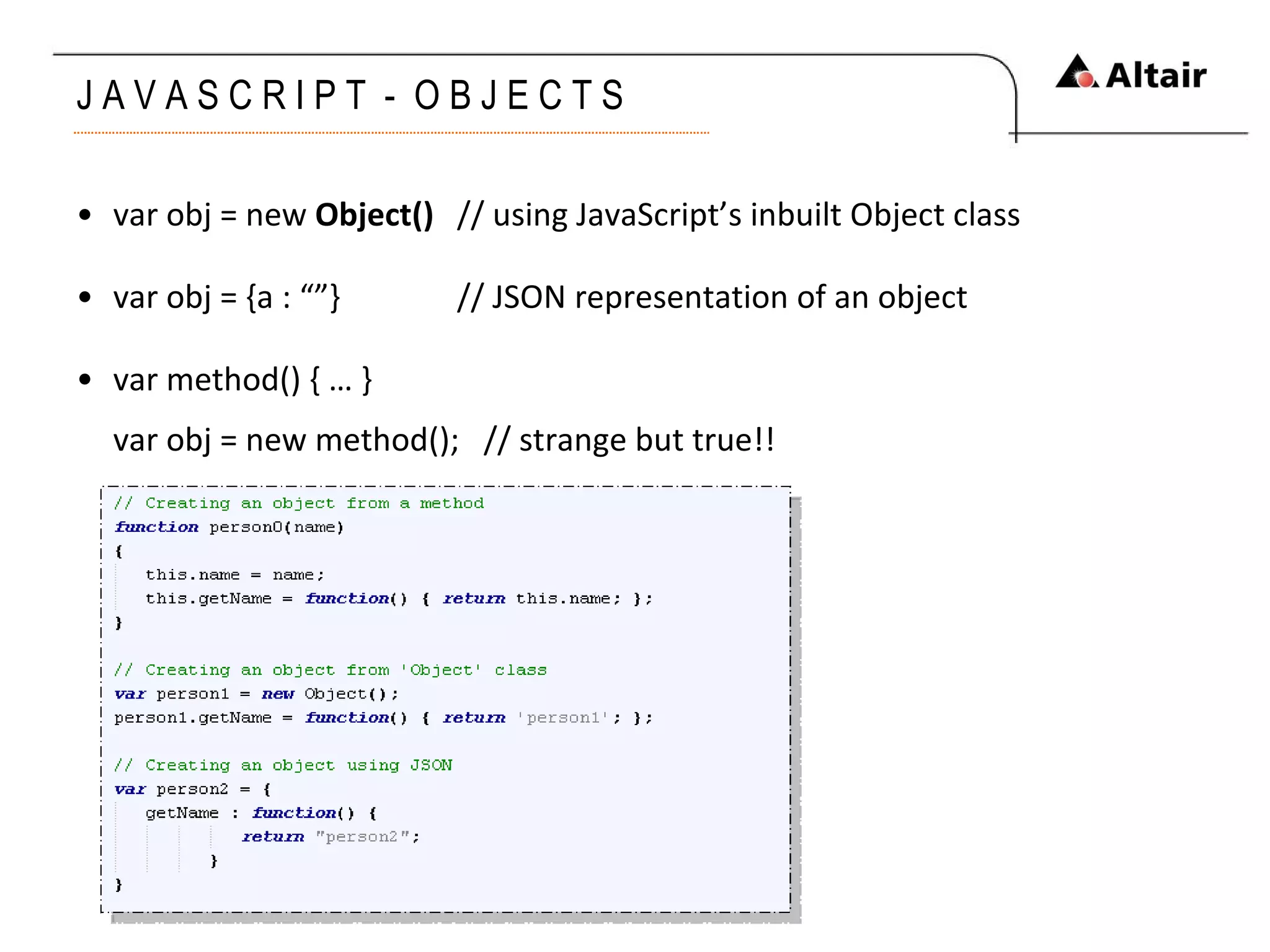
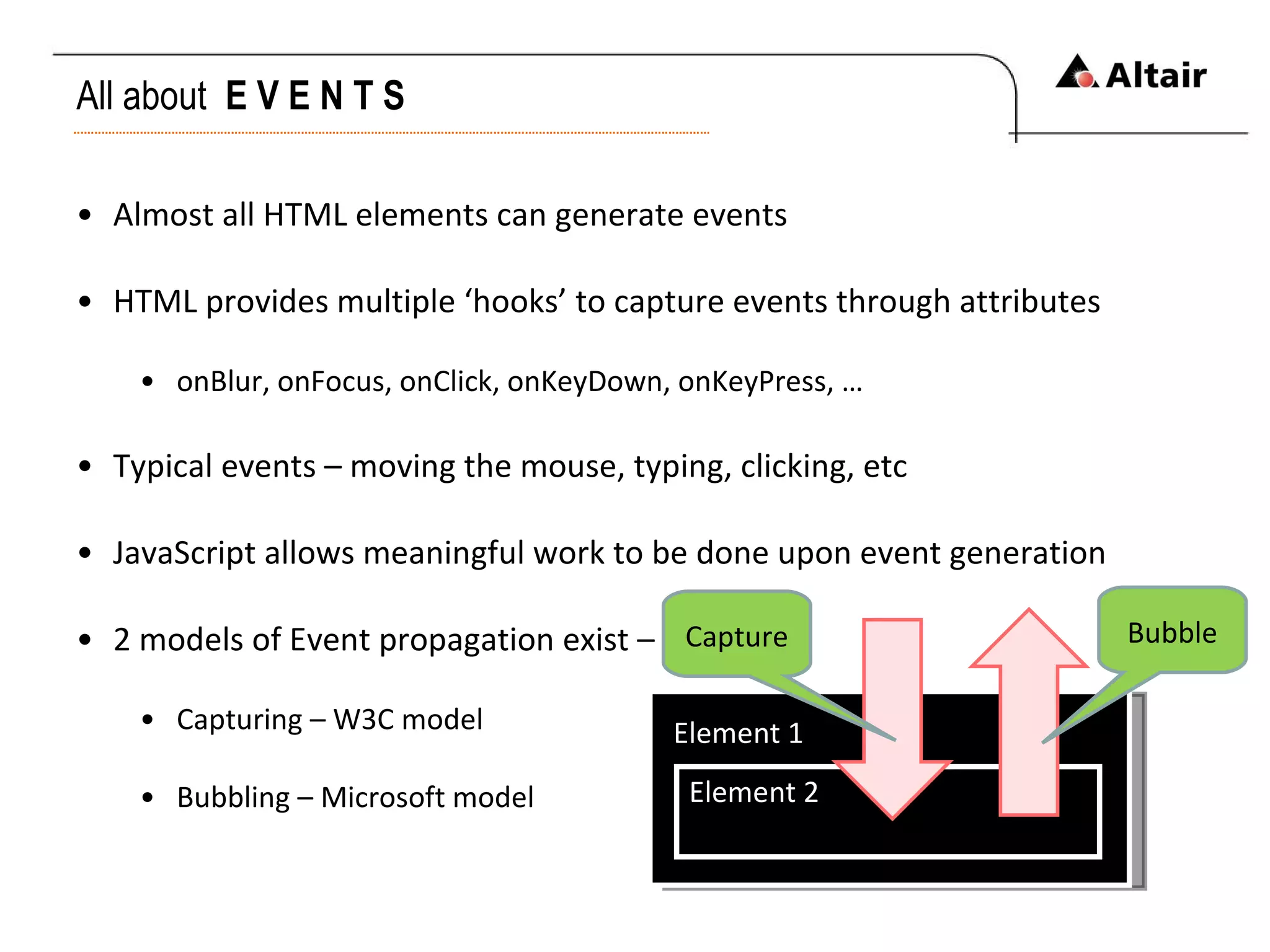
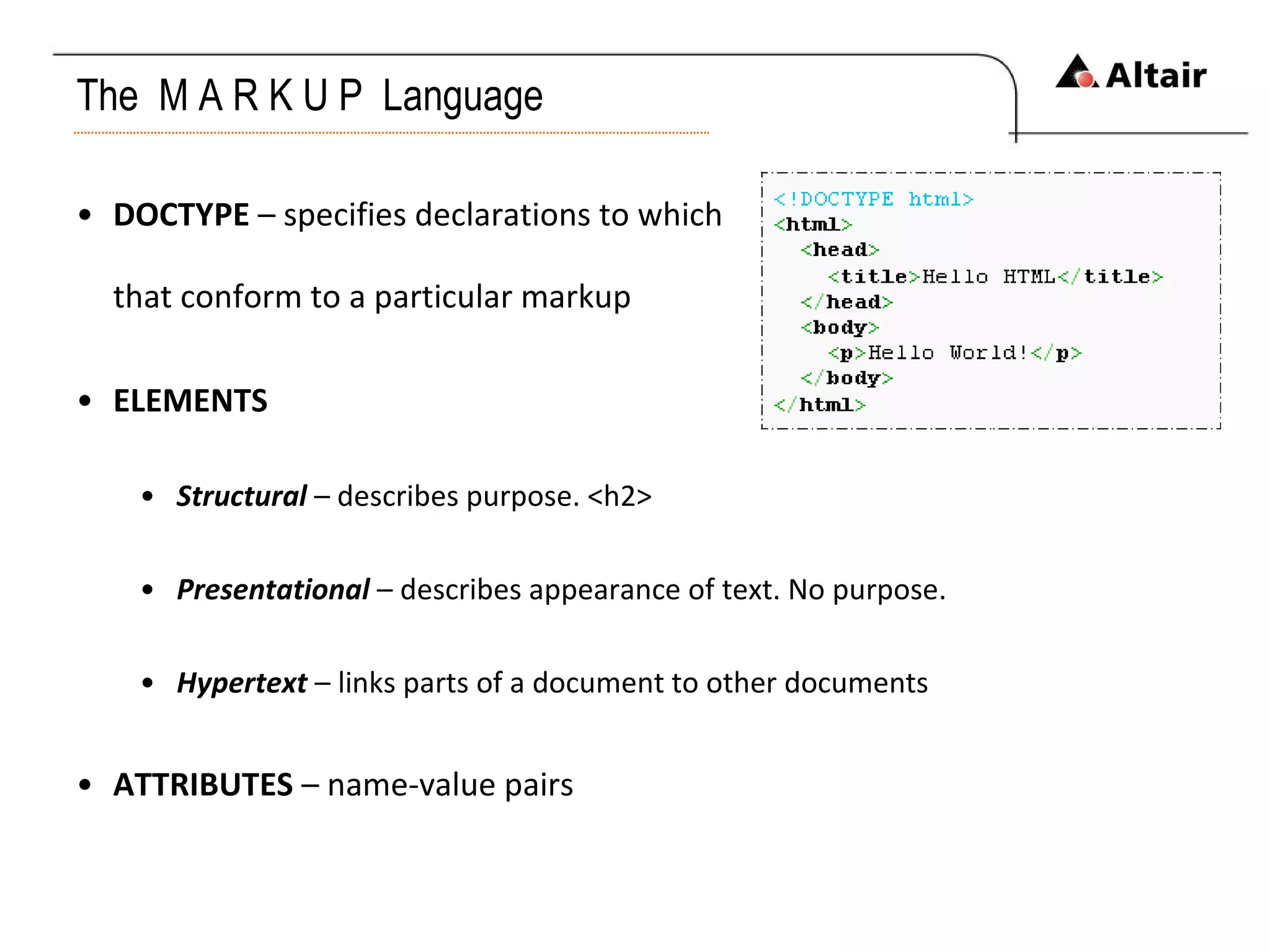
The document provides an overview of web technologies focusing on HTML, CSS, and JavaScript, detailing their evolution, syntax, and functionality. It discusses the historical development of HTML versions, the importance of CSS for styling web pages, and the features and capabilities of JavaScript for dynamic web content. Additionally, it emphasizes the challenges of XHTML adoption and the significance of event-driven programming in modern web development.









![Defining S T Y L E S H E E T S CSS syntax – selector { property : value; } body { color : black; } Class selector – defines different stylesheets for same HTML element [can be