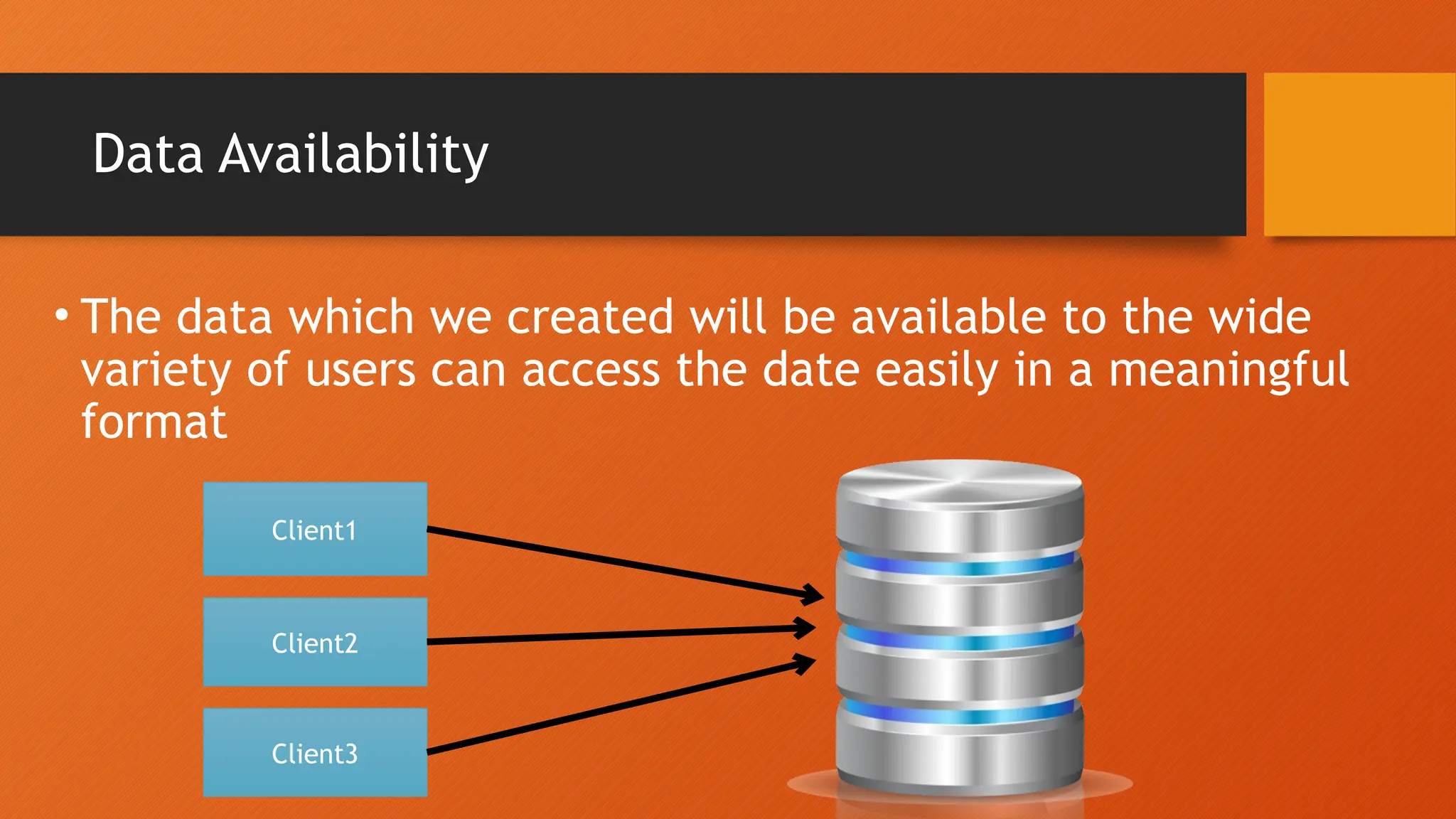
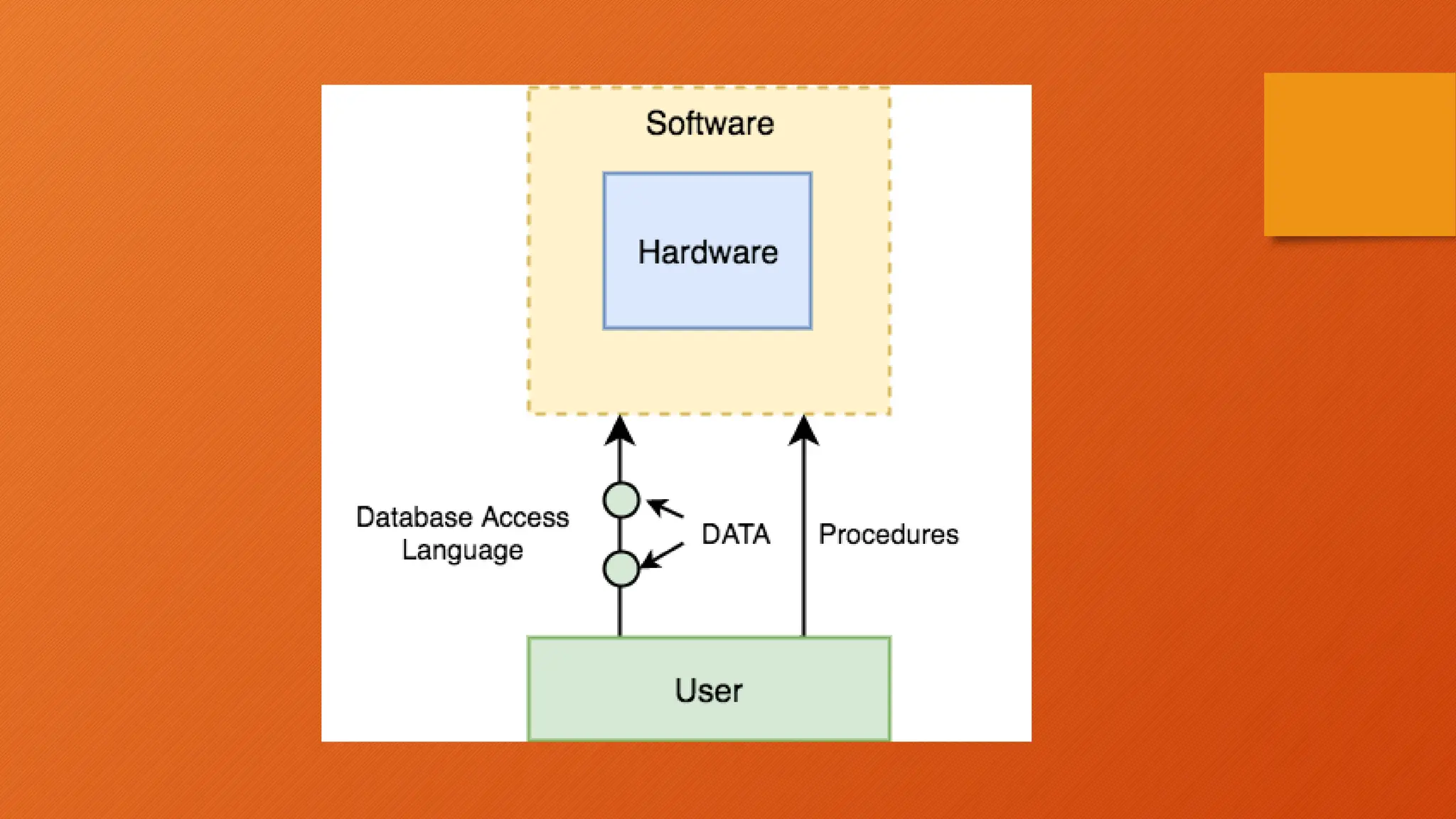
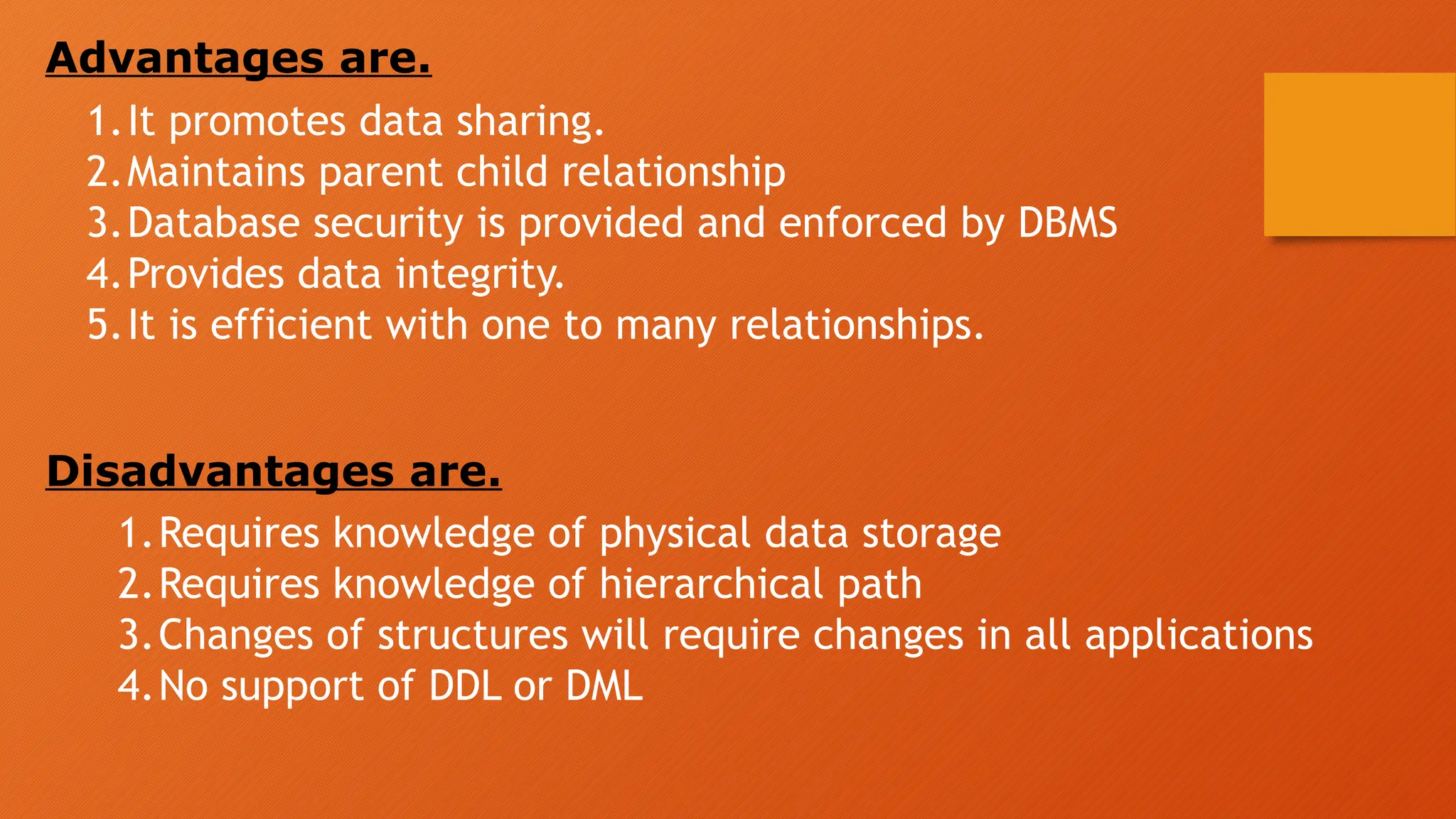
