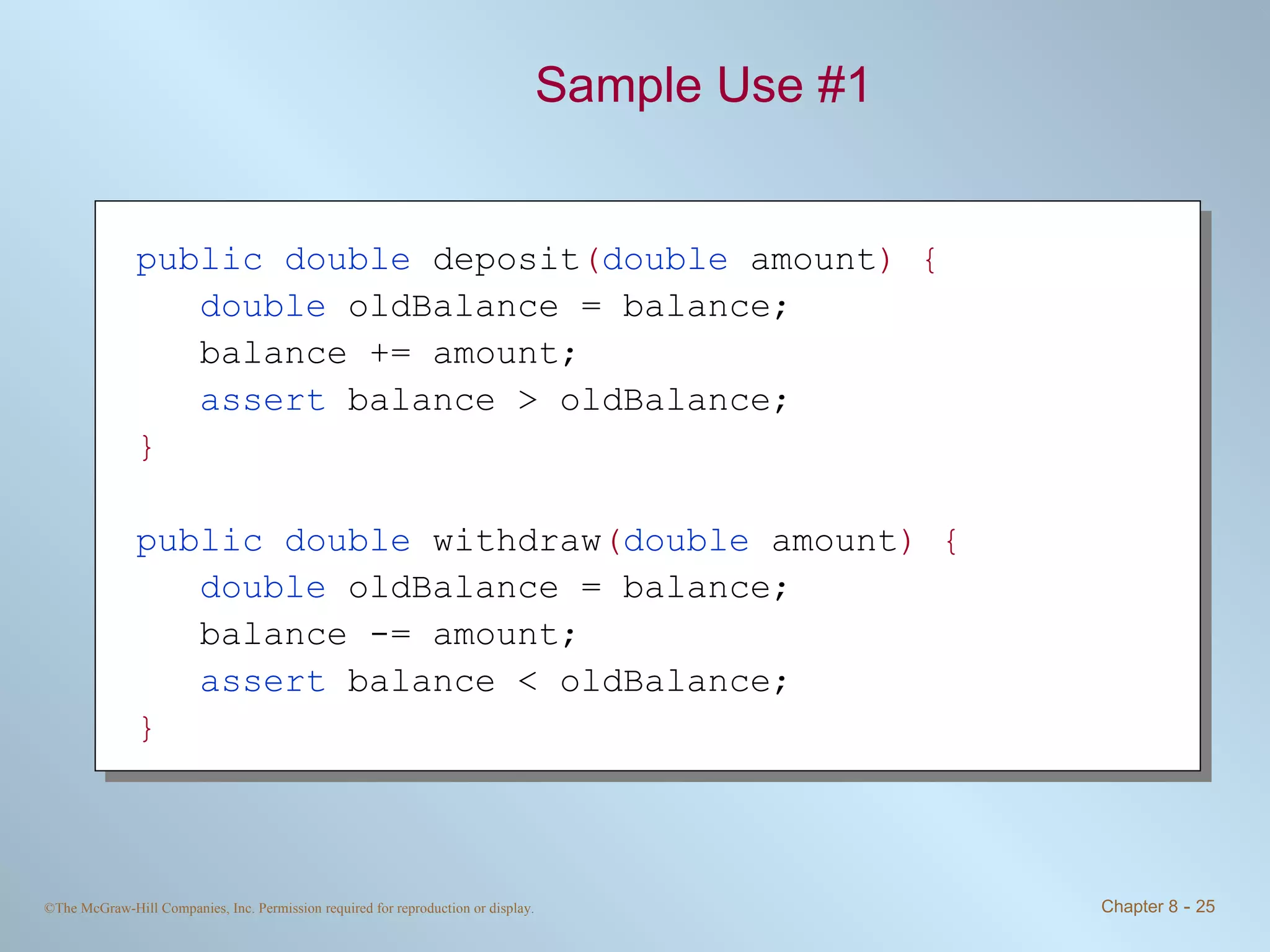
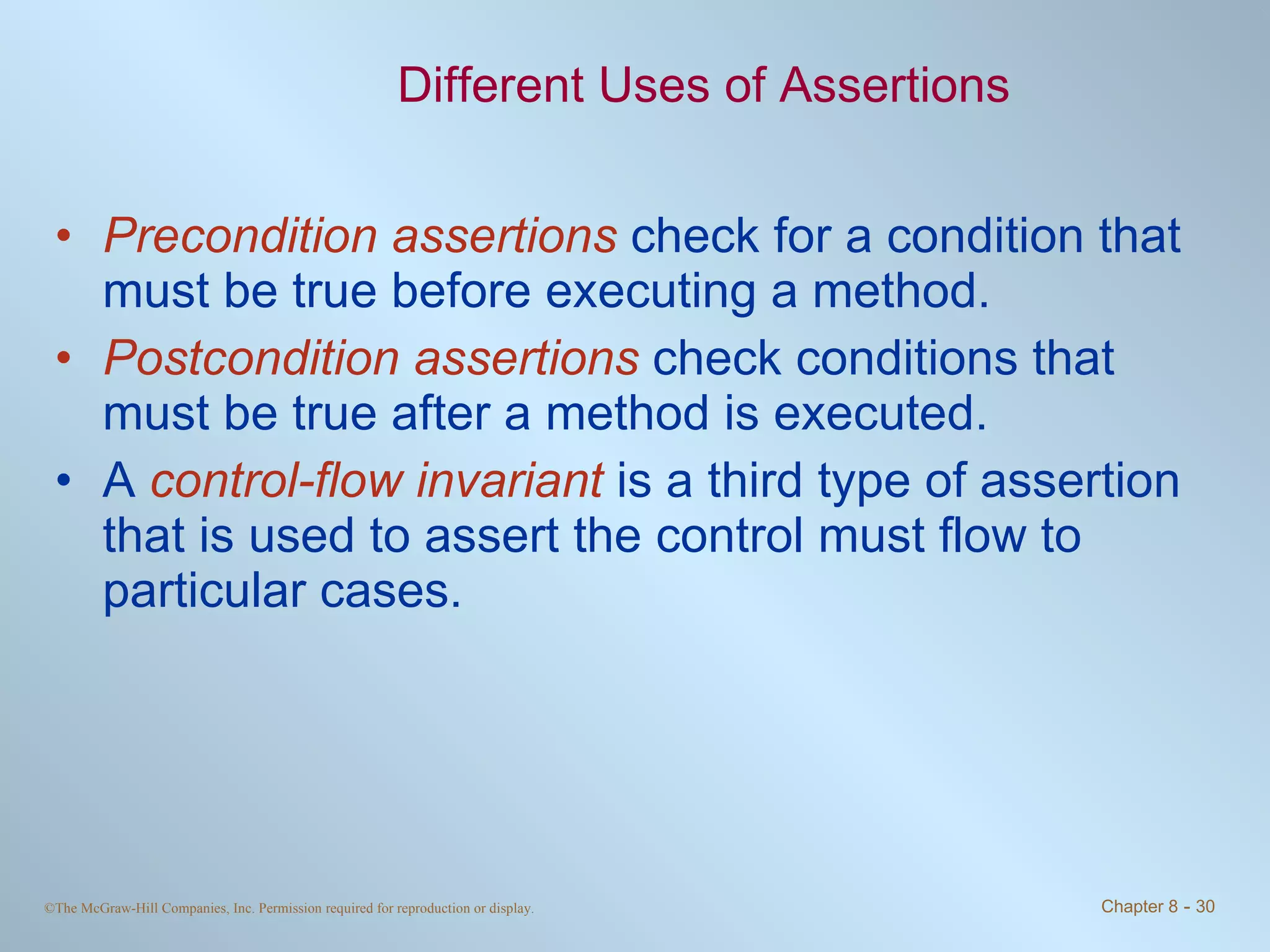
3. Assertions allow checking for expected conditions and throwing errors if conditions are not met. Assertions are enabled during compilation and execution.