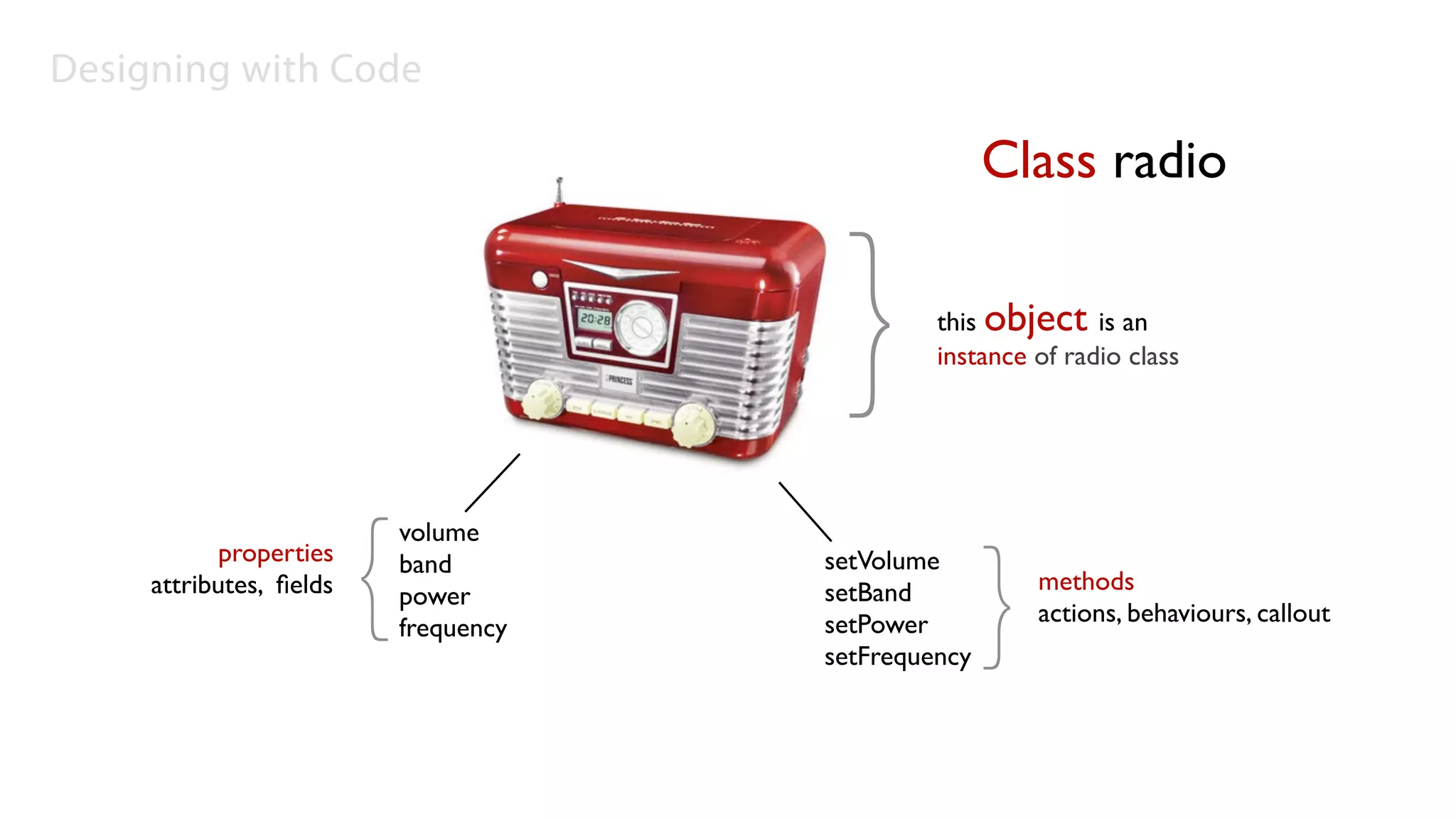
This document provides an introduction to programming concepts useful for designing with code, including object oriented programming, frameworks, syntax, classes, objects, functions, variables, and arrays. It explains that arrays allow the creation of multiple variables without defining a new name for each, making the code shorter and easier to read and update. Arrays can store different data types like images or numbers.





