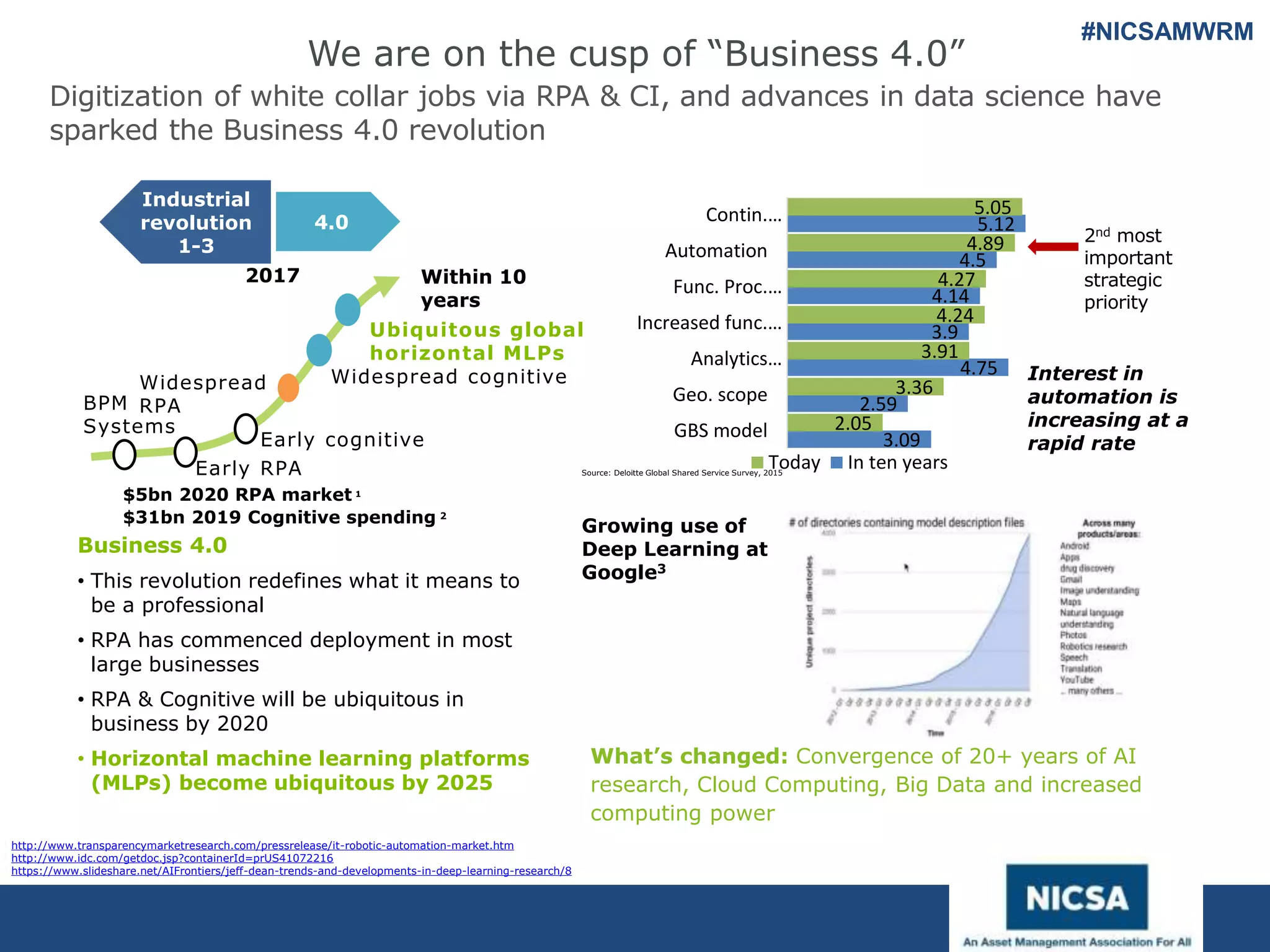
