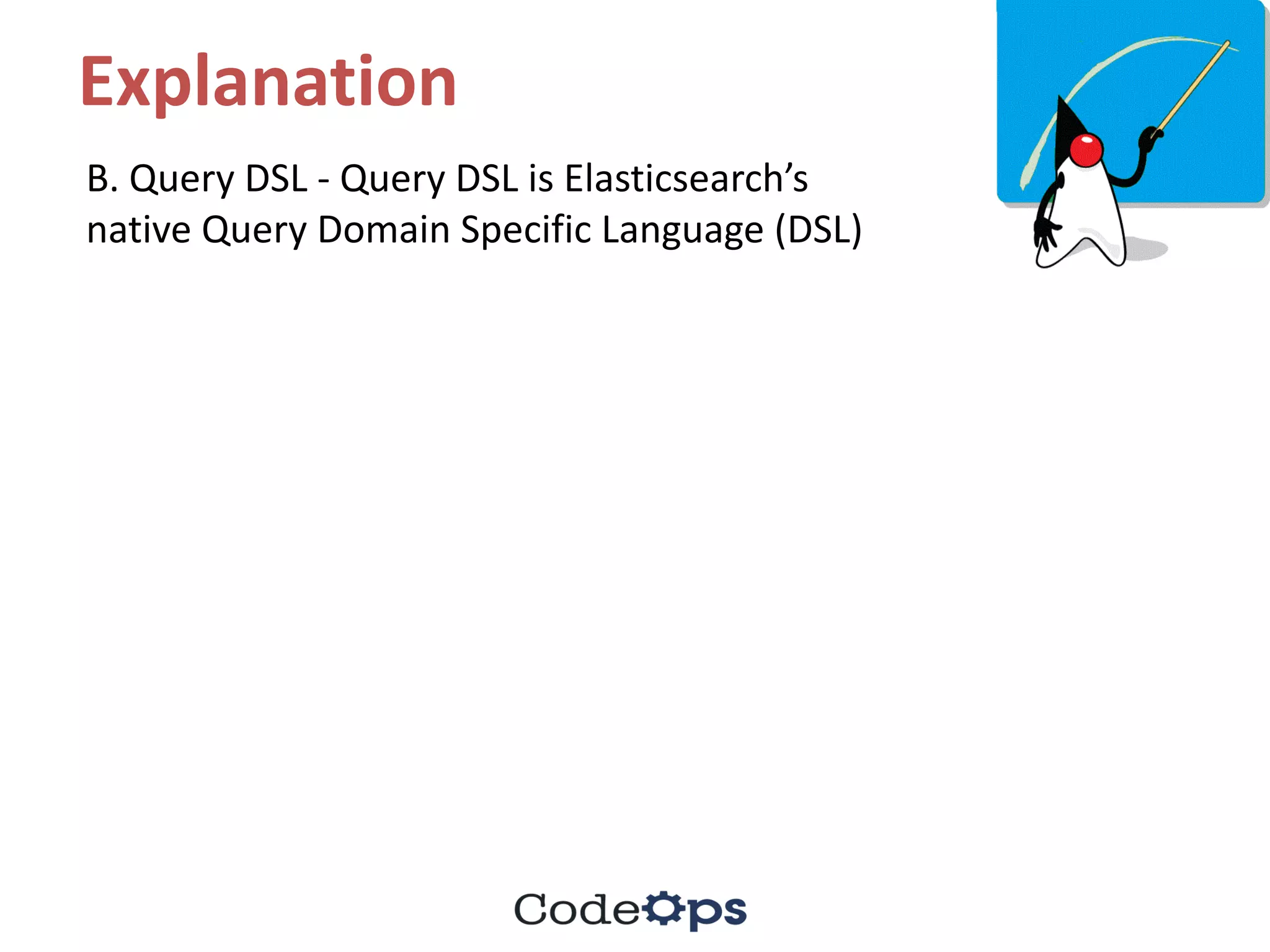
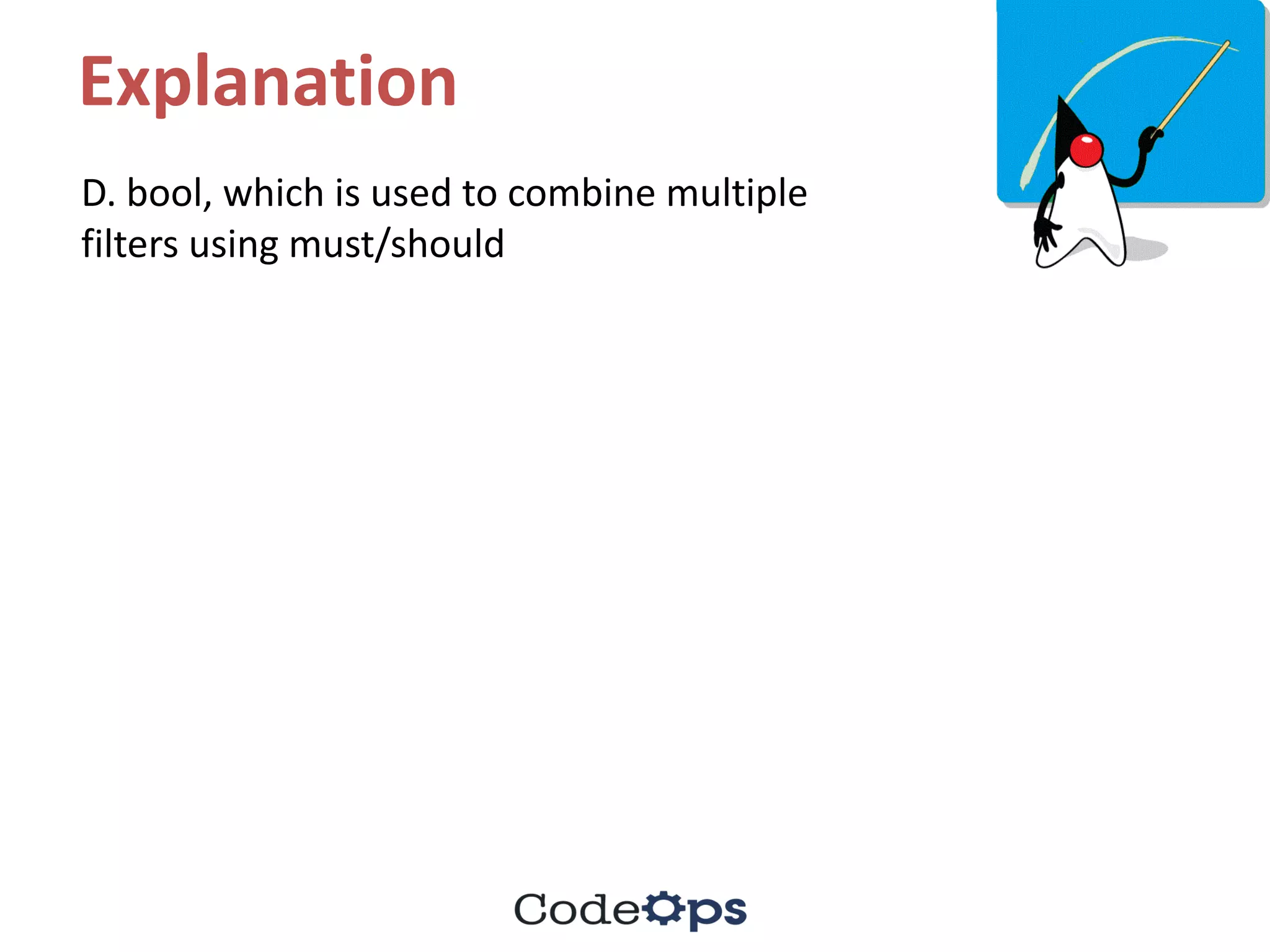
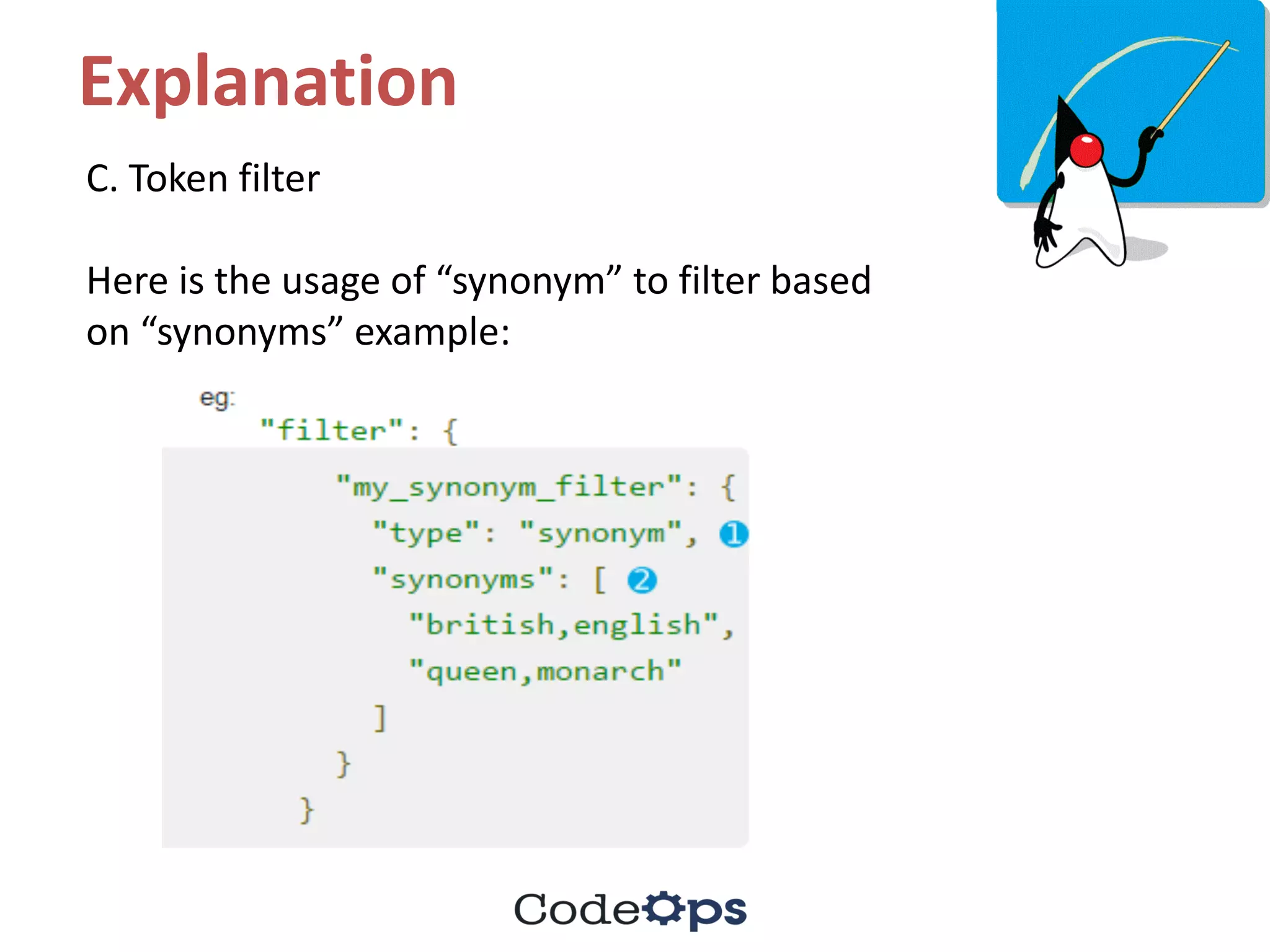
The document contains a series of quiz questions and answers related to Elasticsearch, Java programming, and best practices in coding. It includes explanations for each answer, providing insights into concepts like query DSL, lambda expressions, streams, and exception handling. Additionally, the document lists upcoming meetups and bootcamps related to software development.









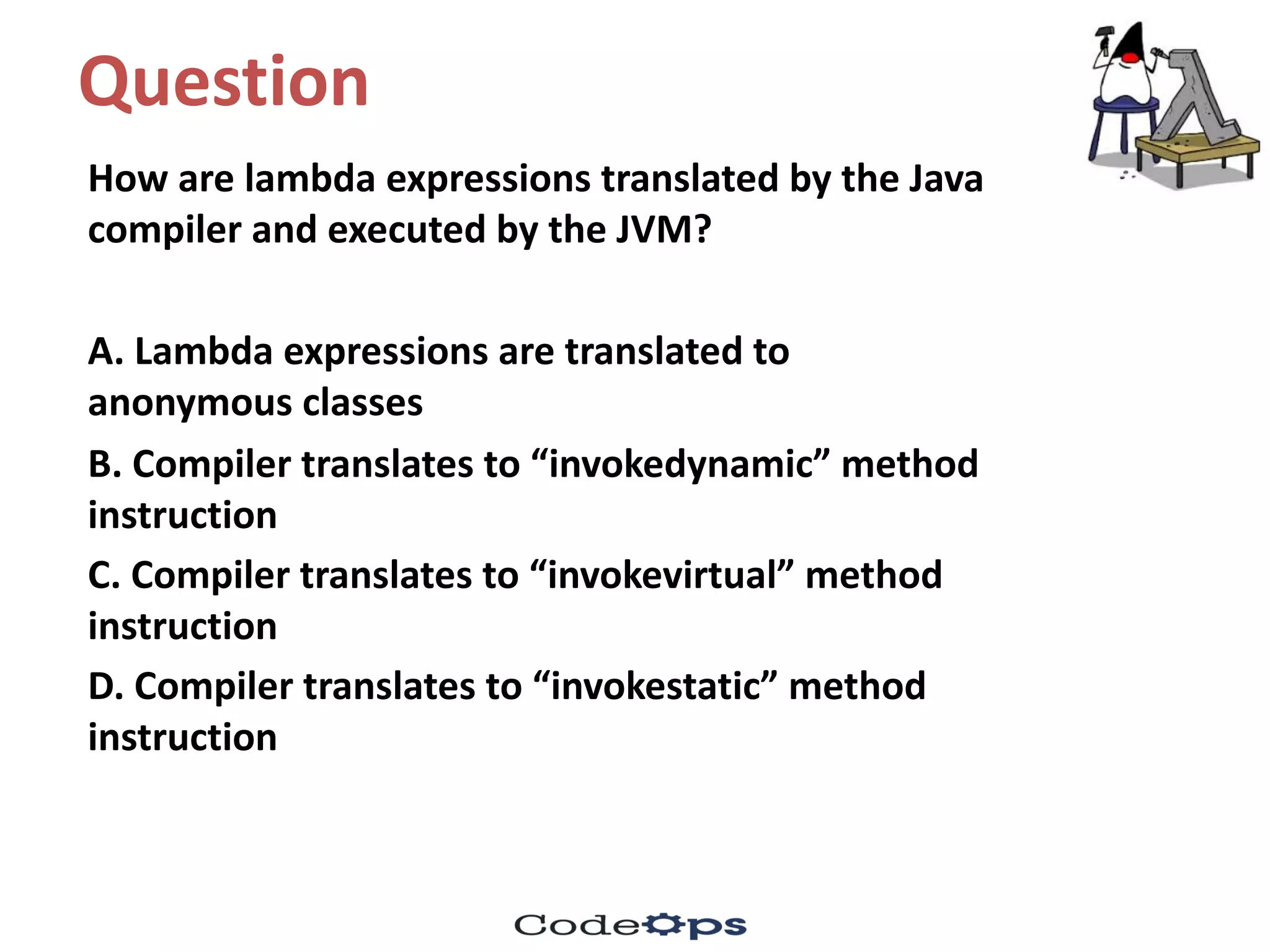
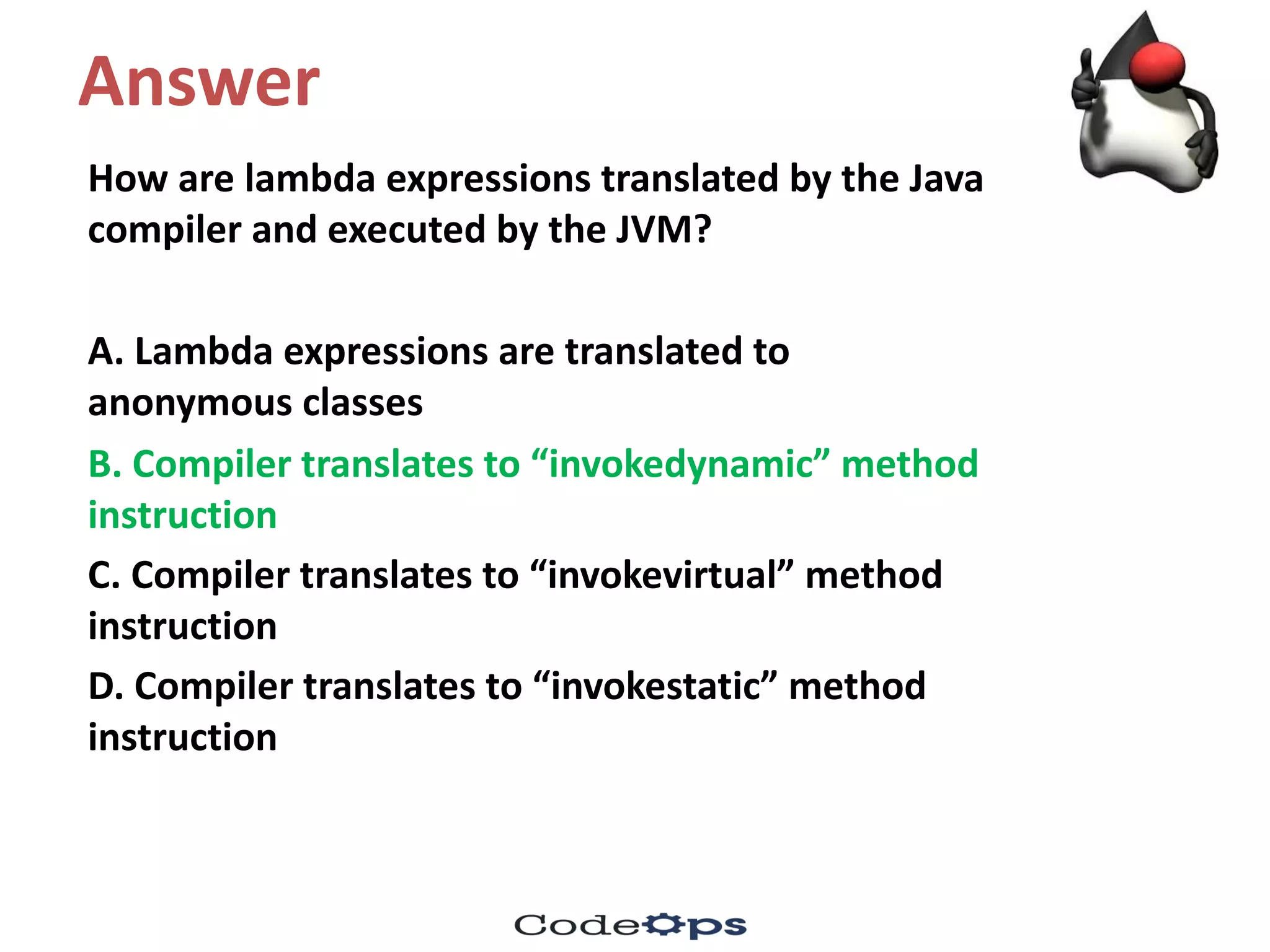
![Explanation
C. invokedynamic method instruction
Lambda functions, streams API, and Joda library as
date/time API were introduced in Java version 8.
