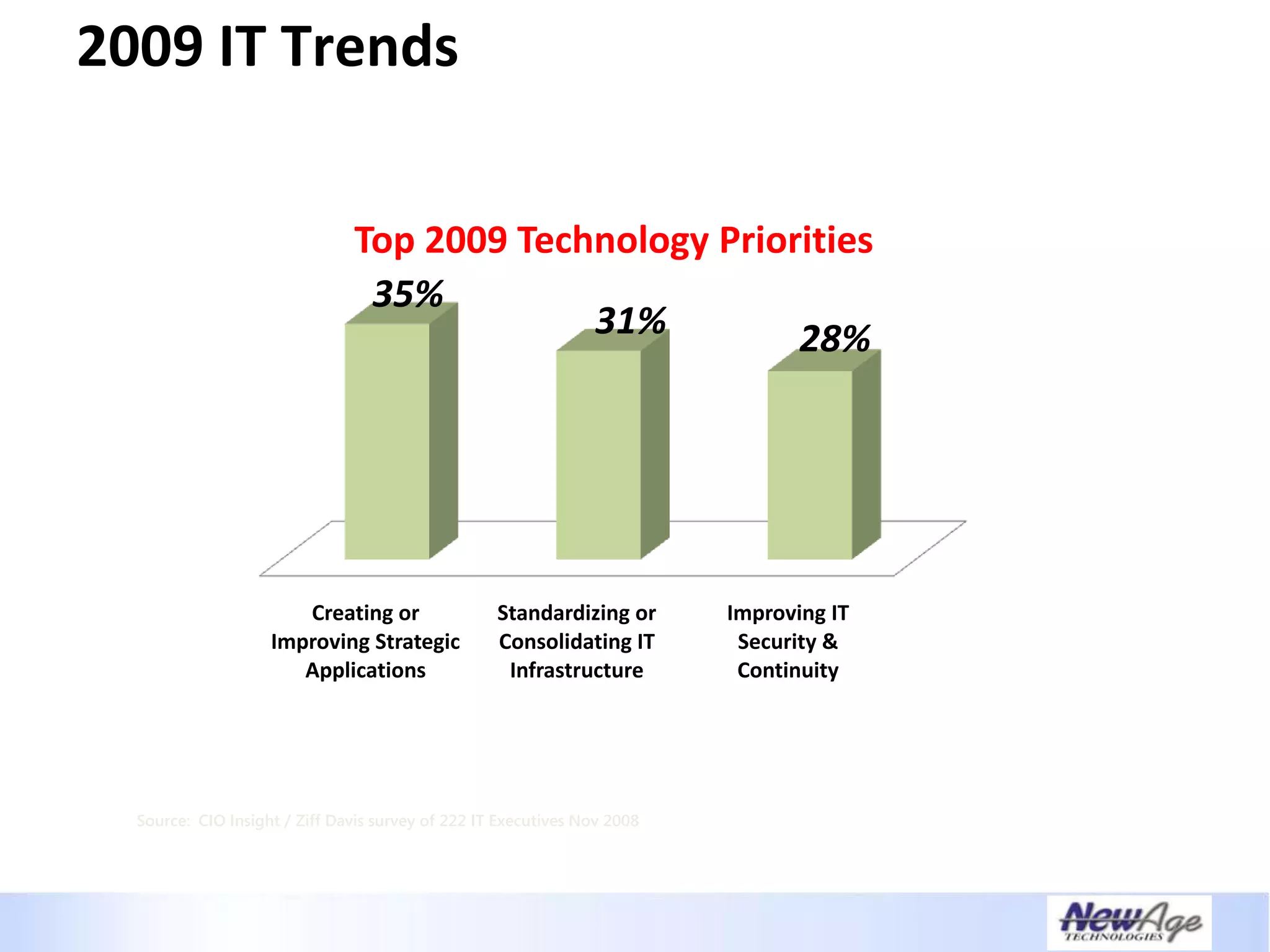
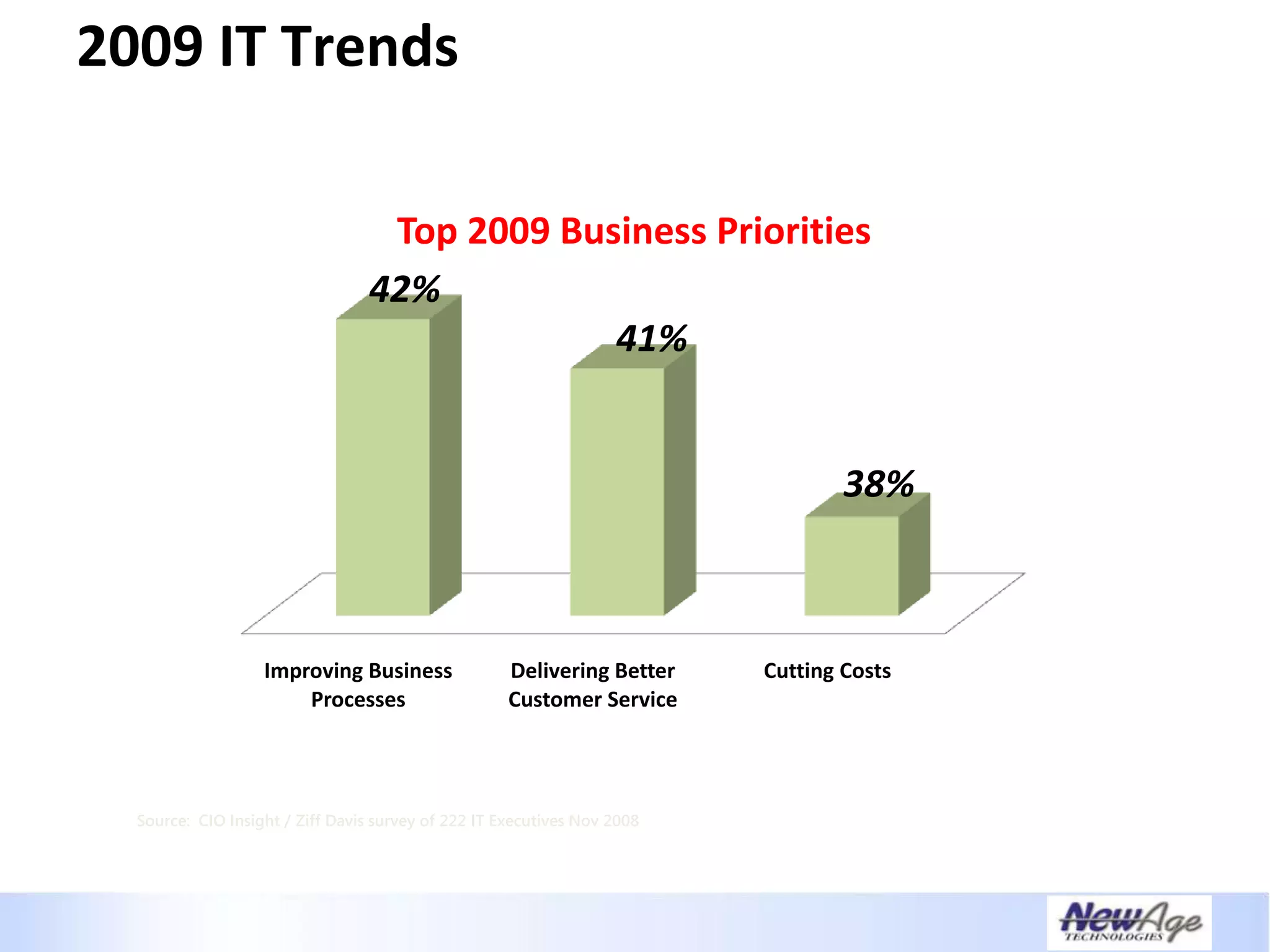
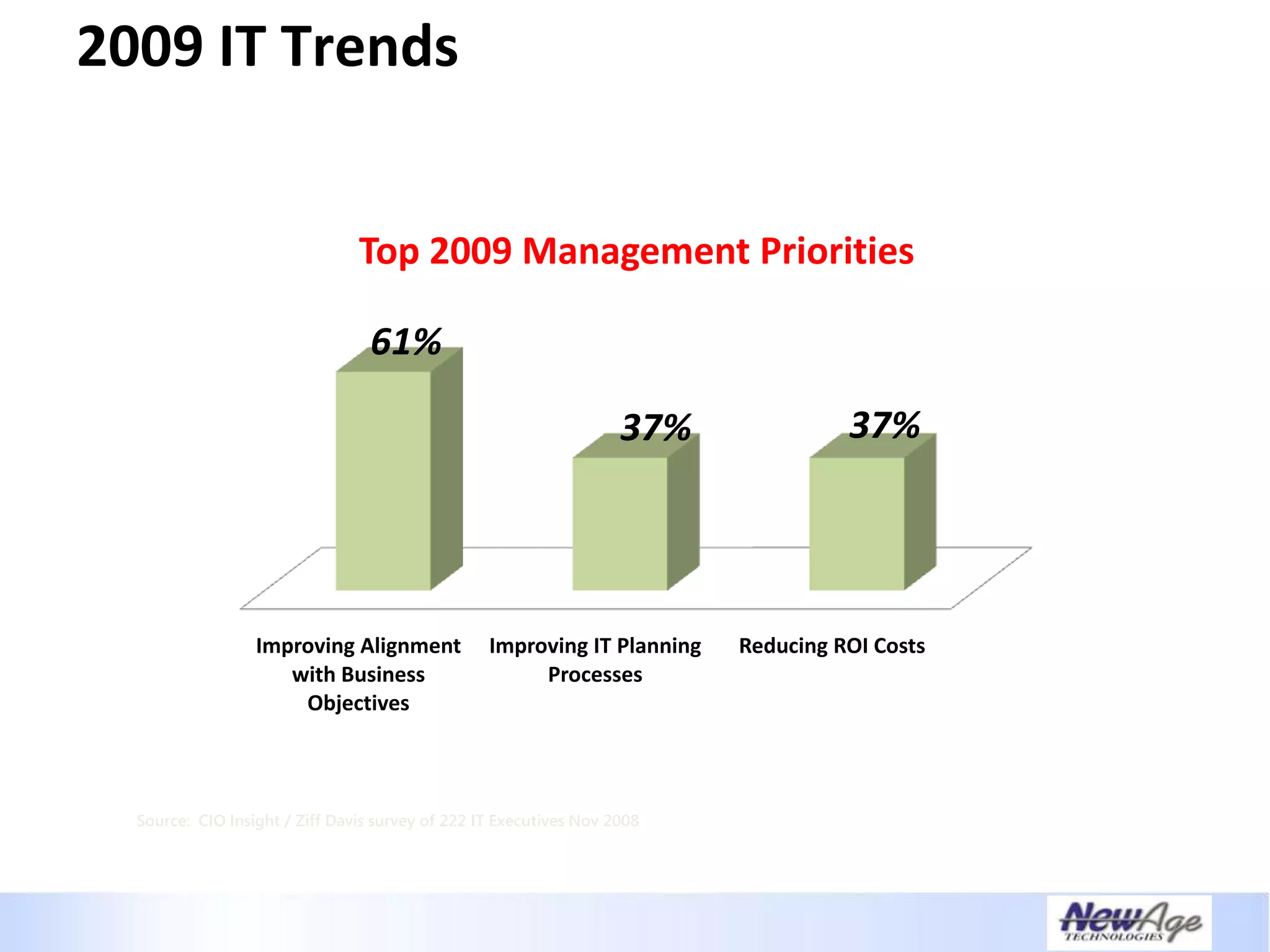
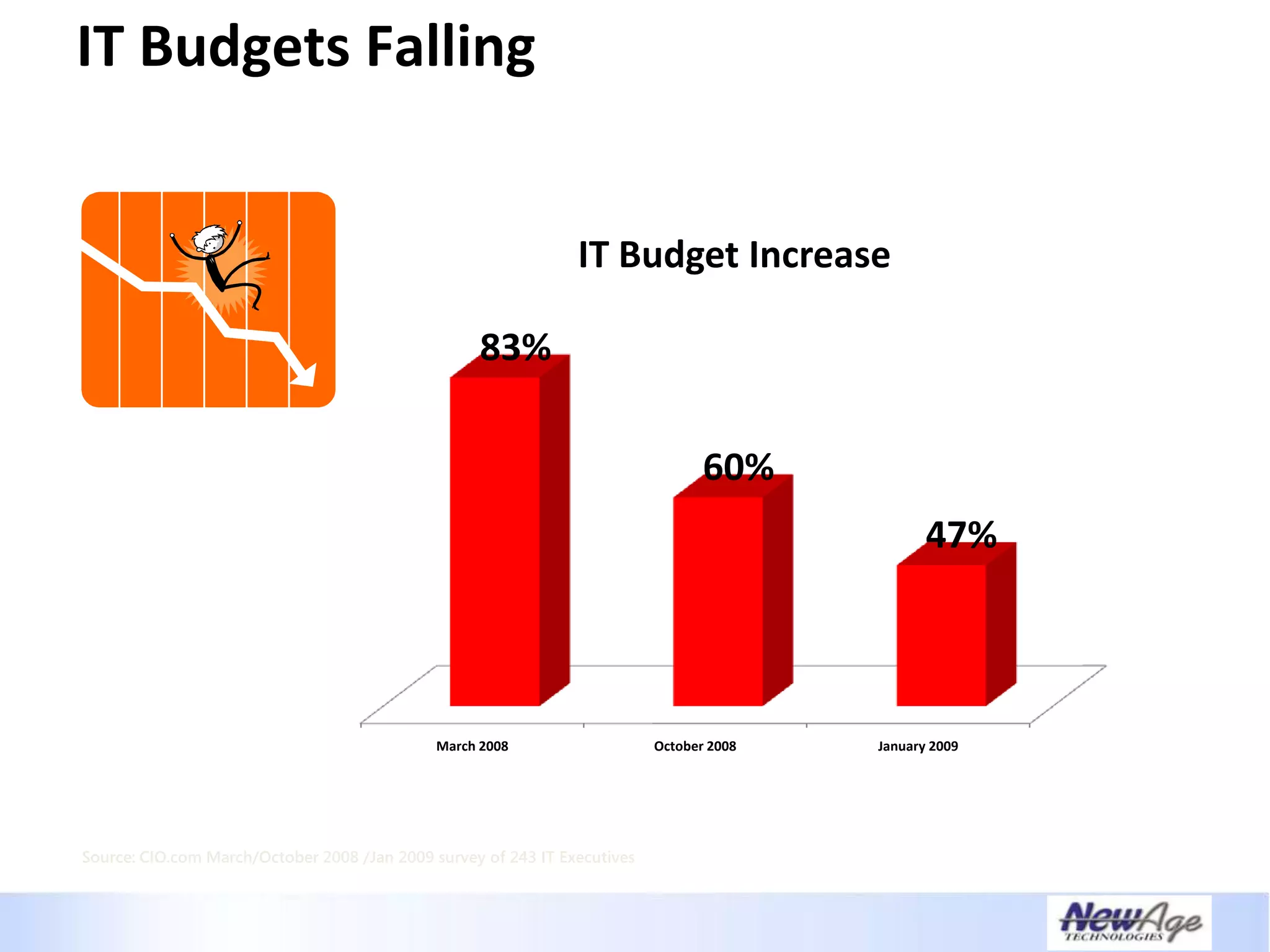
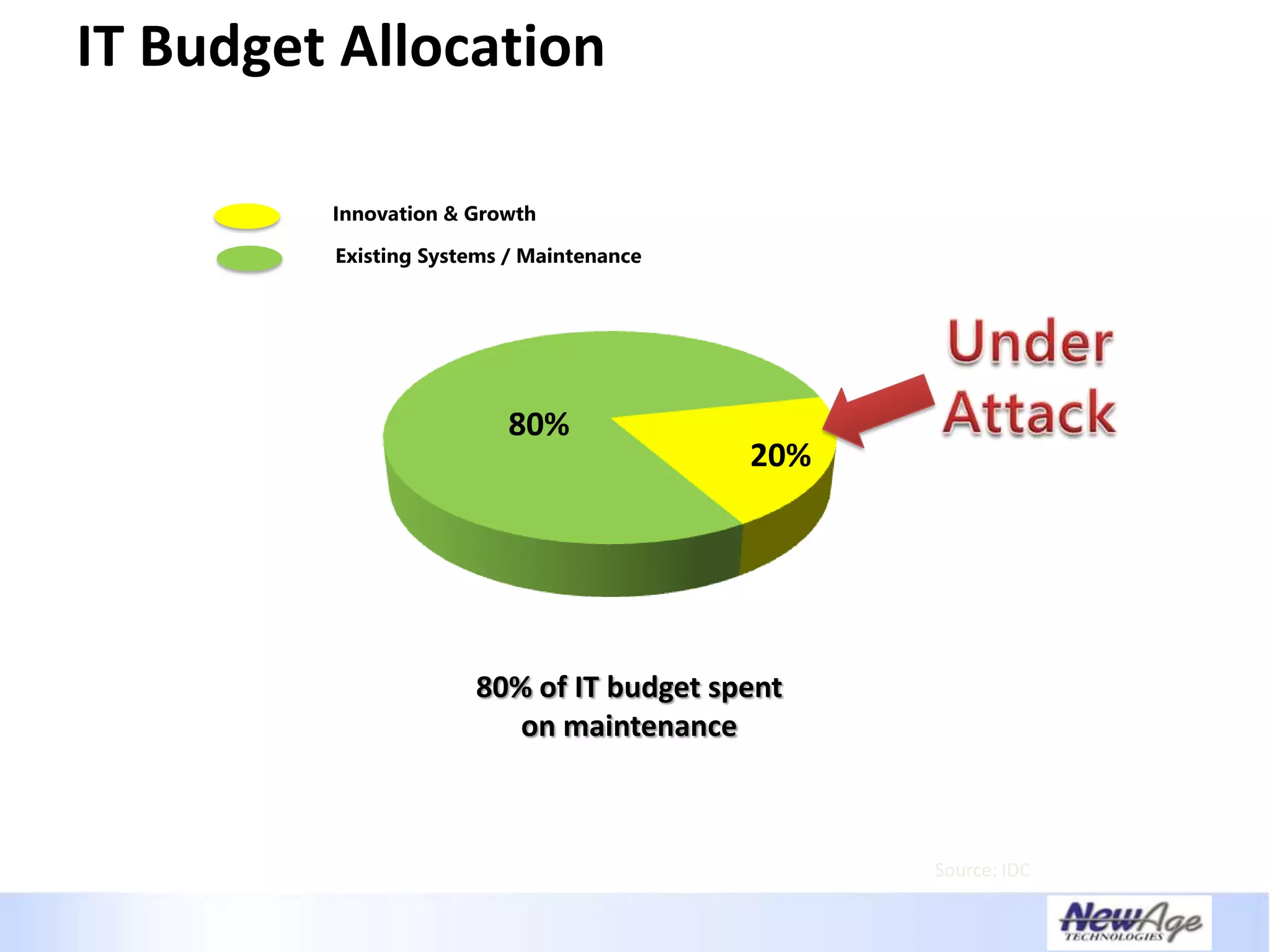