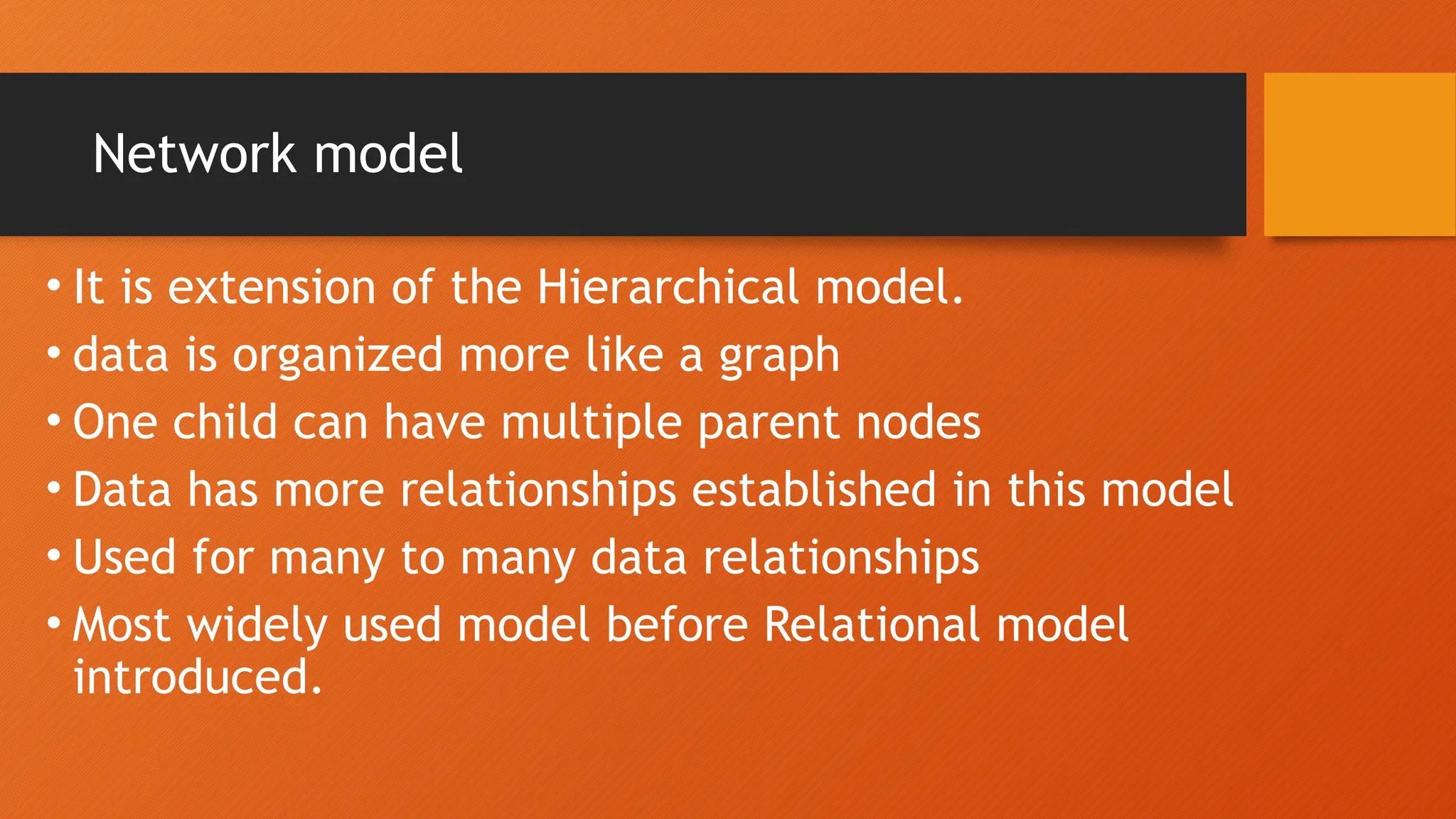
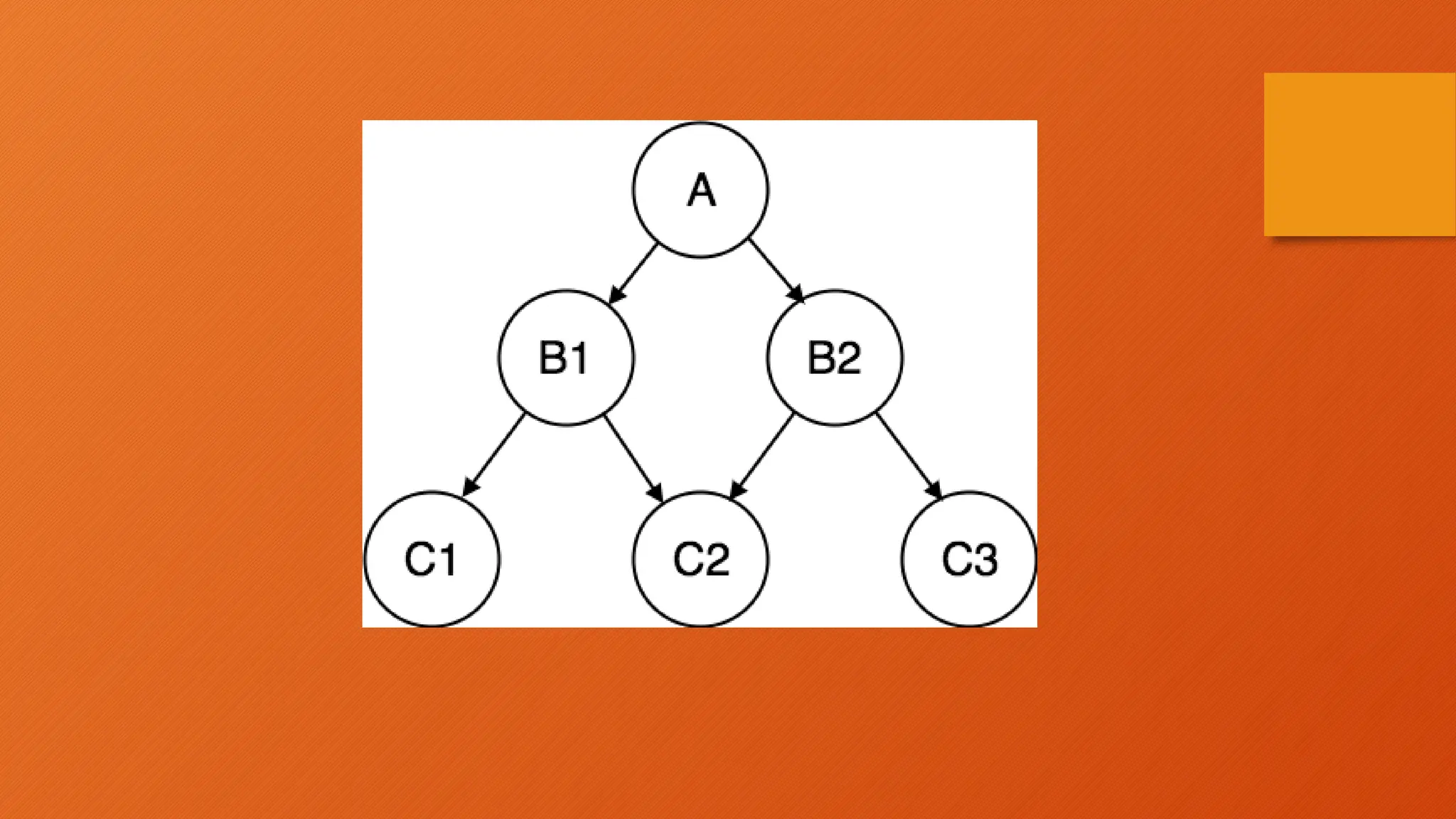
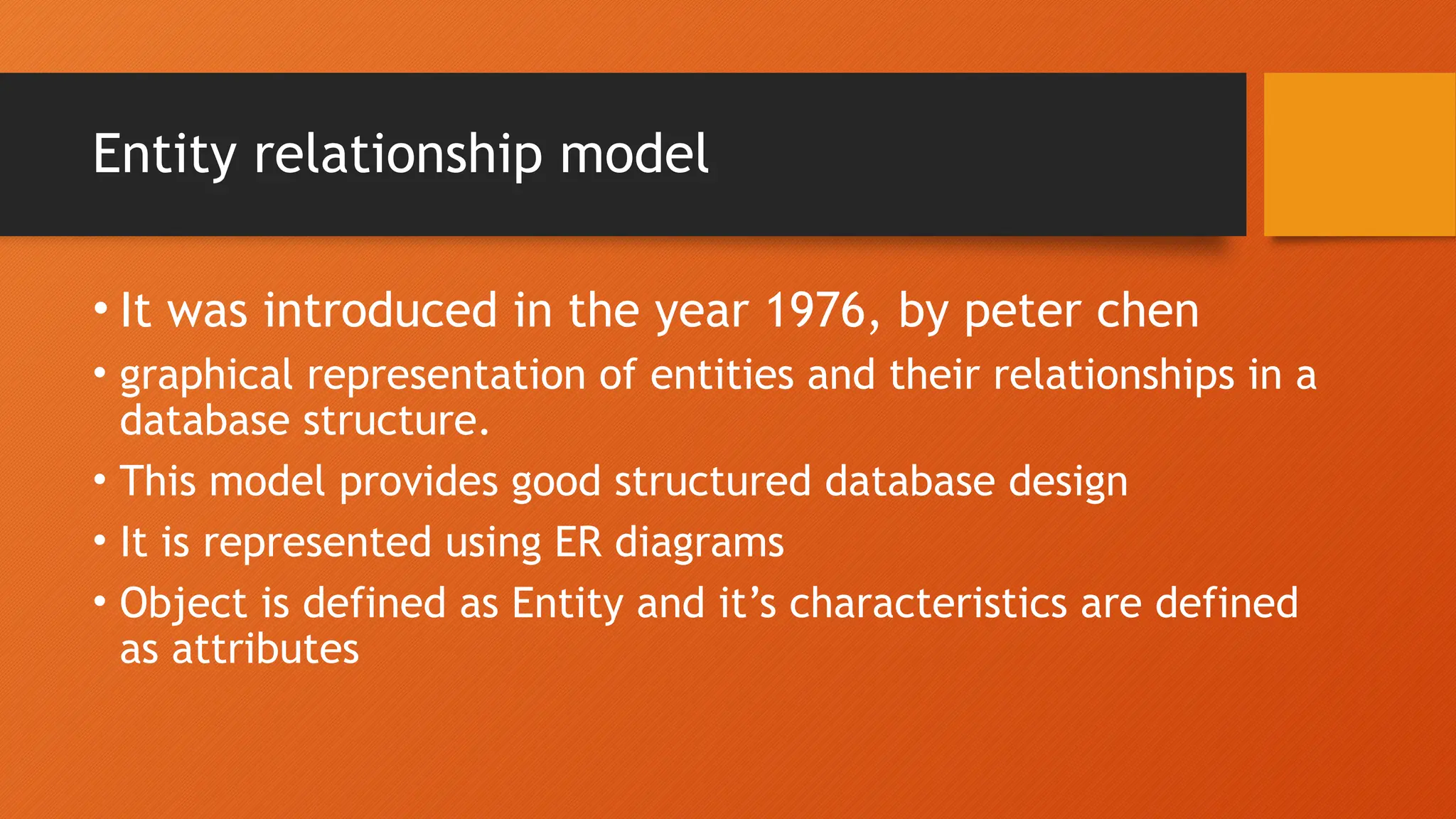
