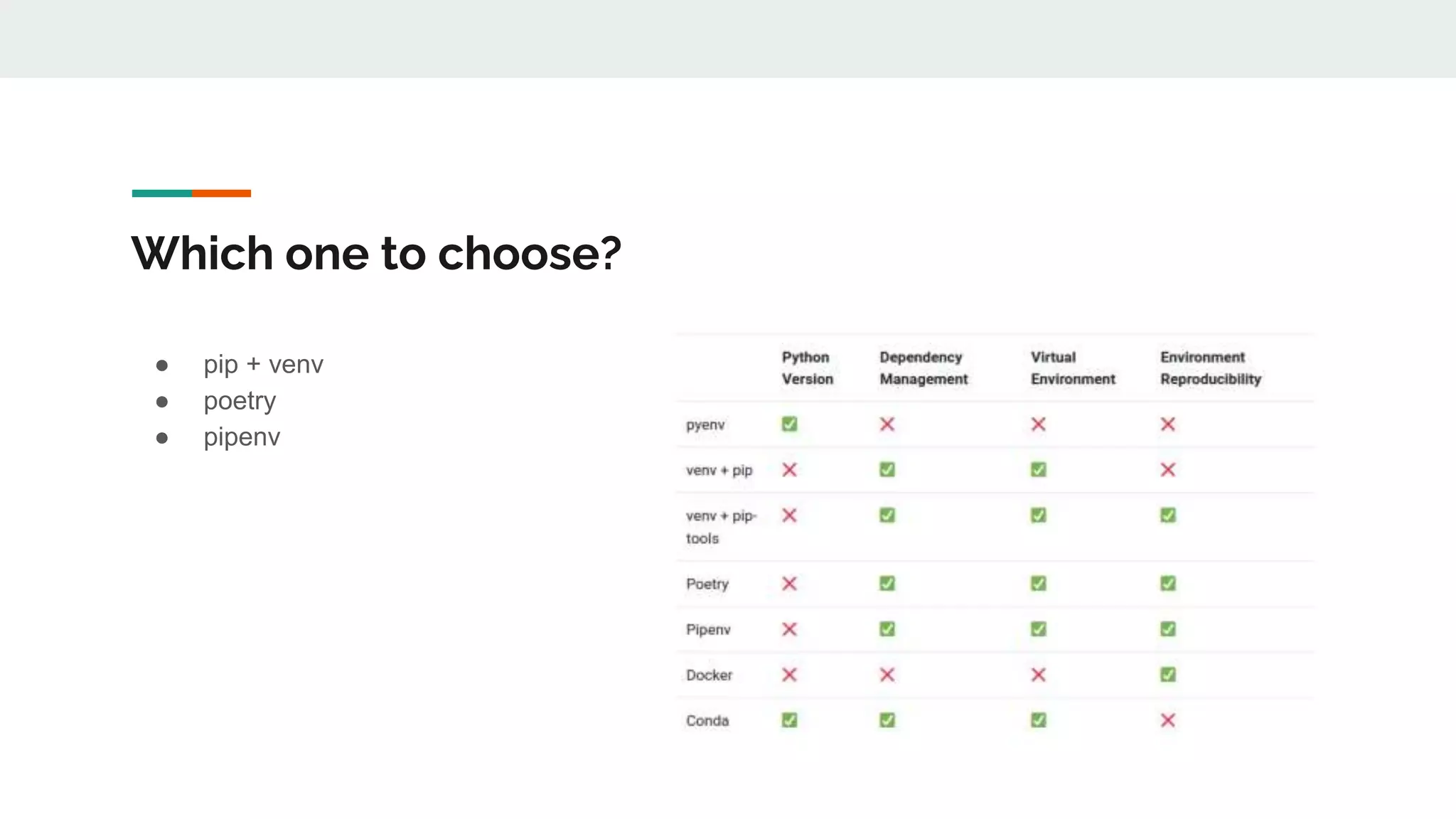
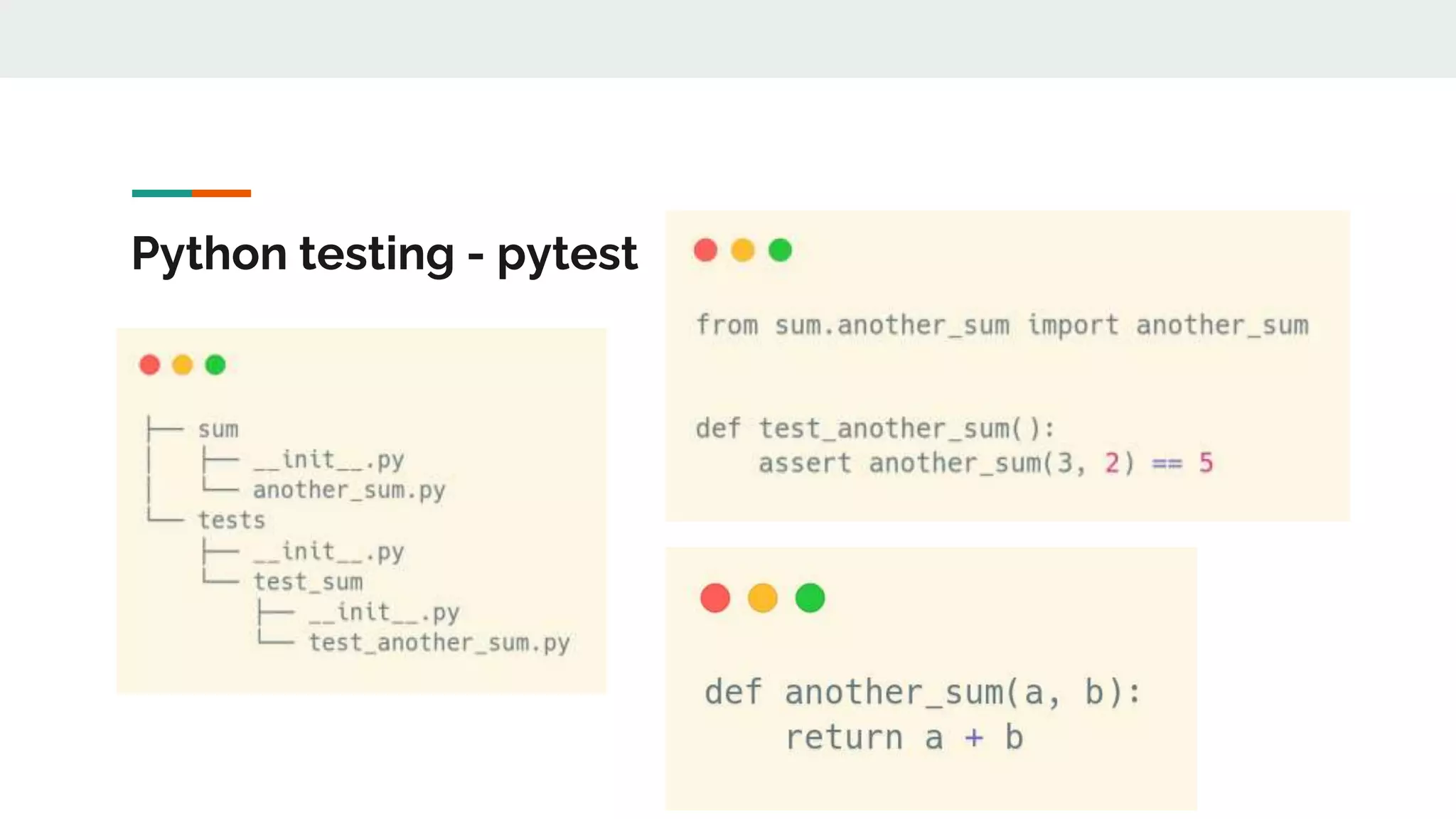
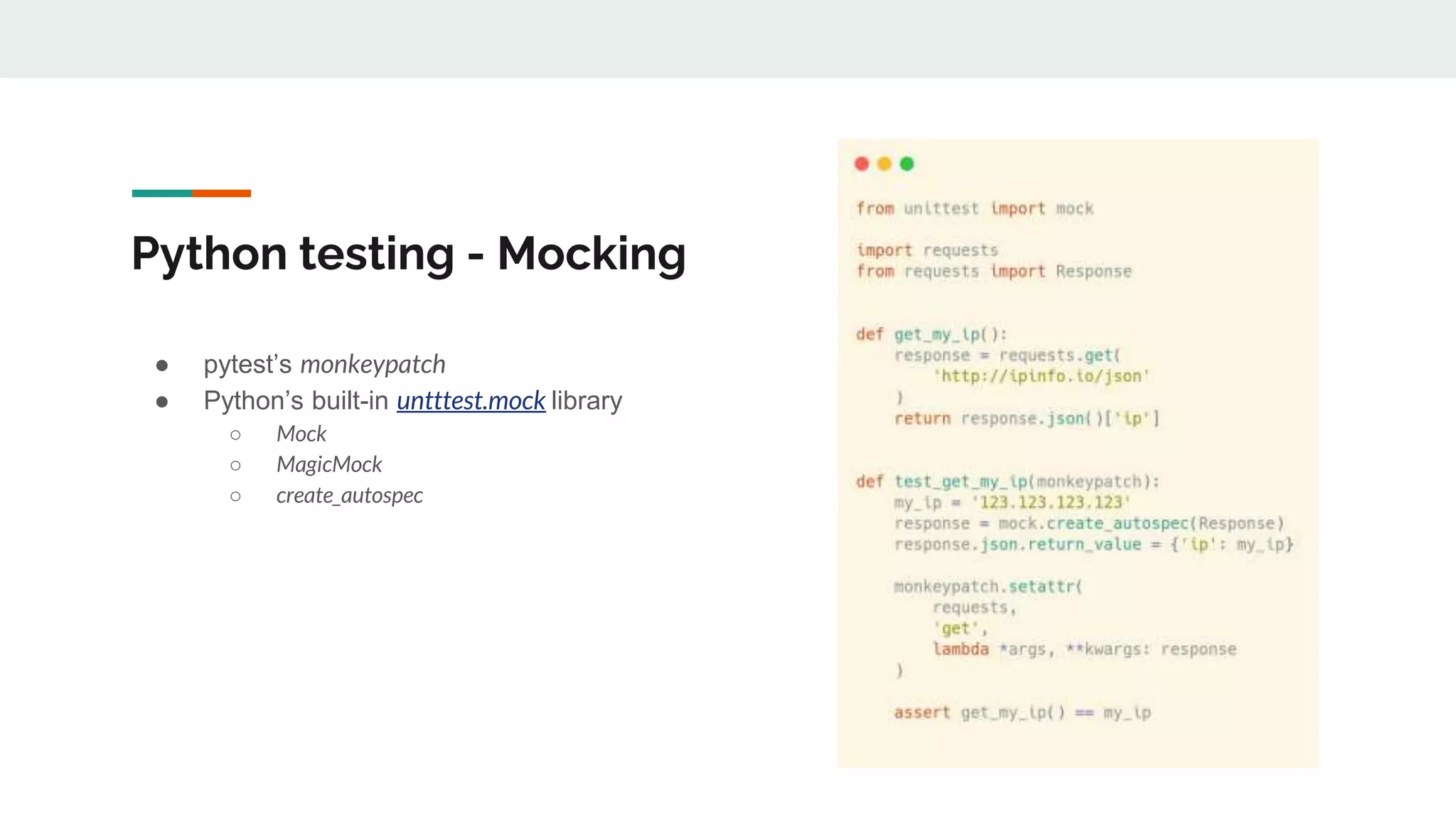
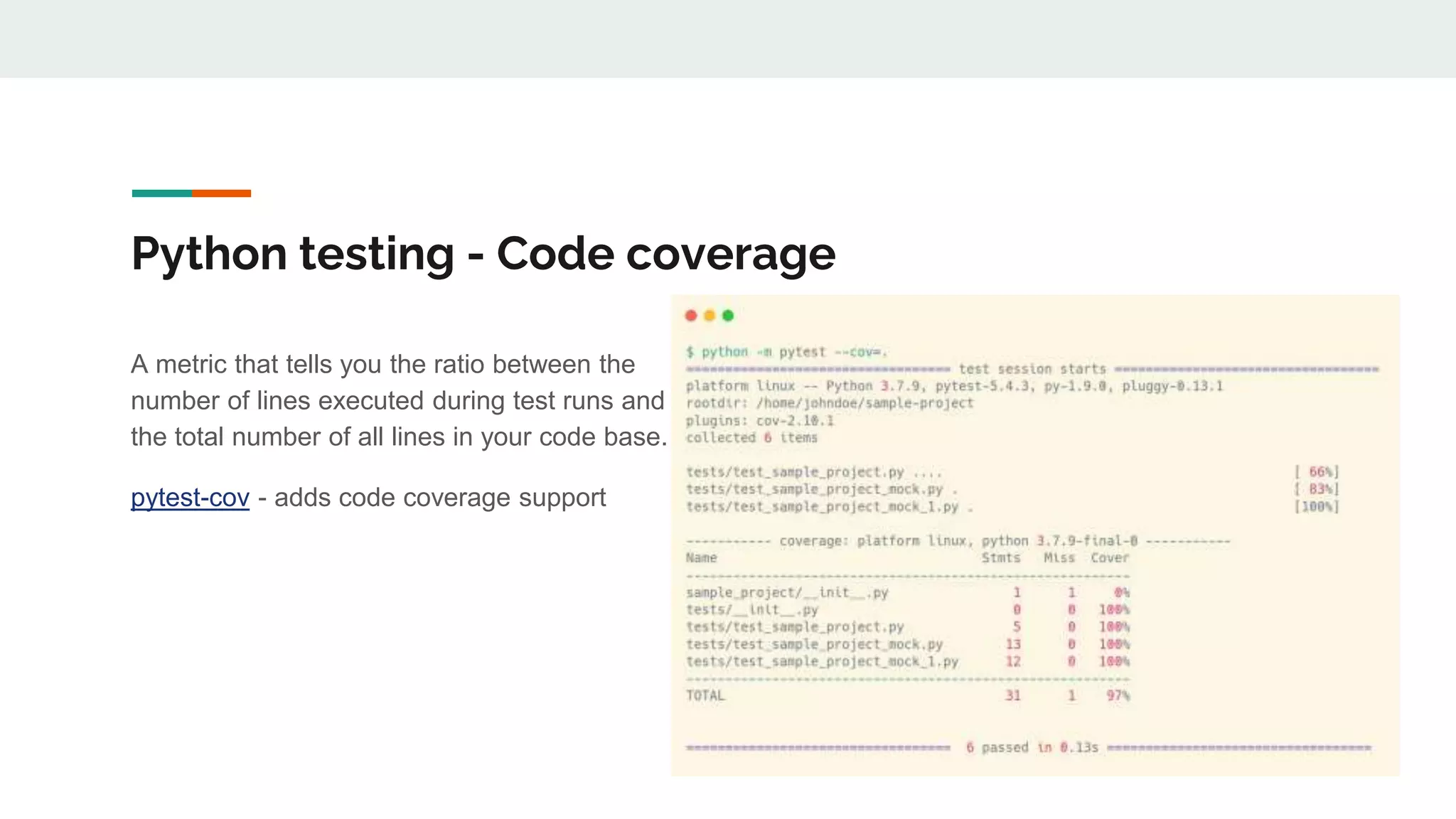
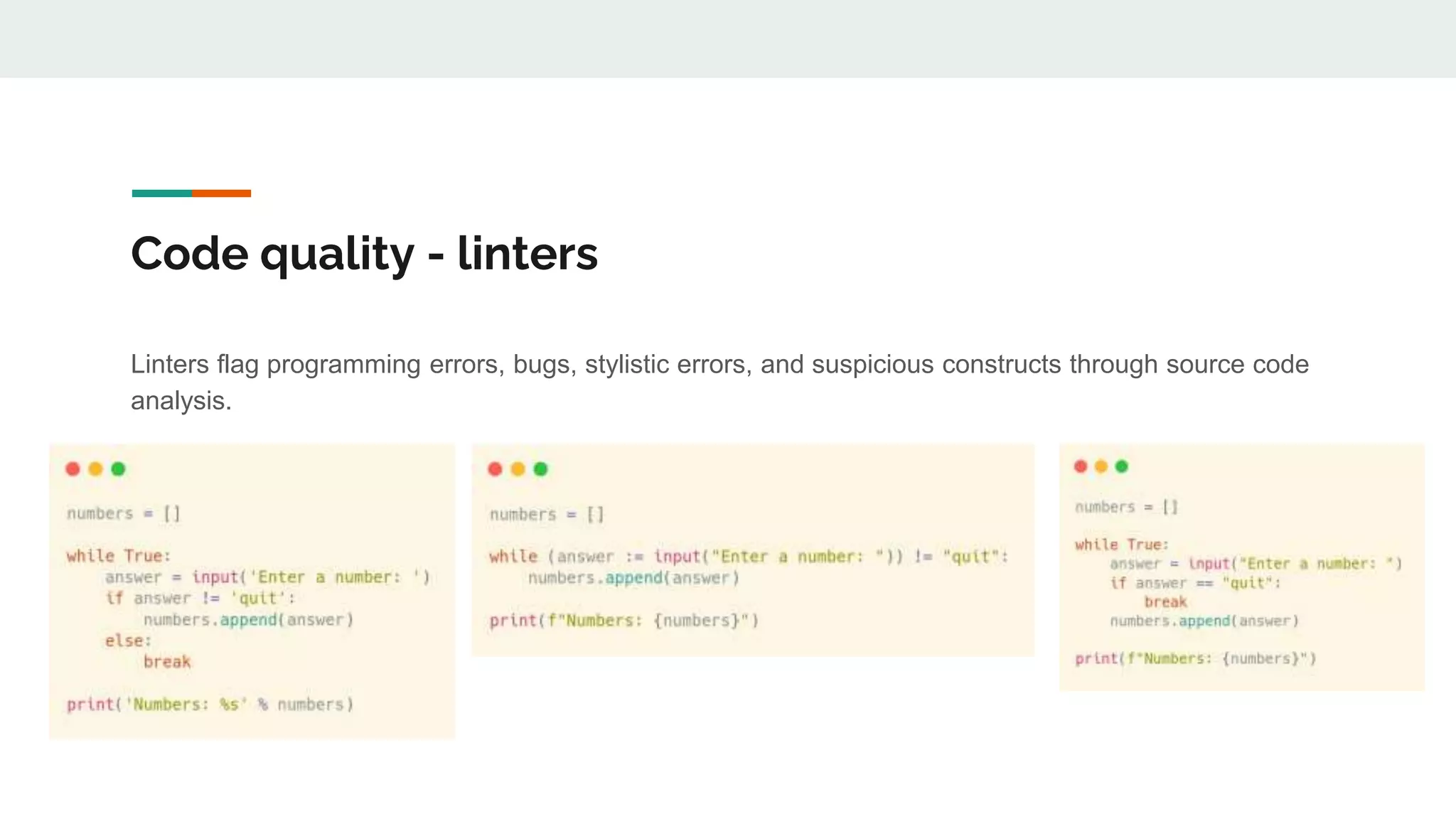
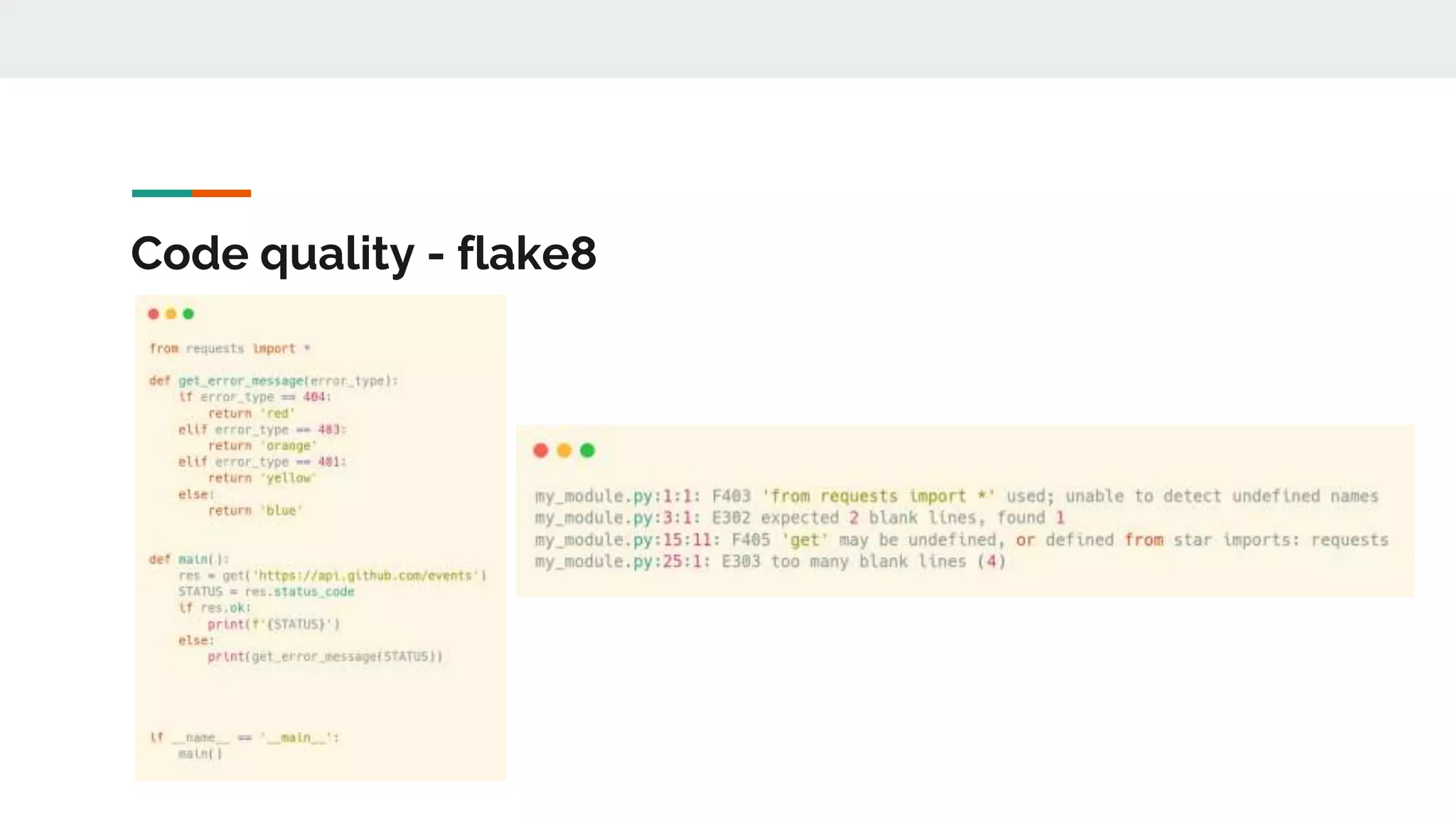