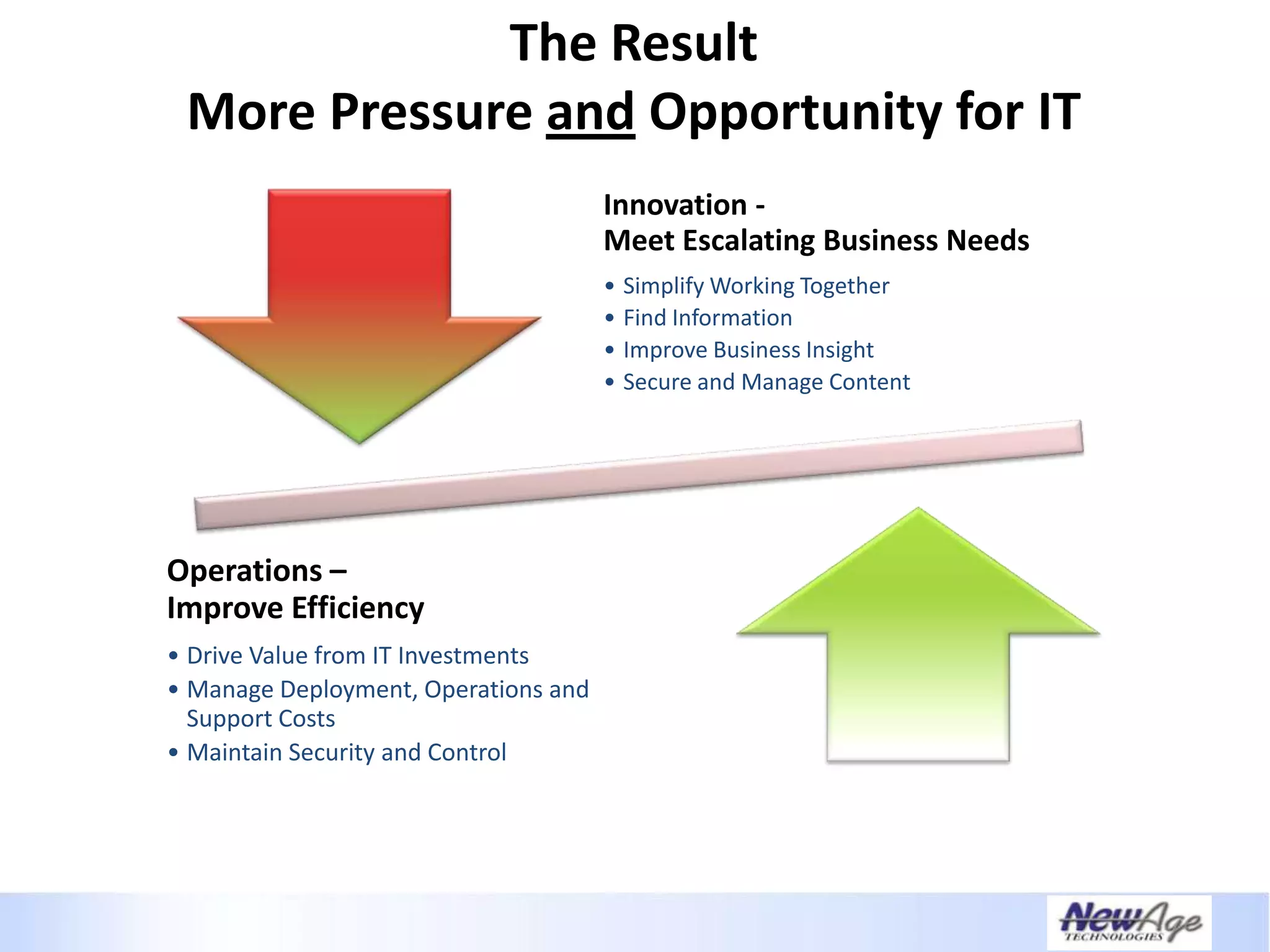
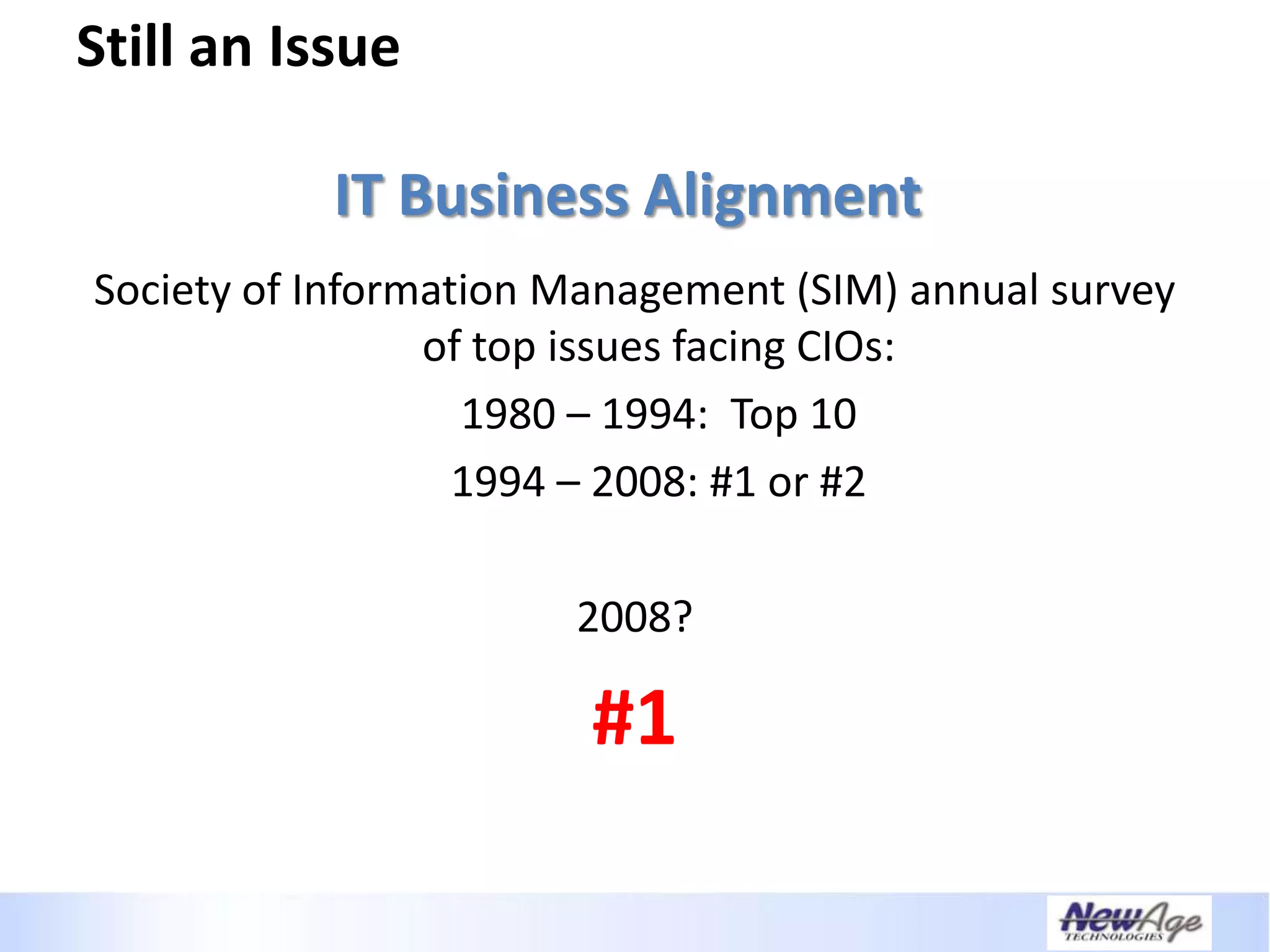
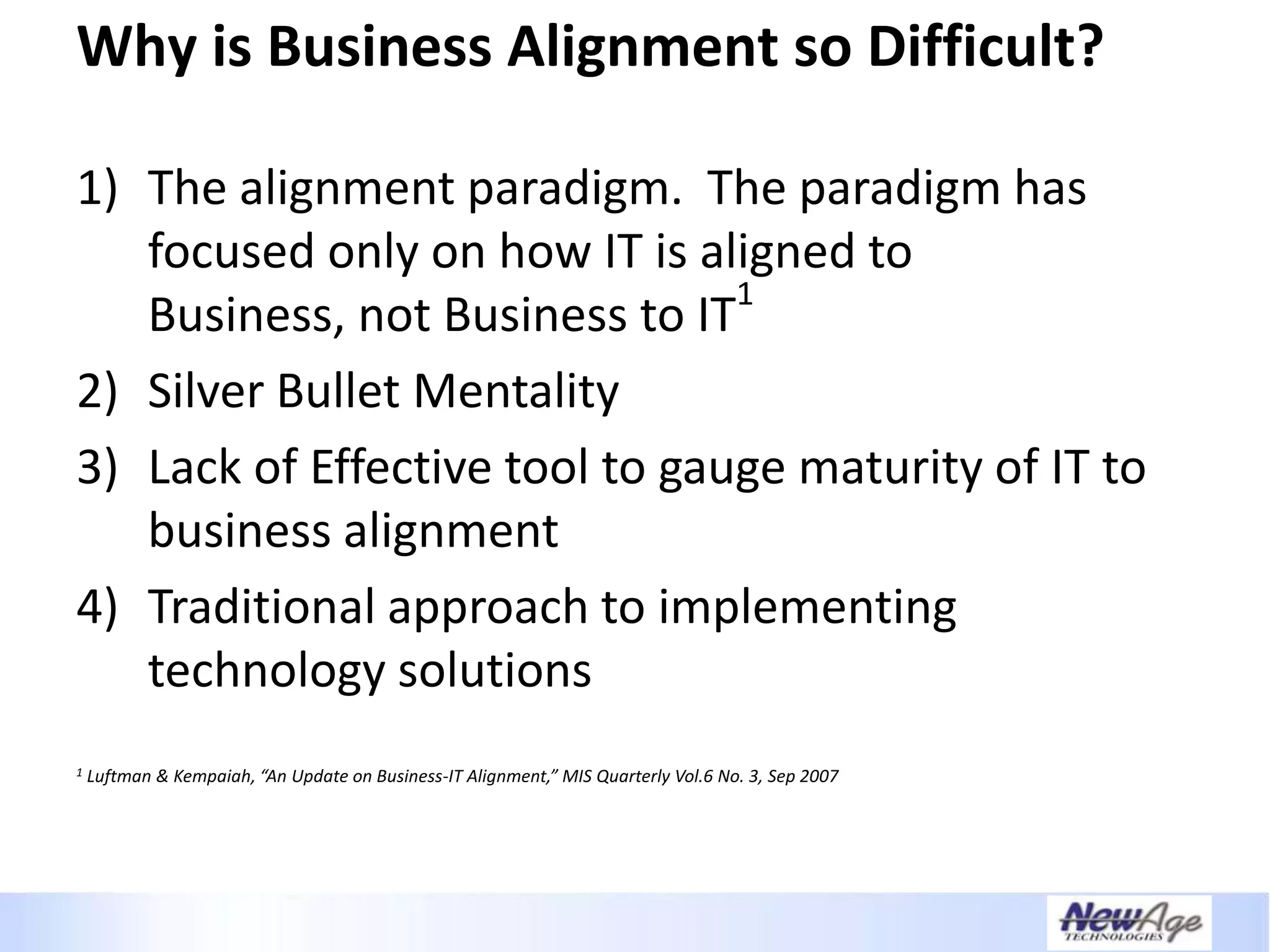
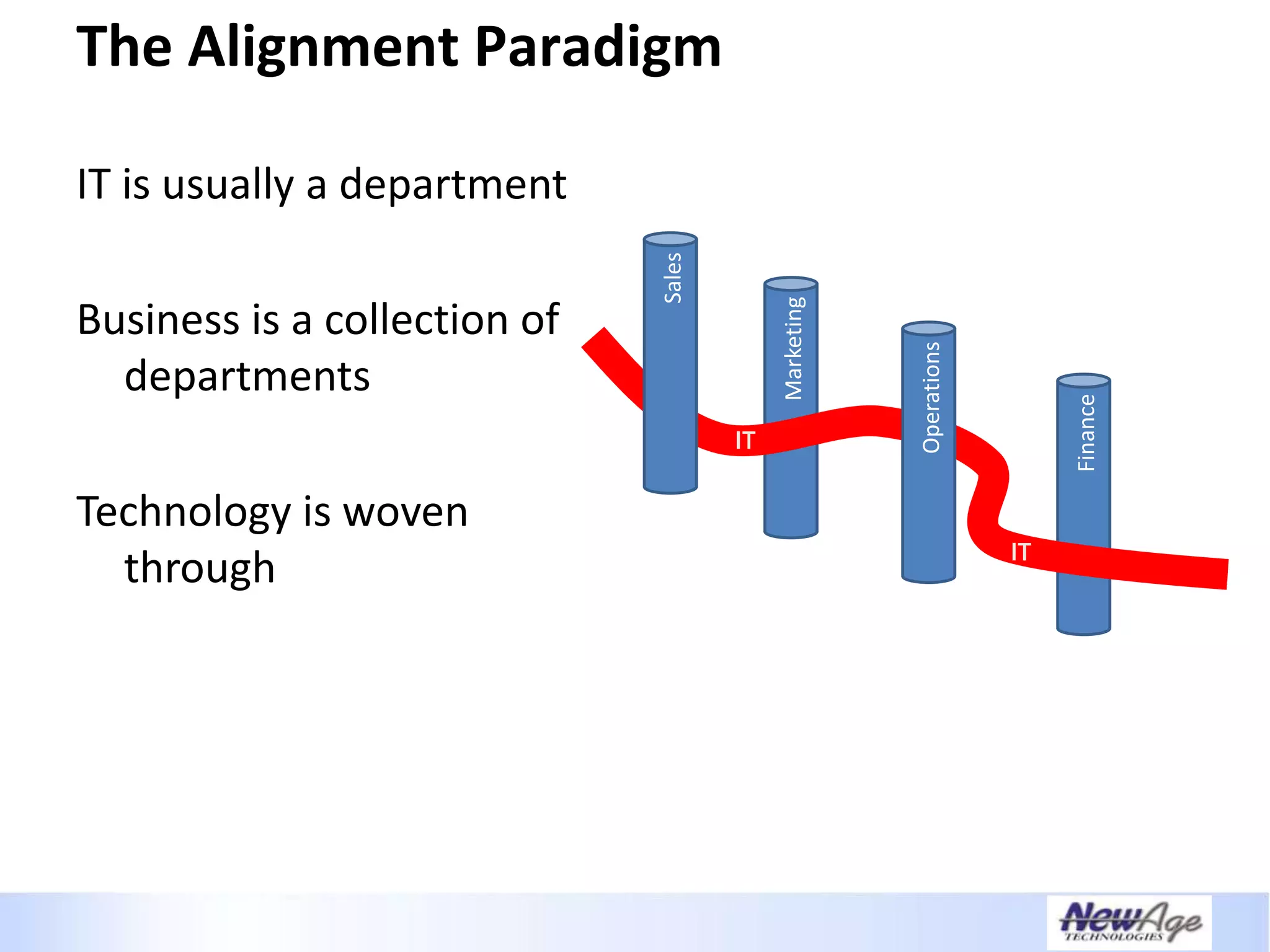
