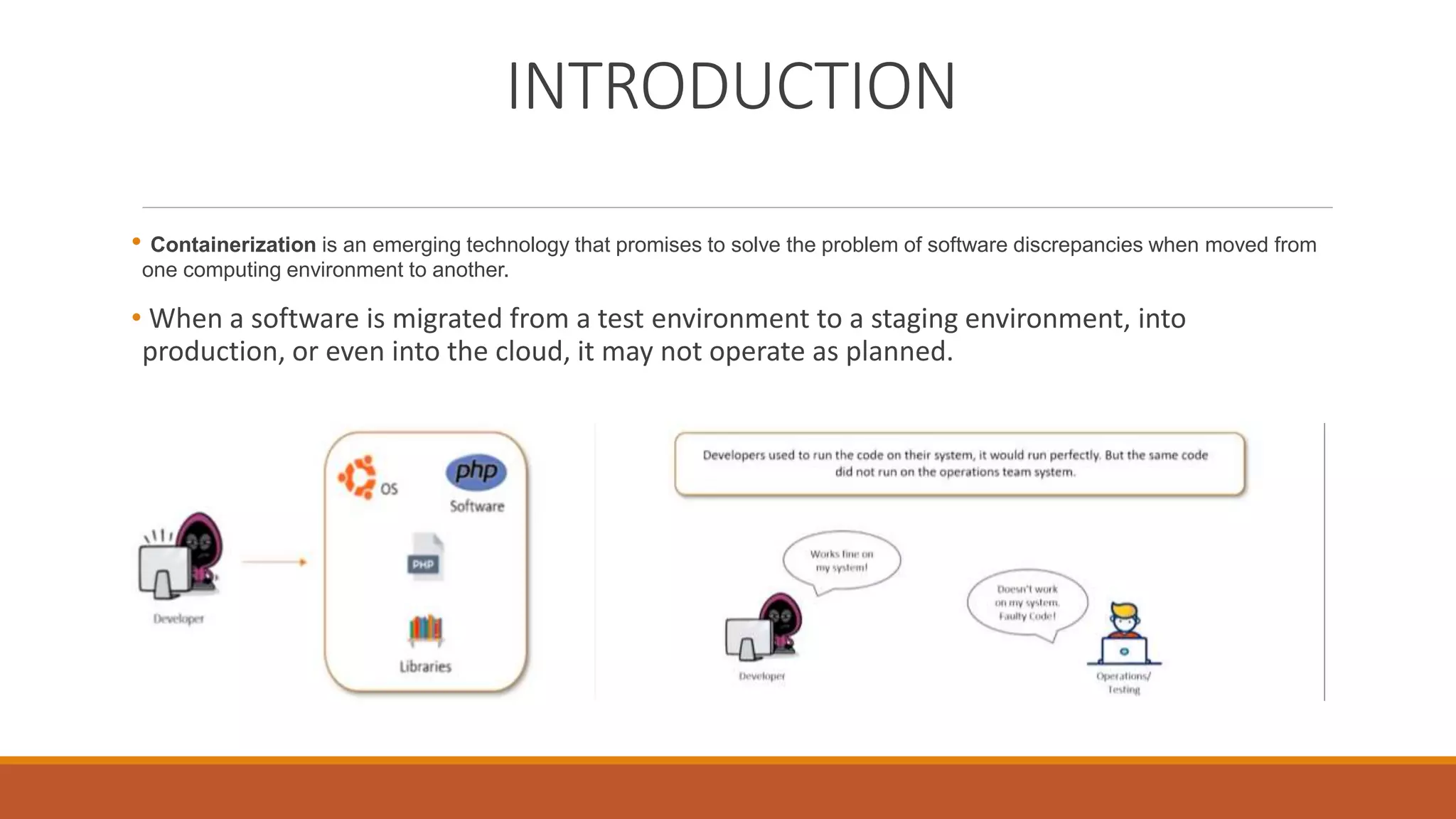
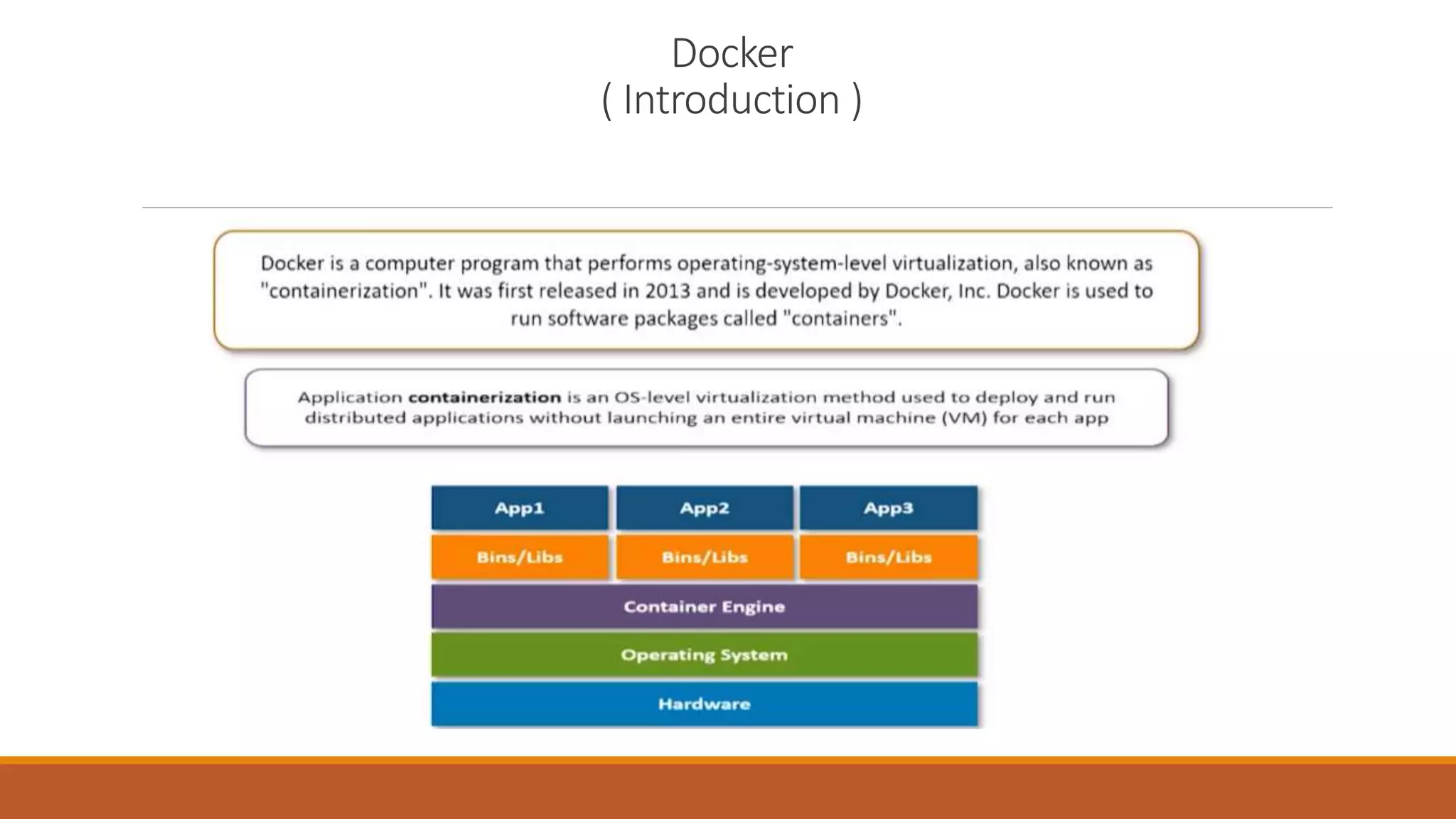
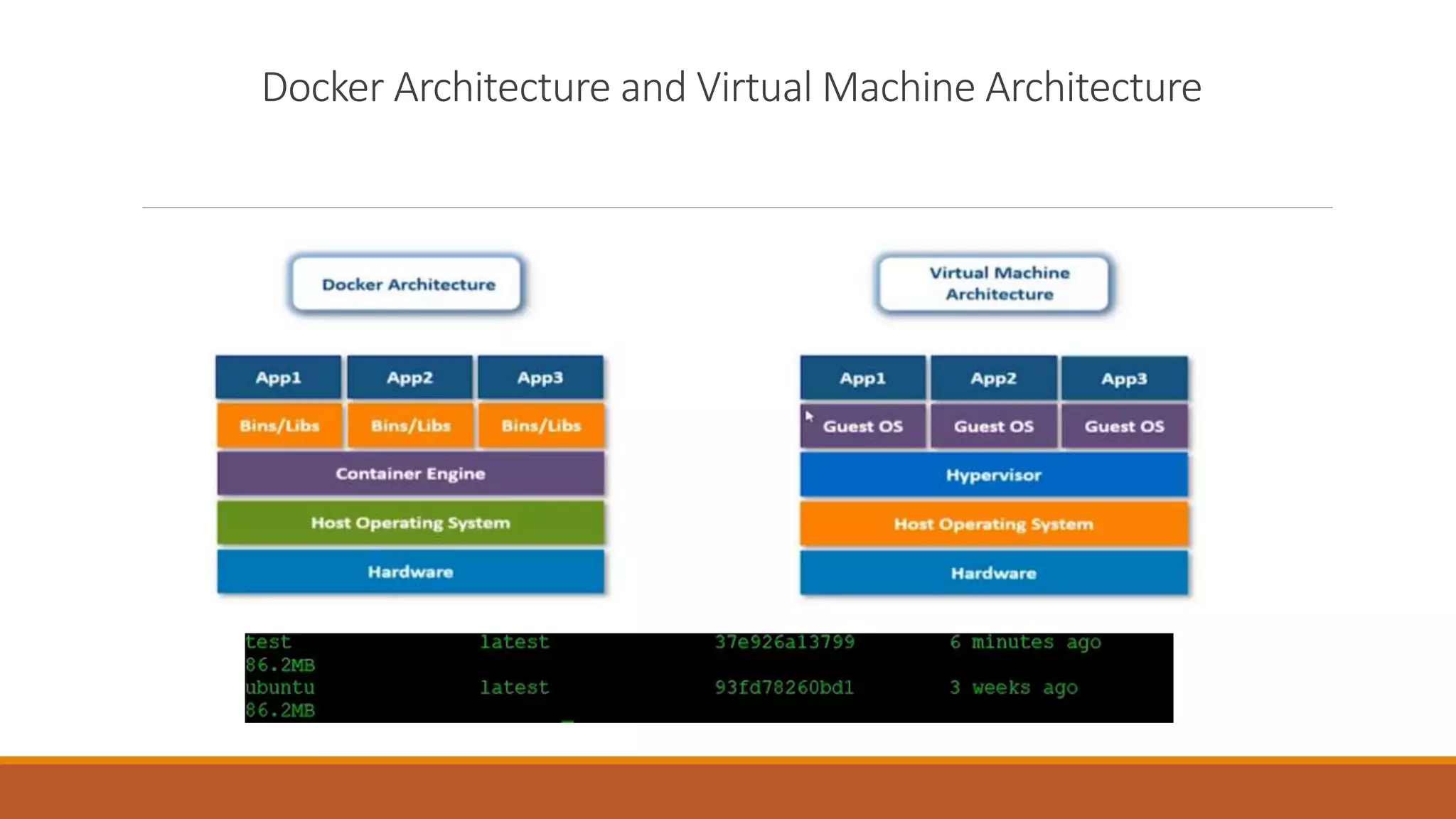
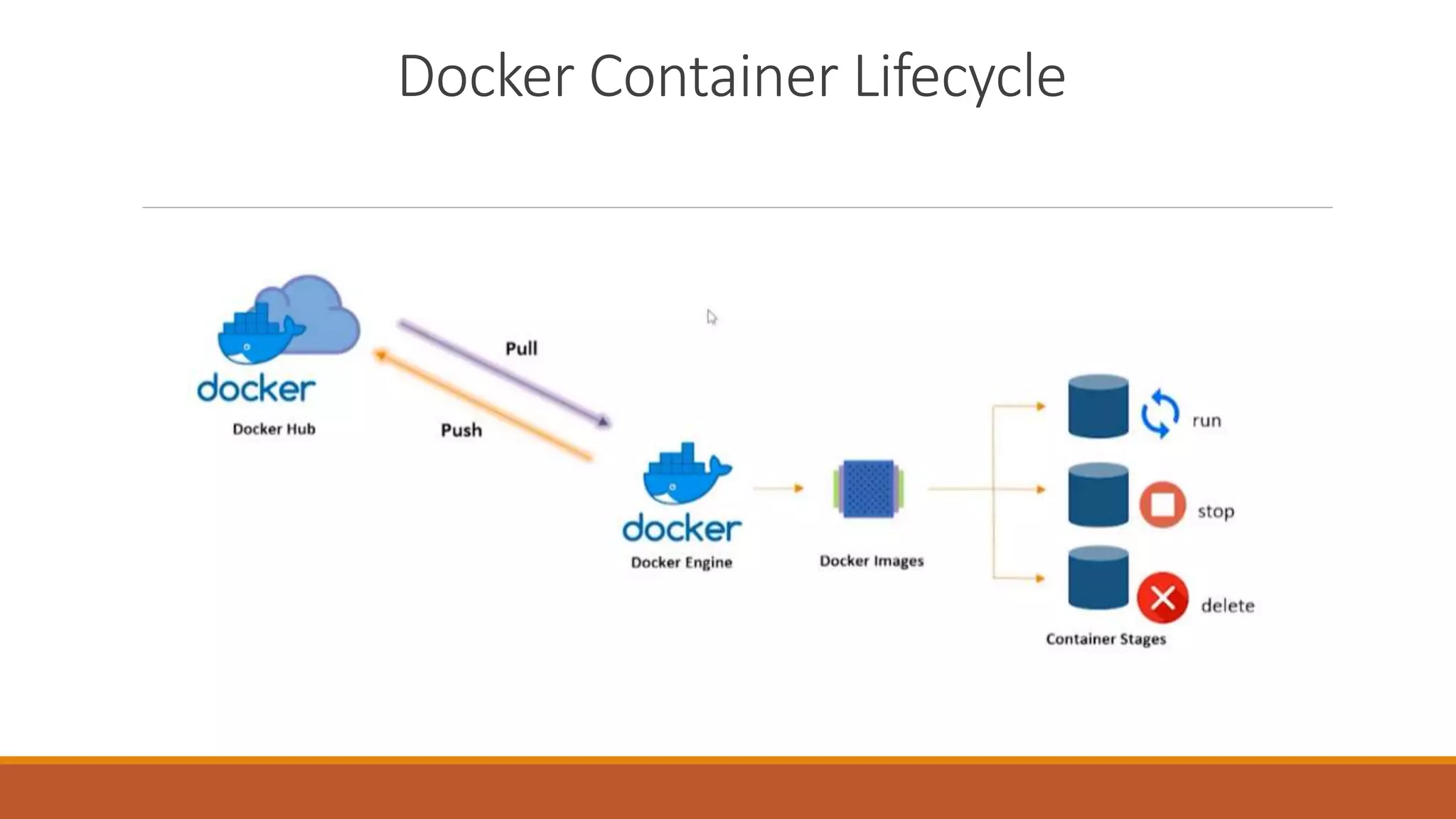
The document discusses containerization and version control systems, emphasizing the use of Docker for managing software environments and GitLab for tracking code changes. It outlines essential concepts such as Docker architecture, container lifecycle, Docker Hub, and commands related to both Docker and Git. Key methodologies like continuous integration and deployment are also covered, demonstrating their role in enhancing software development quality and efficiency.





![Docker Commands
Docker –version
To know docker version present In the machine
docker create [IMAGE]
To create Docker image3
Docker run [image] [command]
To Run Image and create container
Docker rm [container]
To remove container which is in running state
Docker update
To update container](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/containerizationandversioncontrolsystem-200427114237/75/Containerization-and-version-control-system-11-2048.jpg)