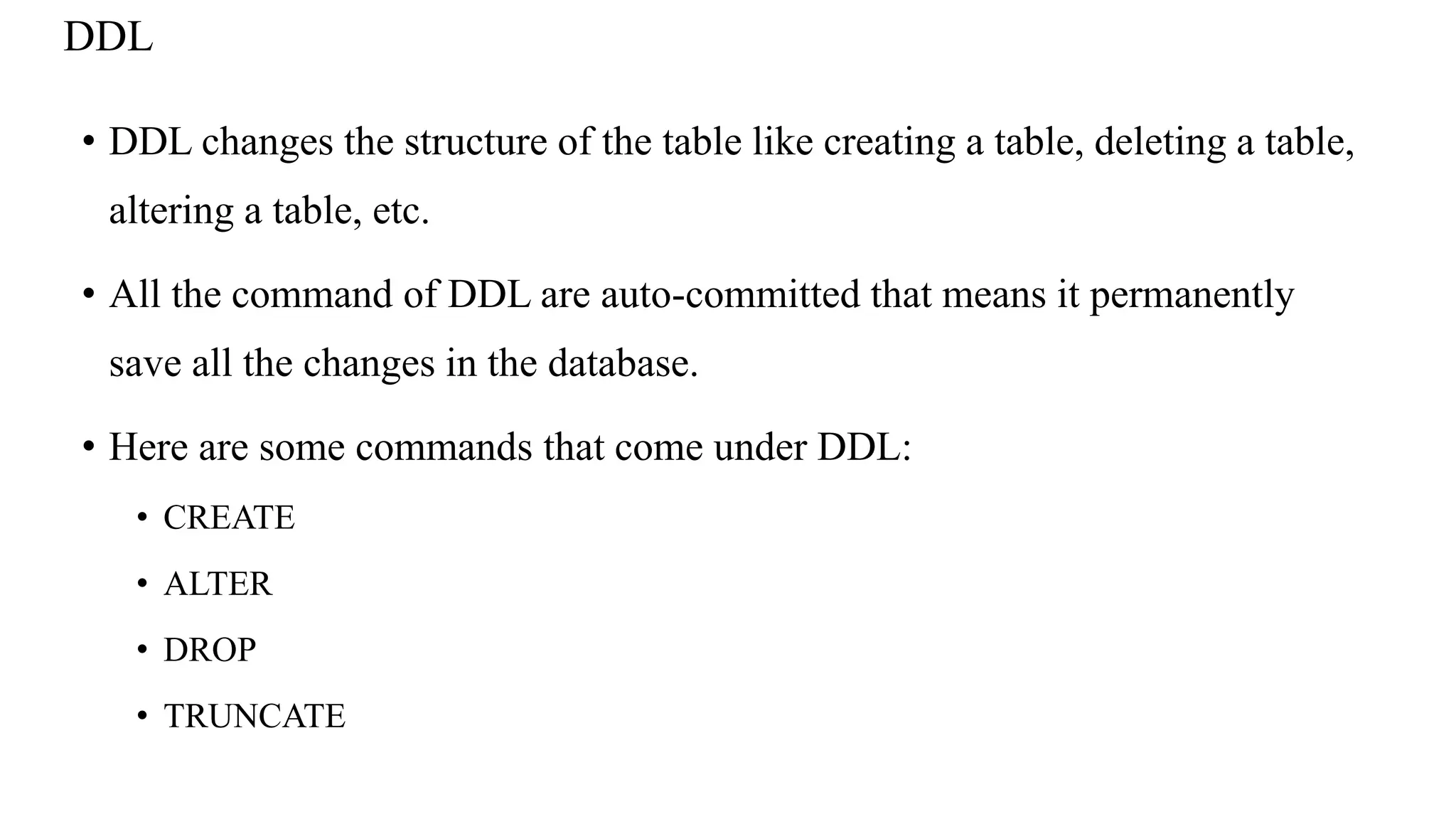
The document outlines SQL commands categorized into five types: DDL (Data Definition Language), DQL (Data Query Language), DML (Data Manipulation Language), DCL (Data Control Language), and TCL (Transaction Control Language). DDL is used for database schema creation and modification, while DQL retrieves data, DML manipulates existing data, DCL manages user privileges, and TCL handles transaction control. Additionally, the document describes database design phases, including conceptual, logical, and physical design, with examples related to an outpatient management system.









![CREATE Command for DATABASE
SQL Server Database can be Created, Alter by
• Graphically using SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS) or
• Using Query
CREATE DATABASE [Database_Name_You_Want_To_Create]
Example :
CREATE DATABASE CRMS;](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab1-240609141755-3ecd06b8/75/database-management-system-sql-commands-lab-sql-11-2048.jpg)
![Alter Command for DATABASE
Rename the Database
• Graphically using SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS) or
• Using Alter Command
ALTER DATABASE [Database_Name_You_Want_To_Rename] Modify Name = [NEW_DB_NAME]
Example :
ALTER DATABASE CRMS Modify Name= ‘CRMS_DEV’;
Example :
sp_renameDB CRMS Modify Name= ‘CRMS_DEV’;
o Using System Stored Procedure](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab1-240609141755-3ecd06b8/75/database-management-system-sql-commands-lab-sql-12-2048.jpg)
![DROP Command for DATABASE
DROP the Database
• Graphically using SQL Server Management Studio(SSMS) or
• Using DROP Command
DROP DATABASE [Database_Name_You_Want_To_DROP]
Example :
DROP DATABASE CRMS;
Example :
-- This command close database connection form other user
-- and delete the database
ALTER DATABASE CRMS set SINGLE_USER With ROLLBACK immediate;
o Delete Database Using ALTER](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/lab1-240609141755-3ecd06b8/75/database-management-system-sql-commands-lab-sql-13-2048.jpg)