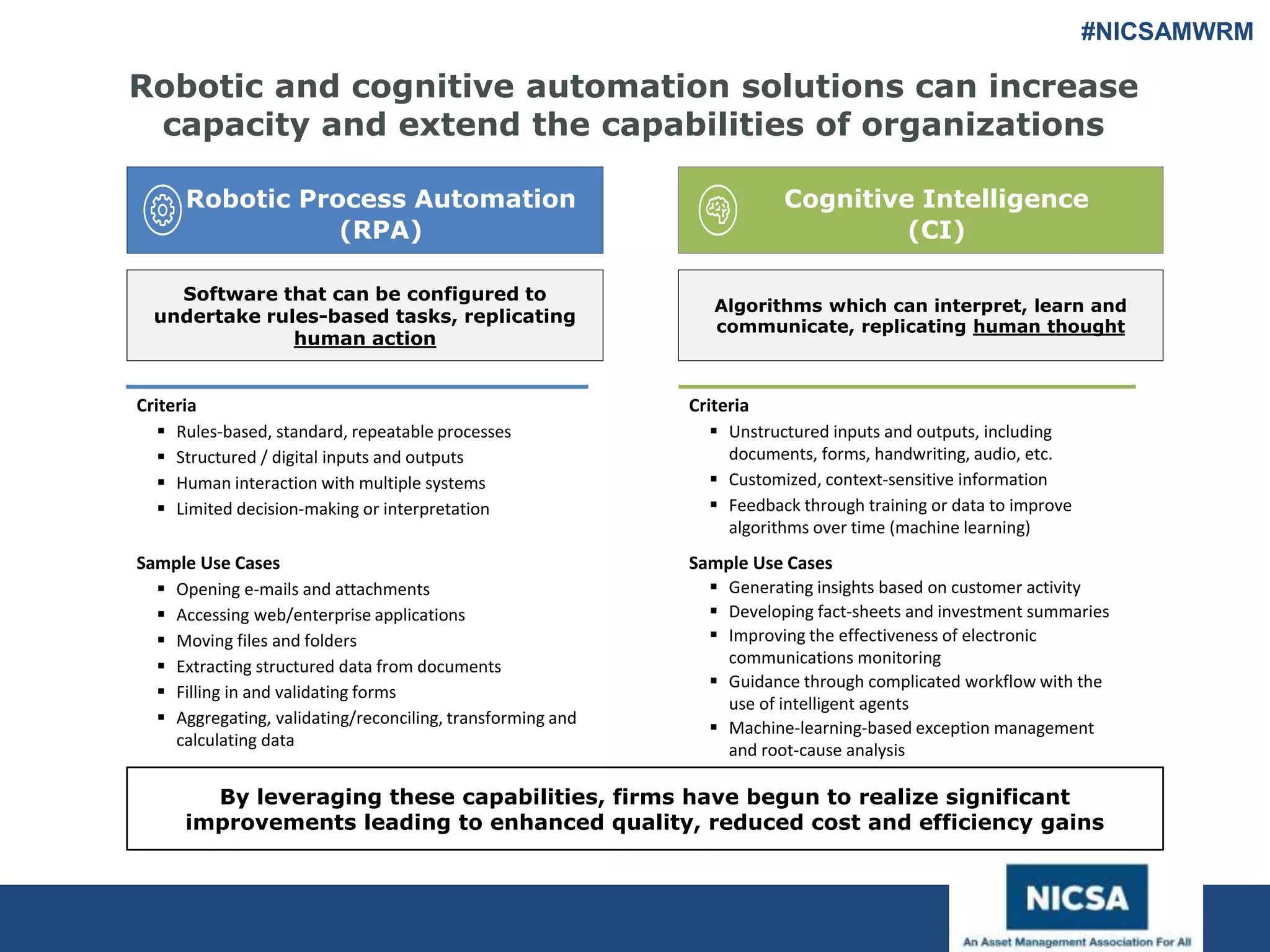
