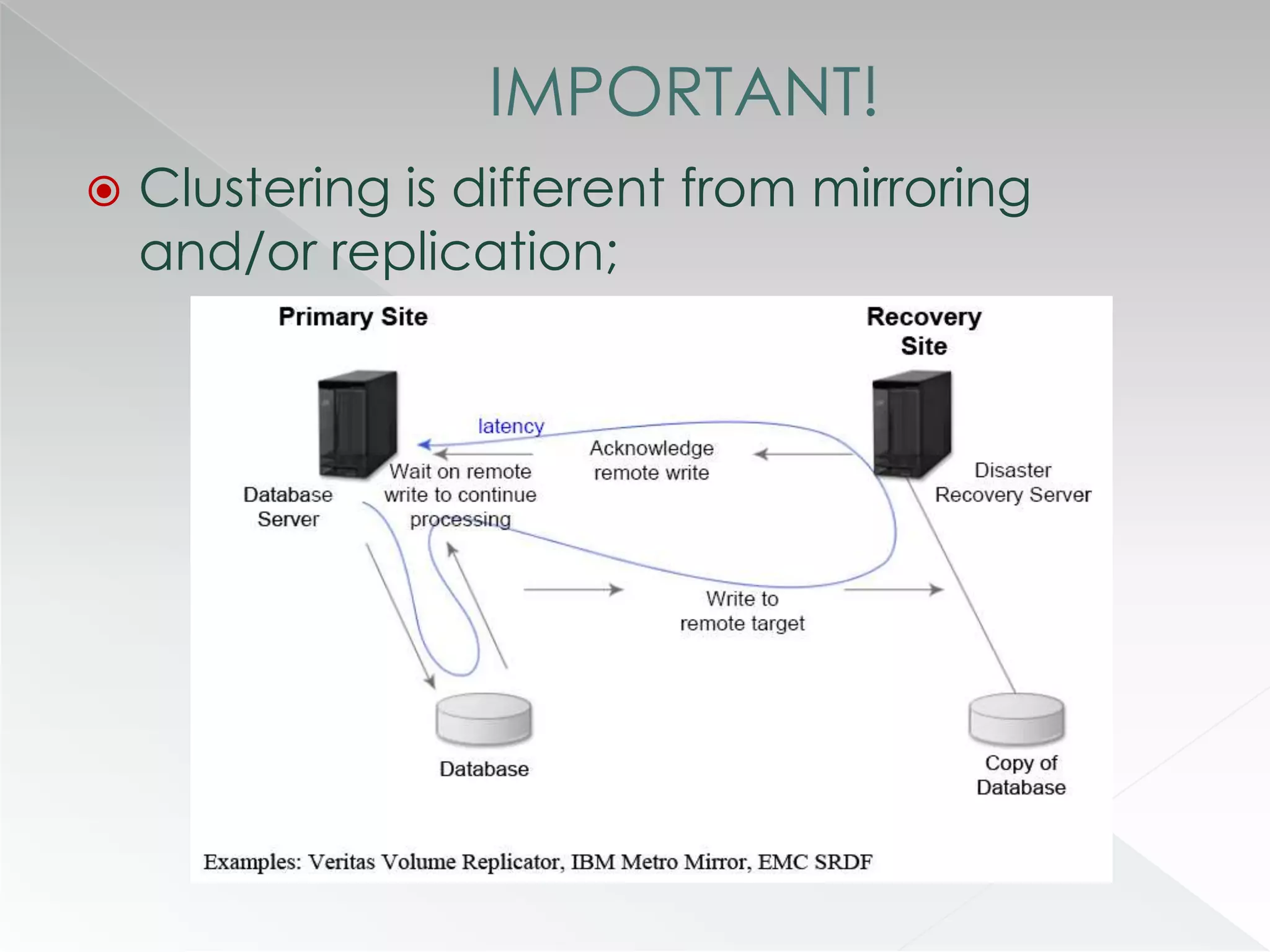
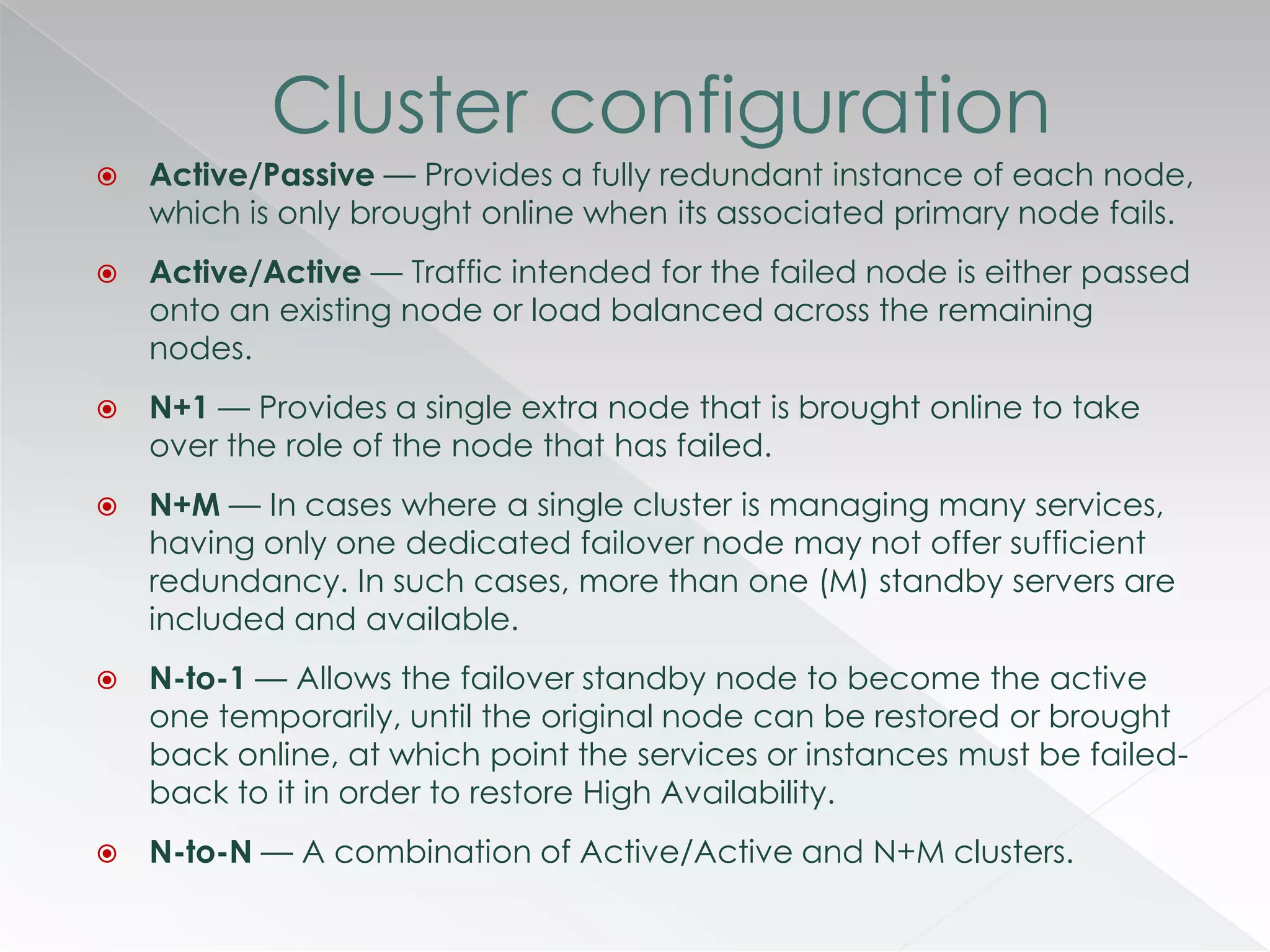
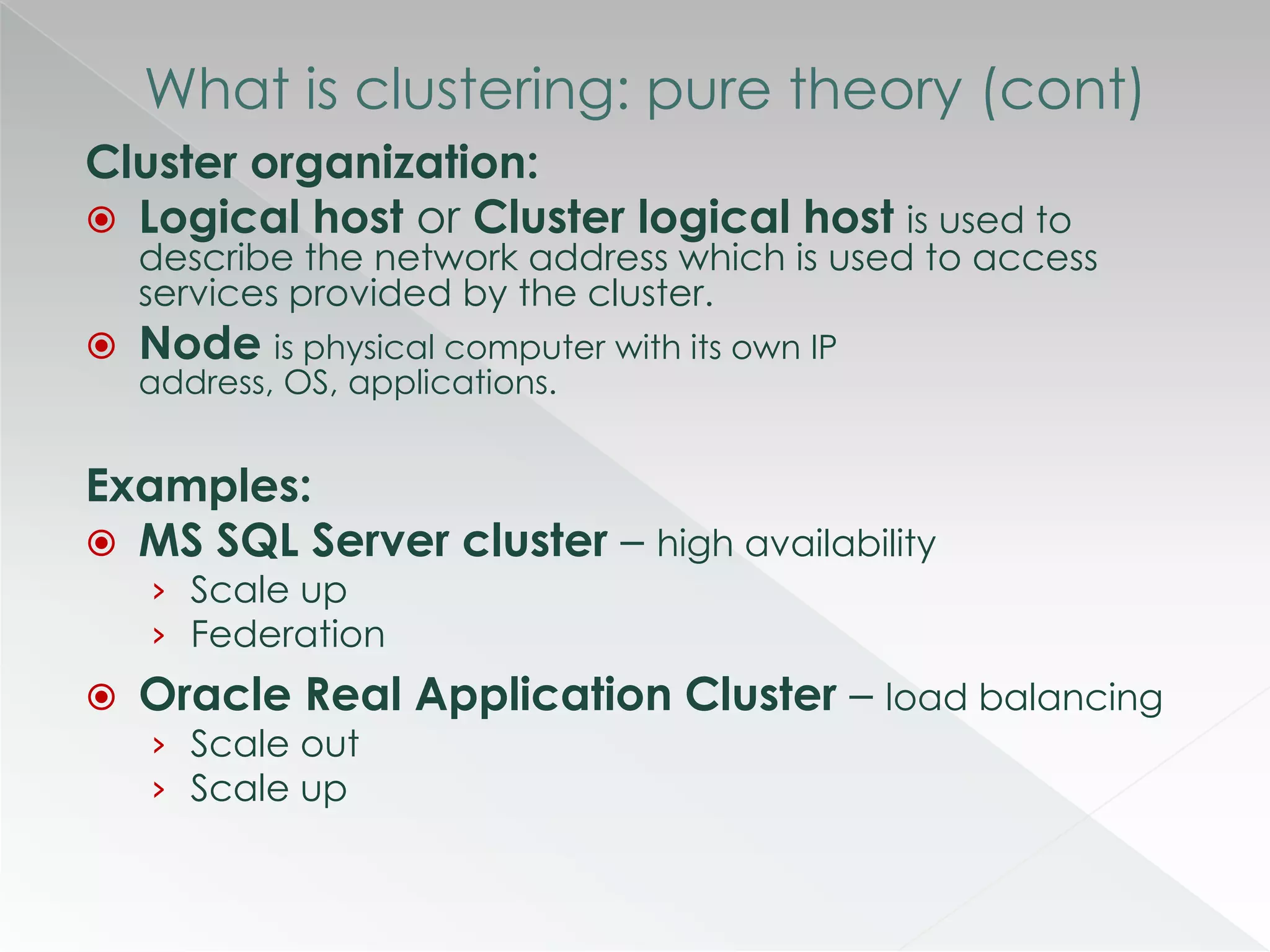
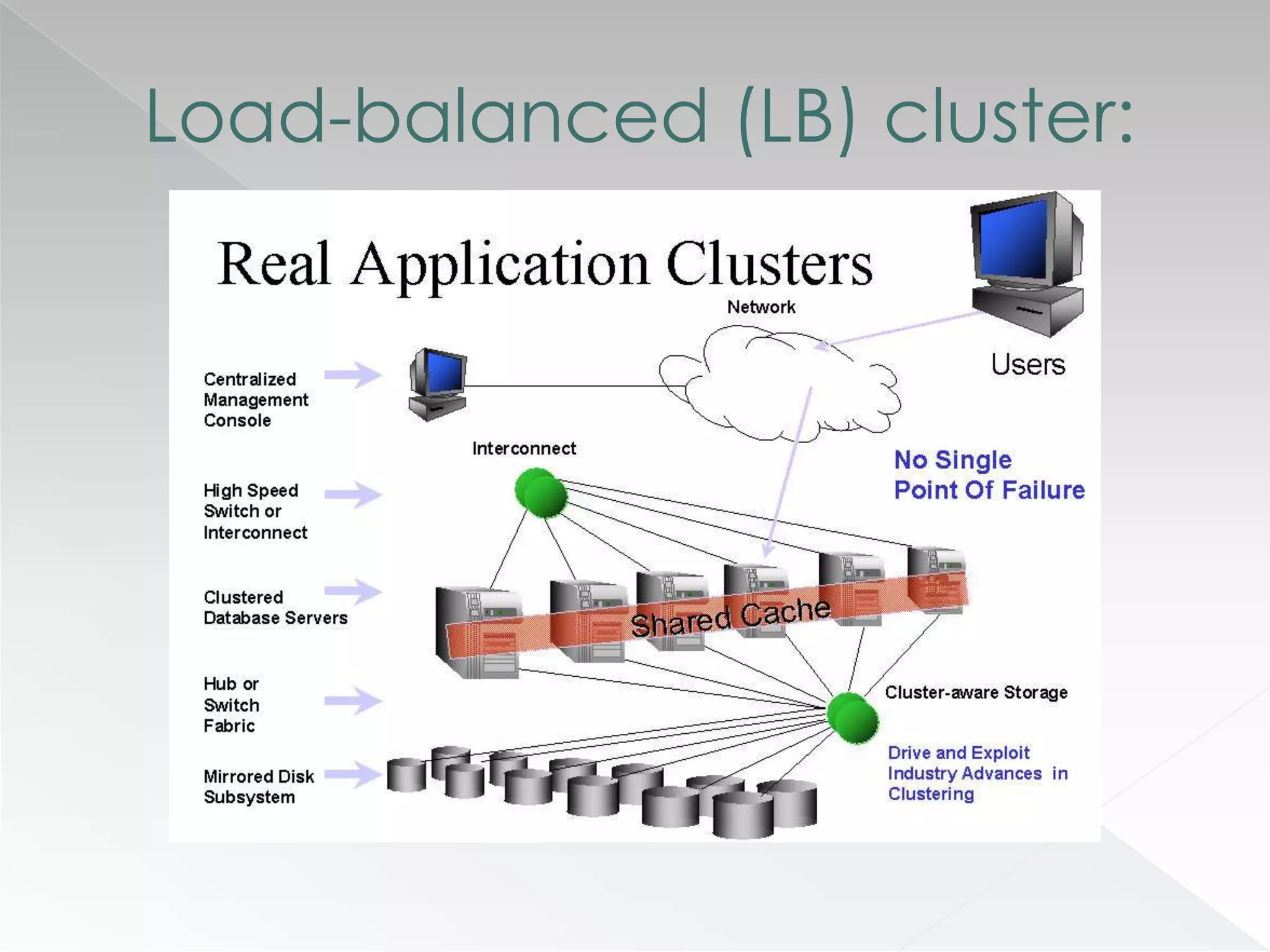
