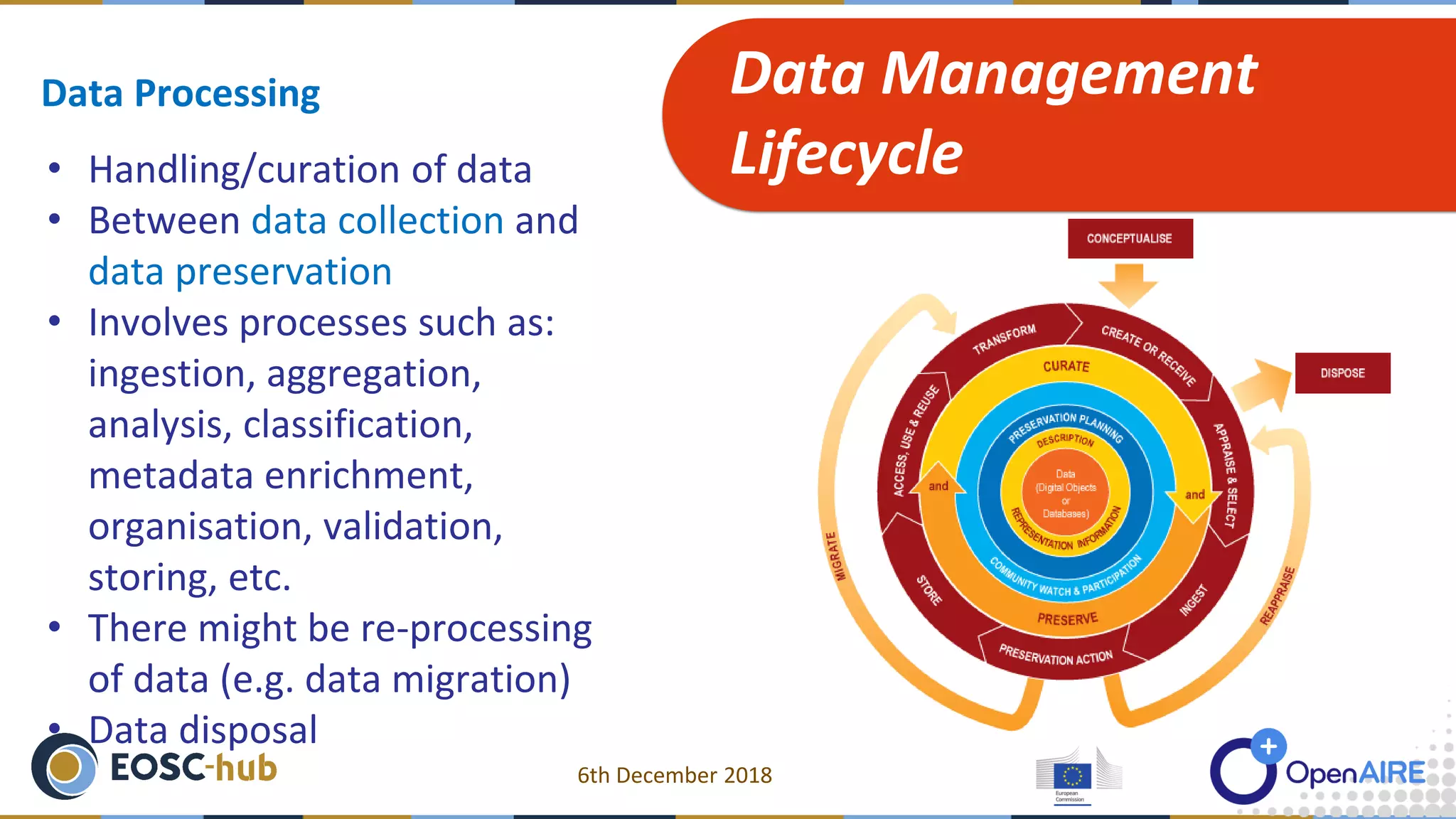
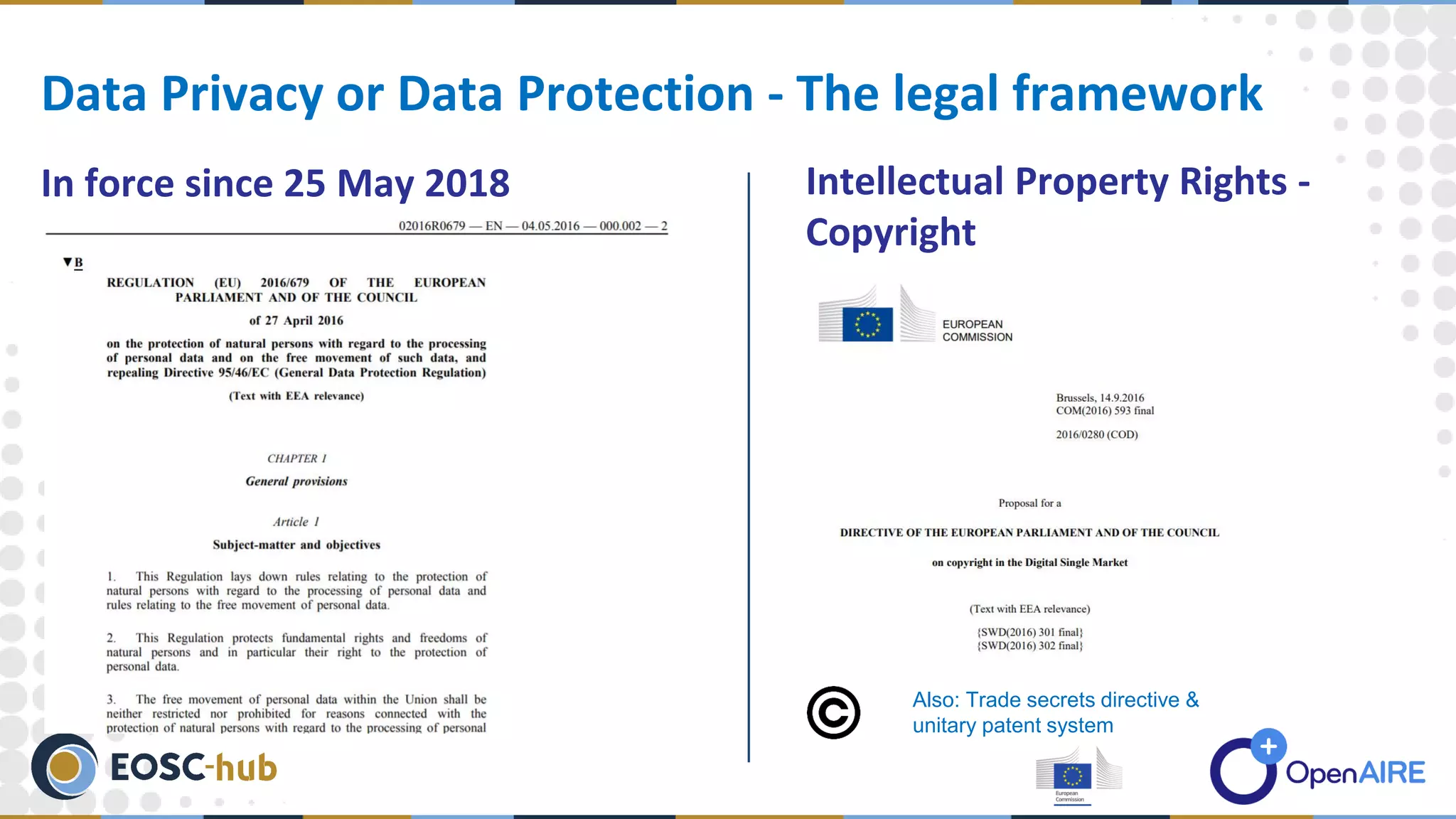
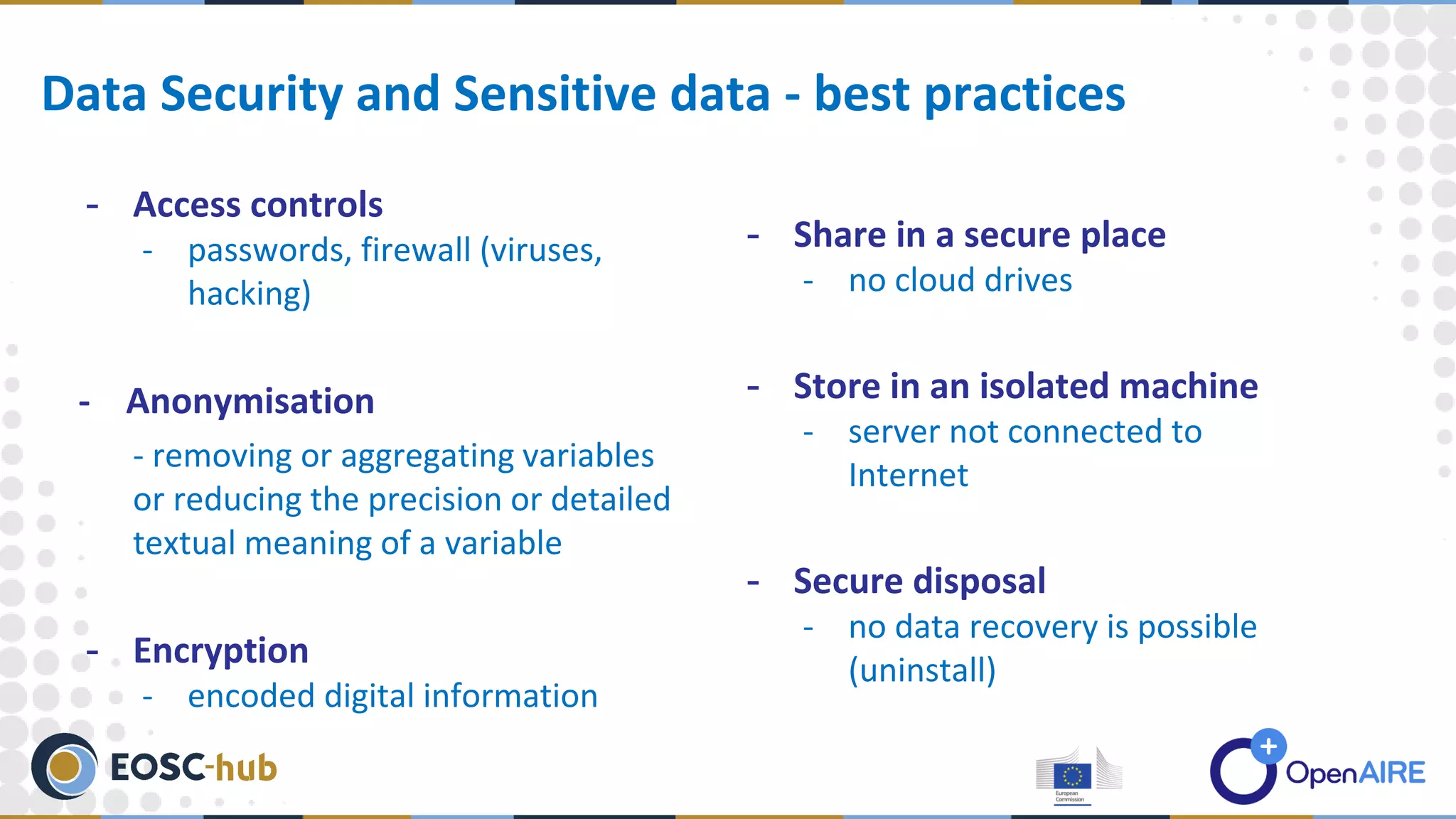
The document discusses data processing and privacy, emphasizing its role in the data management lifecycle, including handling, curation, and the transformation of raw data into meaningful information. It also outlines key elements of data privacy, particularly regarding sensitive data categories and best practices for data security, which became critical following the legal framework established on May 25, 2018. Resources for further guidance on data management and security practices are also provided.