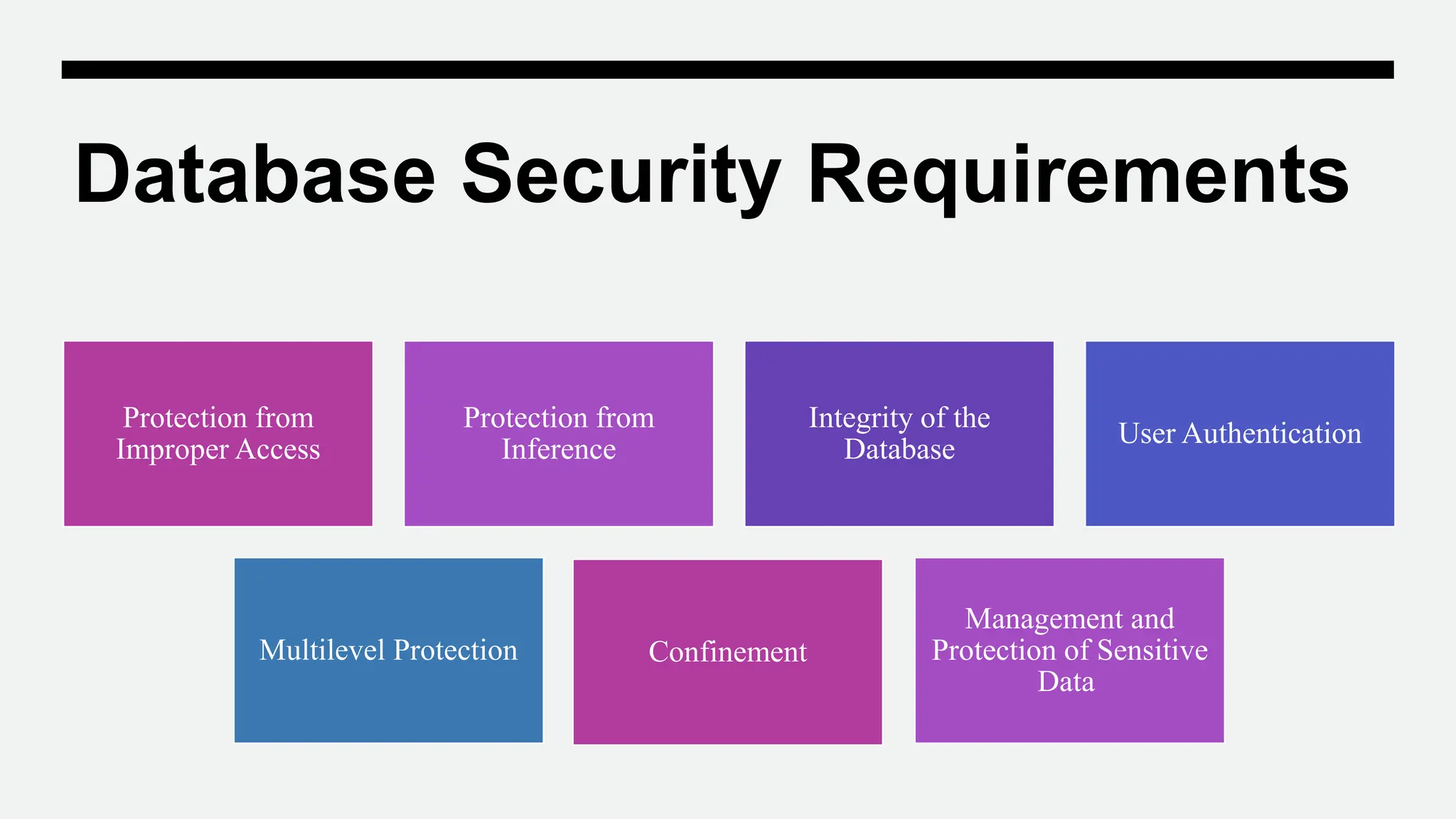
This document discusses database security. It defines database security as protecting the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of a database. It explains why database security is important to prevent compromised intellectual property, damage to brand reputation, and lack of business continuity from data breaches. The concepts of database security include secrecy/confidentiality, integrity, and availability. Threats include insider threats, human error, SQL/NoSQL injection attacks. Security controls include authorization, encryption, authentication, logical controls like firewalls. The document also discusses database security requirements, abstraction, privileges, and advantages of data encryption.