The invokedynamic method instruction was introduced in
Java 7.
[When functional programming support was added in the
form of lambda functions was added in Java 8, the
compiler and JVM were enhanced to use invokedynamic
instruction.]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-17-2048.jpg)
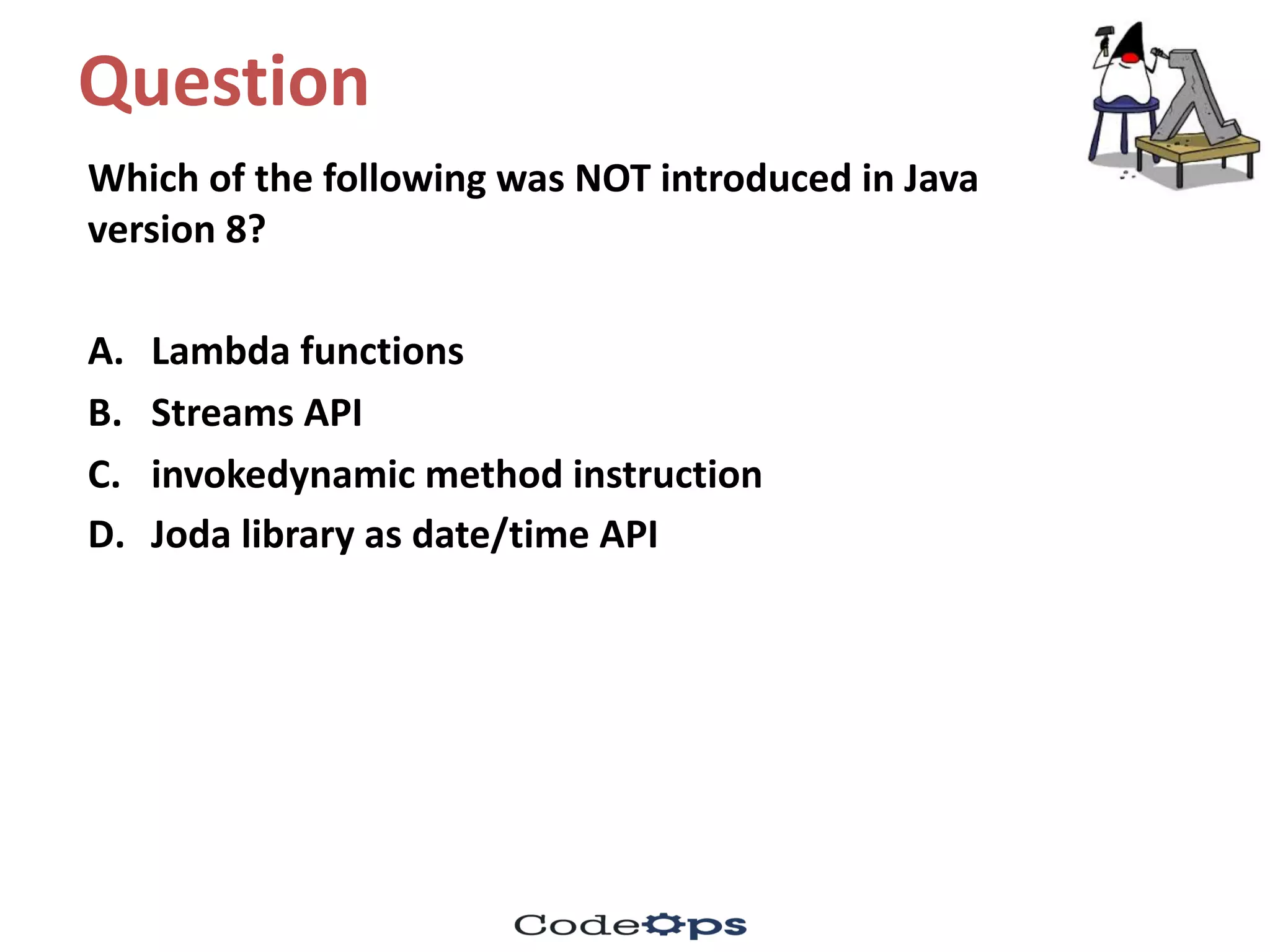
![Question
class Base {}
class DeriOne extends Base {}
class DeriTwo extends Base {}
class ArrayStore {
public static void main(String []args) {
Base [] baseArr = new DeriOne[3];
baseArr[0] = new DeriOne();
baseArr[2] = new DeriTwo();
System.out.println(baseArr.length);
}
}
A. This program prints the following: 3
B. This program prints the following: 2
C. This program throws an ArrayStoreException