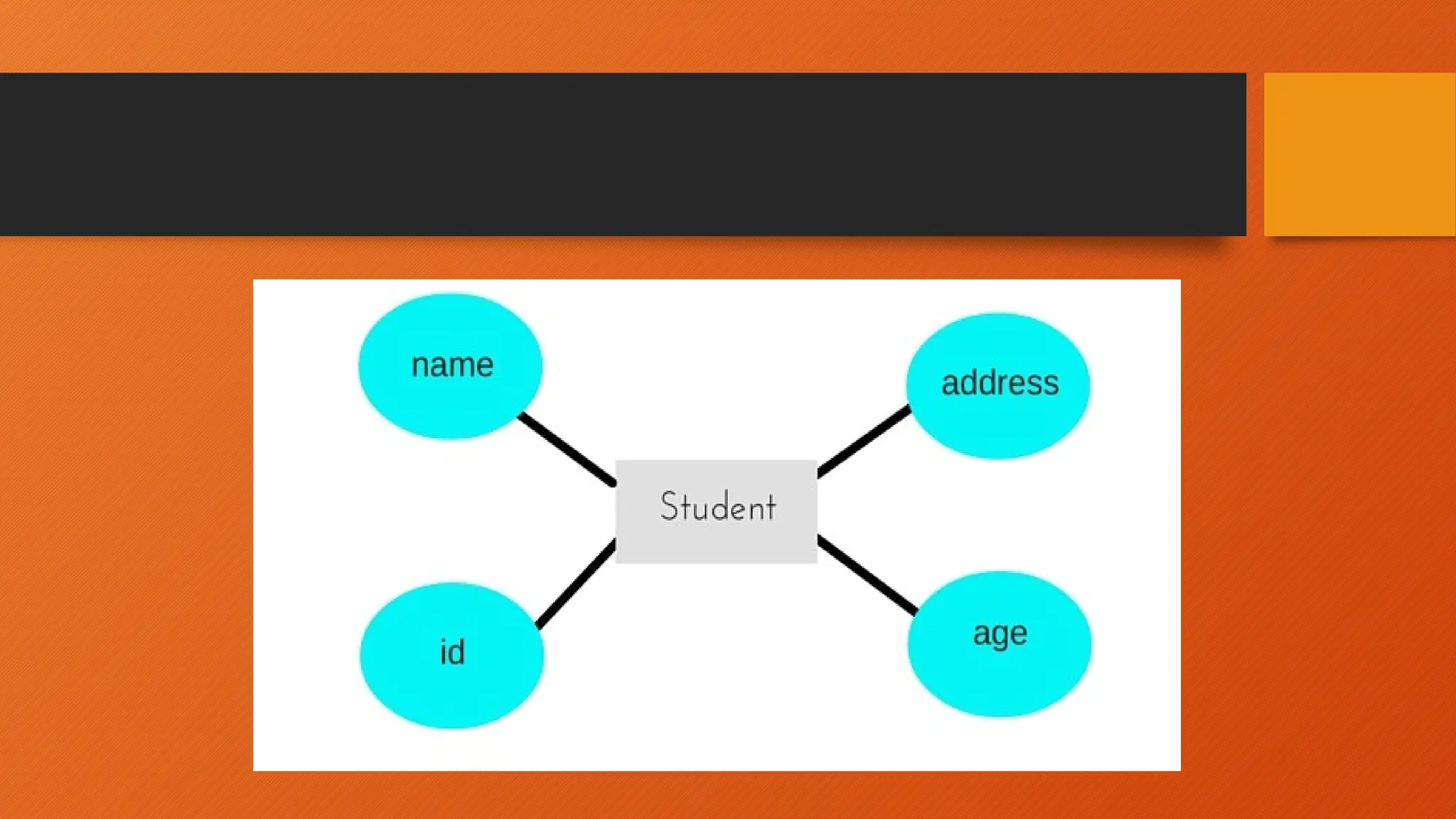
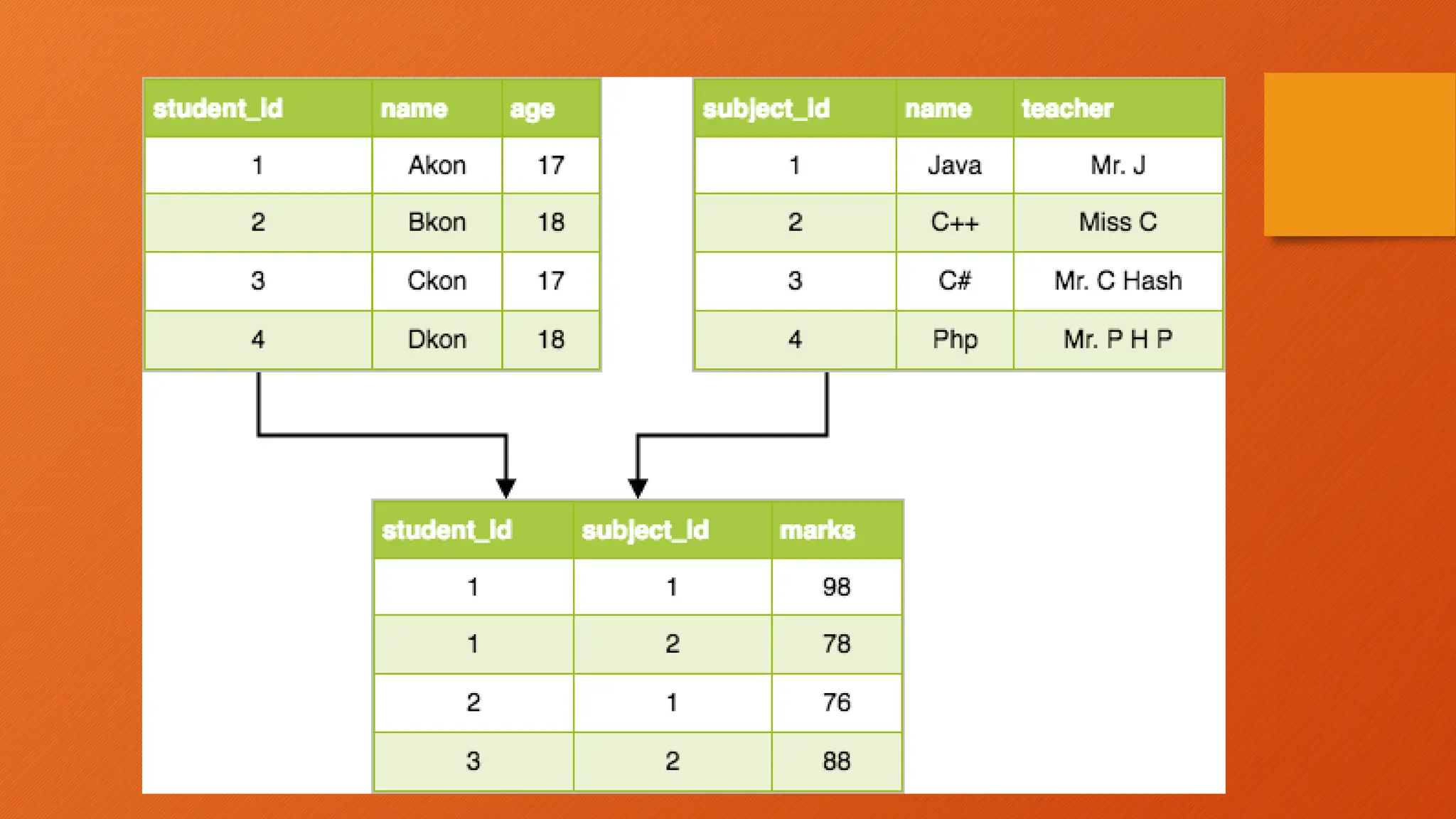
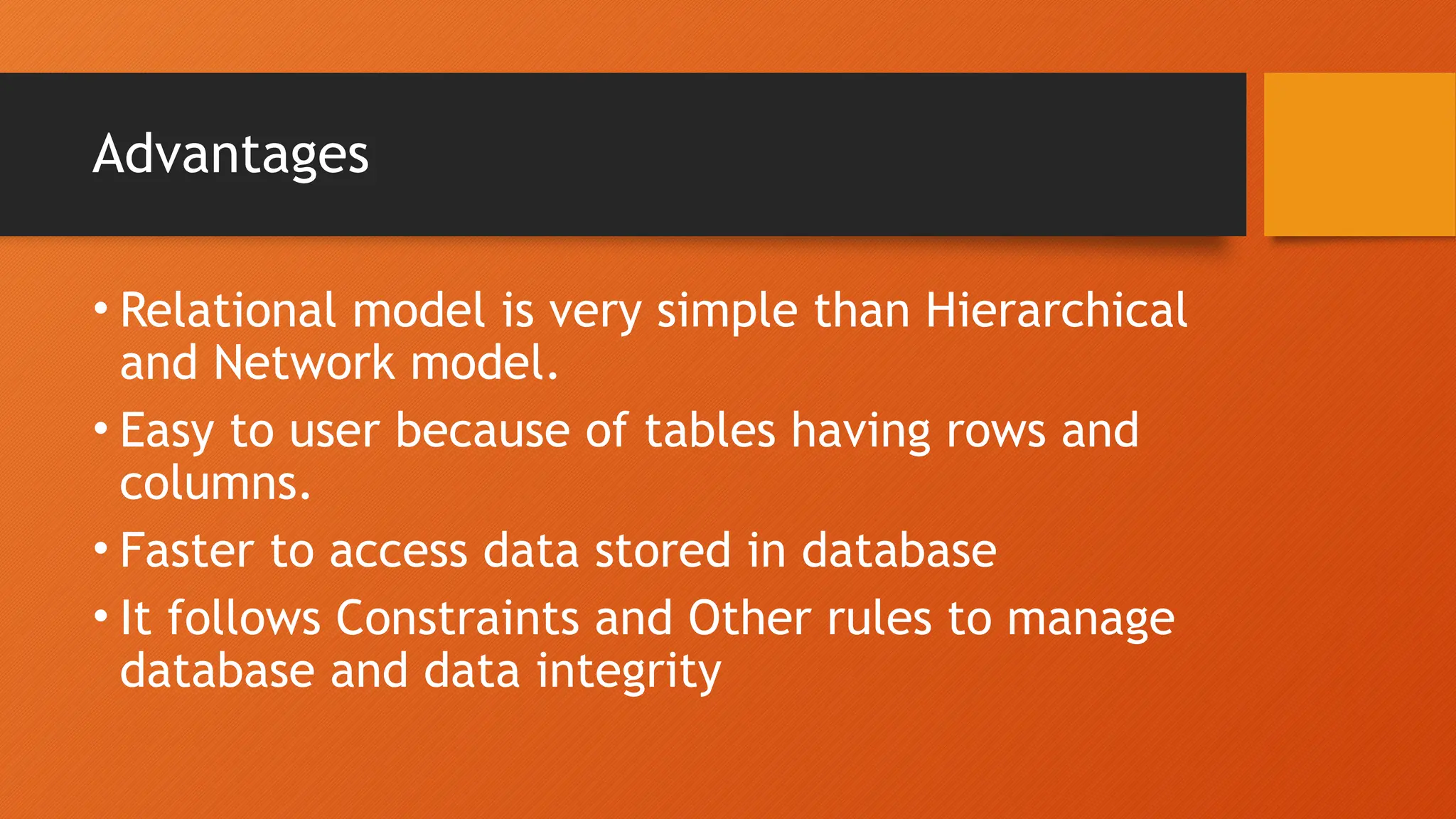
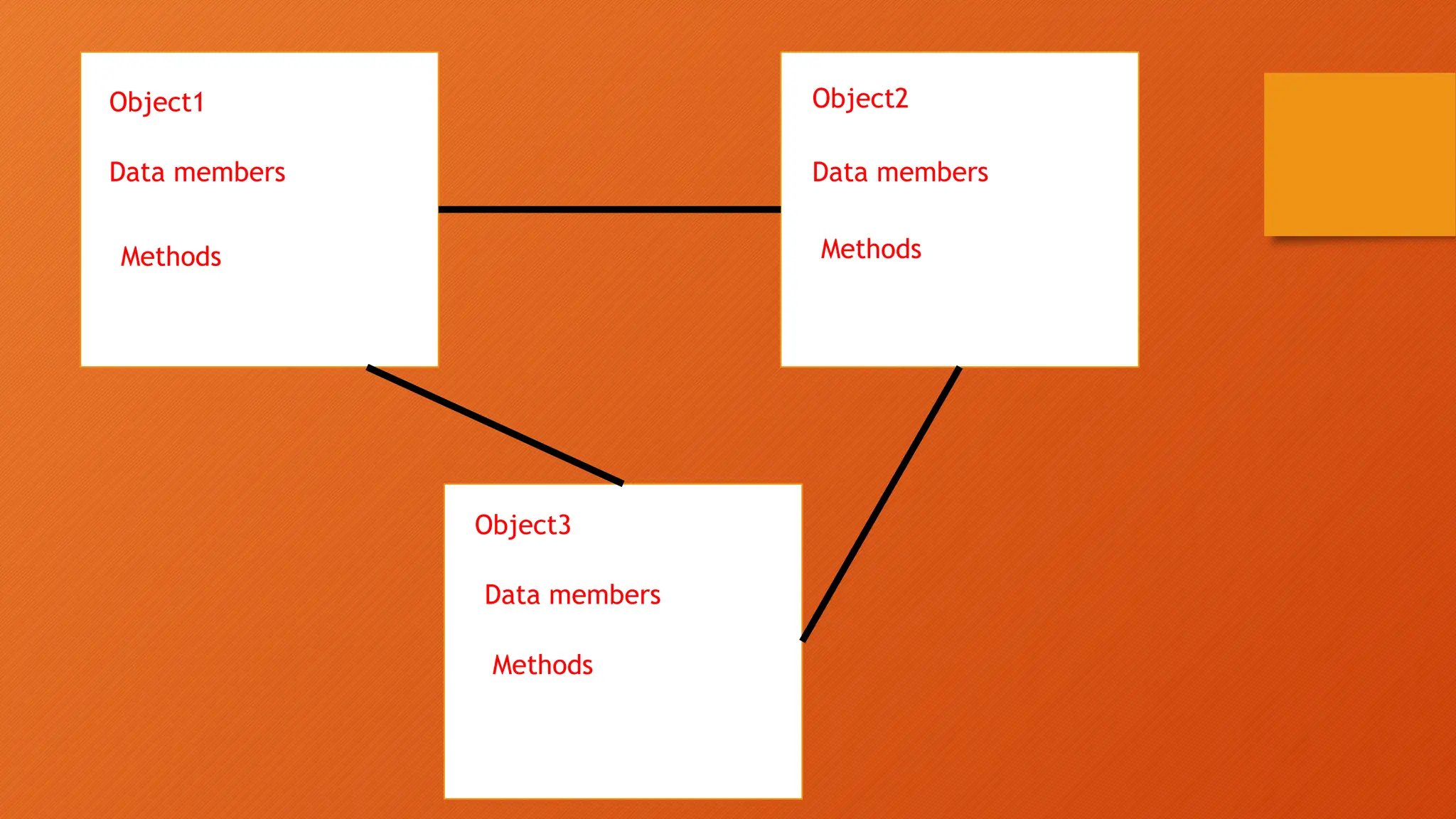
The document outlines the main objectives of database management systems (DBMS), including data availability, integrity, security, and independence, while detailing the evolution of DBMS from flat files to object-oriented databases. It categorizes DBMS based on data models, user concurrency, and distribution methods, and explains various models such as relational, hierarchical, and object-oriented, each with its own advantages and disadvantages. Lastly, it discusses the components of DBMS, including hardware, software, procedures, and user roles, highlighting the importance of data modeling in structuring databases effectively.