![Designing with Code
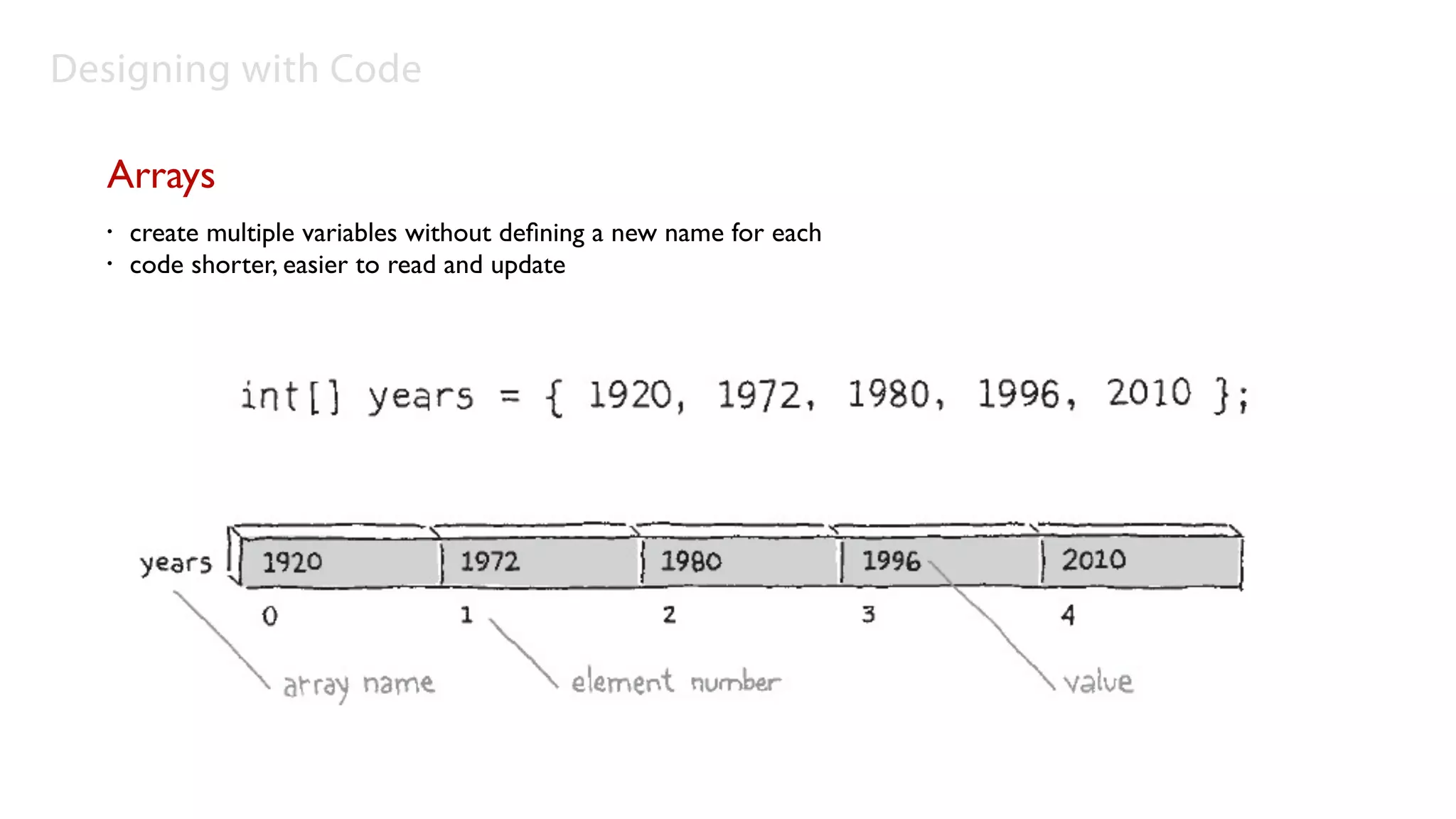
Arrays
• To make an array, just place brackets after the data type: int[] x;
• The beauty of creating an array is the ability to make 2, 10, or
100,000 variable values with only one line of code. For instance, the
following line creates an array of 2,000 integer variables:
int[] x = new int[2000];
• Arrays can also be made of other data types like images:
PImage[] images = new PImage[32];](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/code1-101021091815-phpapp02/75/Coding-for-8-2048.jpg)

![Designing with Code Let the array store
the variables
Arrays
float[] x = new float[3000];
• this examples shows 3000 variables in an array void setup() {
• using repetition loop to work with large arrays keeps the code concise size(240, 120);
• need to know the length of the array smooth();
noStroke();
fill(255, 200);
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
x[i] = random(-1000, 200);
}
}
void draw() {
background(0);
for (int i = 0; i < x.length; i++) {
x[i] += 0.5;
float y = i * 0.4;
arc(x[i], y, 12, 12, 0.52, 5.76);
}
}](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/code1-101021091815-phpapp02/75/Coding-for-10-2048.jpg)
