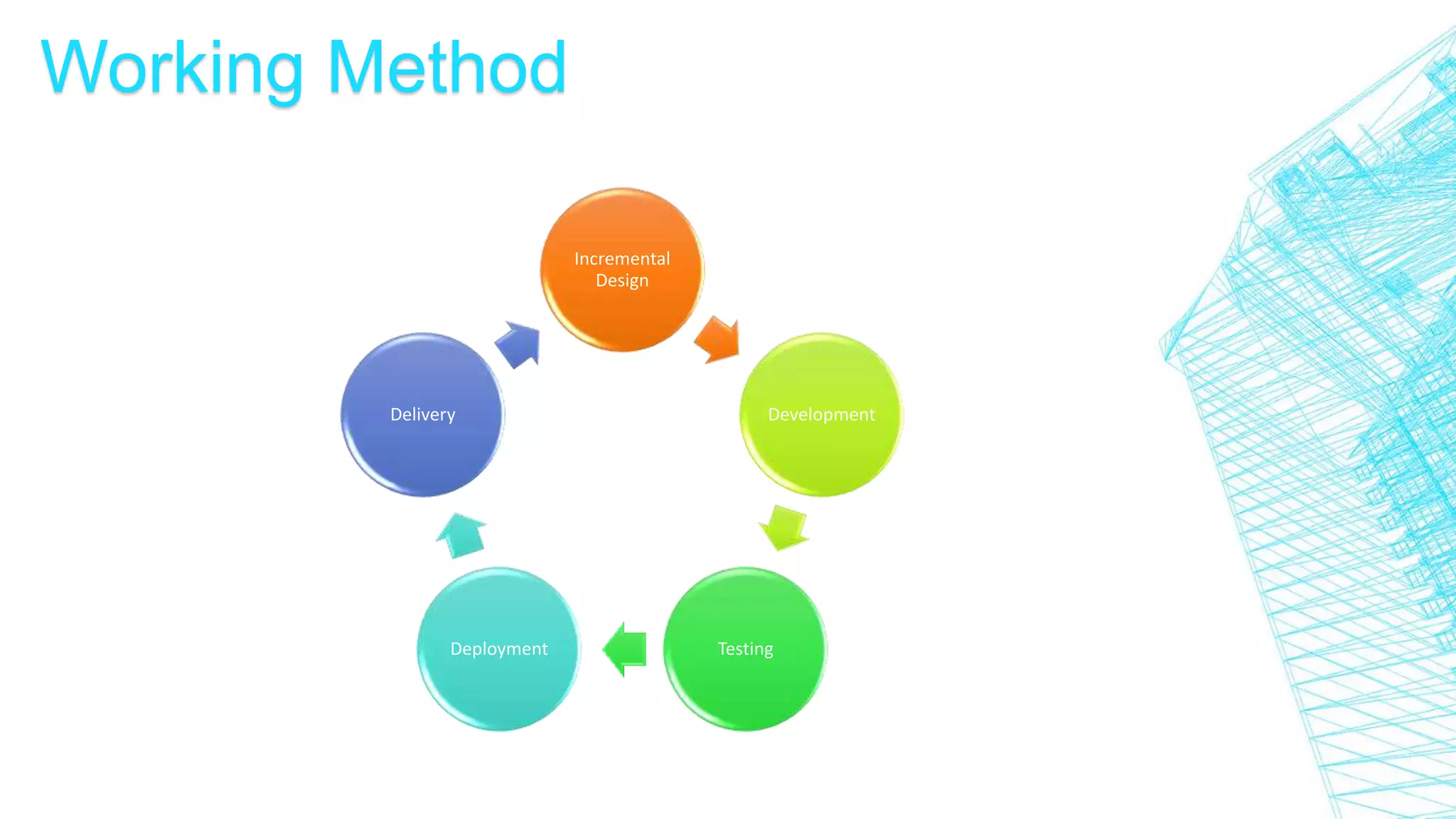
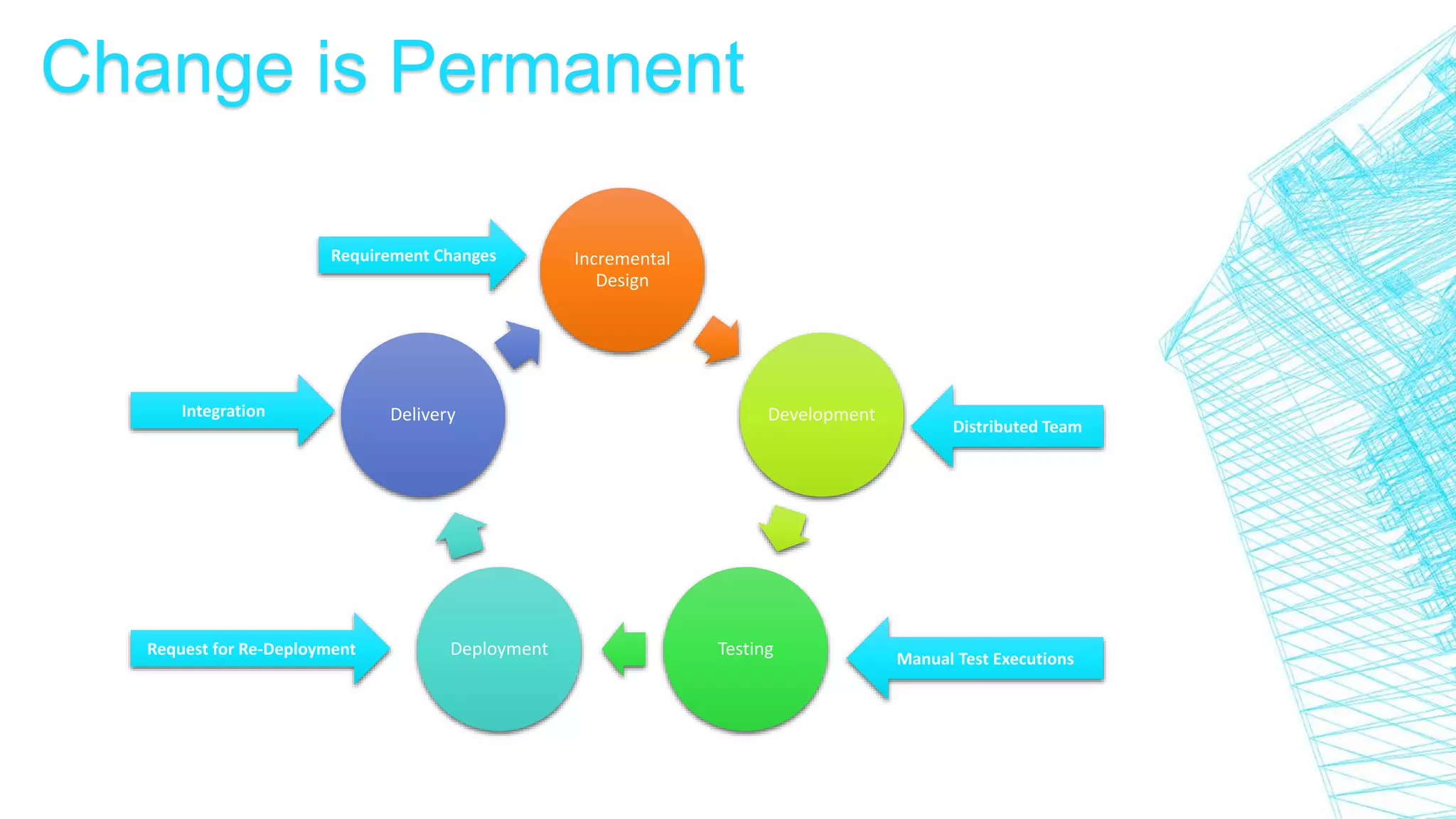
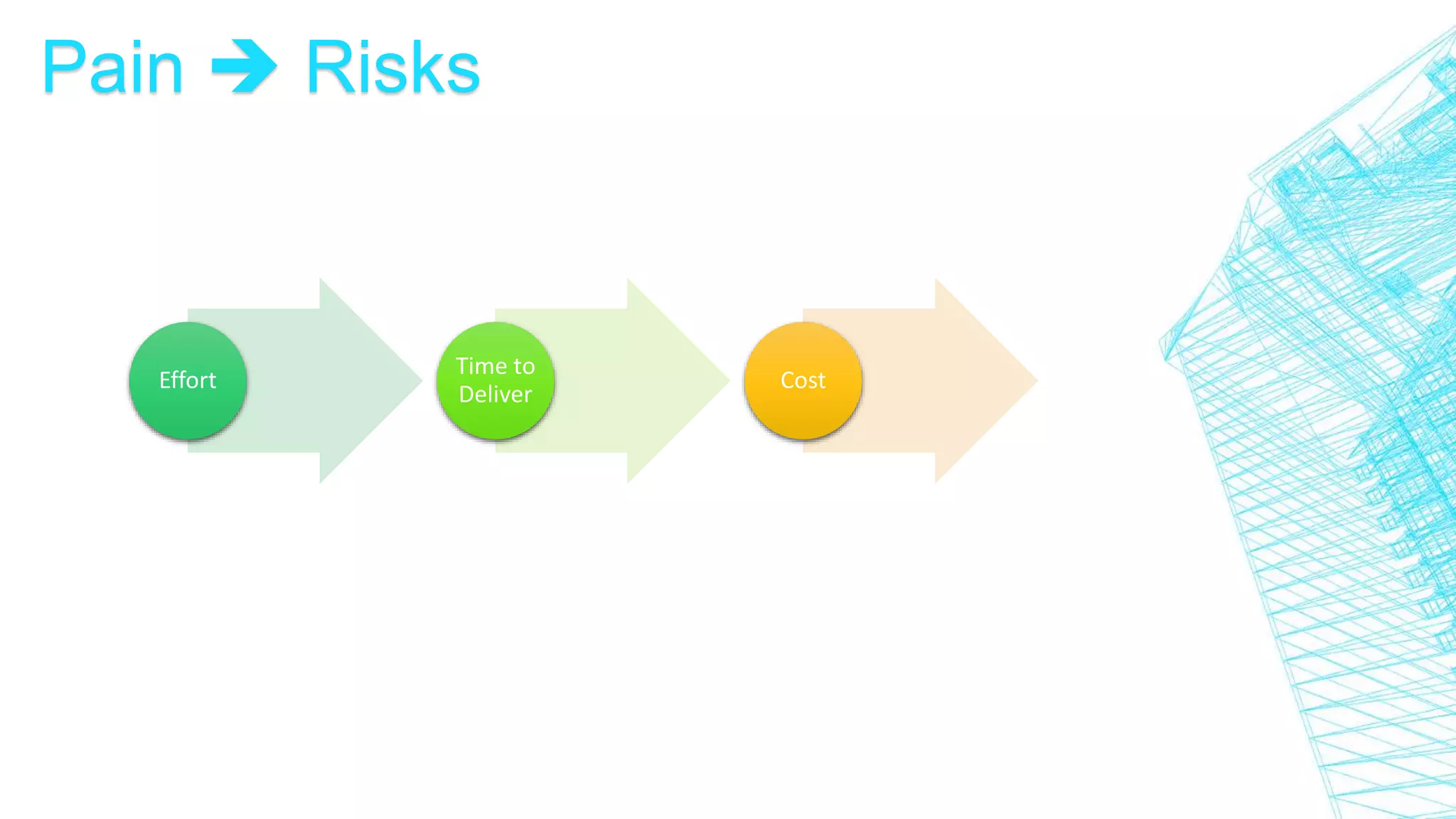