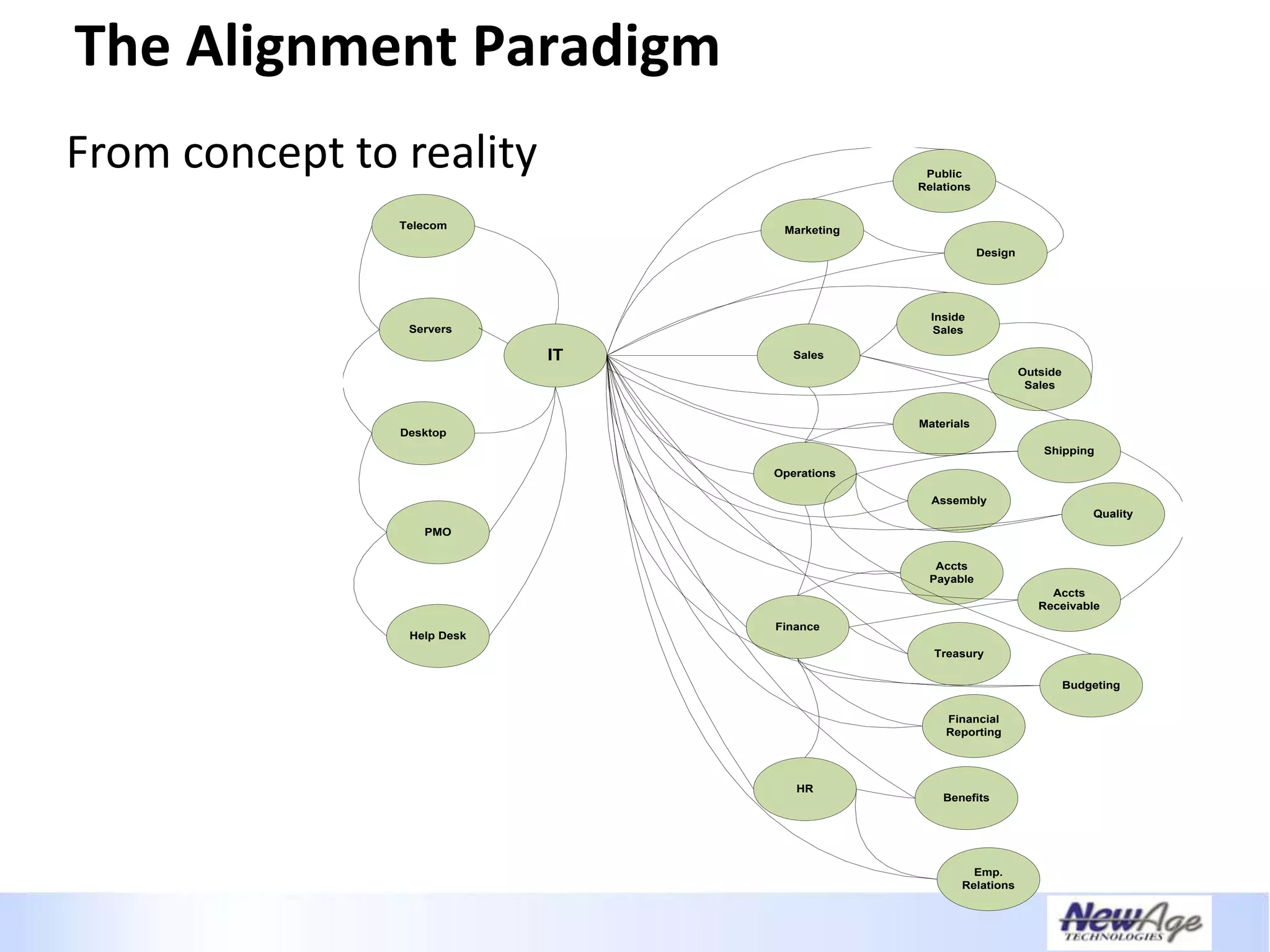
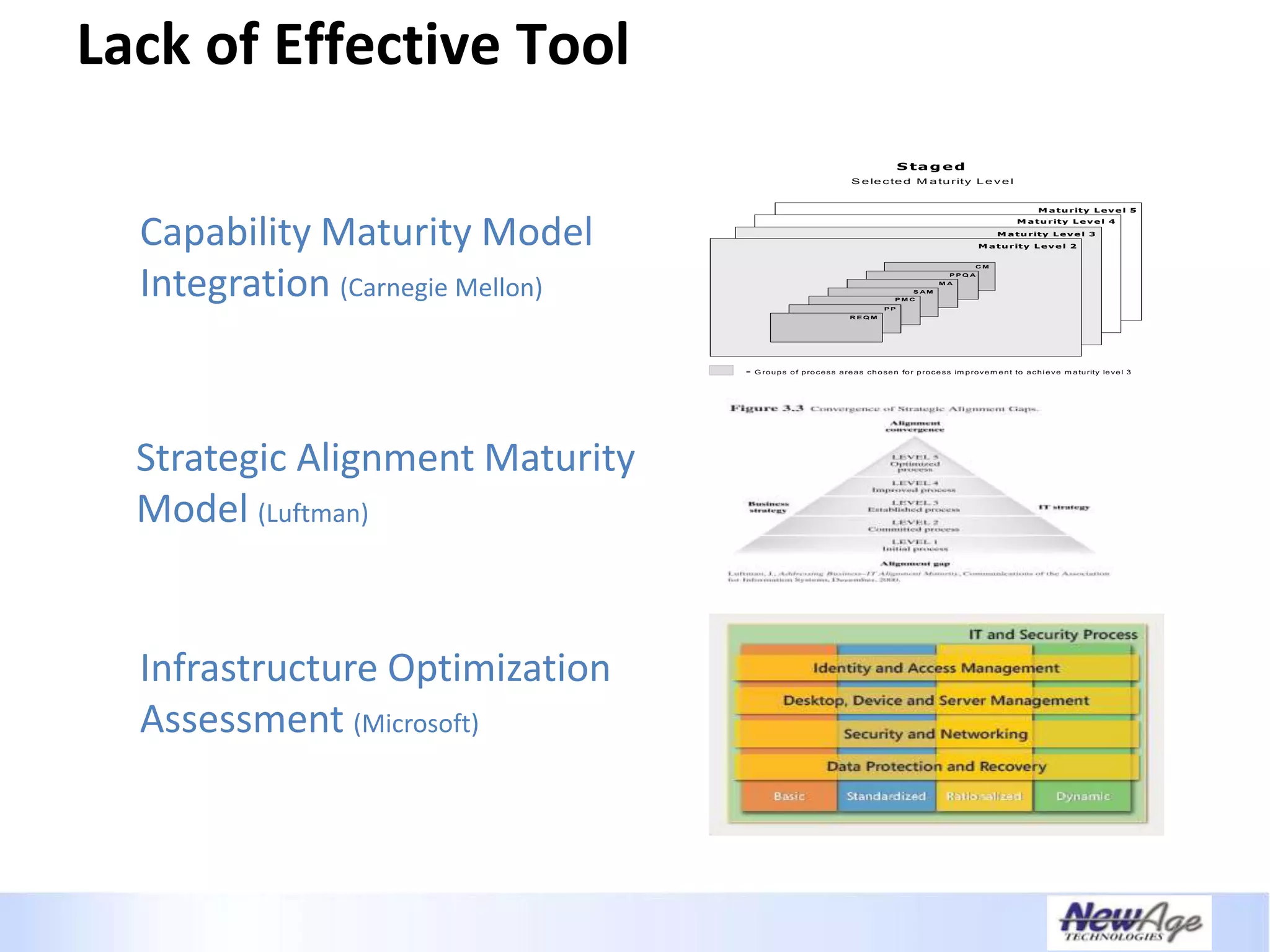
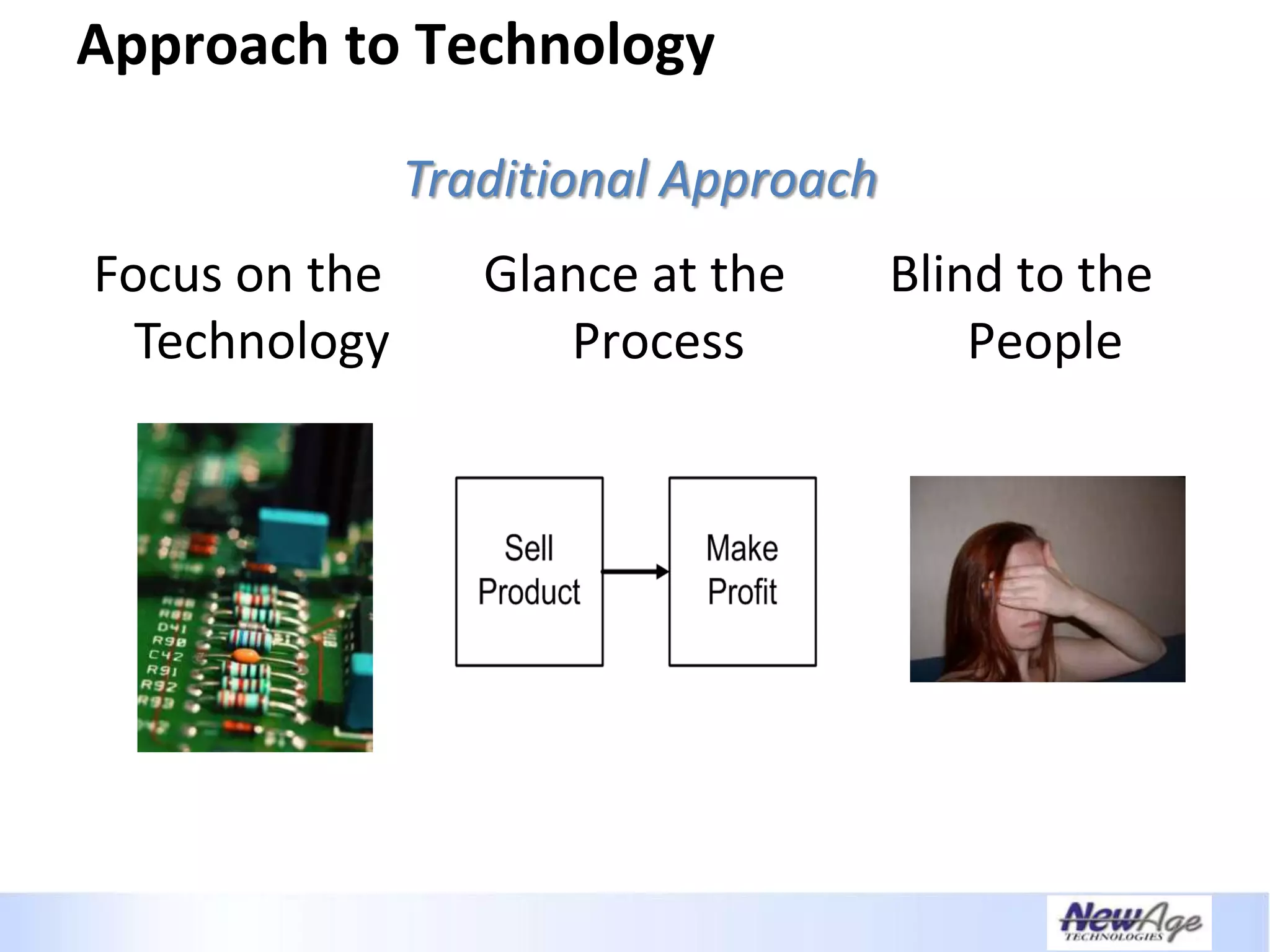
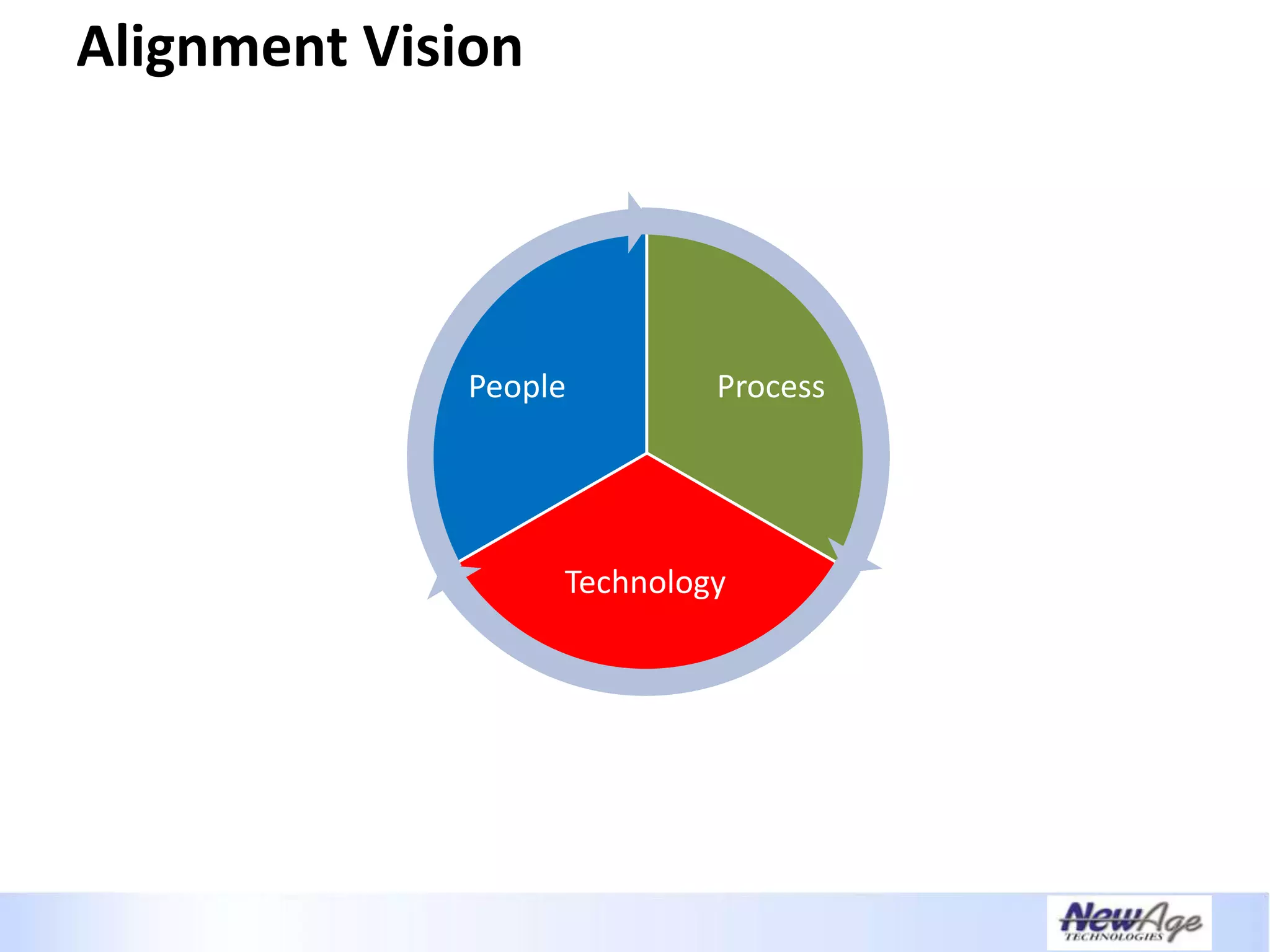
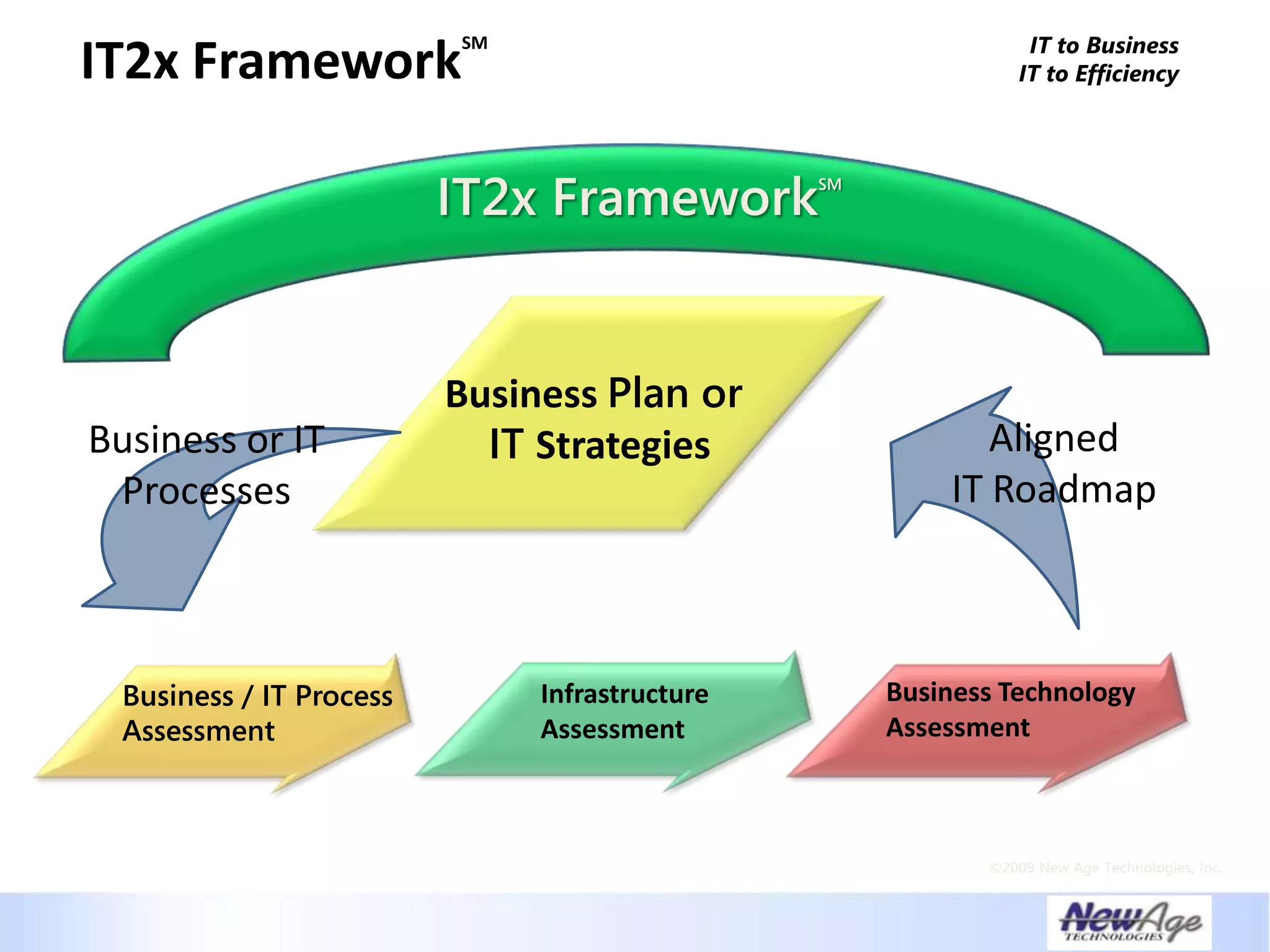
