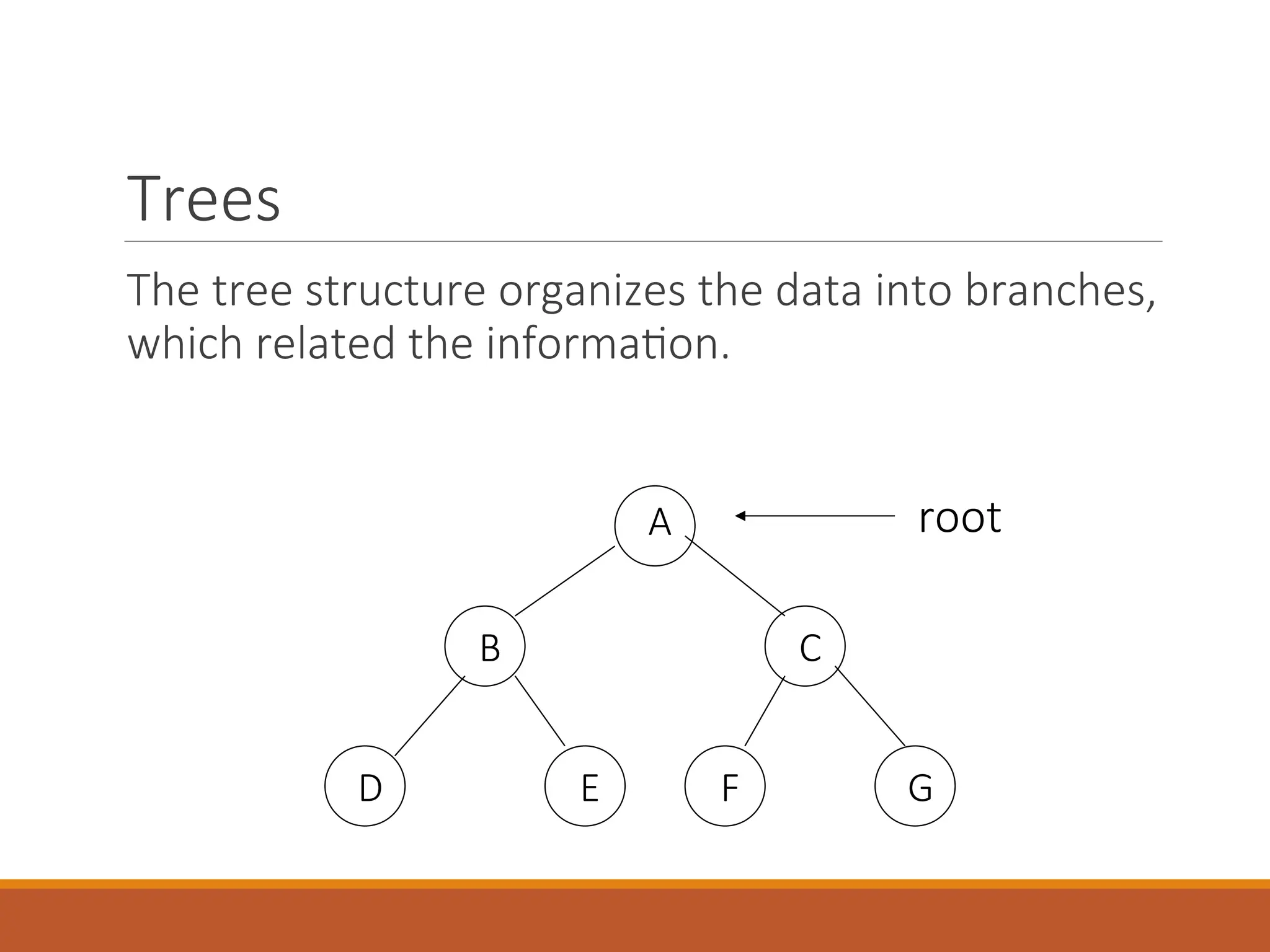
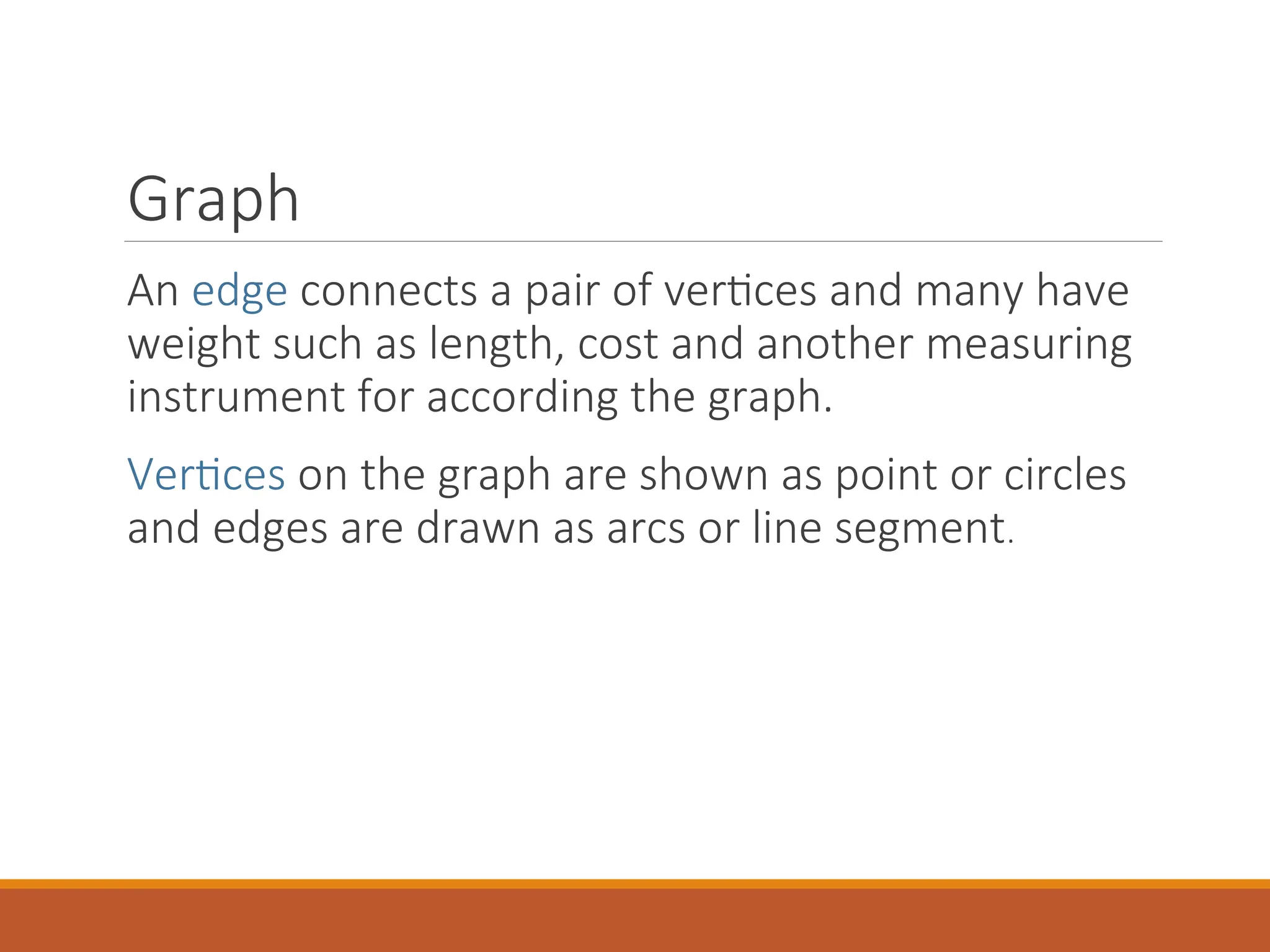
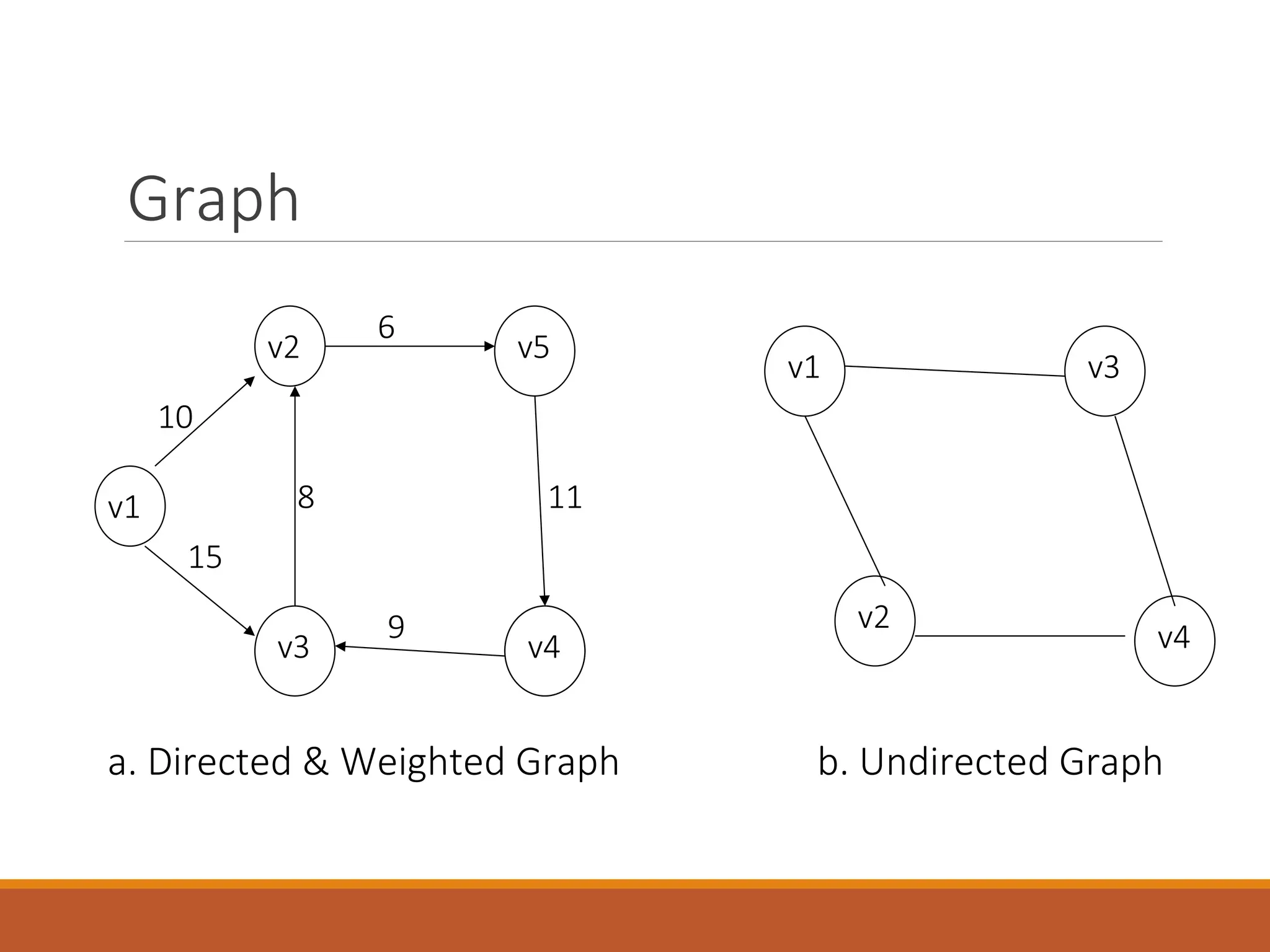
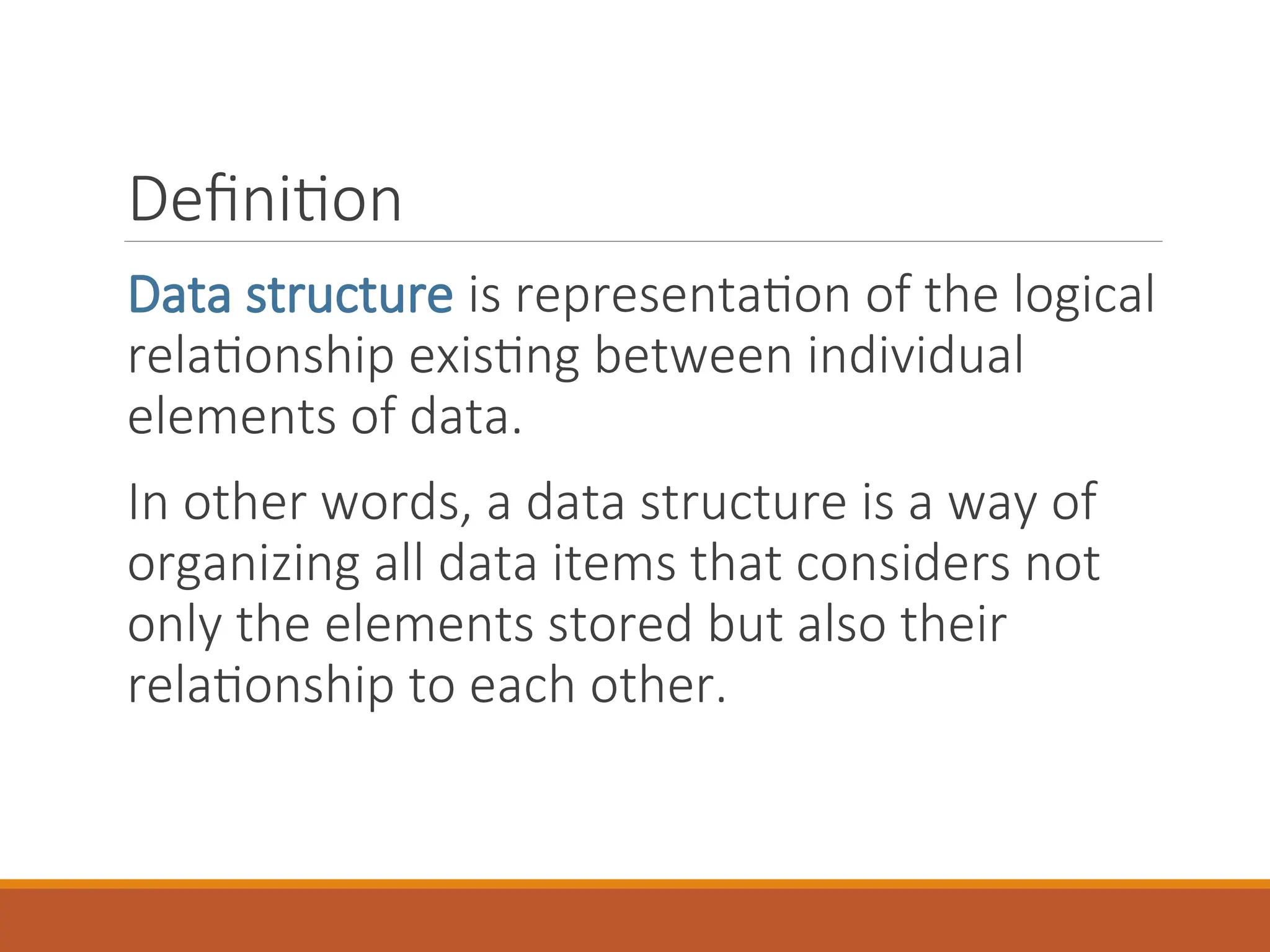
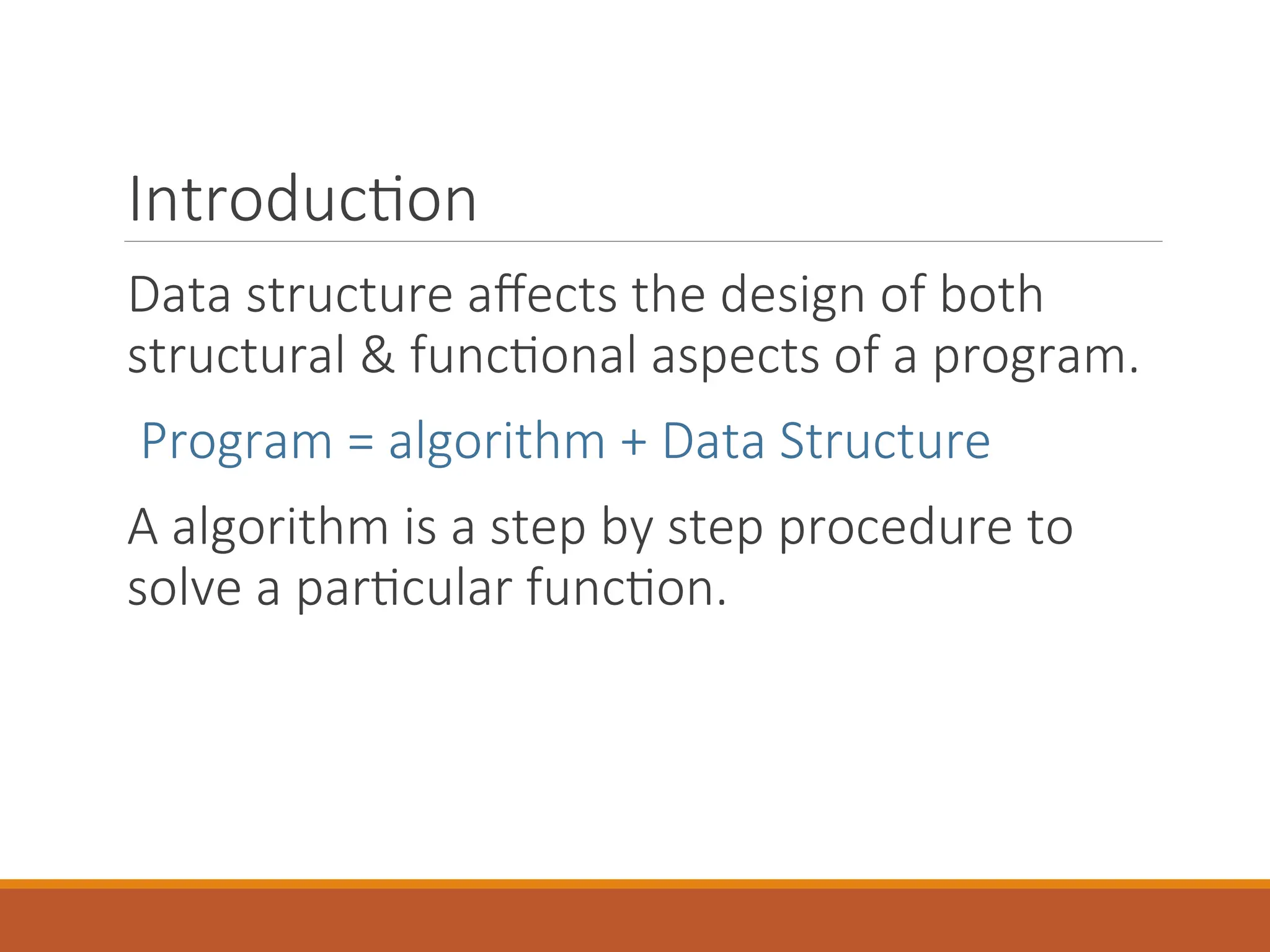