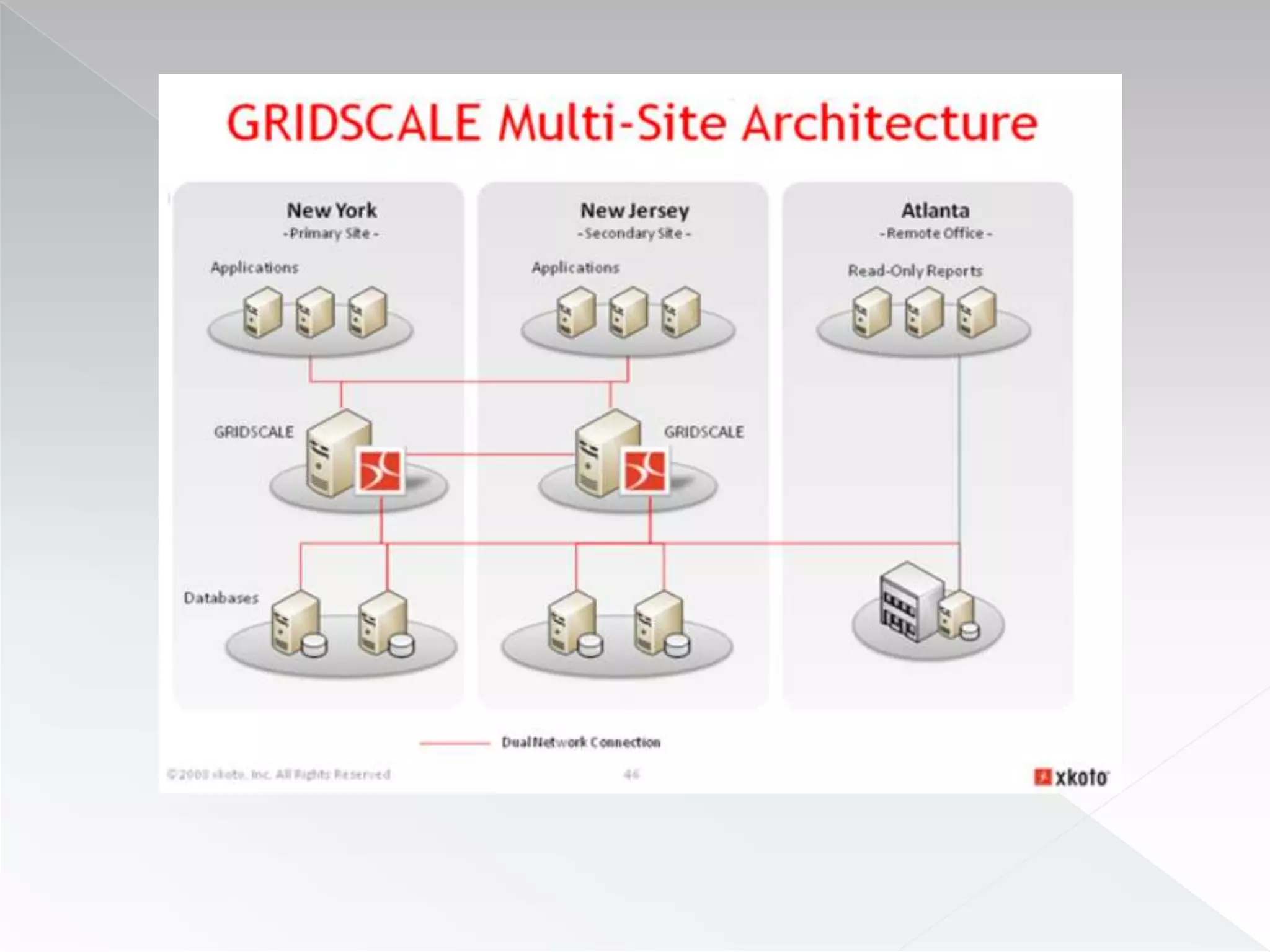
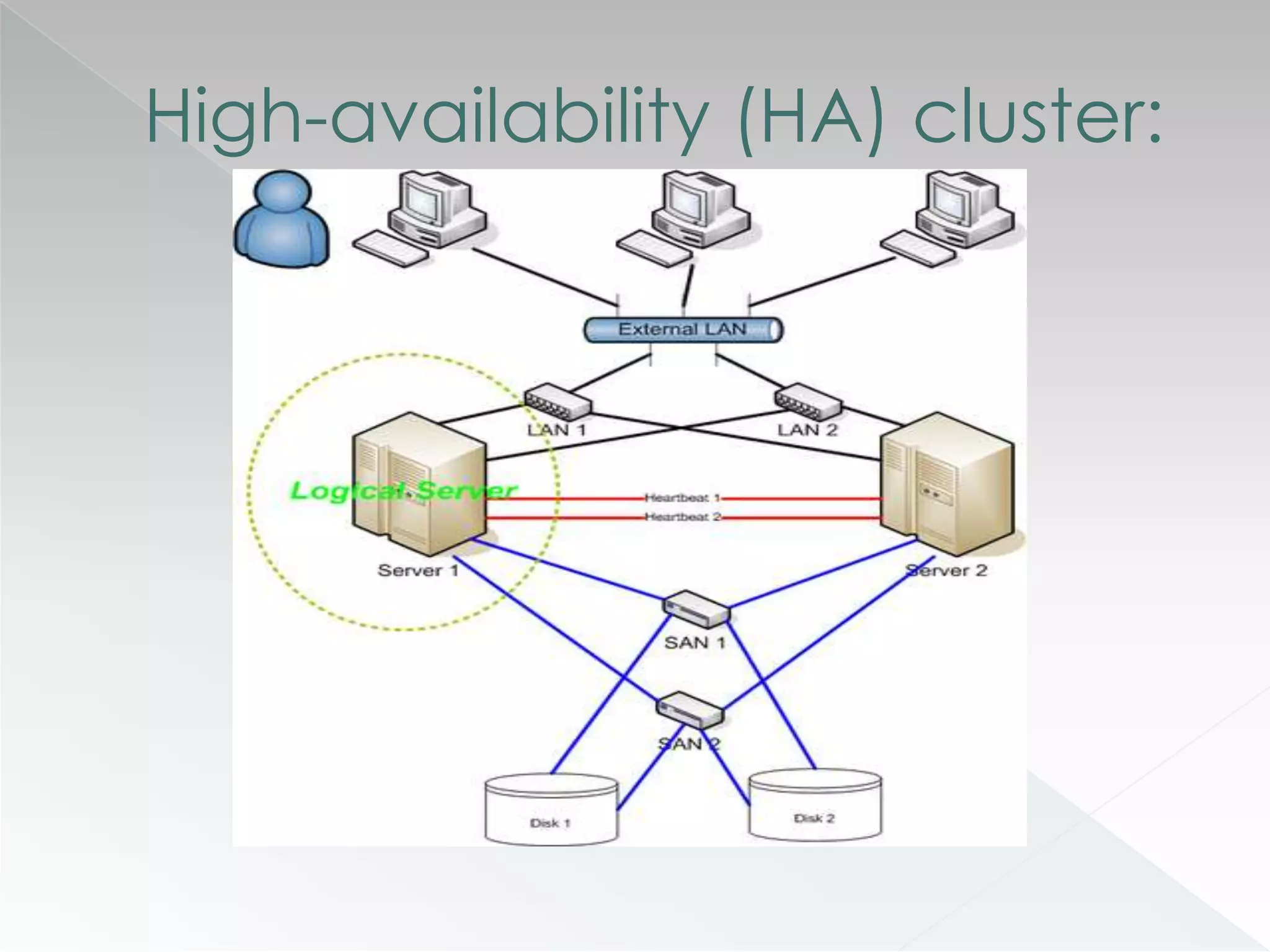
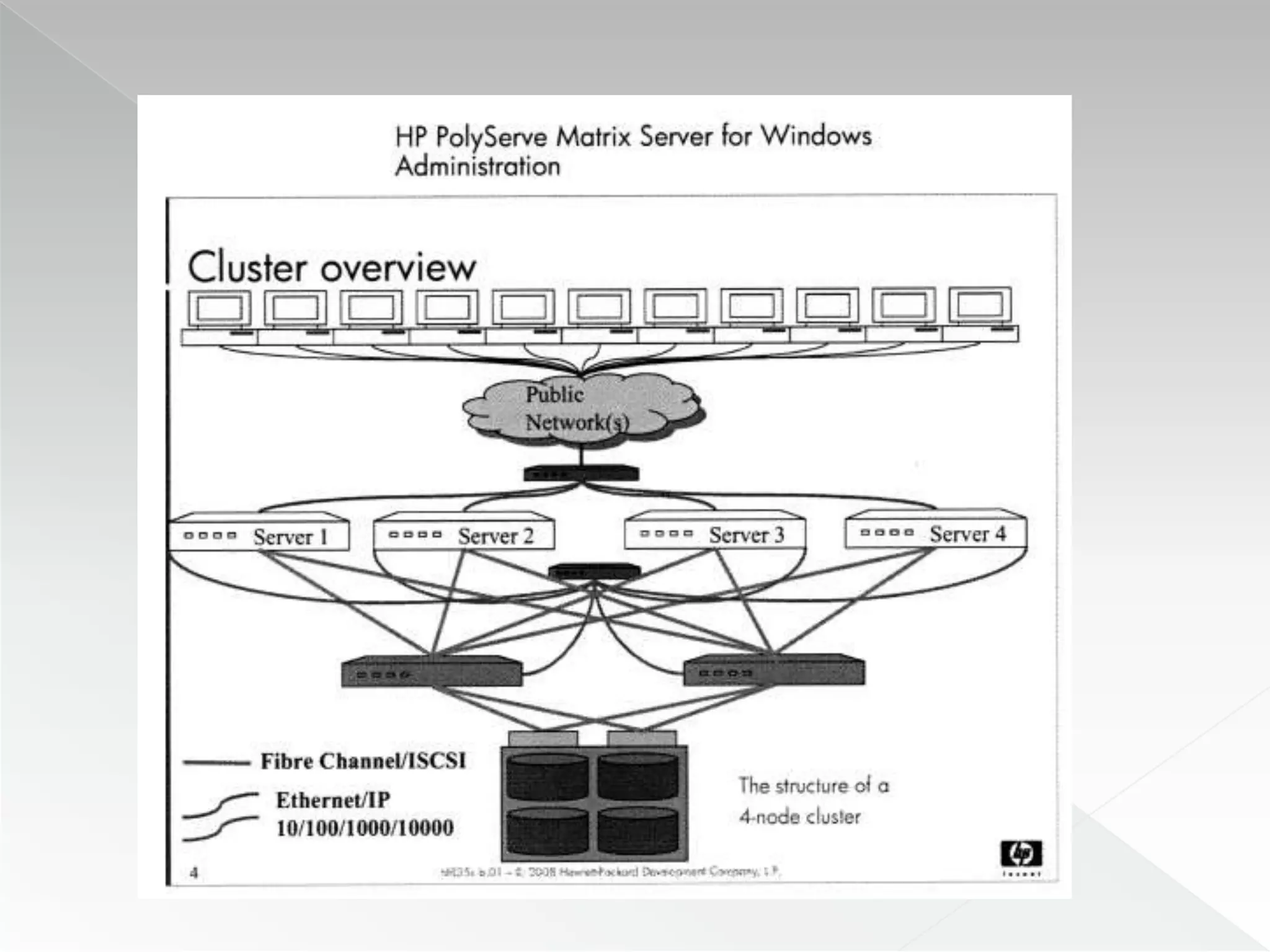
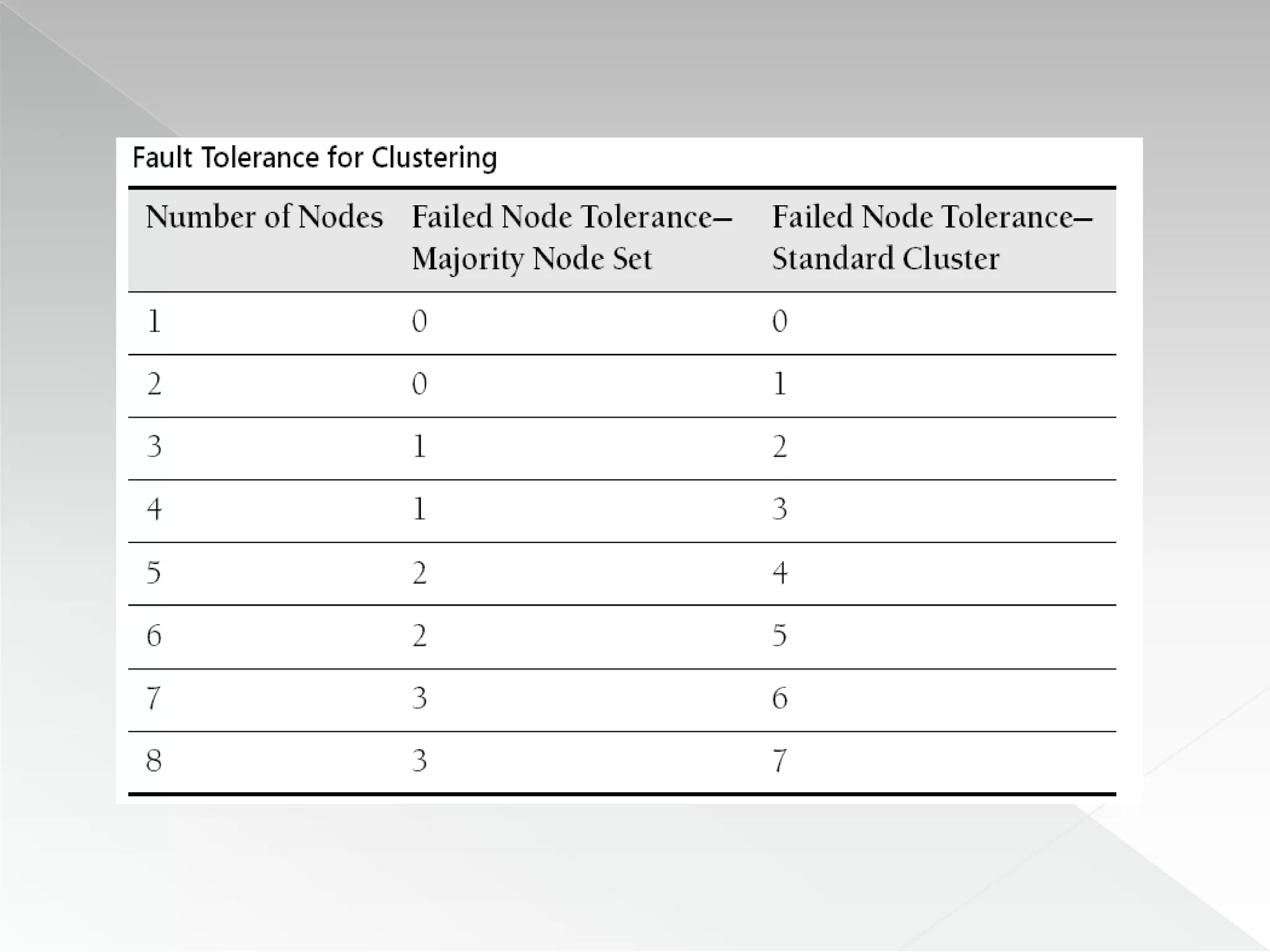
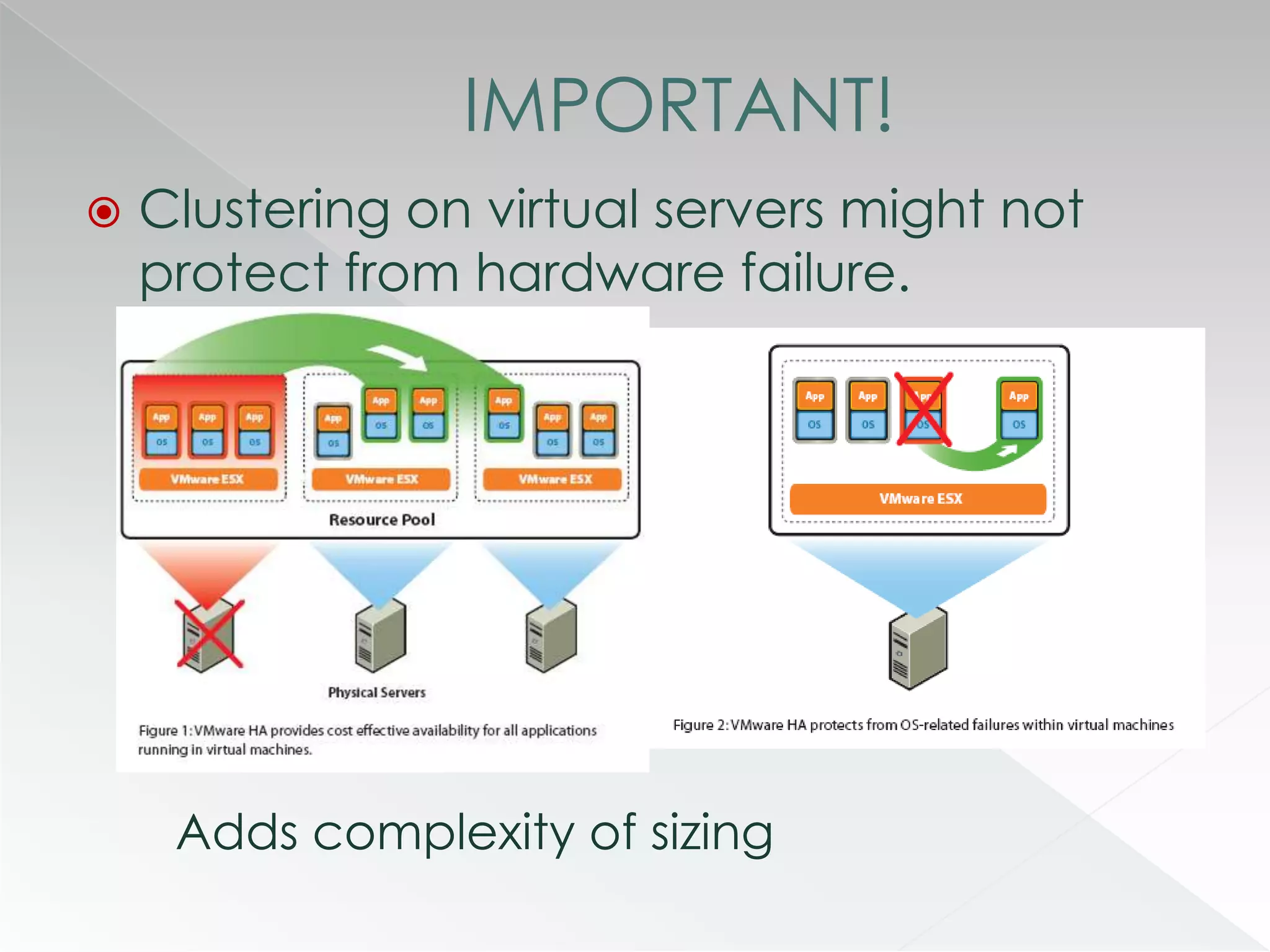