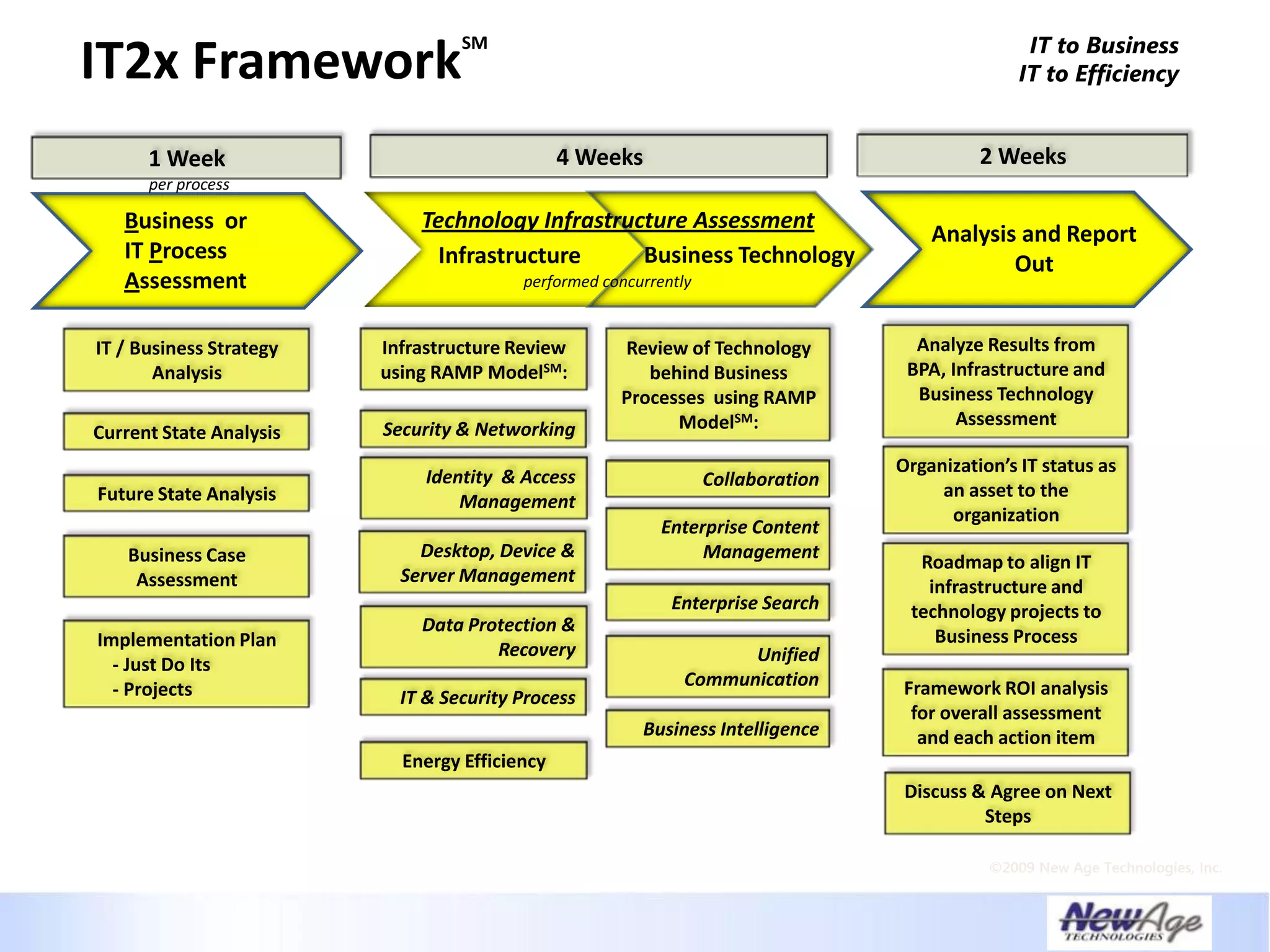
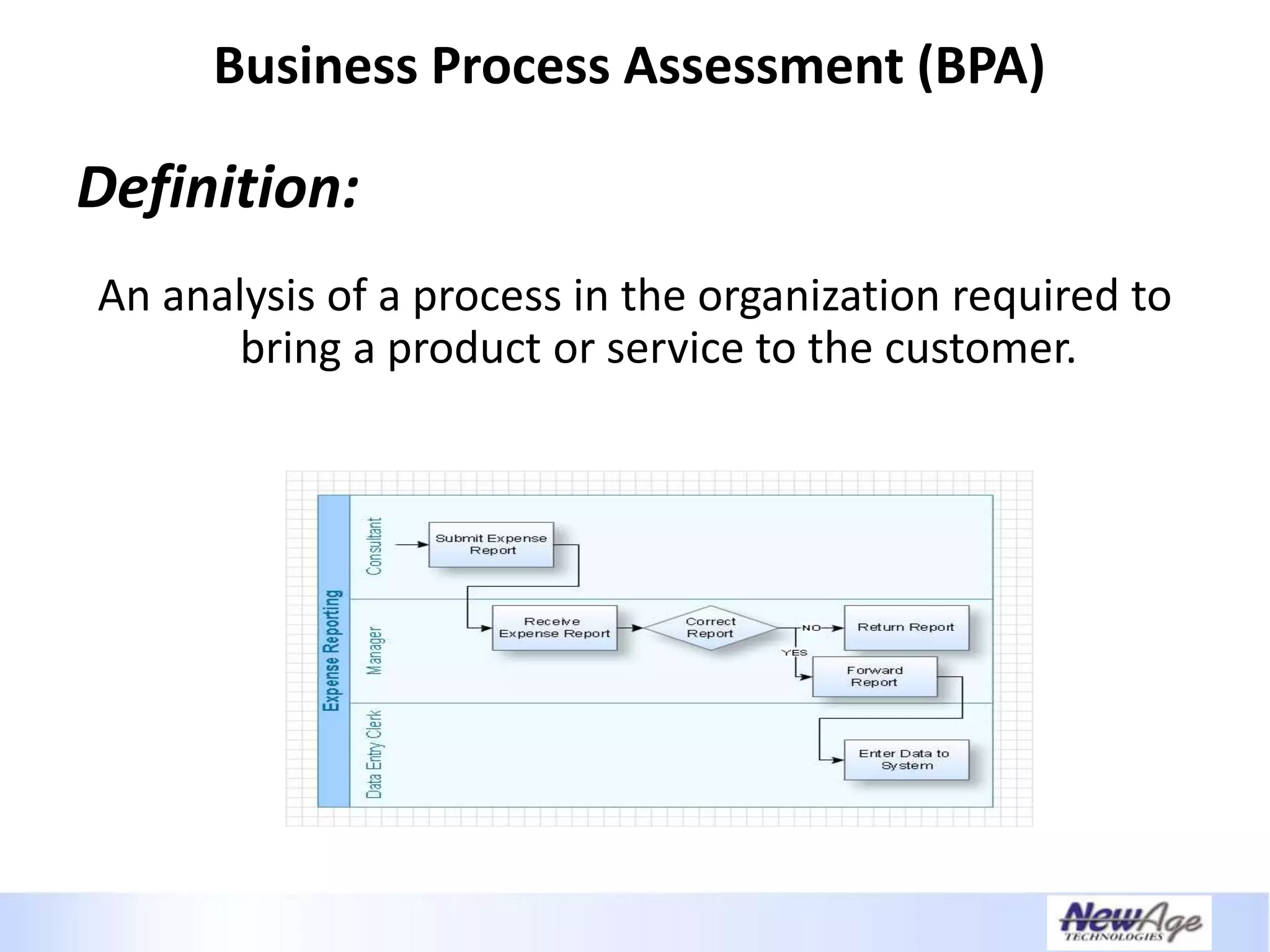
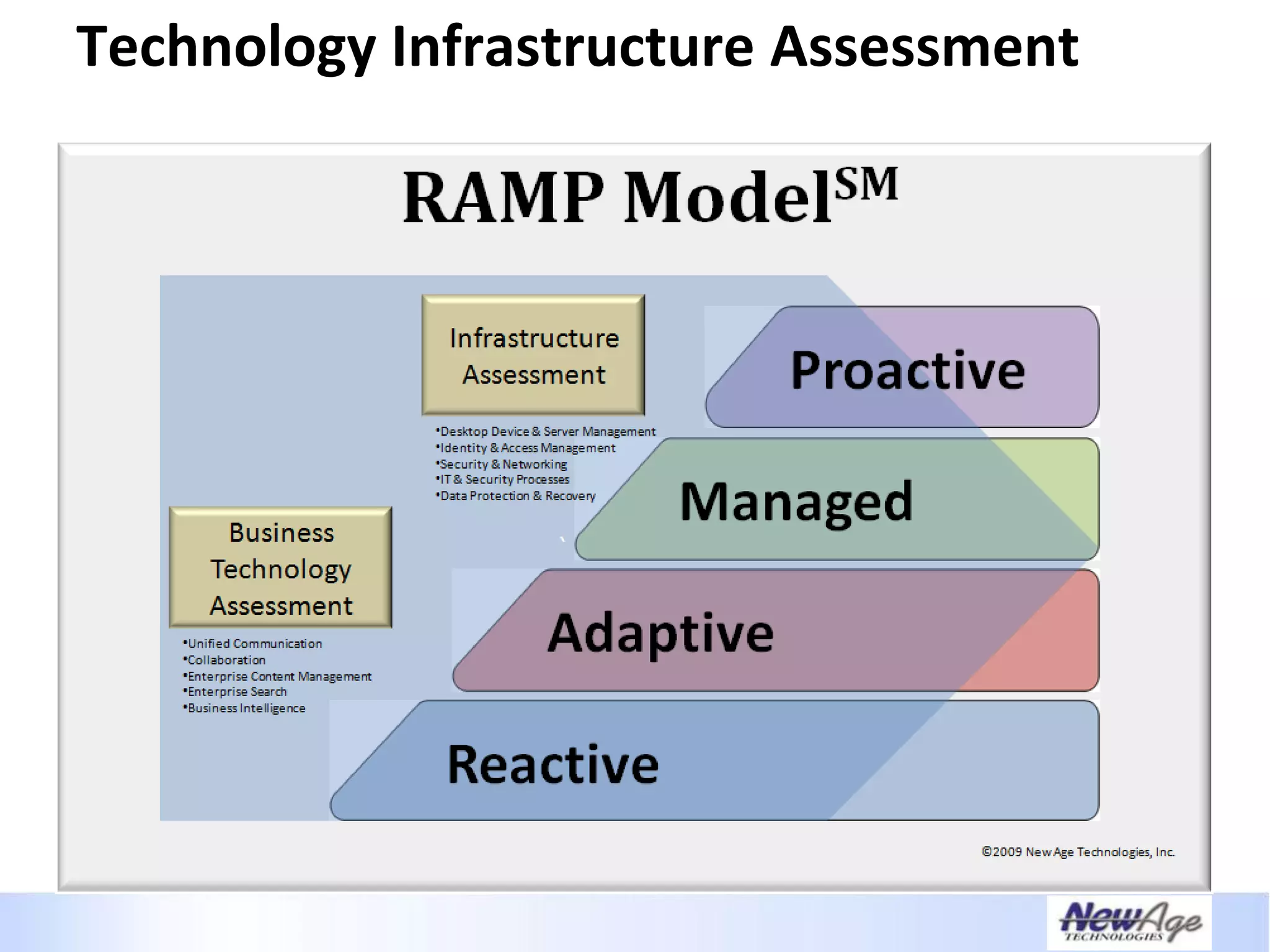
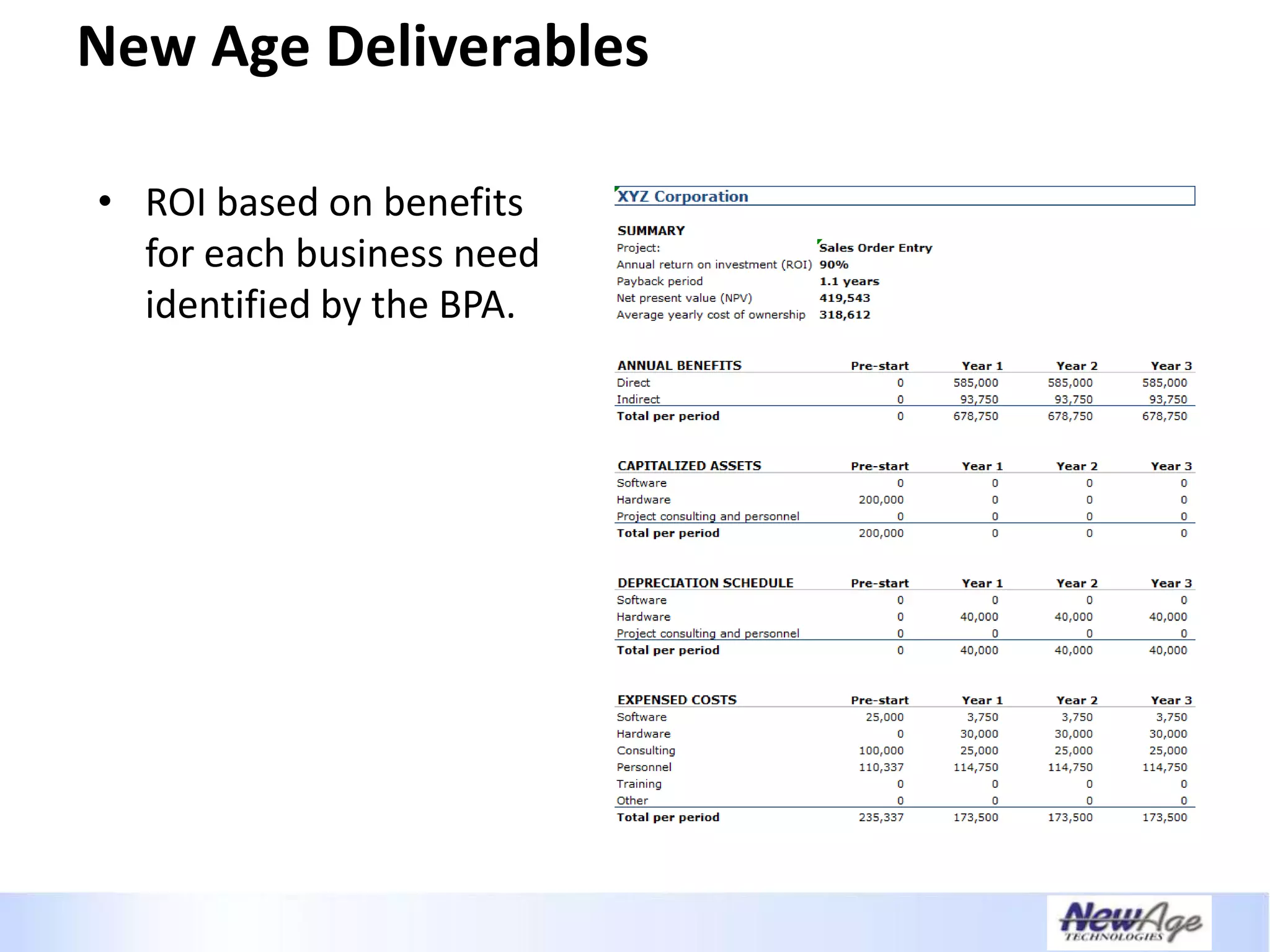
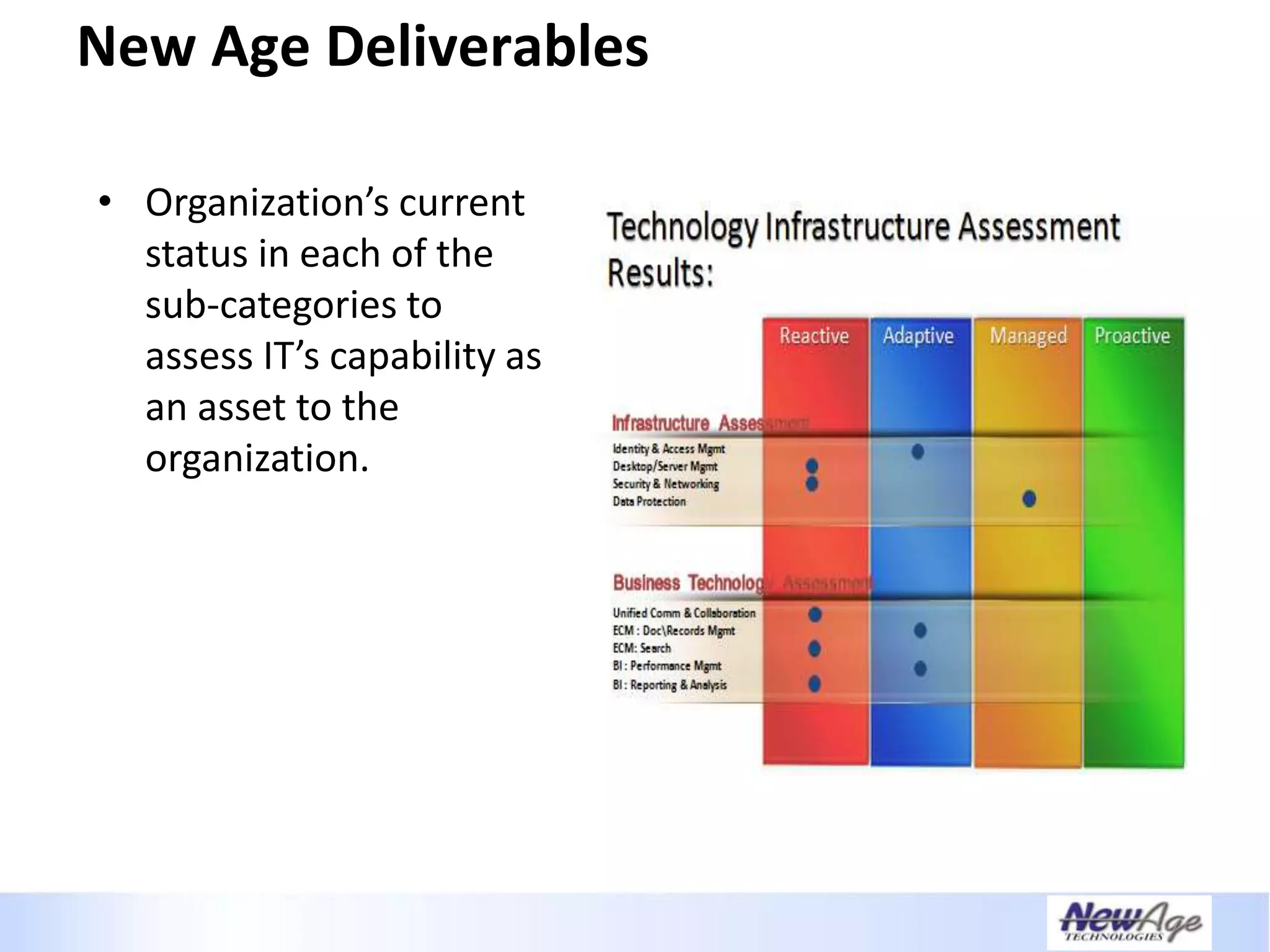
