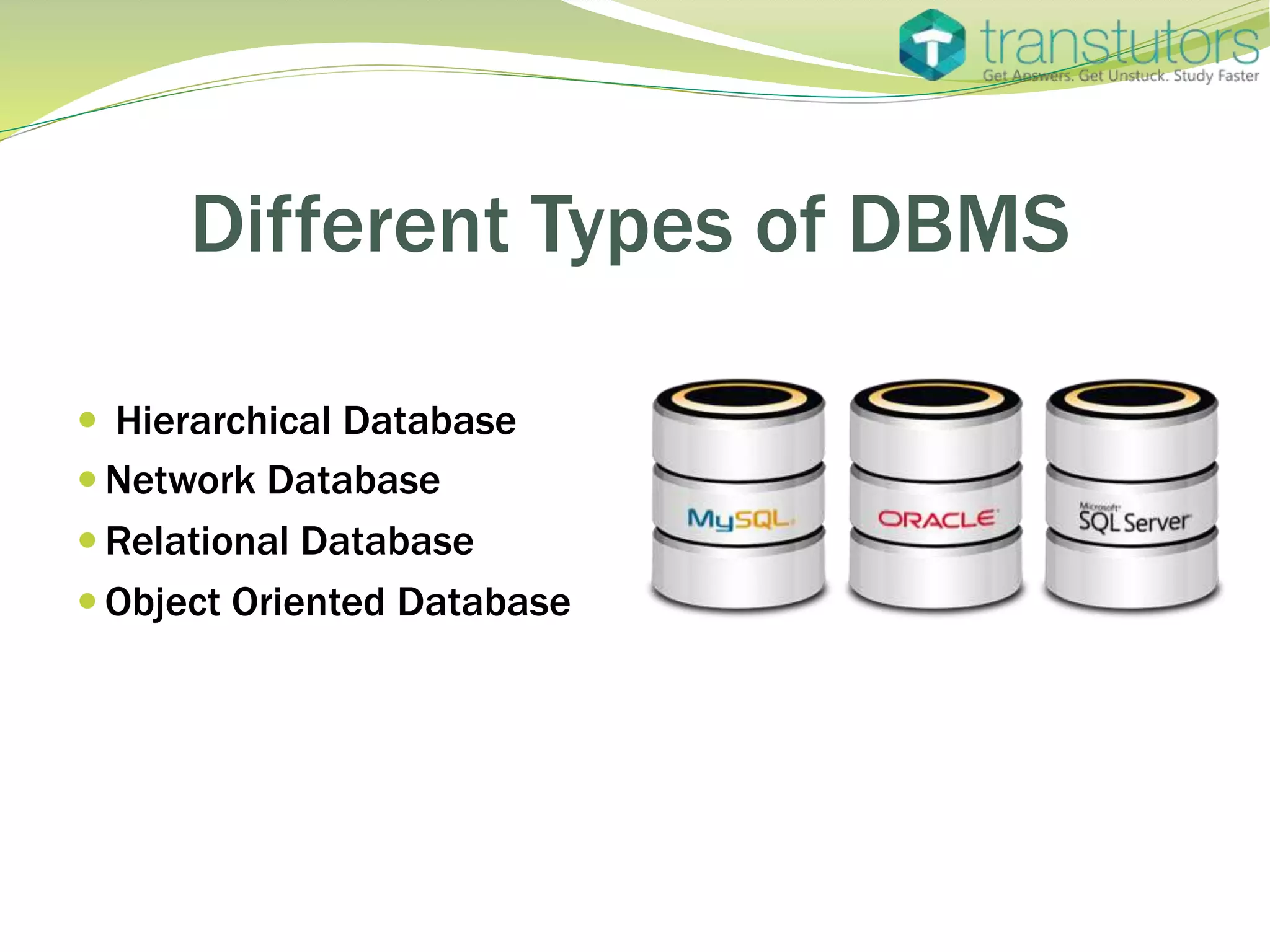
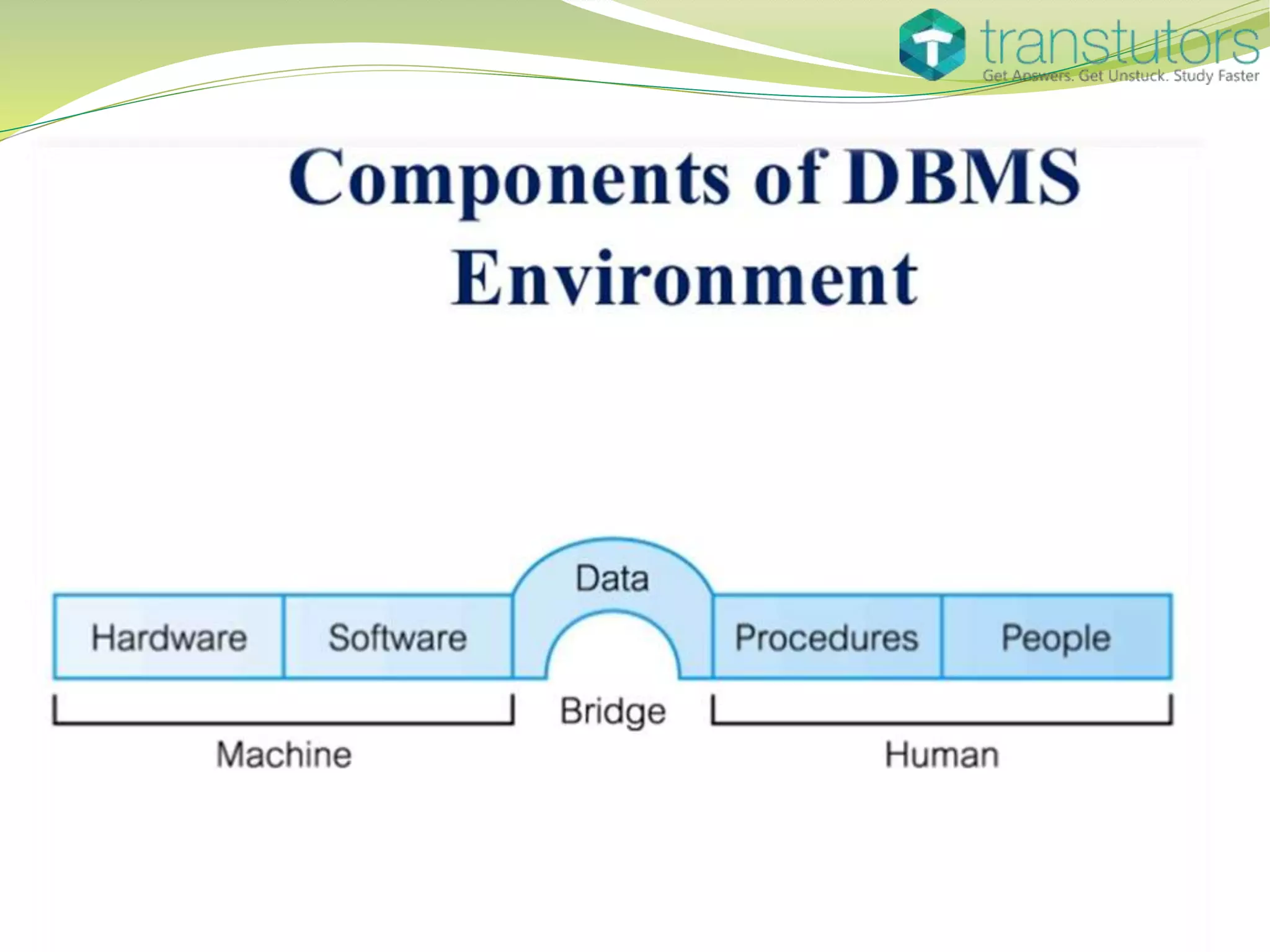
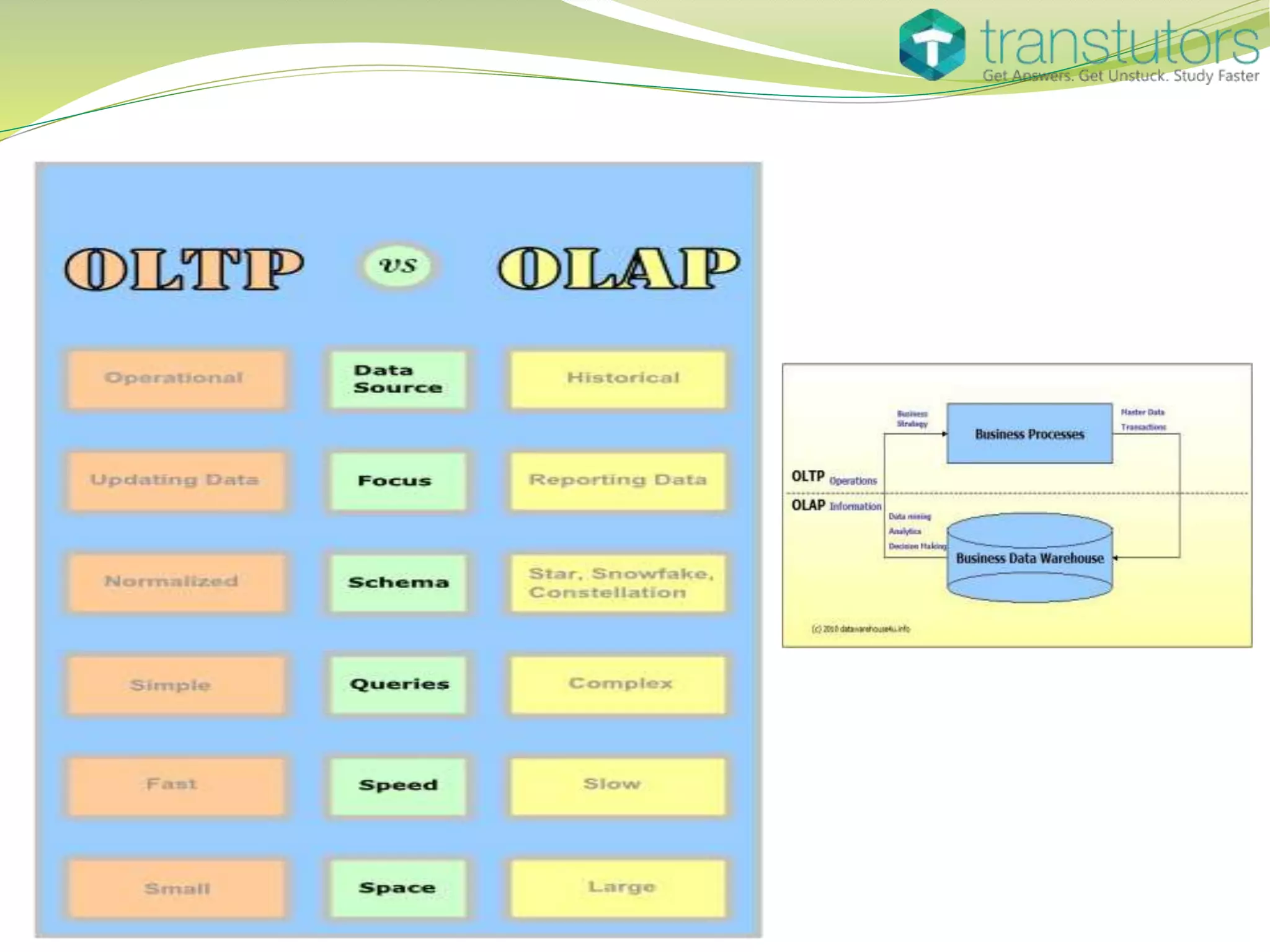
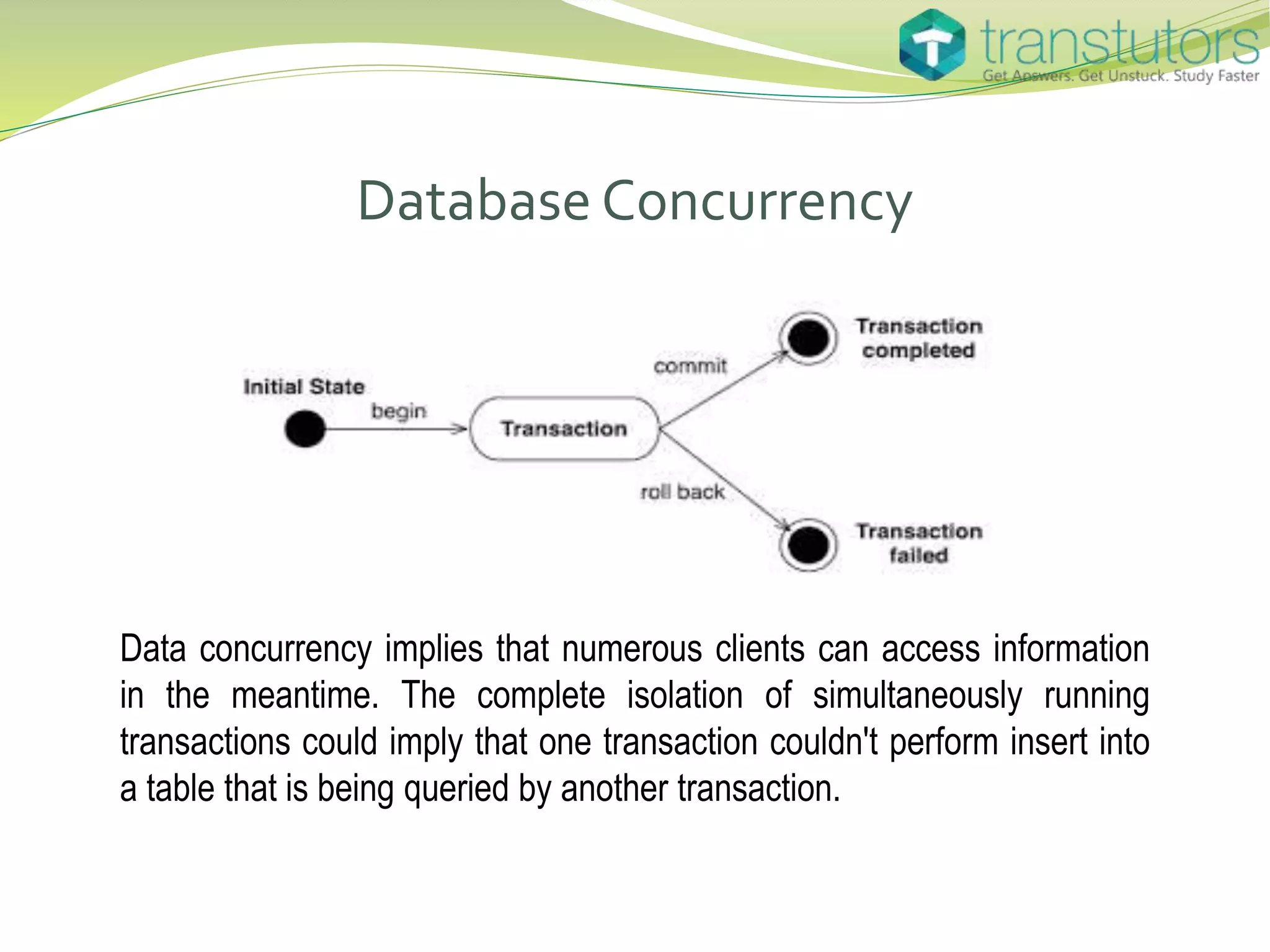
The document discusses database management systems (DBMS), explaining their functions in organizing and managing data, including various types such as hierarchical, network, relational, and object-oriented databases. It also outlines the architecture of client-server interactions and the benefits of distributed DBMS, as well as different types of indexes used in databases. Lastly, it highlights the concept of data concurrency, allowing multiple users to access information simultaneously.