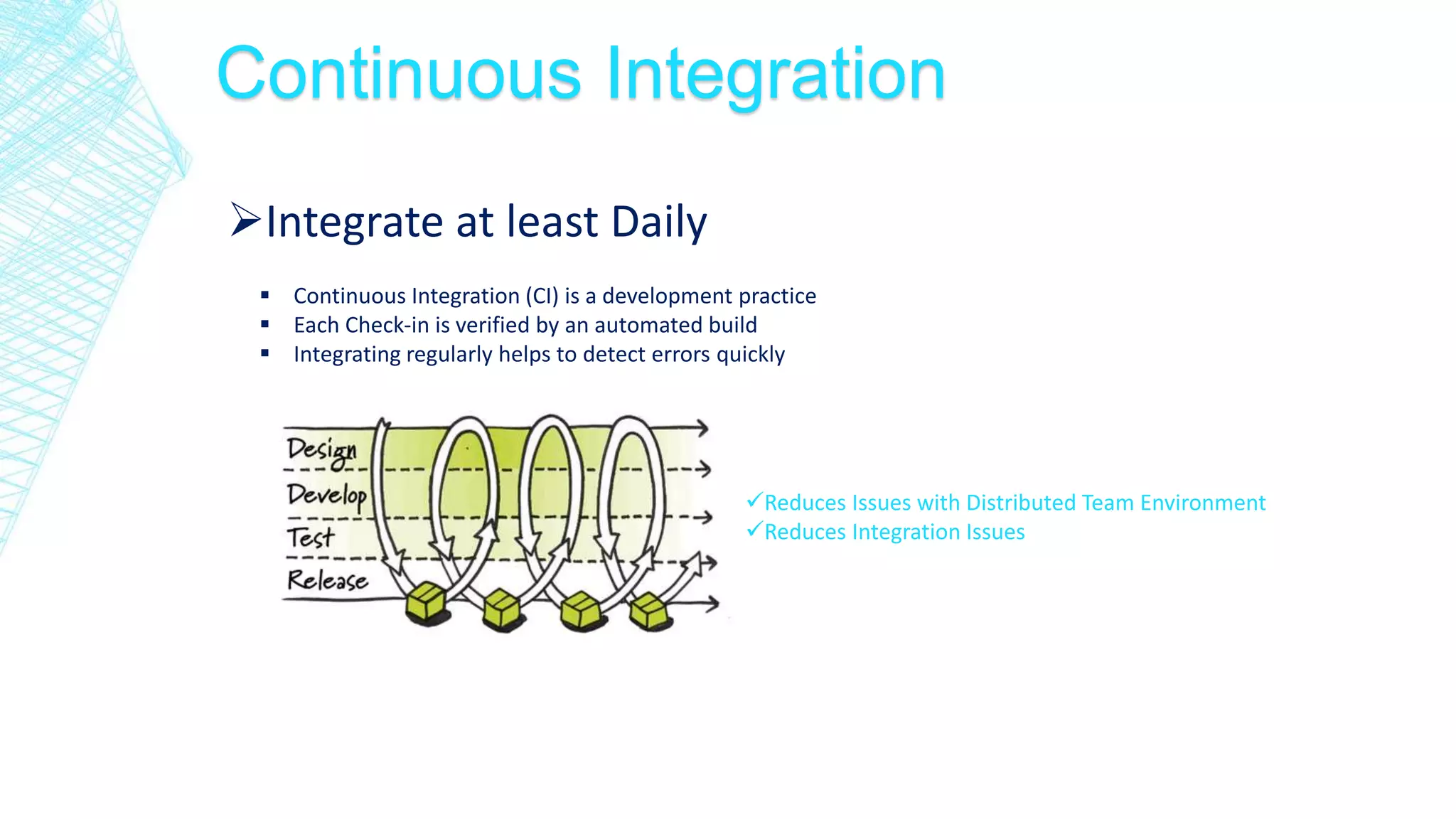
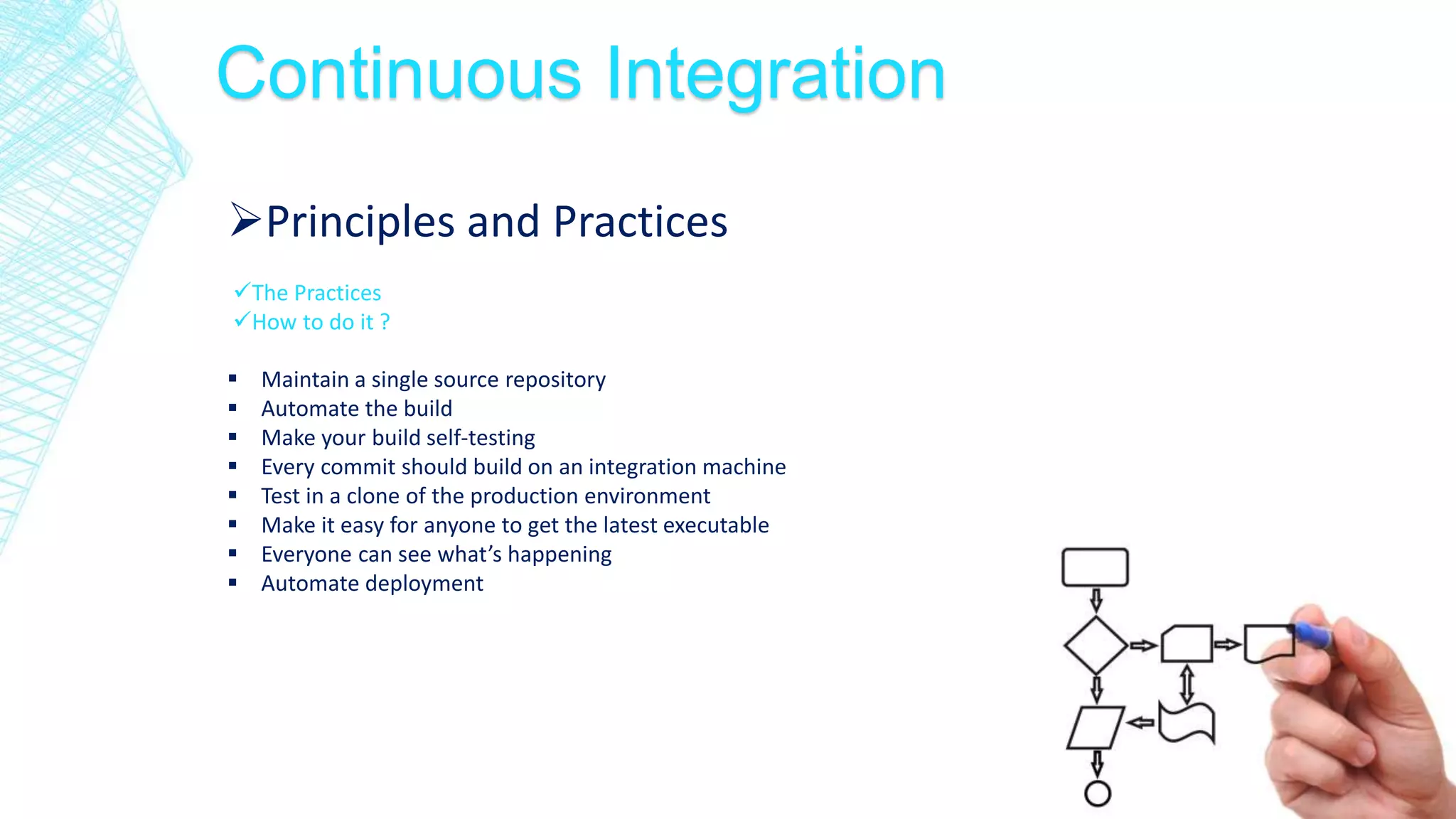
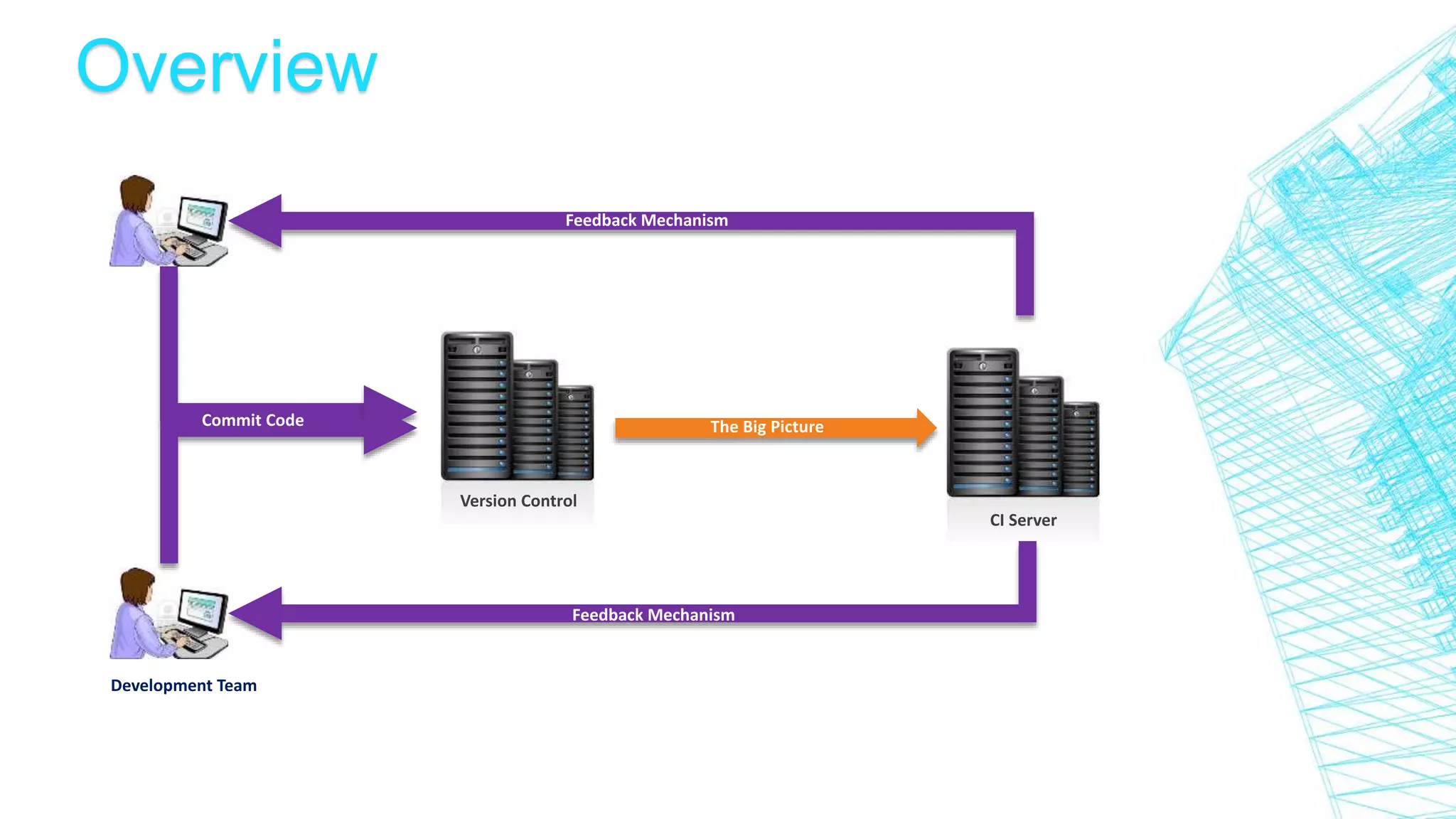