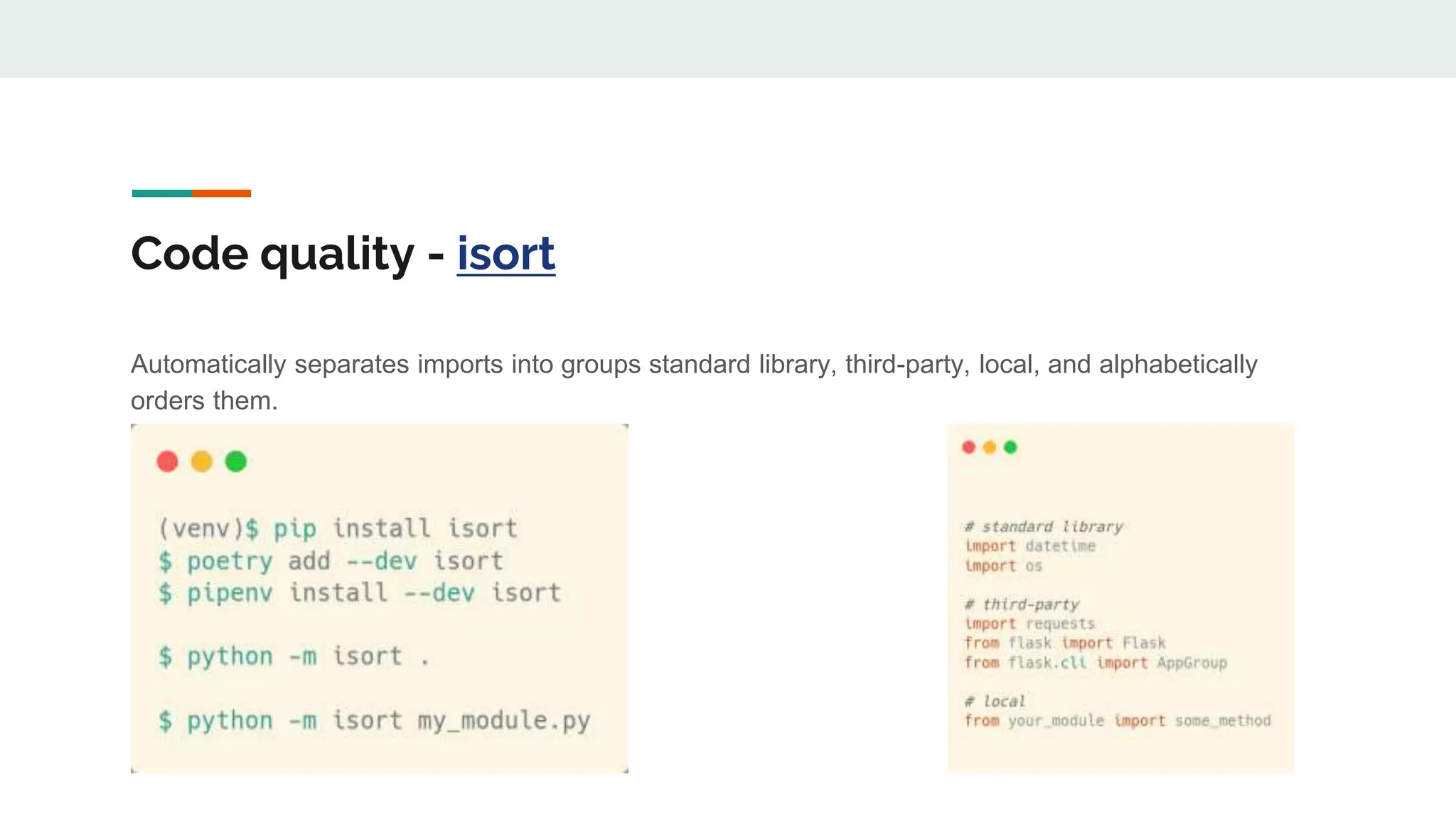
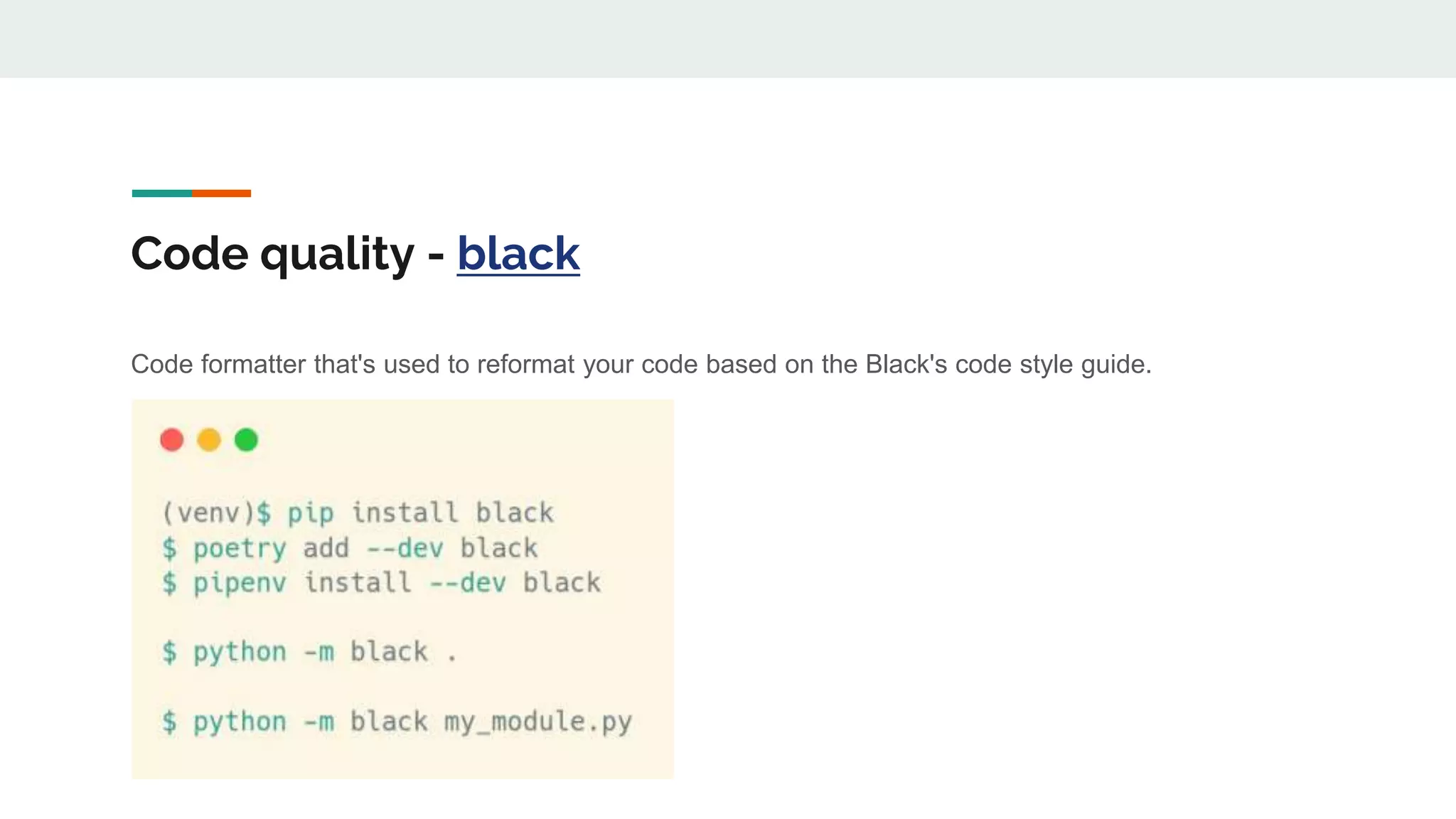
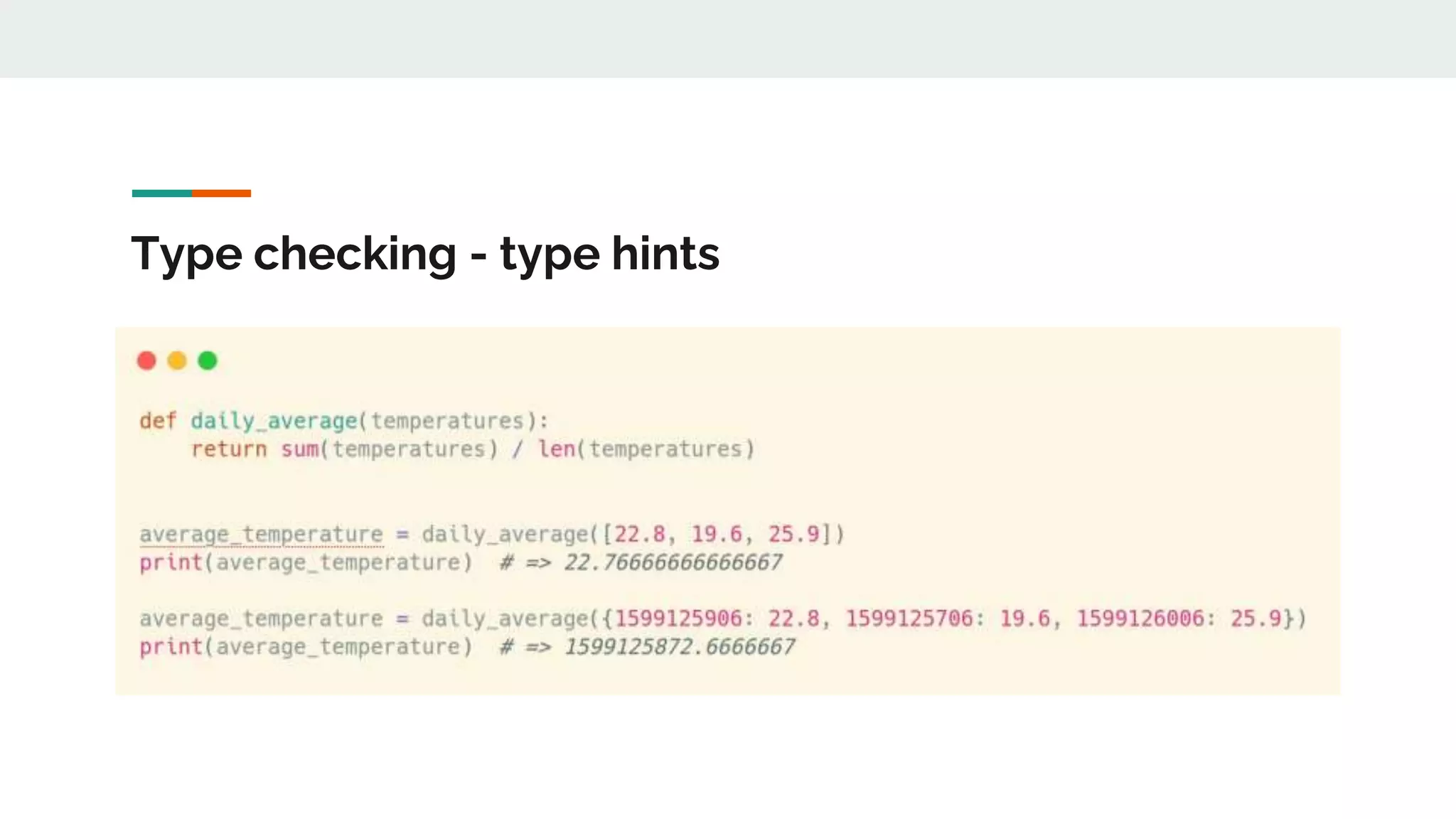
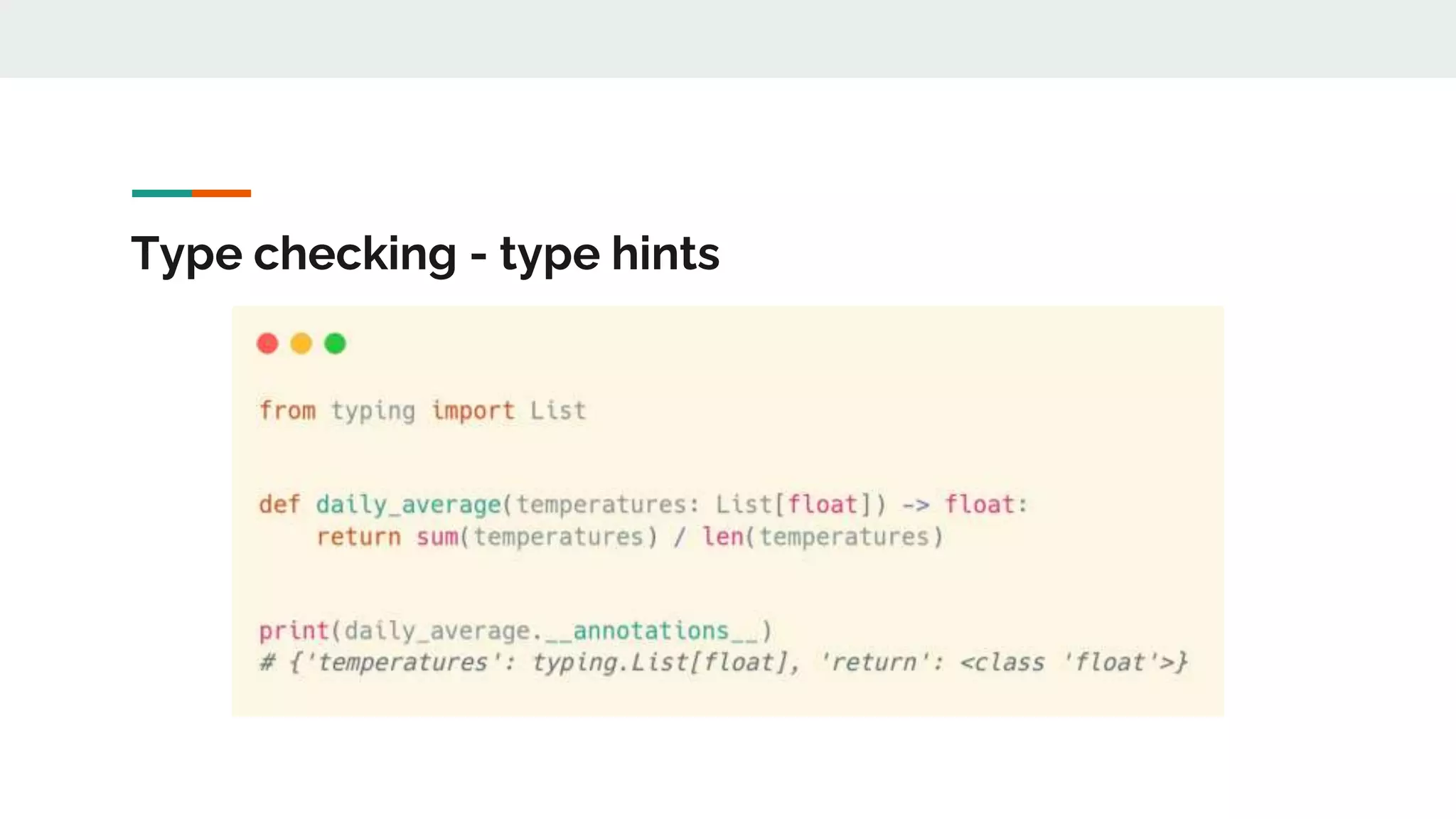
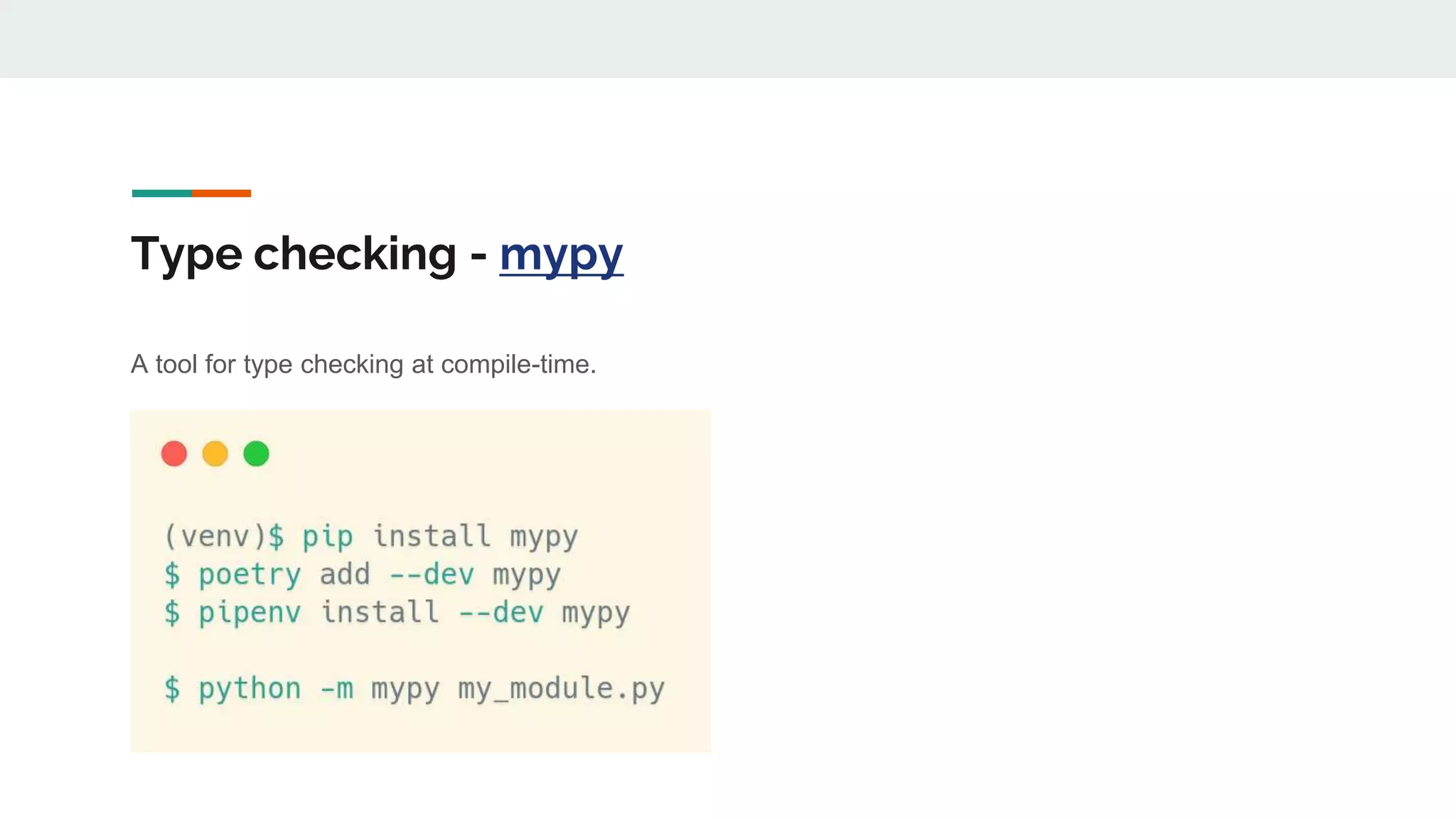
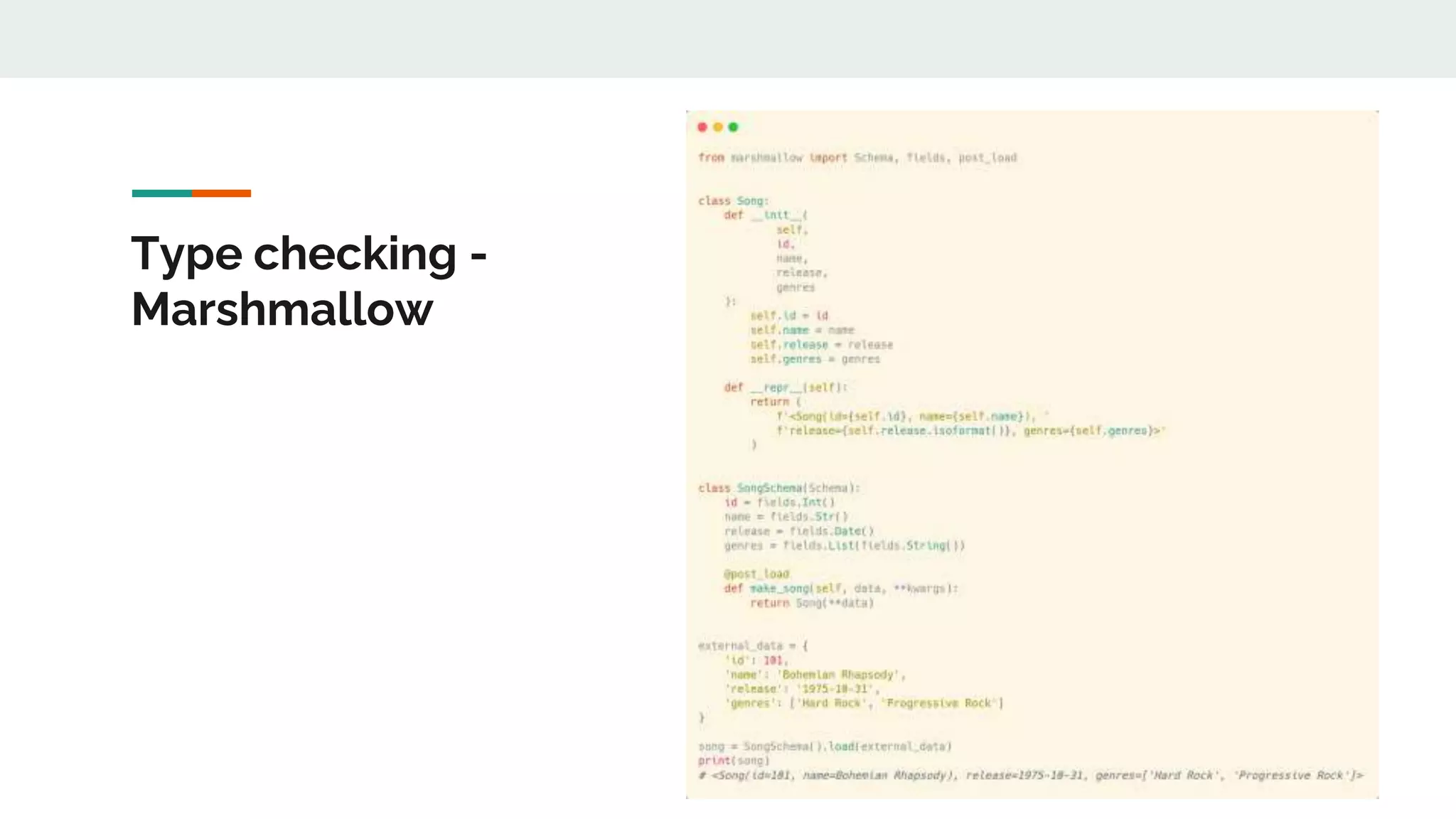
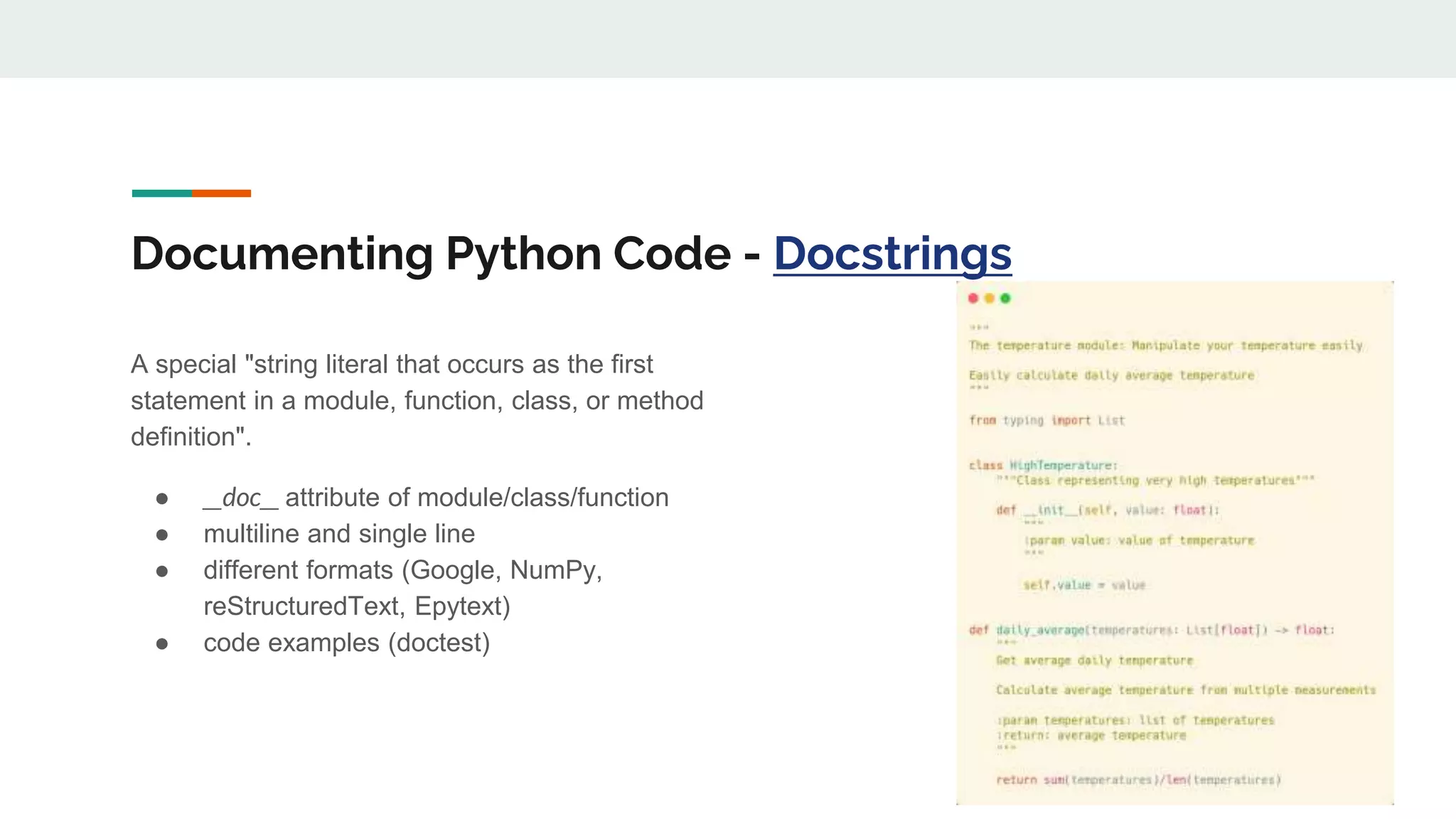