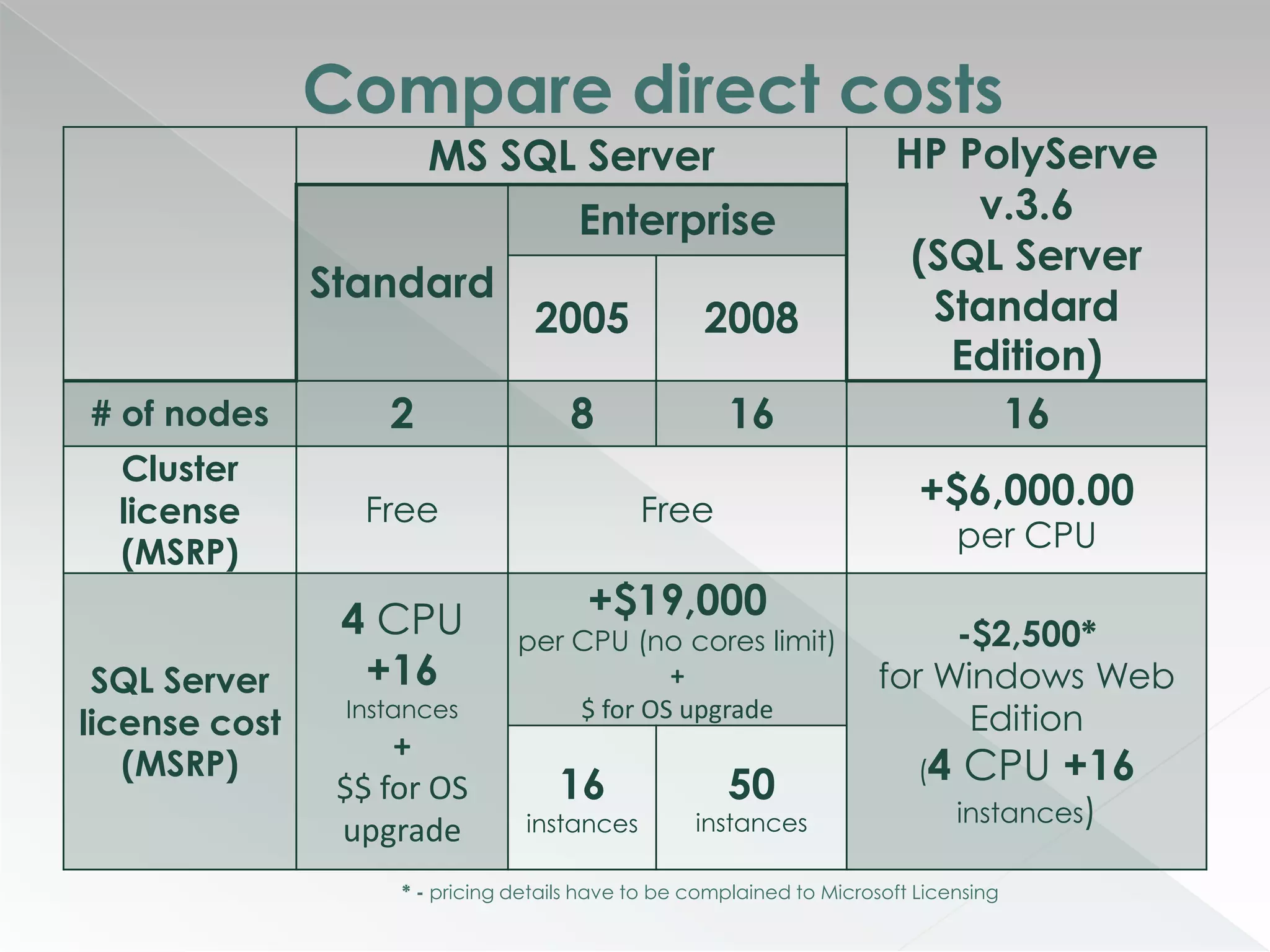
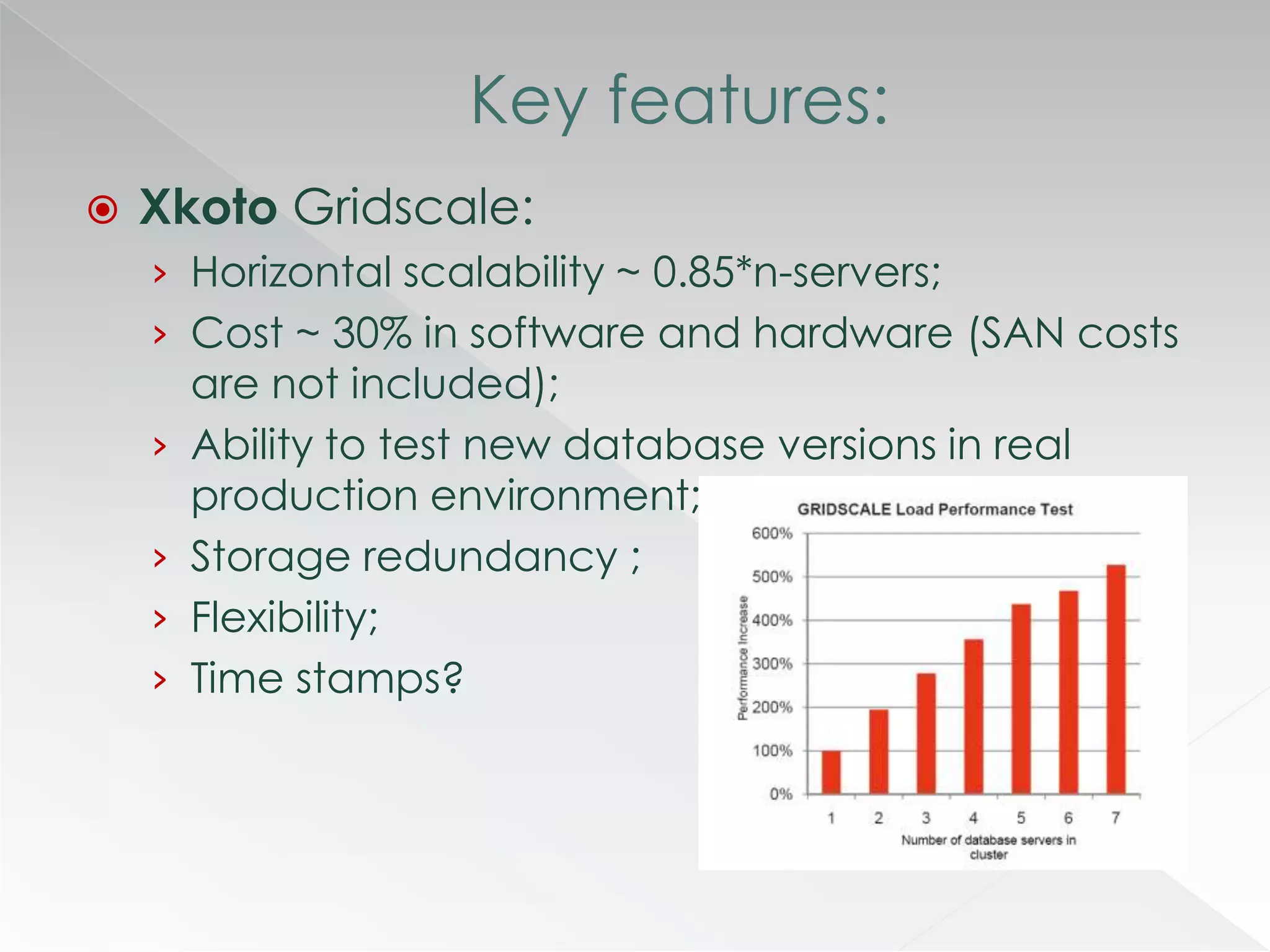
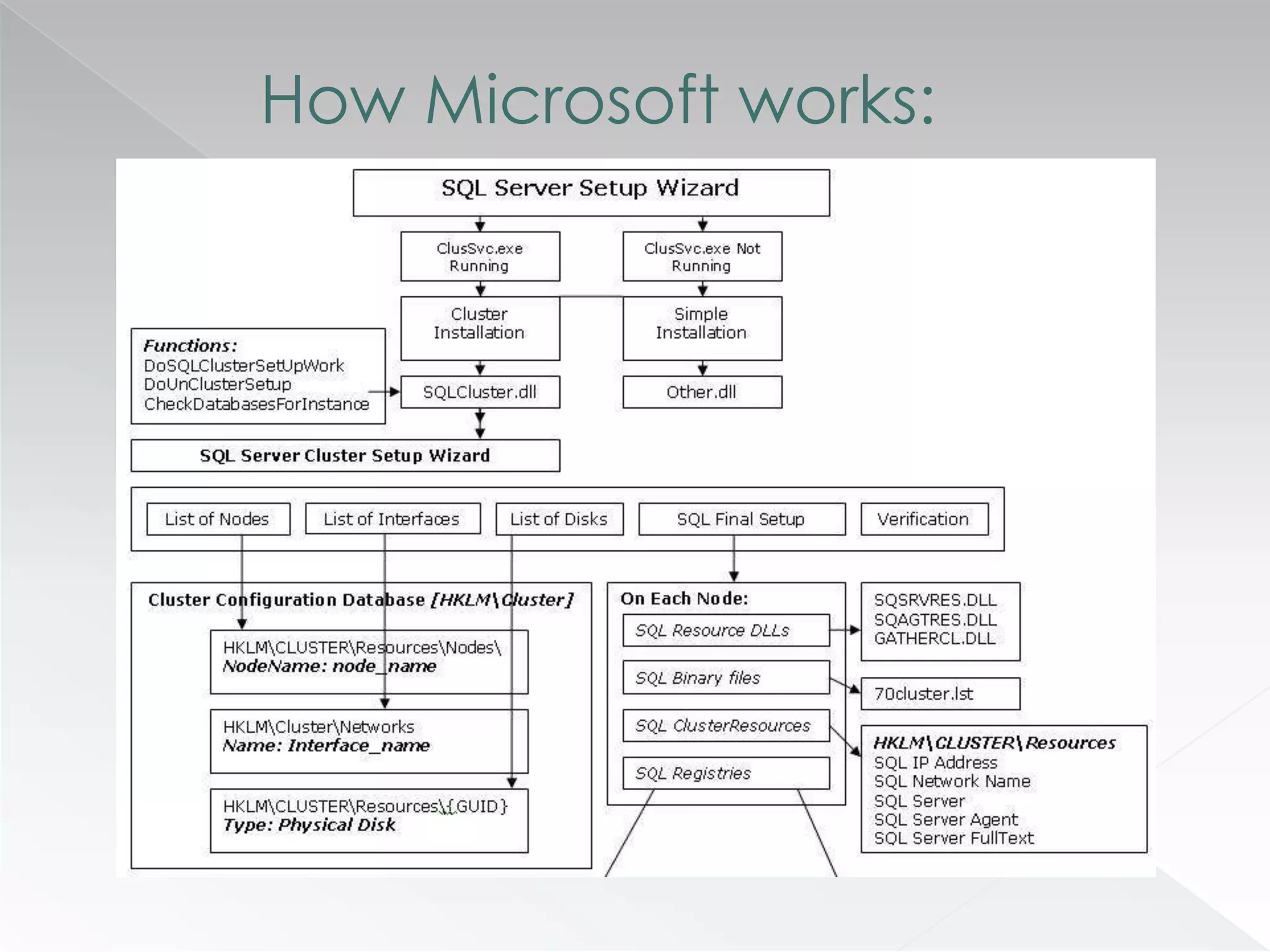
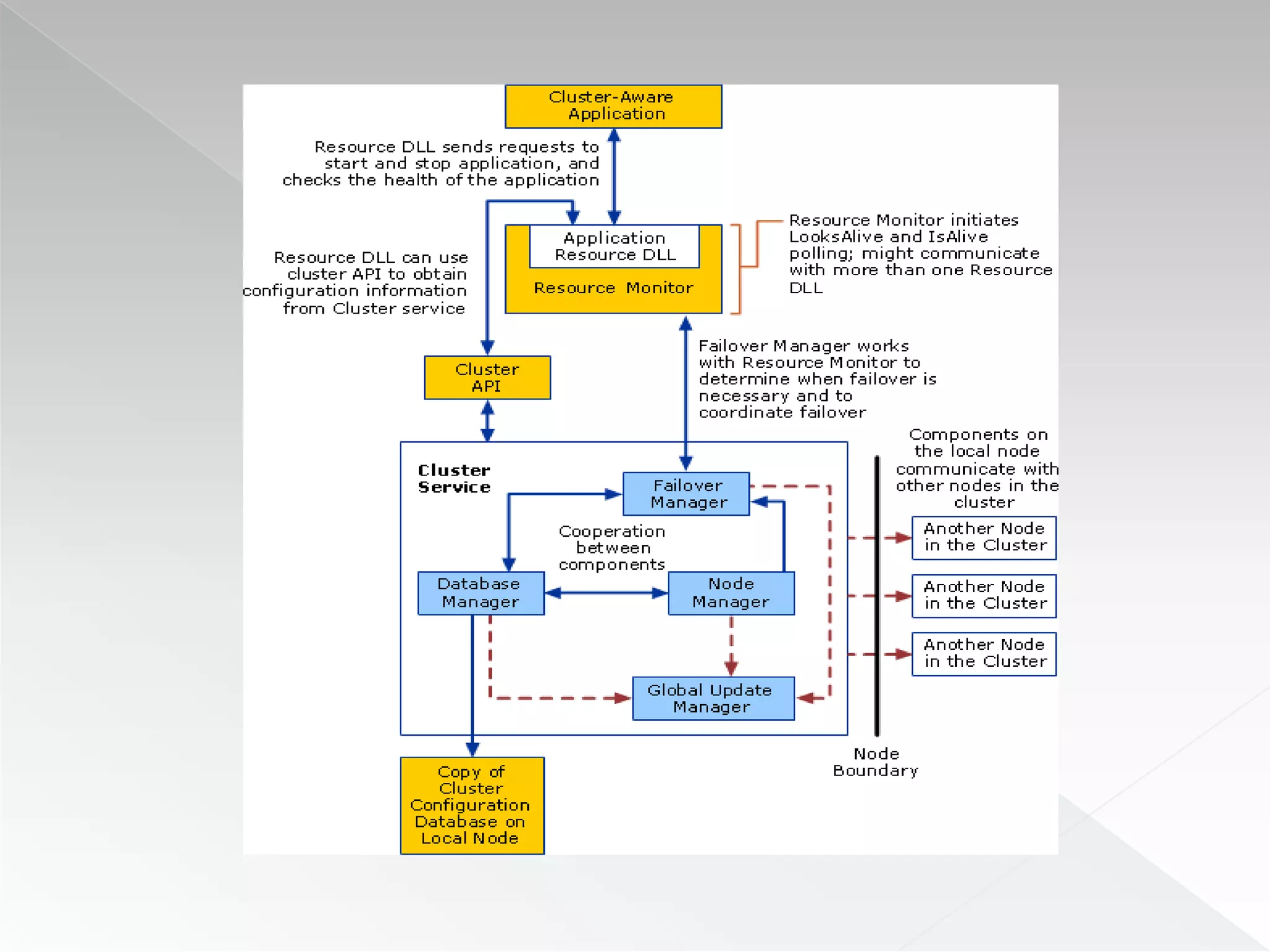