D. This program throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-18-2048.jpg)
![Answer
class Base {}
class DeriOne extends Base {}
class DeriTwo extends Base {}
class ArrayStore {
public static void main(String []args) {
Base [] baseArr = new DeriOne[3];
baseArr[0] = new DeriOne();
baseArr[2] = new DeriTwo();
System.out.println(baseArr.length);
}
}
A. This program prints the following: 3
B. This program prints the following: 2
C. This program throws an ArrayStoreException
D. This program throws an ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-19-2048.jpg)
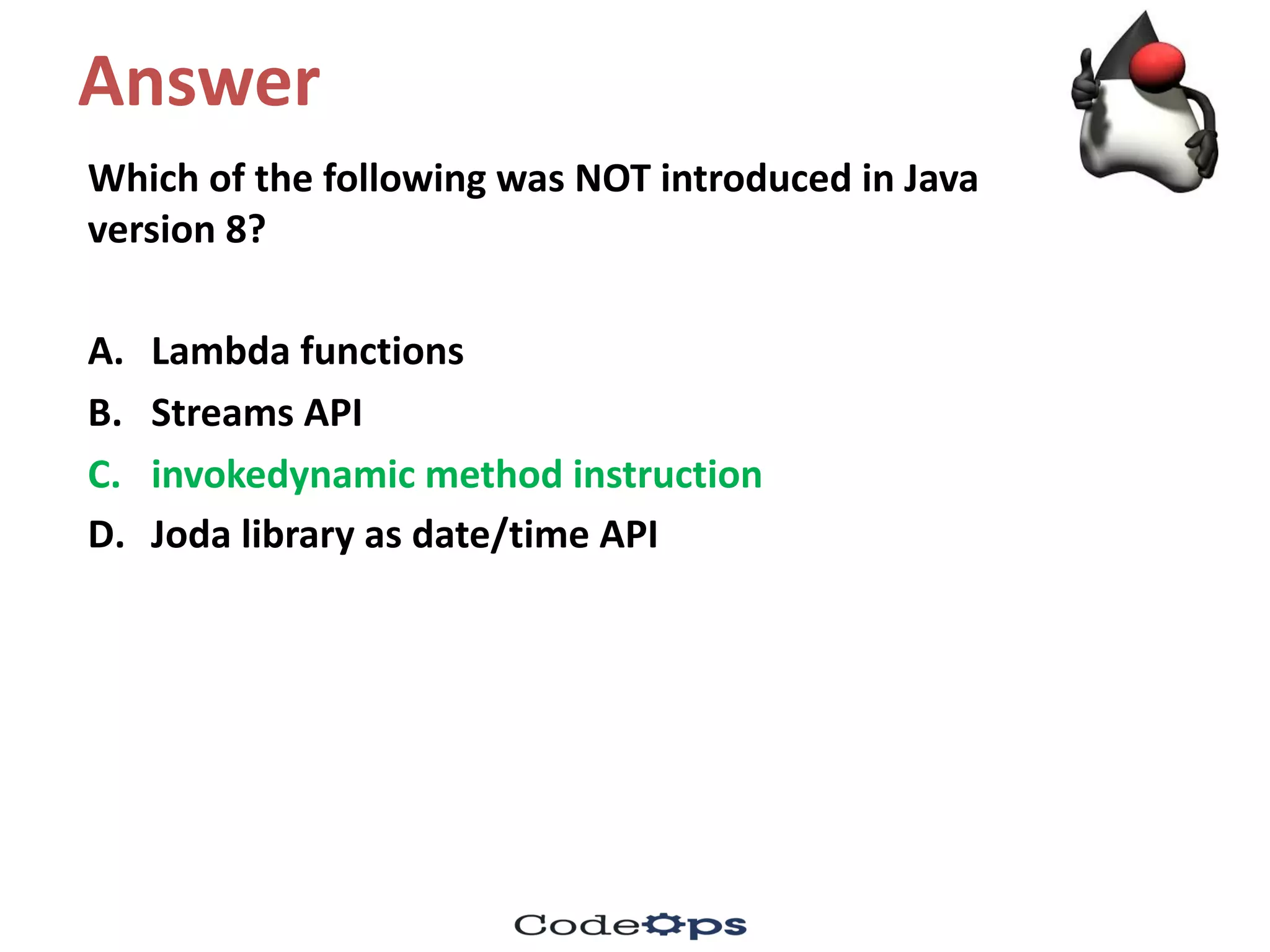
![Explanation
C. This program throws an ArrayStoreException
The variable baseArr is of type Base[] , and it points to
an array of type DeriOne.
