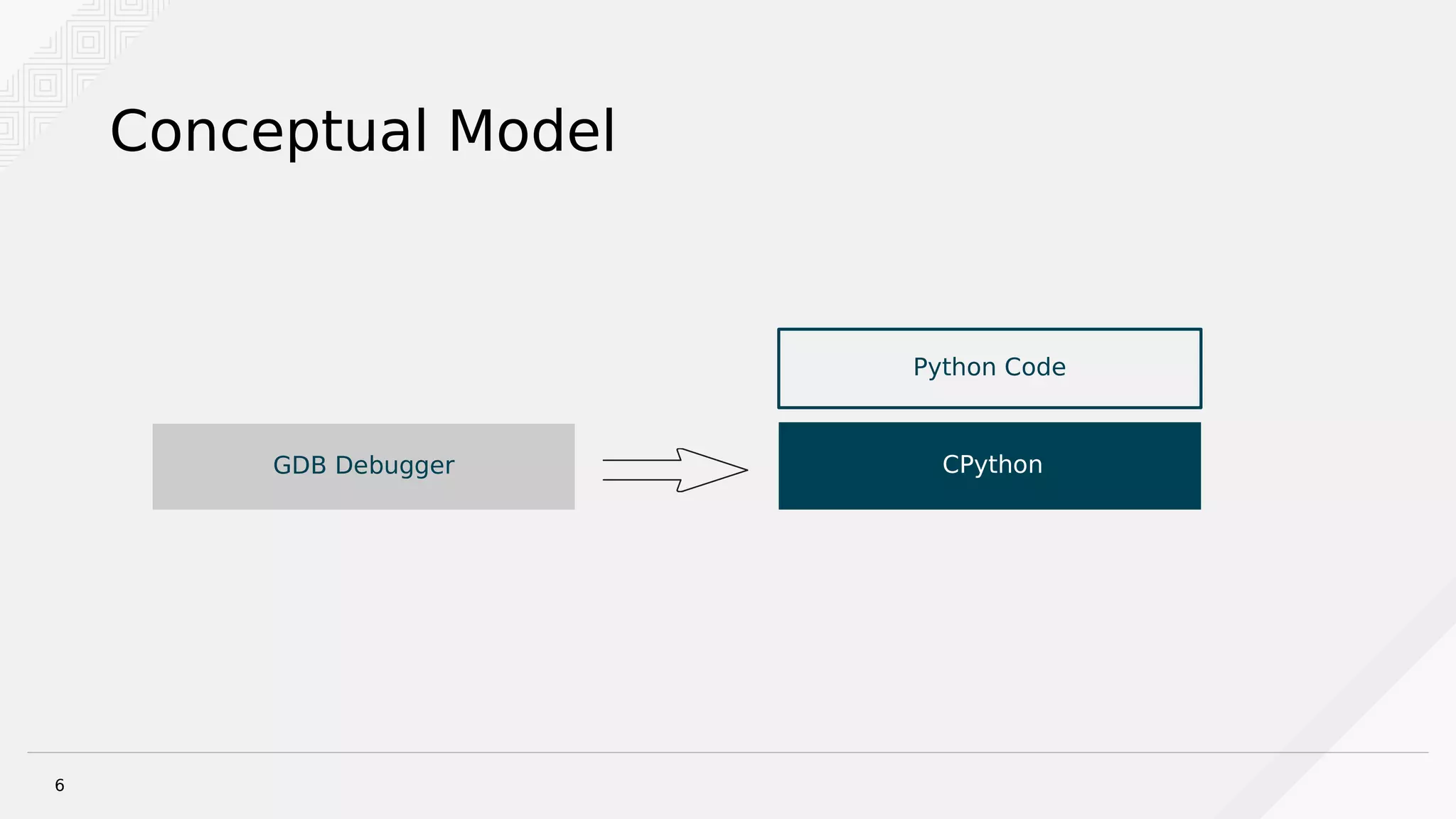
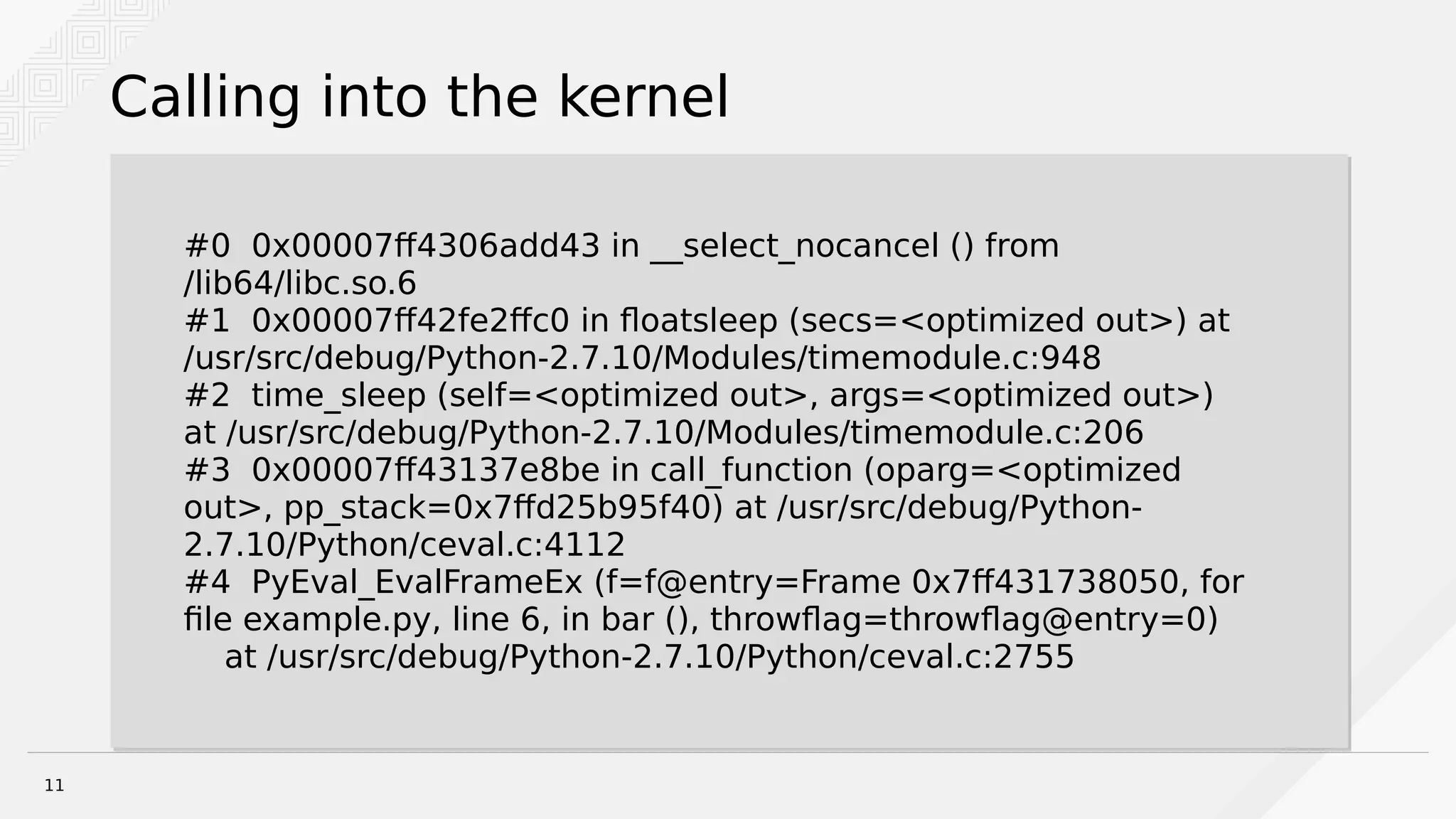
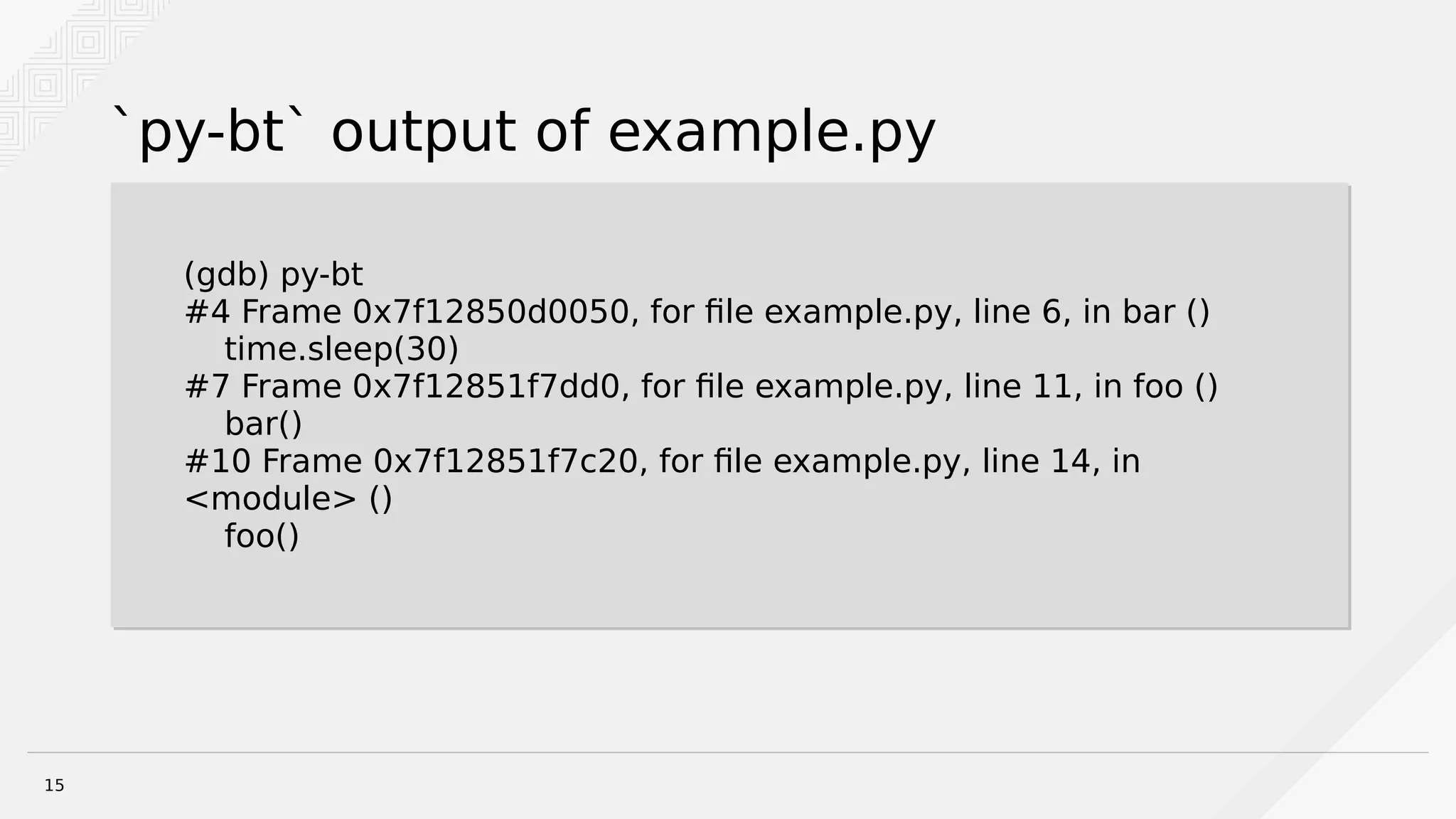
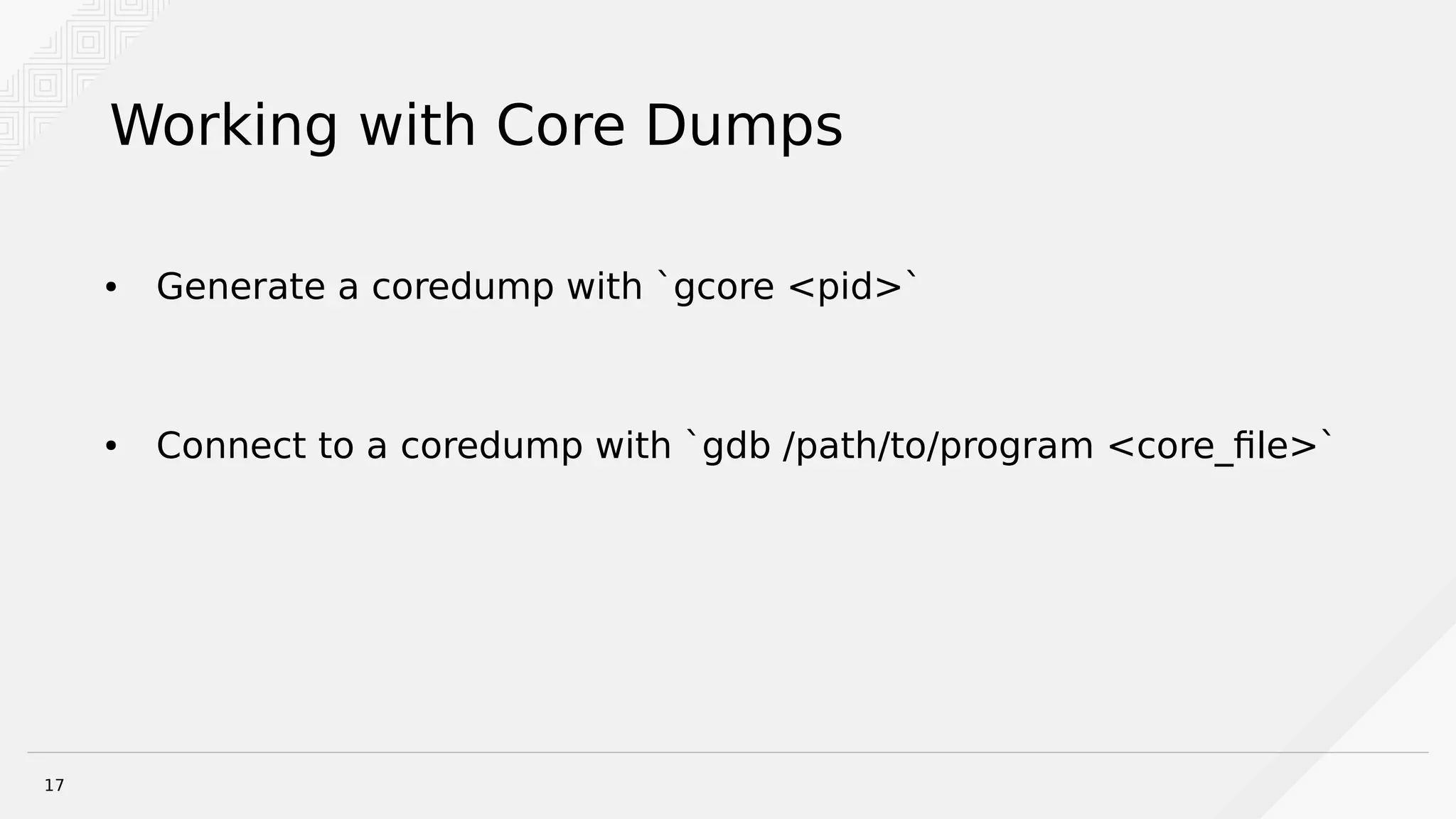
Brian Bouterse discusses using the GNU Debugger (GDB) to debug hung Python processes. GDB can be used to attach to running Python processes and debug issues that occur in production or with remote/rarely occurring problems. The debugger provides tools like stack traces and examining local variables. Python extensions for GDB provide additional functionality for listing source code, switching threads, and more. Debugging with GDB requires installing debug symbols and dealing with optimized-out code. Alternative tools like strace and rpdb can also provide debugging assistance.