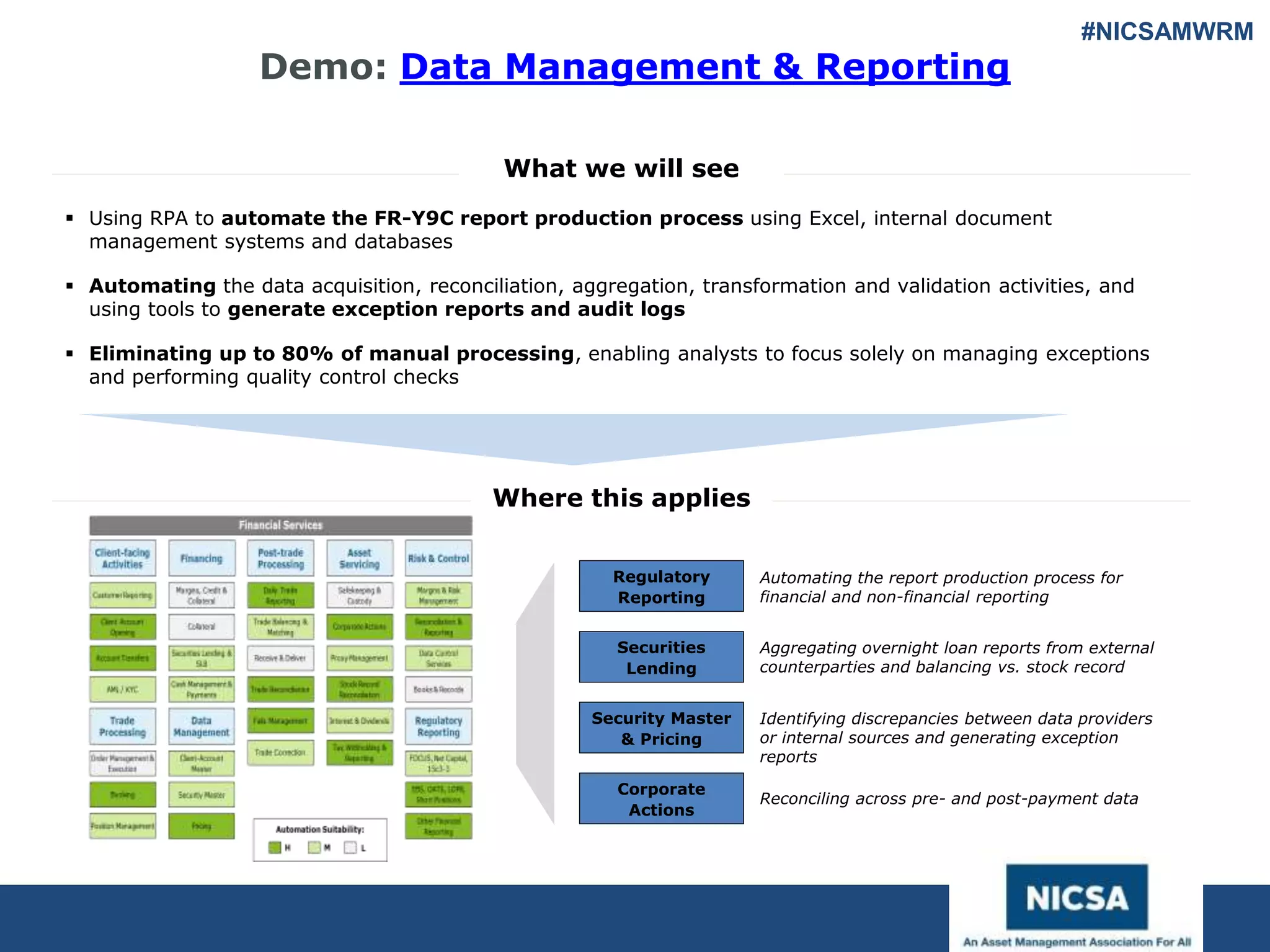
