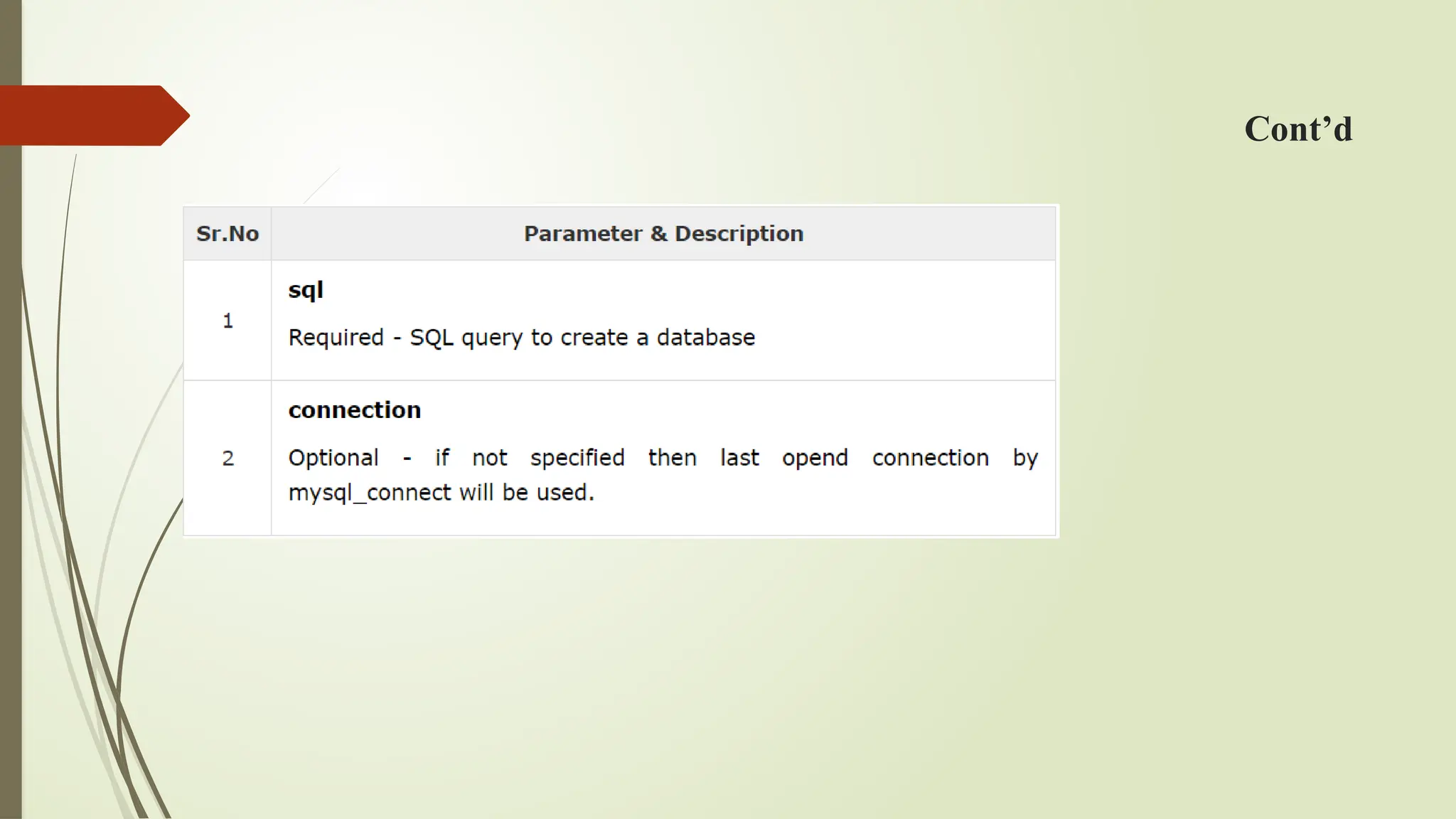
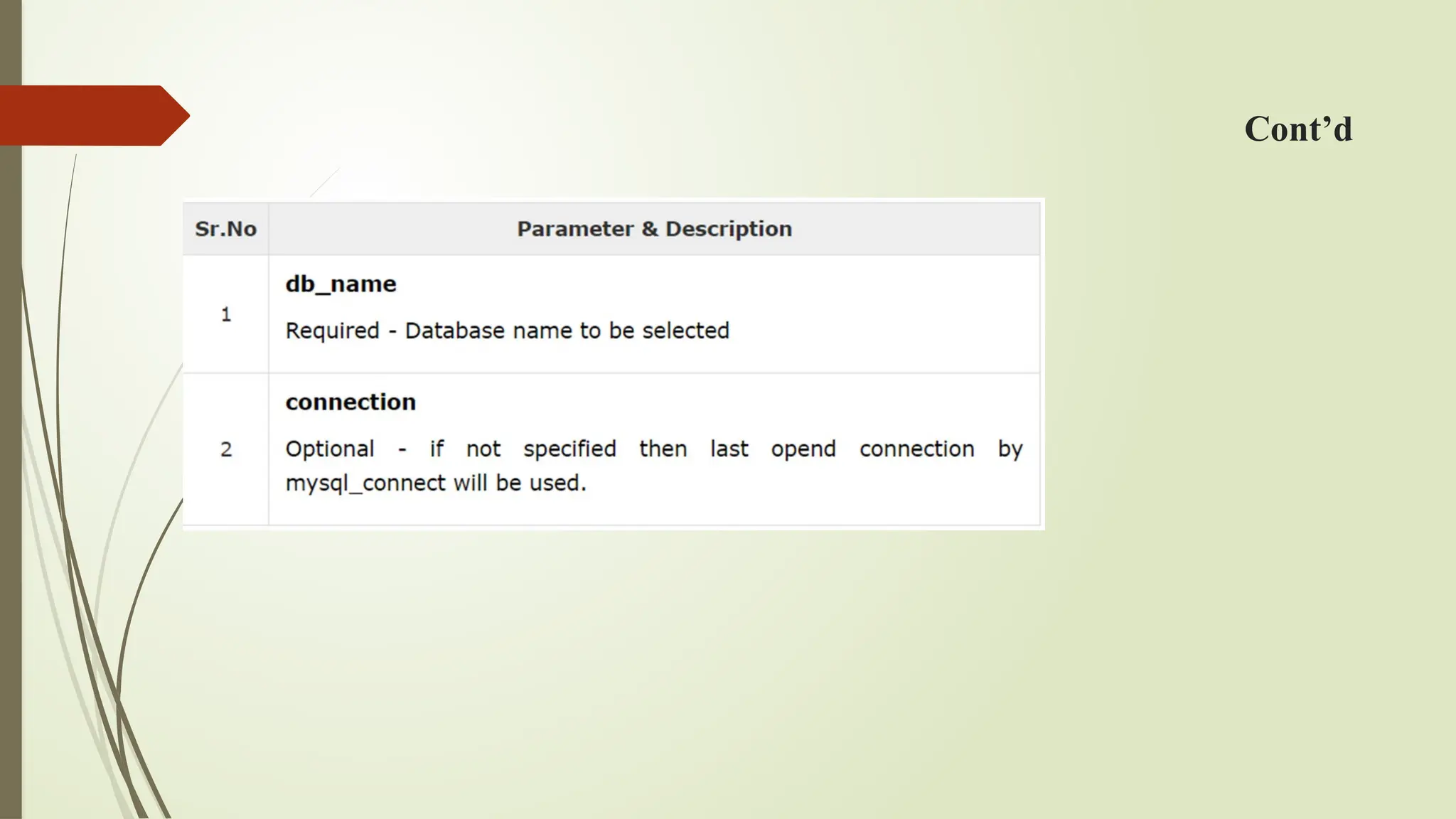
The document provides a guide on connecting to a MySQL database using PHP, detailing how to open, close, select, create, and delete databases and tables. It includes code examples for each operation, highlighting functions like mysql_connect(), mysql_close(), mysql_select_db(), and mysql_query(). Additionally, it emphasizes best practices for inserting data and managing database resources.