different too!] p.right { text-align: right; } .left { text-align: left; } Id selector – style applies to elements with particular ‘id’ attribute value #someStyle { color: red; } - applies to all elements with id = “someStyle” Inline – style properties specified within tag < div style=“border: 1px solid;”>](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webtechday01altair-090817071223-phpapp01/75/Client-Side-Technologies-11-2048.jpg)


![J A V A S C R I P T - Accessing Page Elements window > document > form > … getElementById() – allows you to access any particular element/node using ‘id’ Supported only by the document object getElementByTagName(‘name’) Node based methods and properties like – childNodes, firstChild, lastChild, etc By retrieving the ‘form’ element – most commonly used way document.<formName> document.forms[n]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webtechday01altair-090817071223-phpapp01/75/Client-Side-Technologies-15-2048.jpg)
![J A V A S C R I P T - Variables, Arrays, Functions, Objects var variableName – declaring a variable var a = 23 // a is int a = ‘text’ // a is string var arr = new Array(“a”, “b”), or, [“a”, “b”] – declaring an array length, indexOf(), join(param), pop(), push(param,…), slice(start, end) function someMethod() – declaring a function Even var a = function() is valid Objects can be declared using Object, JSON or functions !](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/webtechday01altair-090817071223-phpapp01/75/Client-Side-Technologies-16-2048.jpg)