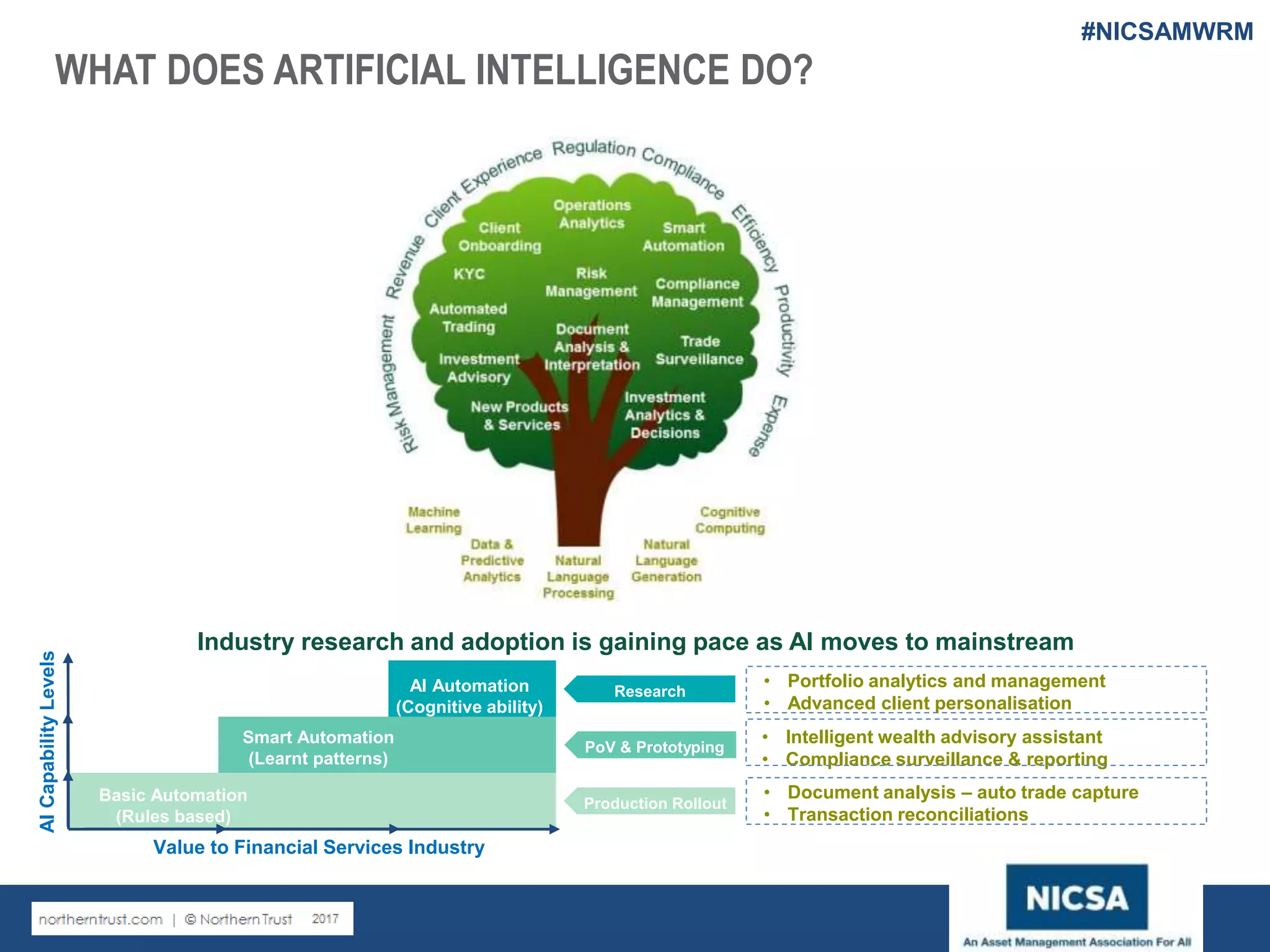