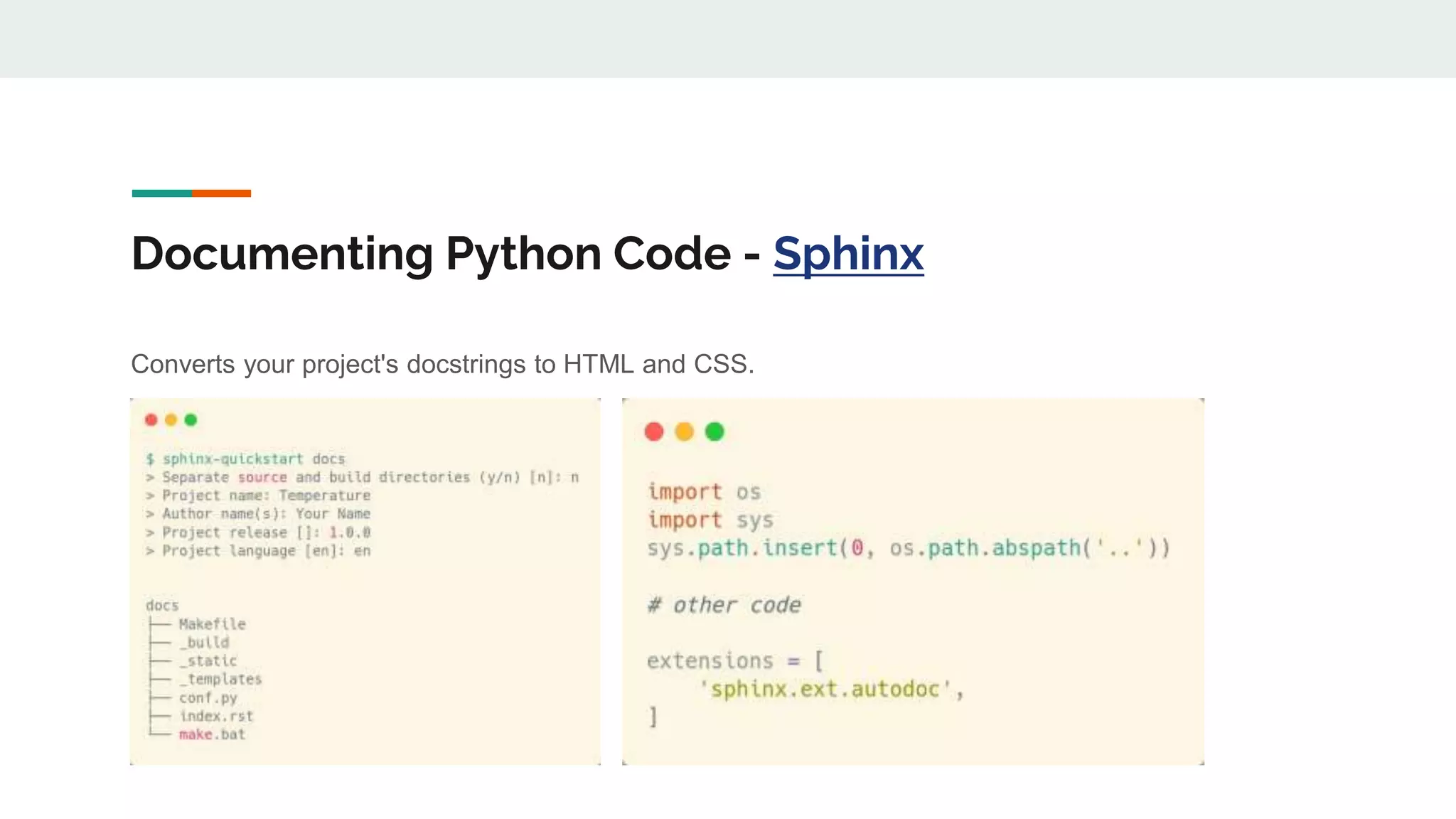
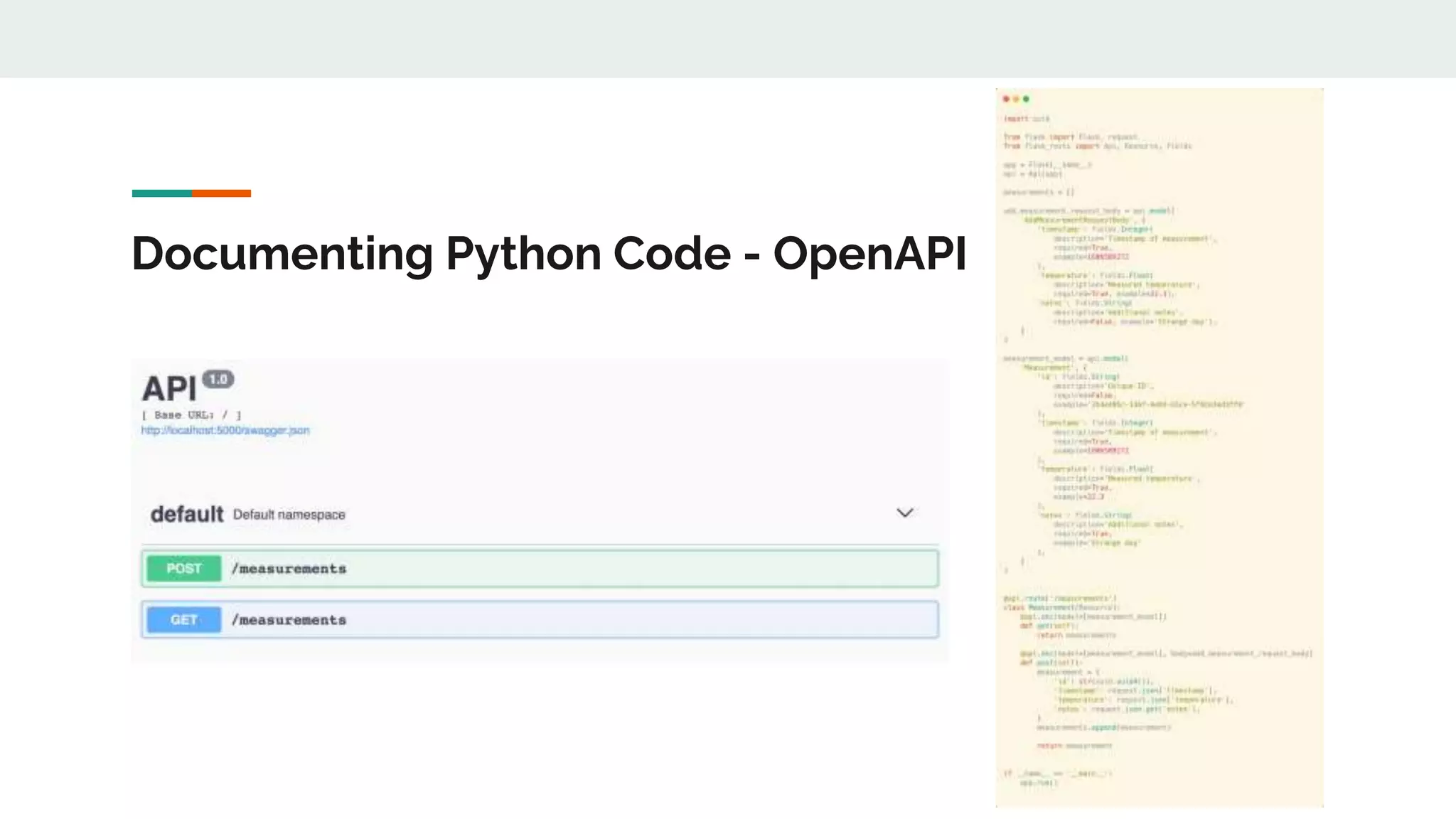
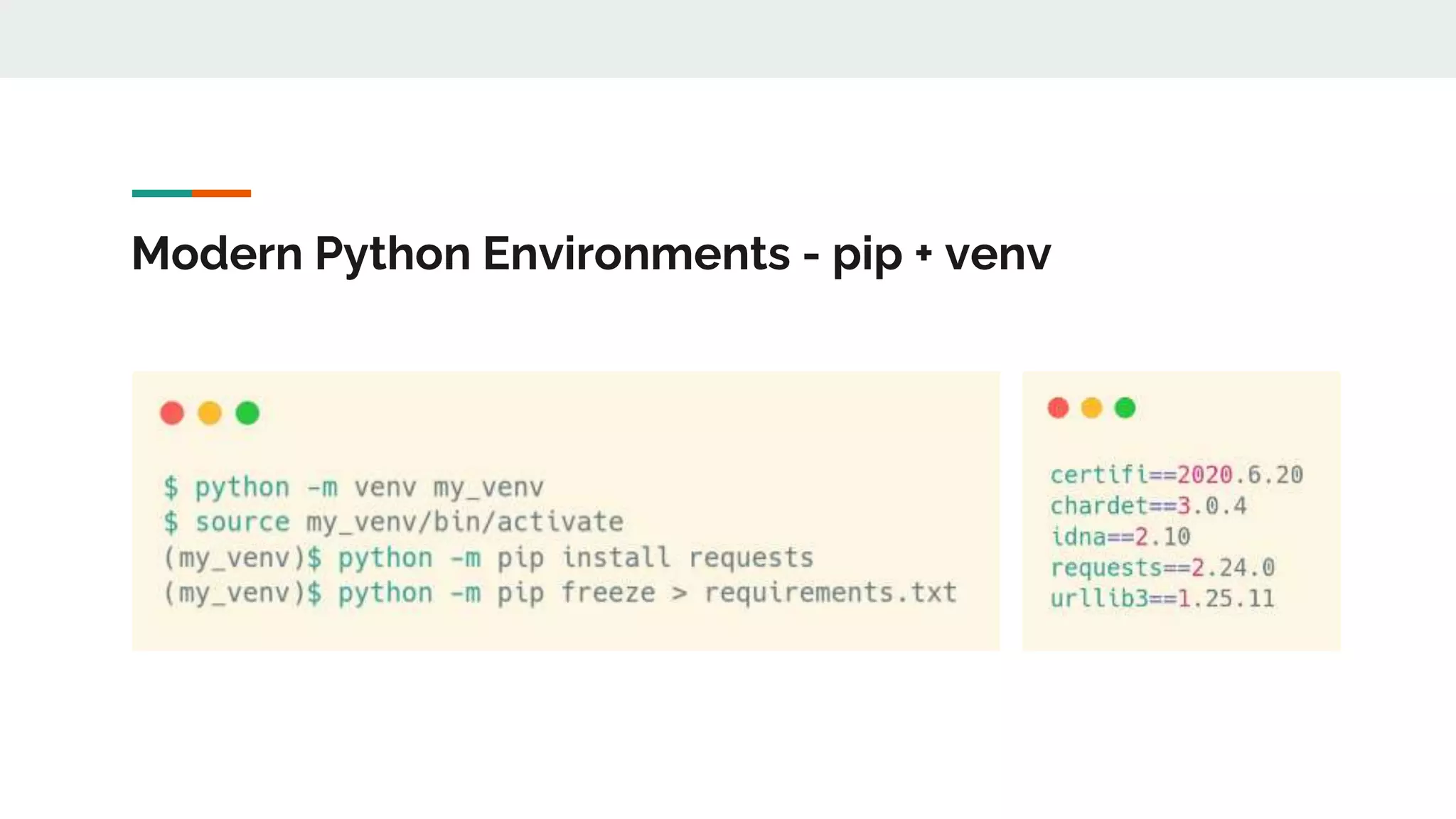
The document provides a comprehensive overview of modern Python development tools, covering virtual environments, dependency management, testing frameworks like pytest, code quality tools, type checking, and documentation practices. It highlights tools such as pyenv, poetry, pipenv, flake8, black, and Sphinx, detailing their functionalities. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of using these tools for efficient and secure Python code development.






![Modern Python Environments - Poetry
Powerful CLI used for creating and managing Python projects.
● Create a new project: $ poetry new <project-name>
● Install a dependency: $ poetry add [--dev] <package name>
● Run a command inside the virtual environment: $ poetry run python -m pytest
● Dependencies are managed inside pyproject.toml](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completepythontoolboxformoderndevelopers-210413081325/75/Complete-python-toolbox-for-modern-developers-8-2048.jpg)

![Modern Python Environments - pipenv
Managing dependencies and virtual environments.
● Create virtual environment: $ pipenv --python 3.8
● Install a dependency: $ pipenv install [--dev] <package name>
● Run a command inside the virtual environment: $ pipenv run python -m pytest
● Dependencies are managed inside Pipfile](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/completepythontoolboxformoderndevelopers-210413081325/75/Complete-python-toolbox-for-modern-developers-10-2048.jpg)