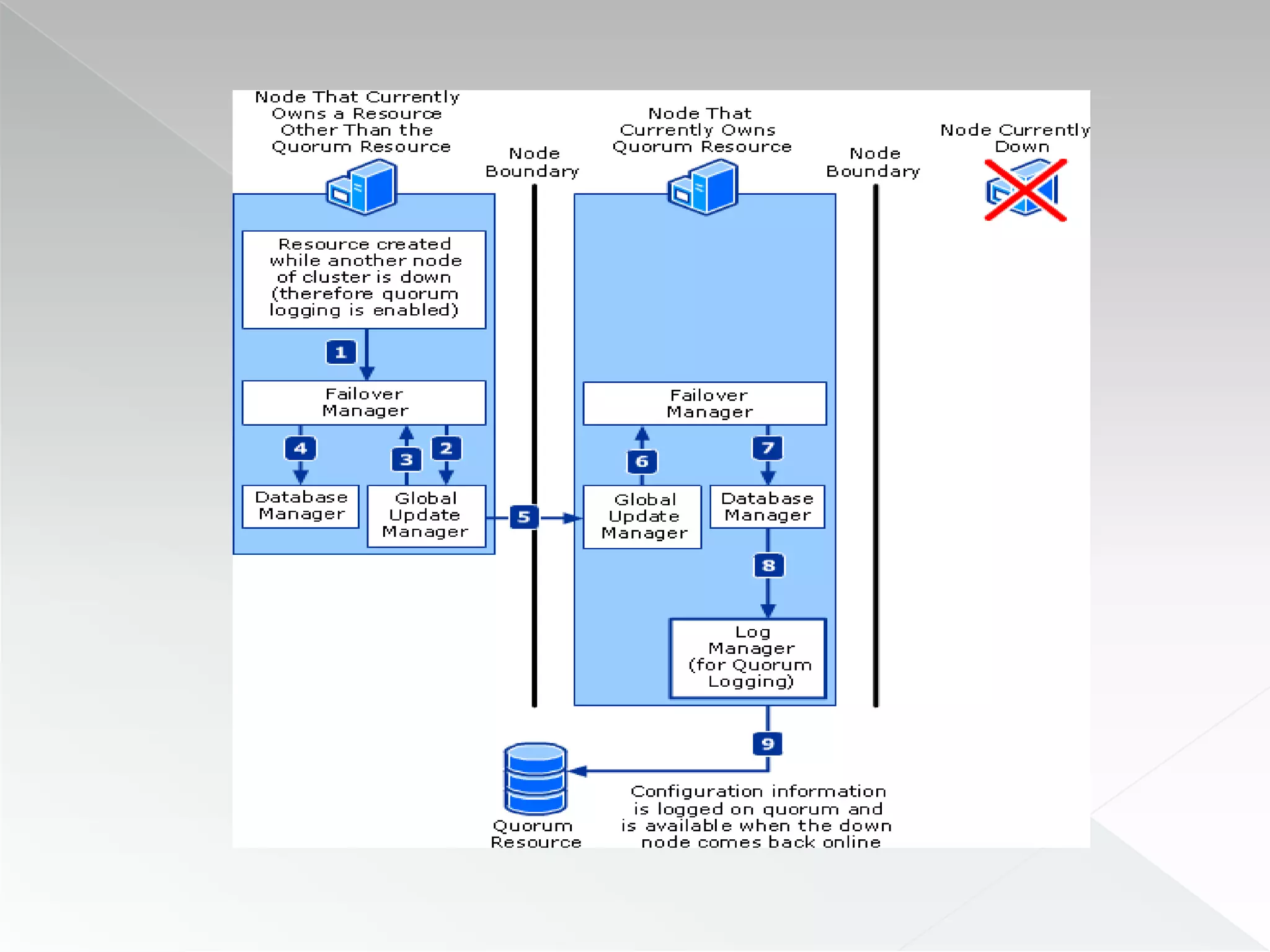
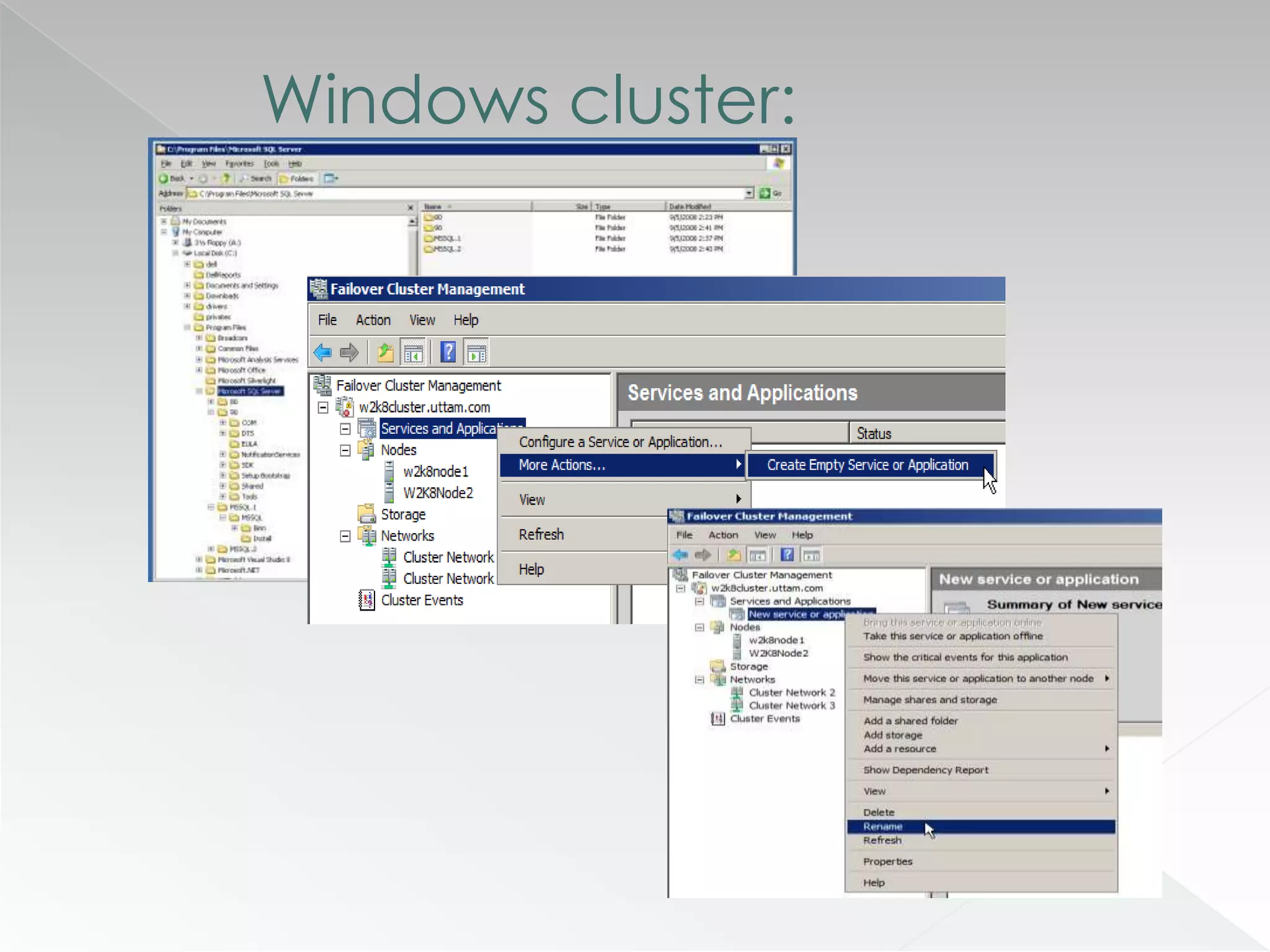
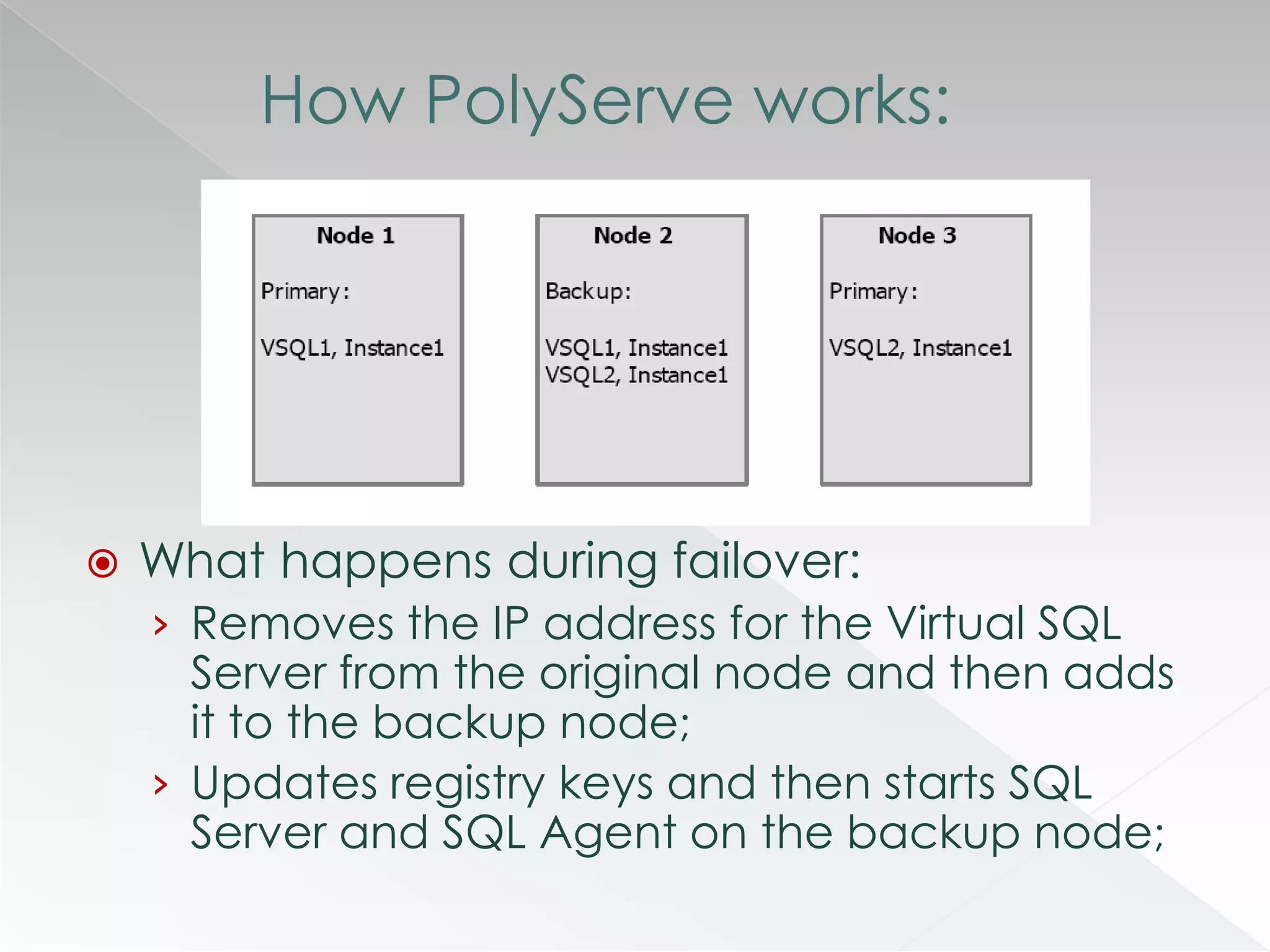
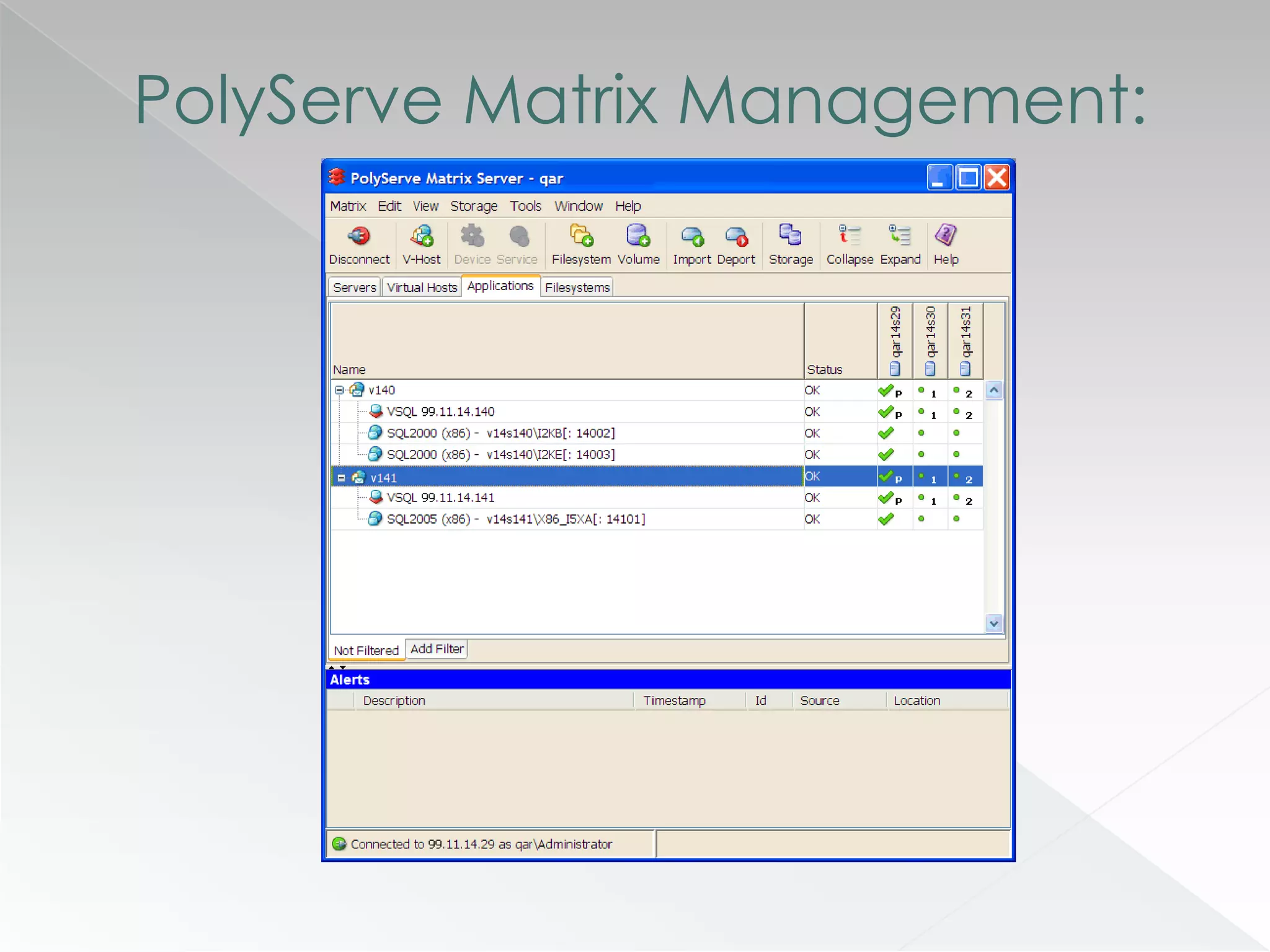