However, in the statement baseArr[2] = new
DeriTwo(), an object of type DeriTwo is assigned to
the type DeriOne, which does not share a parent-child
inheritance relationship-they only have a common
parent, which is Base. Hence, this assignment results
in an ArrayStoreException.
Discussion: What is the best practice here?](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-20-2048.jpg)
![Question
import java.util.*;
class UtilitiesTest {
public static void main(String []args) {
List<Integer> intList = new LinkedList<>();
List<Double> dblList = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.println(intList.getClass() == dblList.getClass());
}
}
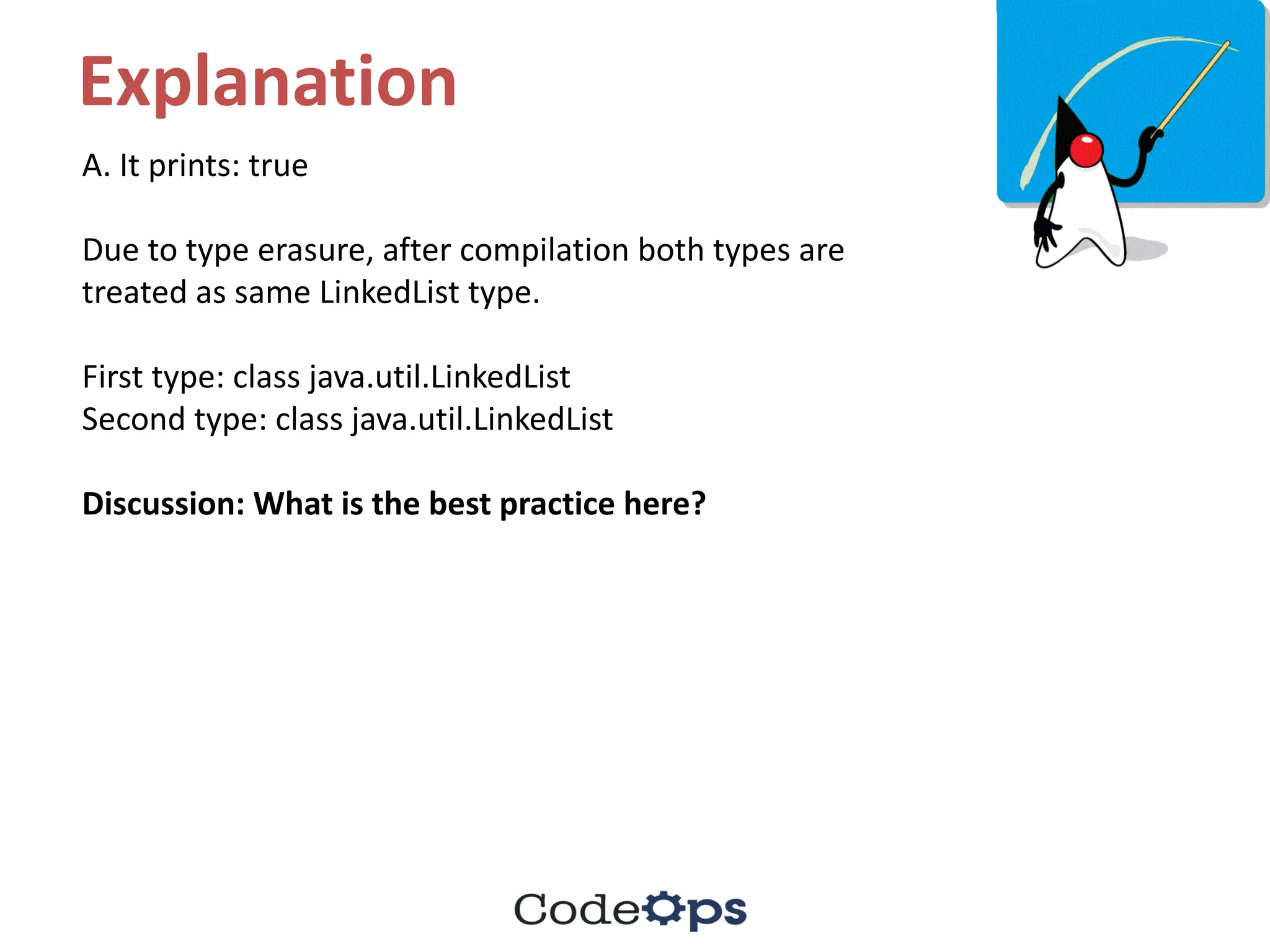
A. It prints: true
B. It prints: false