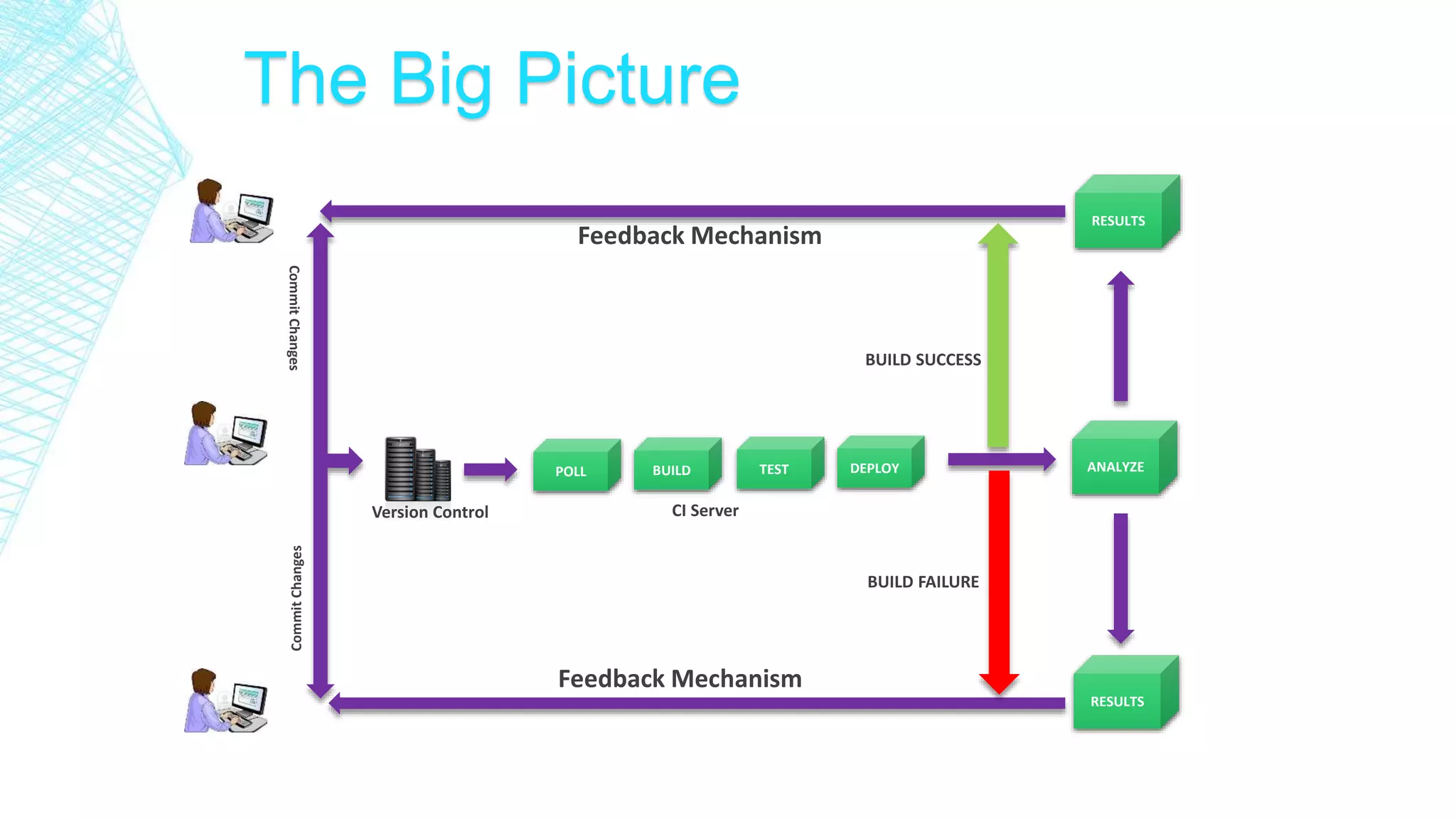
This document discusses continuous integration for Oracle Database objects. It defines continuous integration as integrating code changes at least daily to verify changes through automated builds. This helps detect errors quickly and reduces issues that arise from distributed teams and manual testing. The document recommends principles like source control, automated builds and testing, and making each commit trigger an integration build. It demonstrates how tools like Jenkins, Maven, UTPLSQL and SonarQube can be used together in a continuous integration pipeline to continuously build, test and analyze code changes.