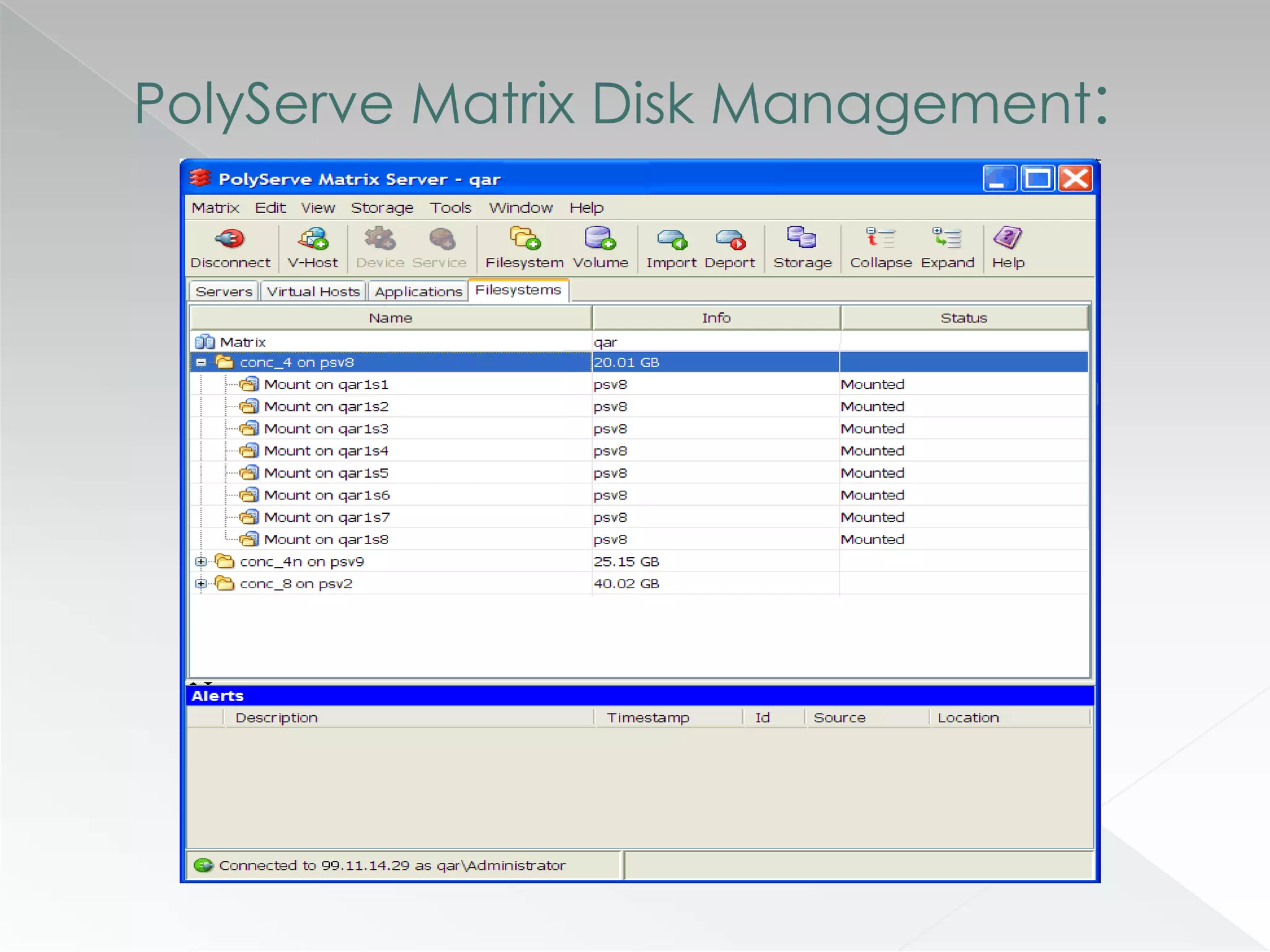
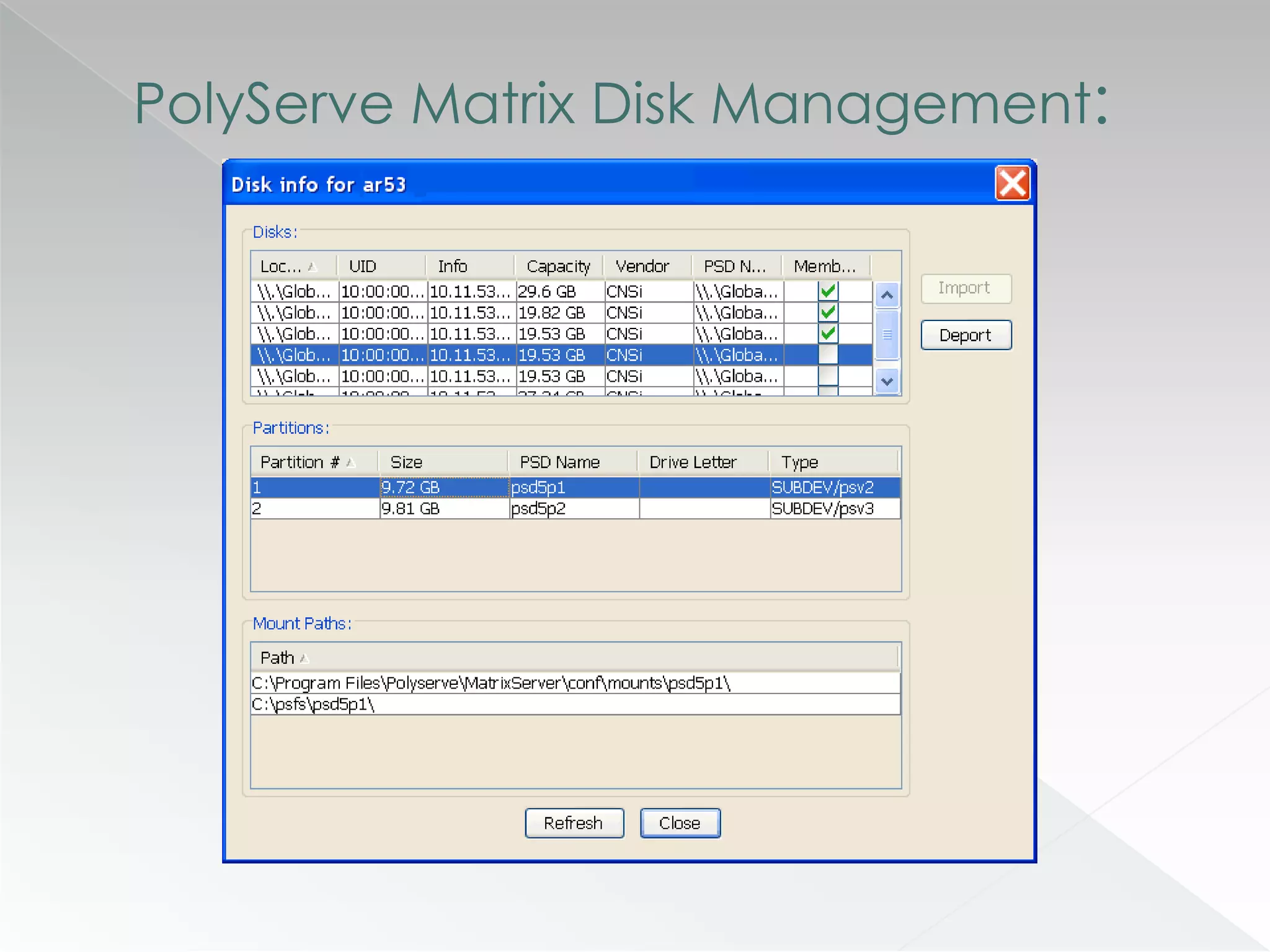
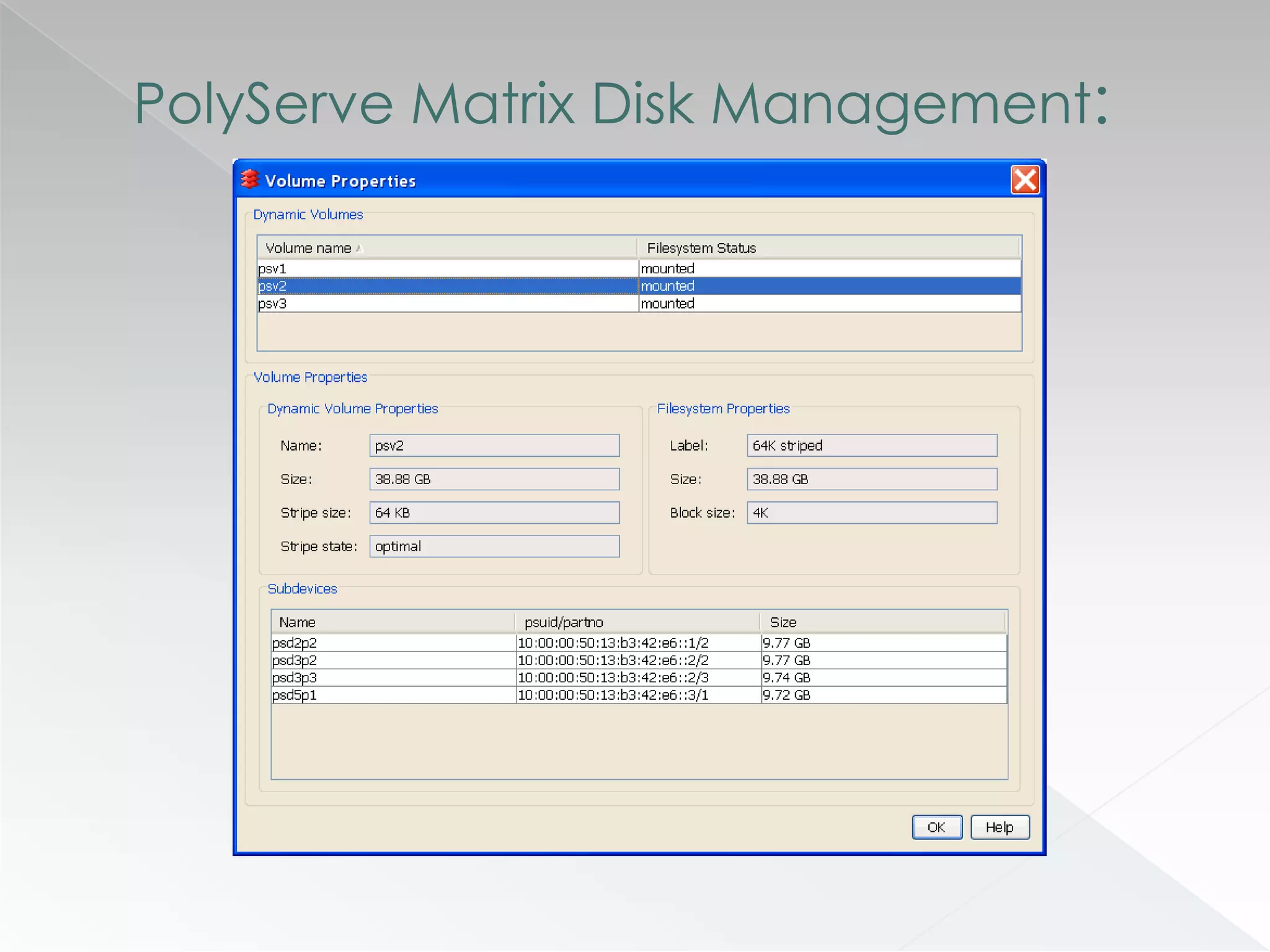
The document discusses various clustering technologies, particularly in relation to Microsoft SQL Server, focusing on their definitions, categorizations, and configurations aimed at improving database availability and performance. It highlights the differences between clustering, mirroring, and replication while outlining essential features of different clustering types, such as high-availability clusters and load-balancing clusters. Additionally, the document emphasizes the importance of hardware quality, cost-benefit analyses for implementation, and considerations when evaluating clustering solutions.