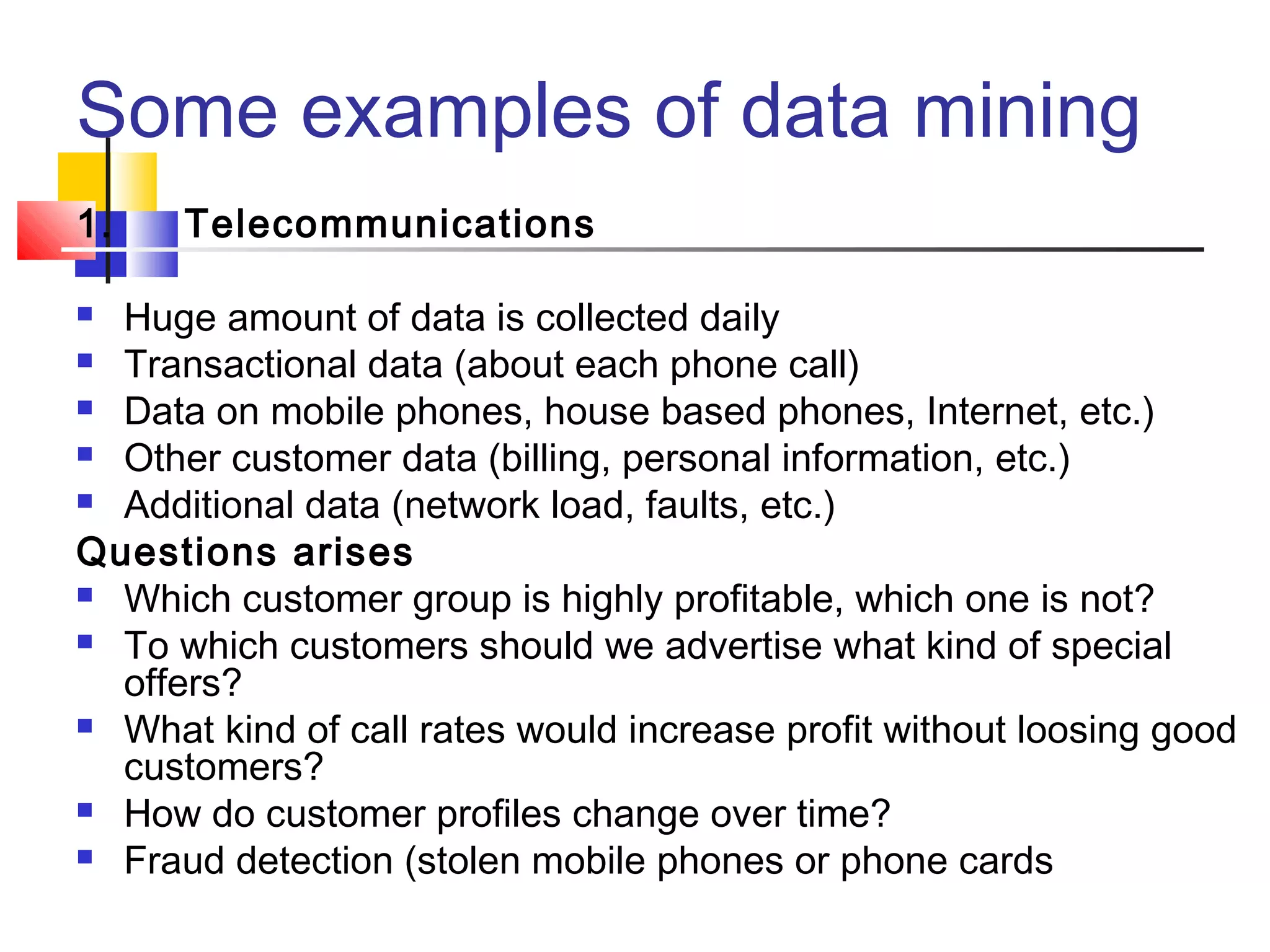
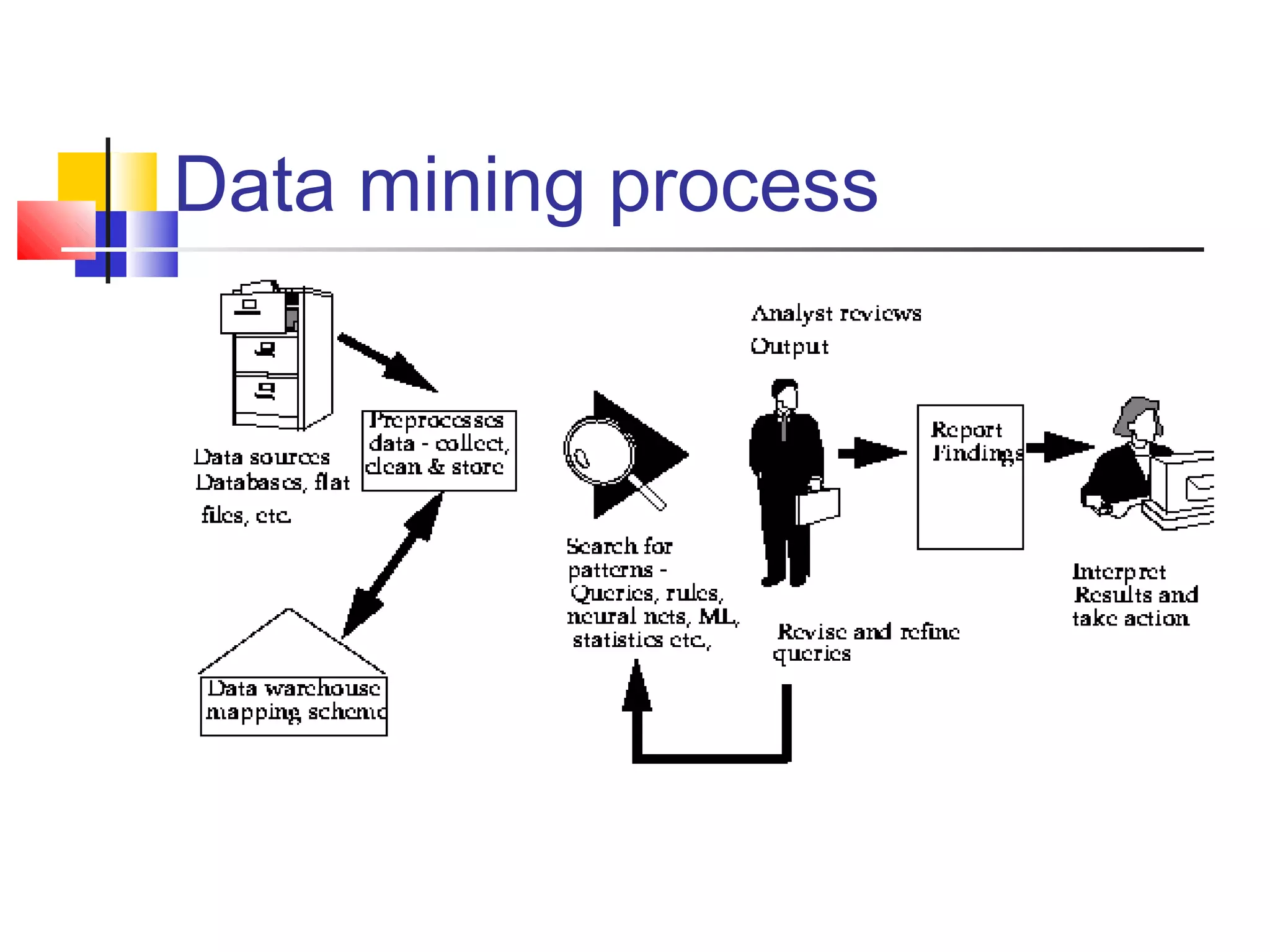
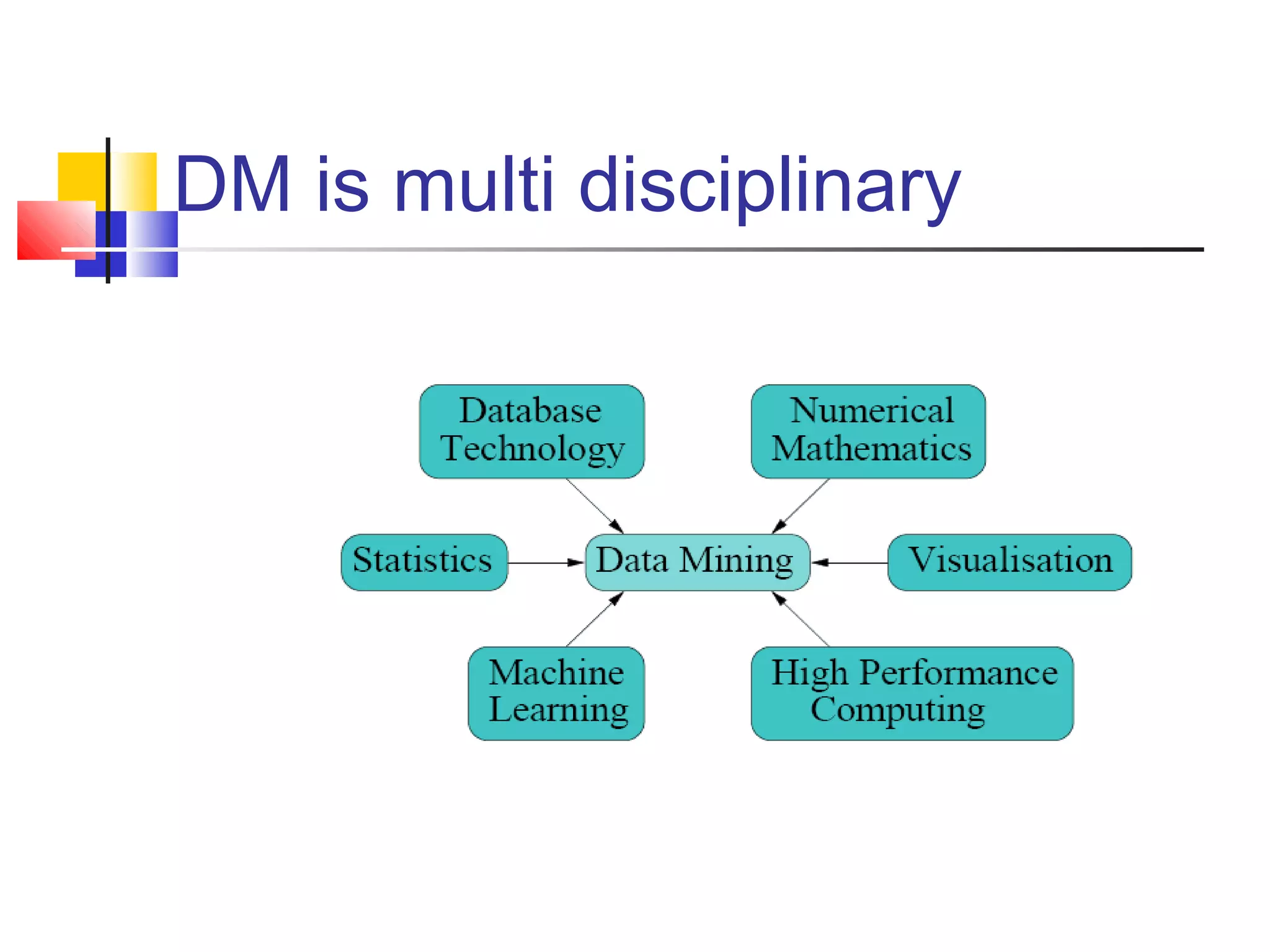
Data mining is the process of analyzing large amounts of data to discover hidden patterns and relationships. It allows companies to focus on the most important information to help support business decisions. Data is being collected in enormous quantities, ranging from terabytes to petabytes, from sources like customer transactions, mobile phone usage, health records, and more. Data mining techniques can be used to extract useful insights from this data, such as identifying profitable customer segments, predicting customer churn, detecting fraud, and informing marketing strategies. It provides value by supporting functions like segmentation, targeting, churn reduction, and risk assessment.