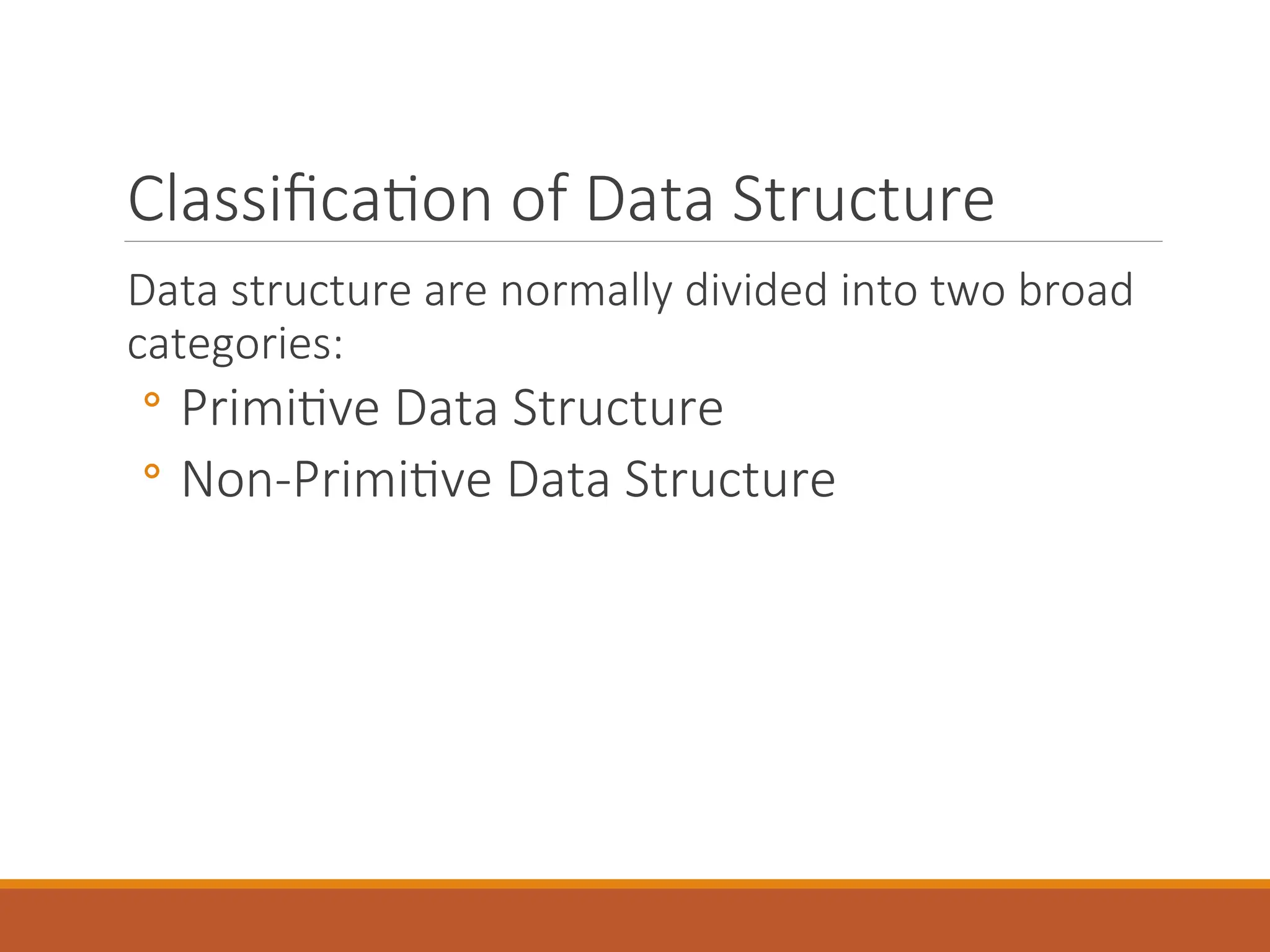
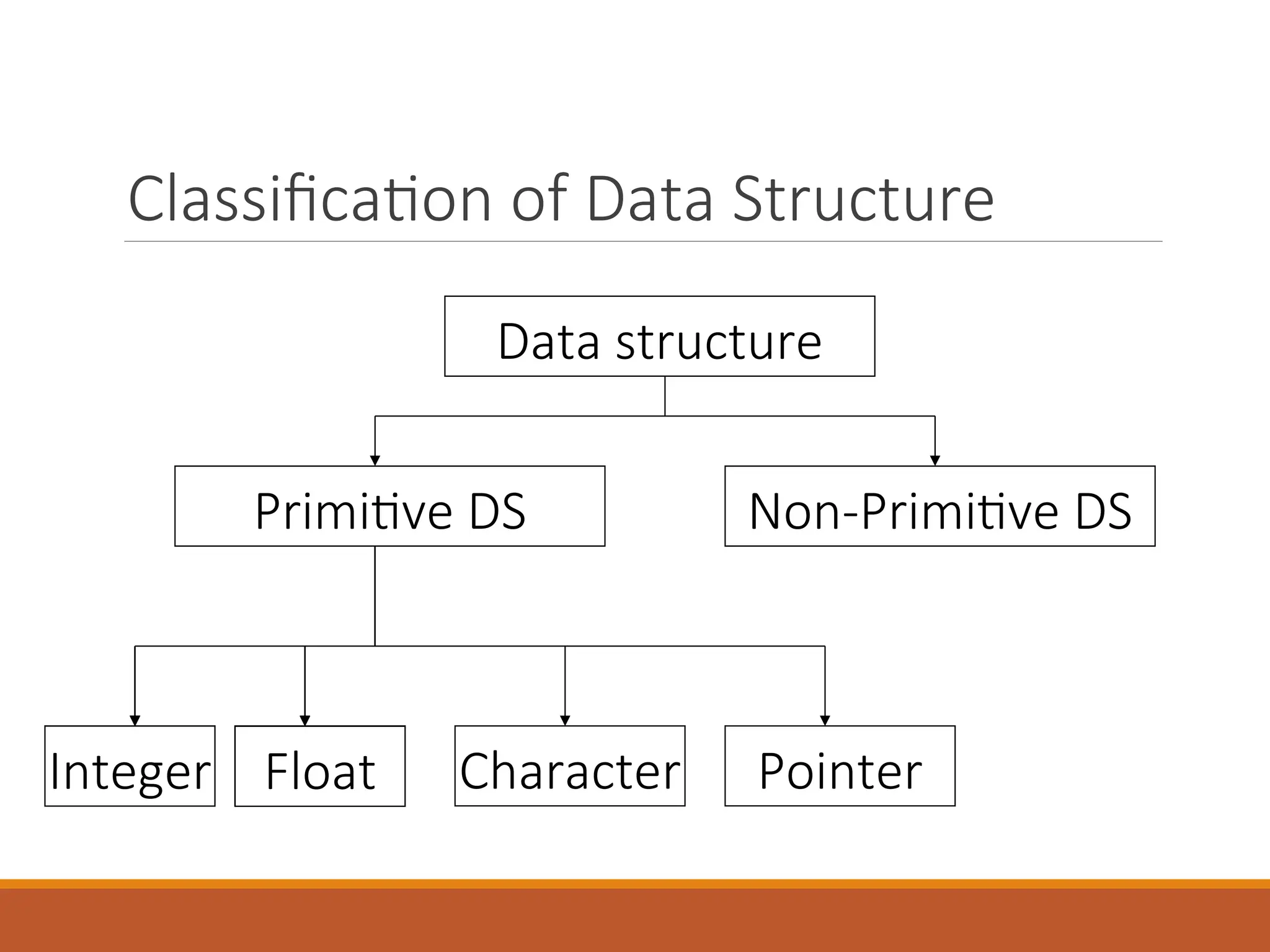
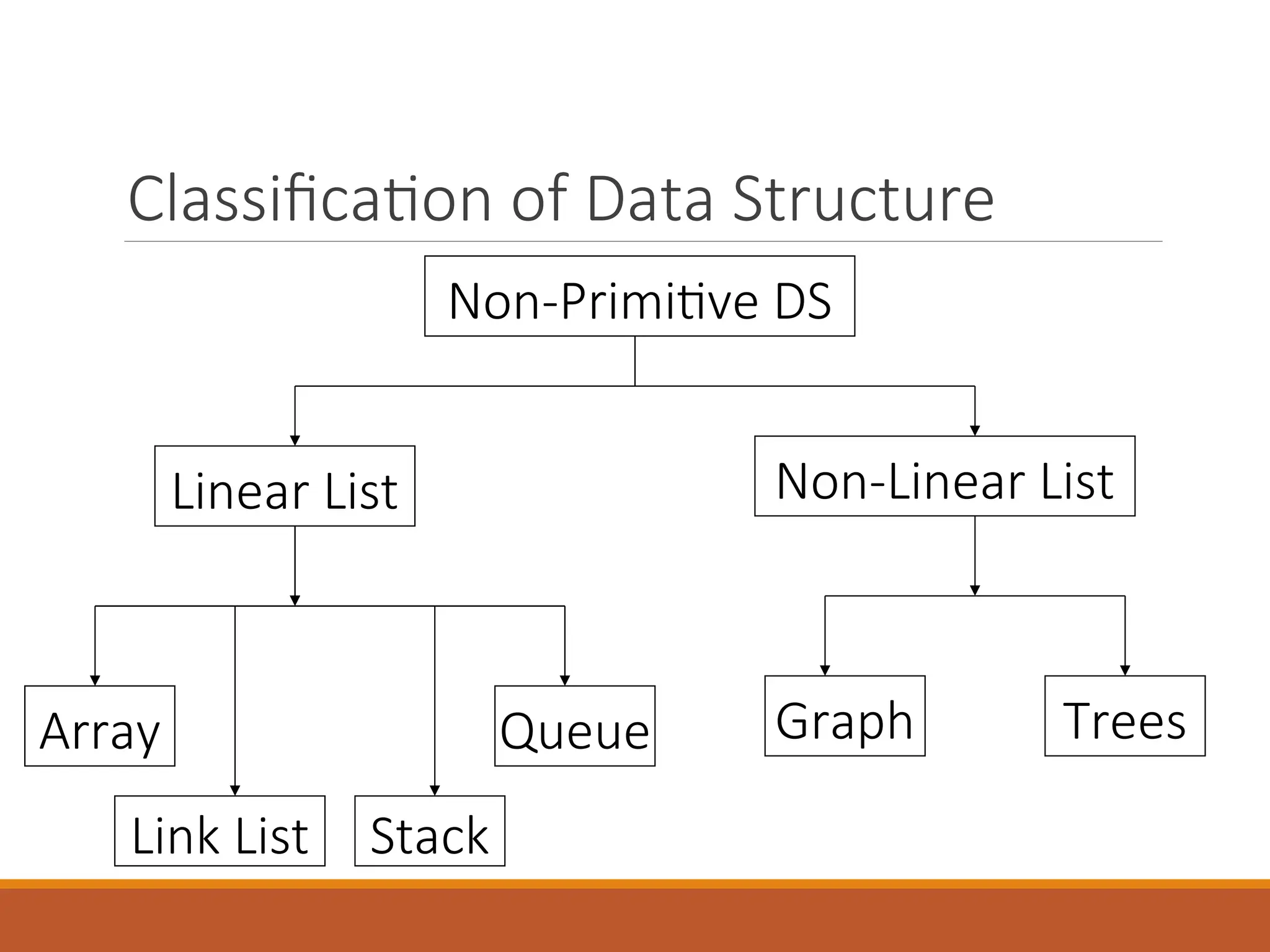
The document provides an introduction to data structures, defining them as a way to organize data based on the logical relationships between individual elements. It categorizes data structures into primitive (e.g., integers, floats) and non-primitive (e.g., lists, stacks, queues, trees, graphs), highlighting the importance of selecting appropriate structures for algorithms. Additionally, it discusses various operations associated with data structures, outlining their implementation and relevant concepts.



![Arrays
Simply, declaration of array is as follows:
int arr[10]
Where int specifies the data type or type of
elements arrays stores.
“arr” is the name of array & the number specified
inside the square brackets is the number of
elements an array can store, this is also called sized
or length of array.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-241211020256-1e7d3572/75/data-structure-algorithm-example-and-example-14-2048.jpg)
![Arrays
Following are some of the concepts to be
remembered about arrays:
◦ The individual element of an array can be
accessed by specifying name of the array,
following by index or subscript inside square
brackets.
◦ The first element of the array has index zero[0].