C. It results in a compiler error
D. It results in a runtime exception](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-21-2048.jpg)
![Answer
import java.util.*;
class UtilitiesTest {
public static void main(String []args) {
List<Integer> intList = new LinkedList<>();
List<Double> dblList = new LinkedList<>();
System.out.println(intList.getClass() == dblList.getClass());
}
}
A. It prints: true
B. It prints: false
C. It results in a compiler error
D. It results in a runtime exception](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-22-2048.jpg)
![Question
Consider the following program:
class AutoCloseableTest {
public static void main(String []args) {
try (Scanner consoleScanner = new Scanner(System.in)) {
consoleScanner.close(); // CLOSE
consoleScanner.close();
}
}
}
Which one of the following statements is correct?
A. This program terminates normally without throwing any exceptions
B. This program throws an IllegalStateException
C. This program throws an IOException
D. This program throws an AlreadyClosedException
E. This program results in a compiler error in the line marked with the
comment CLOSE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-24-2048.jpg)
![Answer
Consider the following program:
class AutoCloseableTest {
public static void main(String []args) {
try (Scanner consoleScanner = new Scanner(System.in)) {
consoleScanner.close(); // CLOSE
consoleScanner.close();
}
}
}
Which one of the following statements is correct?
A. This program terminates normally without throwing any exceptions
B. This program throws an IllegalStateException
C. This program throws an IOException
D. This program throws an AlreadyClosedException
E. This program results in a compiler error in the line marked with the
comment CLOSE](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-25-2048.jpg)








![Question
Consider the following program and determine the output:
class Test {
public void print(Integer i) {
System.out.println("Integer");
}
public void print(int i) {
System.out.println("int");
}
public void print(long i) {
System.out.println("long");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Test test = new Test();
test.print(10);
}
}
A. The program results in a compiler error (“ambiguous overload”)
B. long
C. Integer
D. int](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-36-2048.jpg)
![Answer
Consider the following program and determine the output:
class Test {
public void print(Integer i) {
System.out.println("Integer");
}
public void print(int i) {
System.out.println("int");
}
public void print(long i) {
System.out.println("long");
}
public static void main(String args[]) {
Test test = new Test();
test.print(10);
}
}
A. The program results in a compiler error (“ambiguous overload”)
B. long
C. Integer
D. int](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/fifthmeetup-javabestpracticesandelasticsearch1-oct-16-quiz-161001161047/75/Core-Java-Best-practices-and-bytecodes-quiz-37-2048.jpg)