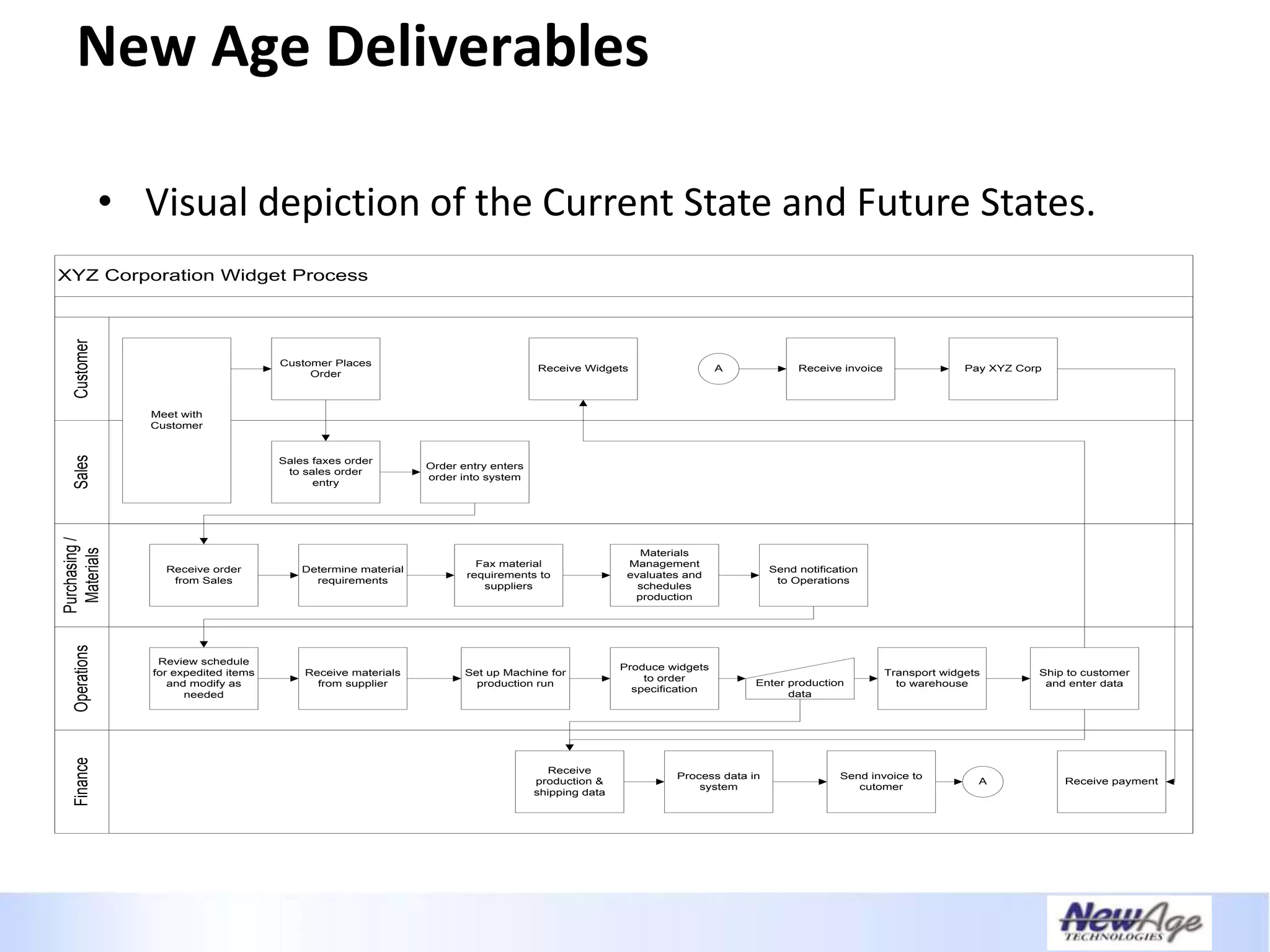
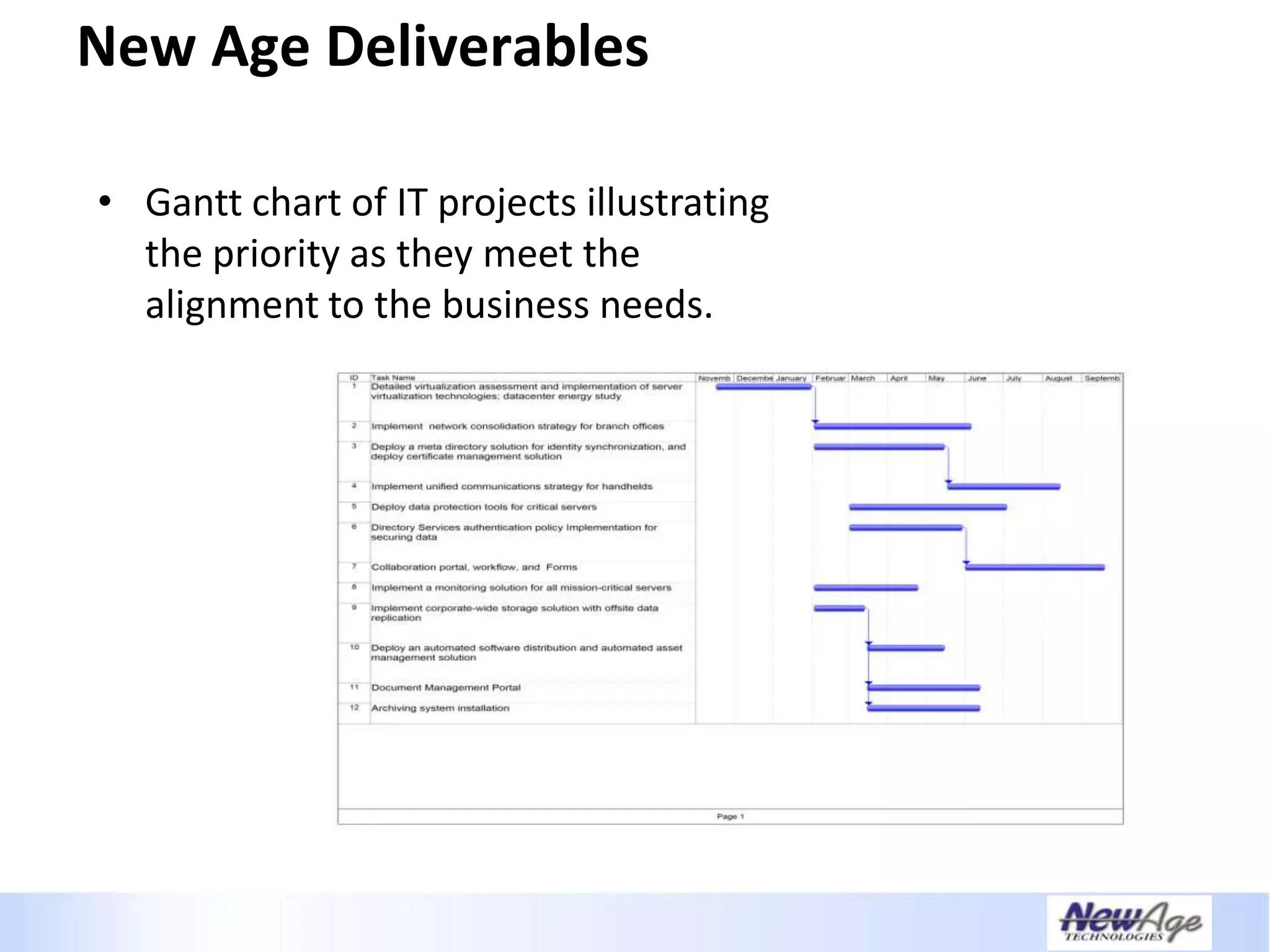
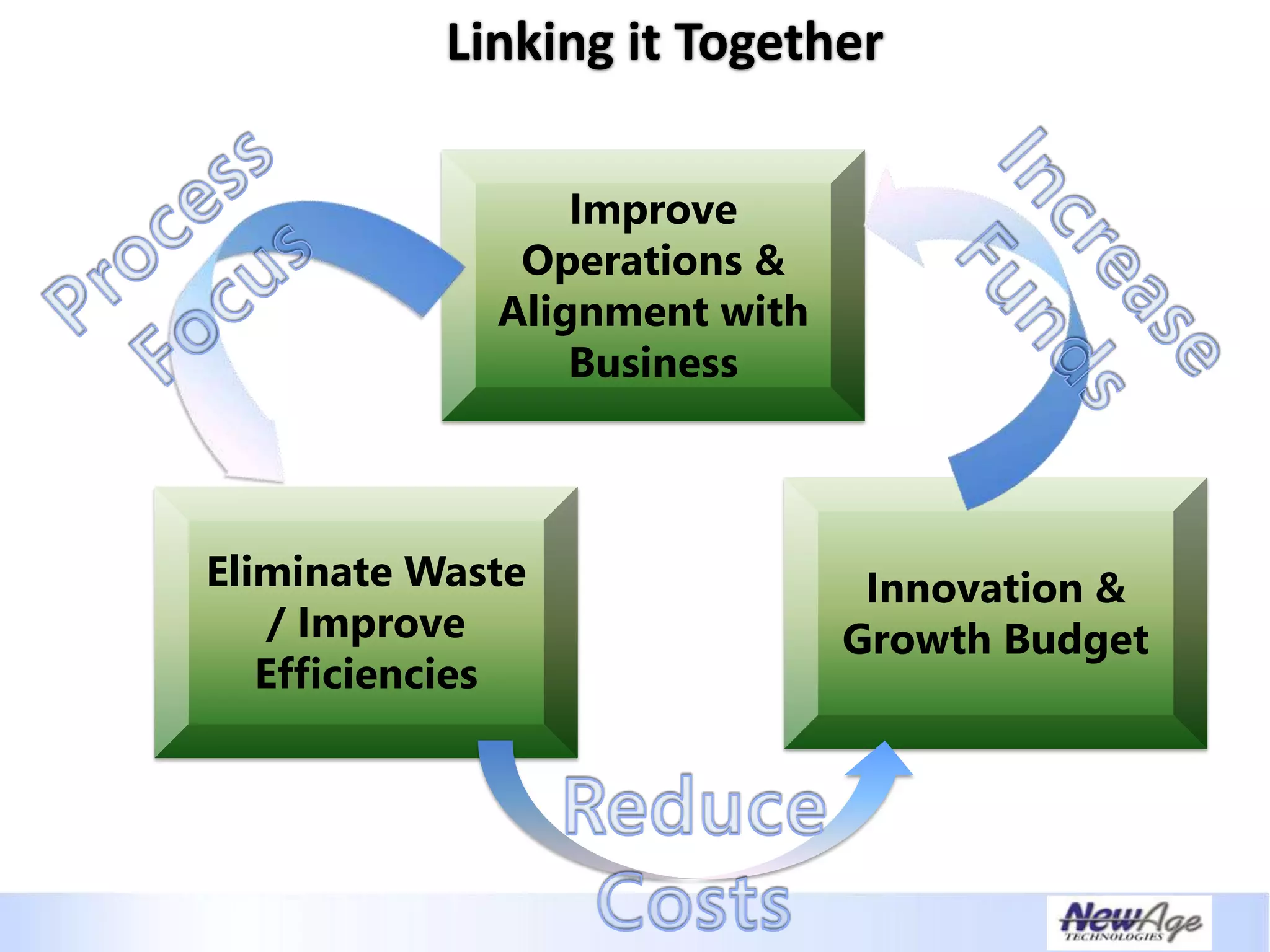
The document discusses IT business alignment and how creating dependence between IT and business leaders is necessary to achieve alignment. It outlines challenges to alignment like focusing only on how IT aligns to business, a lack of tools to measure maturity, and traditional technology-focused solutions. The document proposes an IT2x framework that takes a process-centric approach involving both IT and business to identify projects supporting business goals. This framework aims to eliminate waste, allow more budget for innovation, and provide metrics to improve efficiency and alignment through a shared understanding of goals.