It means the first element and last element will
be specified as: arr[0] and arr[9] respectively.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-241211020256-1e7d3572/75/data-structure-algorithm-example-and-example-15-2048.jpg)


![Arrays
◦ For example: Reading an array
for(i=0; i <= 9; i++)
scanf(“%d”,&arr[i]);
◦ For example: Writing an array
for(i=0; i<=9; i++)
printf(“%d”,arr[i]);](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-241211020256-1e7d3572/75/data-structure-algorithm-example-and-example-18-2048.jpg)



![Lists
Technically each such element is referred to as a node, therefore a list
can be defined as a collection of nodes as show bellow:
Head
AAA BBB CCC
Information field
Pointer field
[Linear Liked List]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-241211020256-1e7d3572/75/data-structure-algorithm-example-and-example-22-2048.jpg)


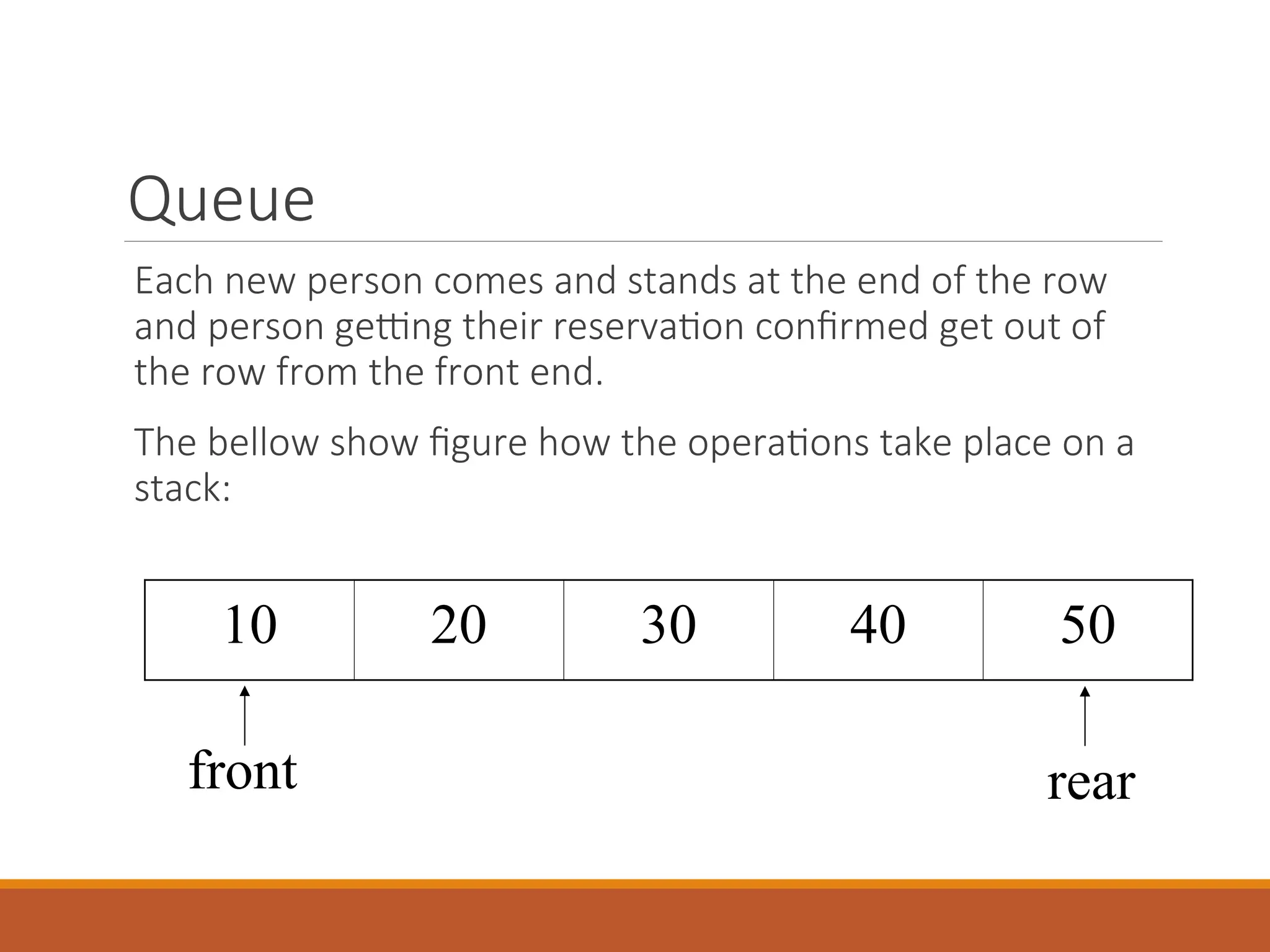
![Stack
Insertion of element into stack is called PUSH and deletion of
element from stack is called POP.
The bellow show figure how the operations take place on a
stack:
PUSH POP
[STACK]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/20-241211020256-1e7d3572/75/data-structure-algorithm-example-and-example-26-2048.jpg)