![ Continuous Integration [HUDSON]
Automated Polling [HUDSON SVN]
Automated Build [HUDSON SVN MAVEN]
Automated Test [HUDSON SVN MAVEN UTPLSQL]
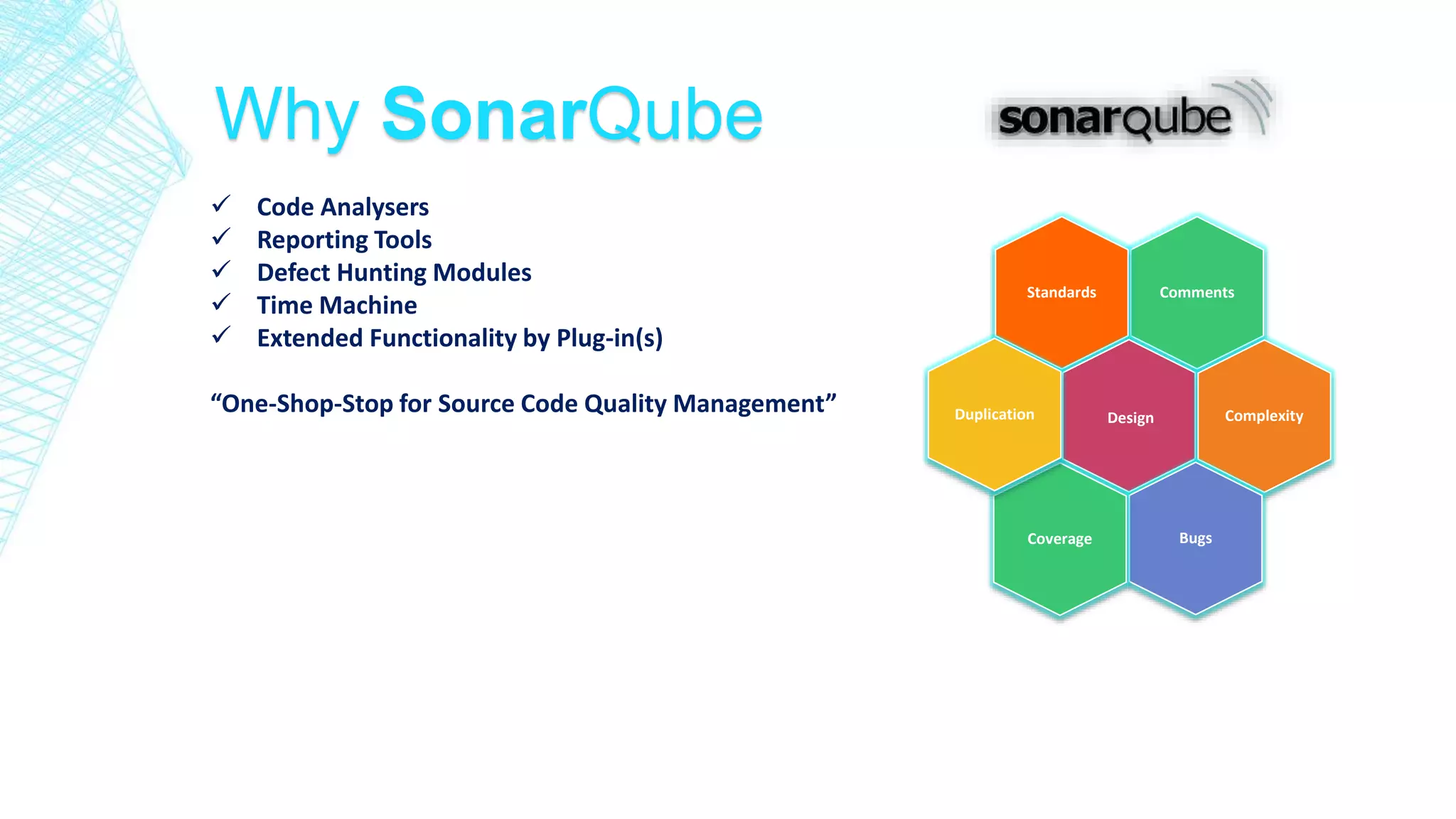
Automated Code Analysis [HUDSON SVN MAVEN UTPLSQL SONAR]
Demonstration
JENKINS SVN MAVEN UTPLSQL SONAR
Summary](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/continuousintegration-general-150224040642-conversion-gate02/75/Continuous-Integration-Oracle-Database-Objects-18-2048.jpg)