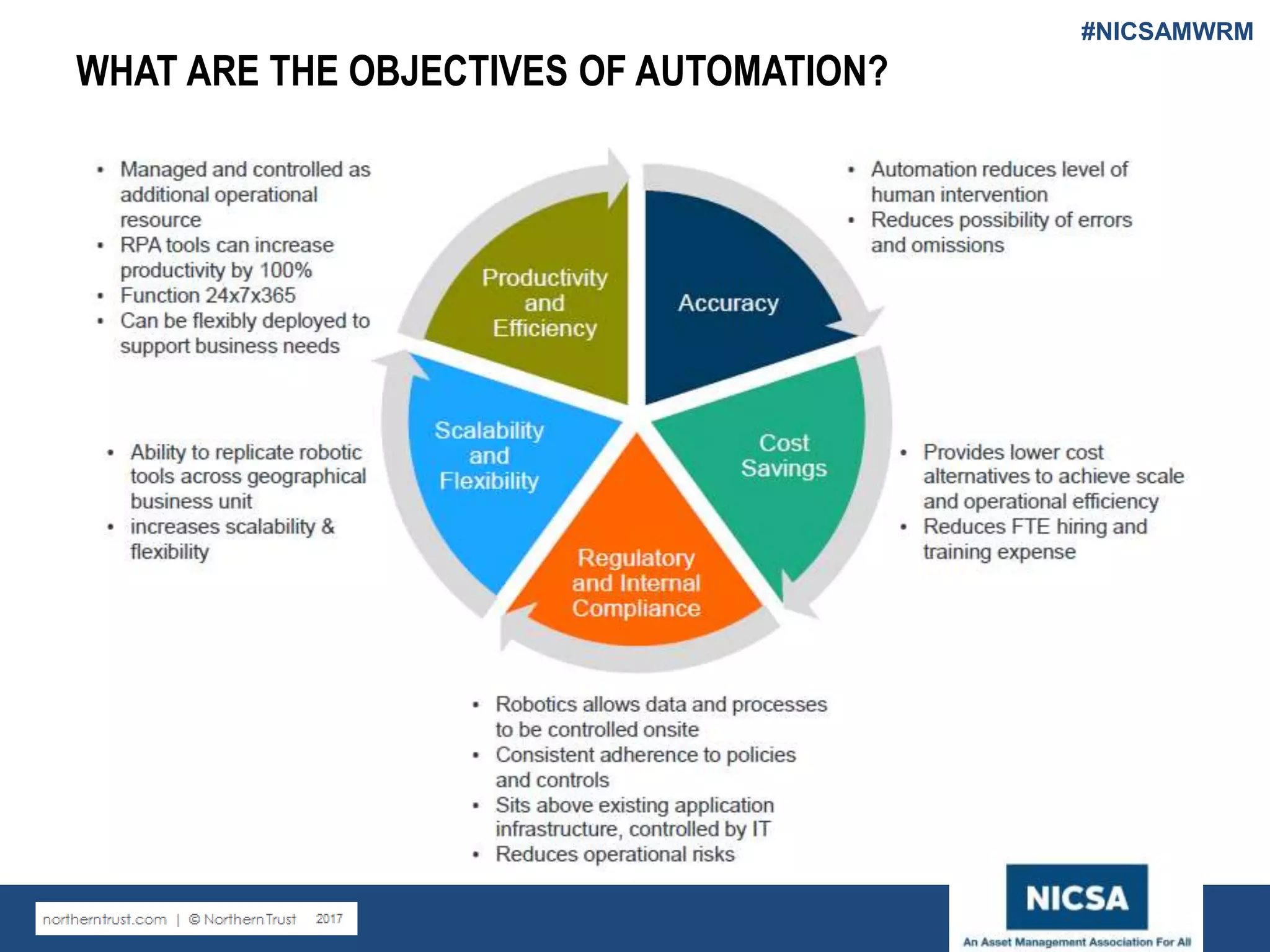
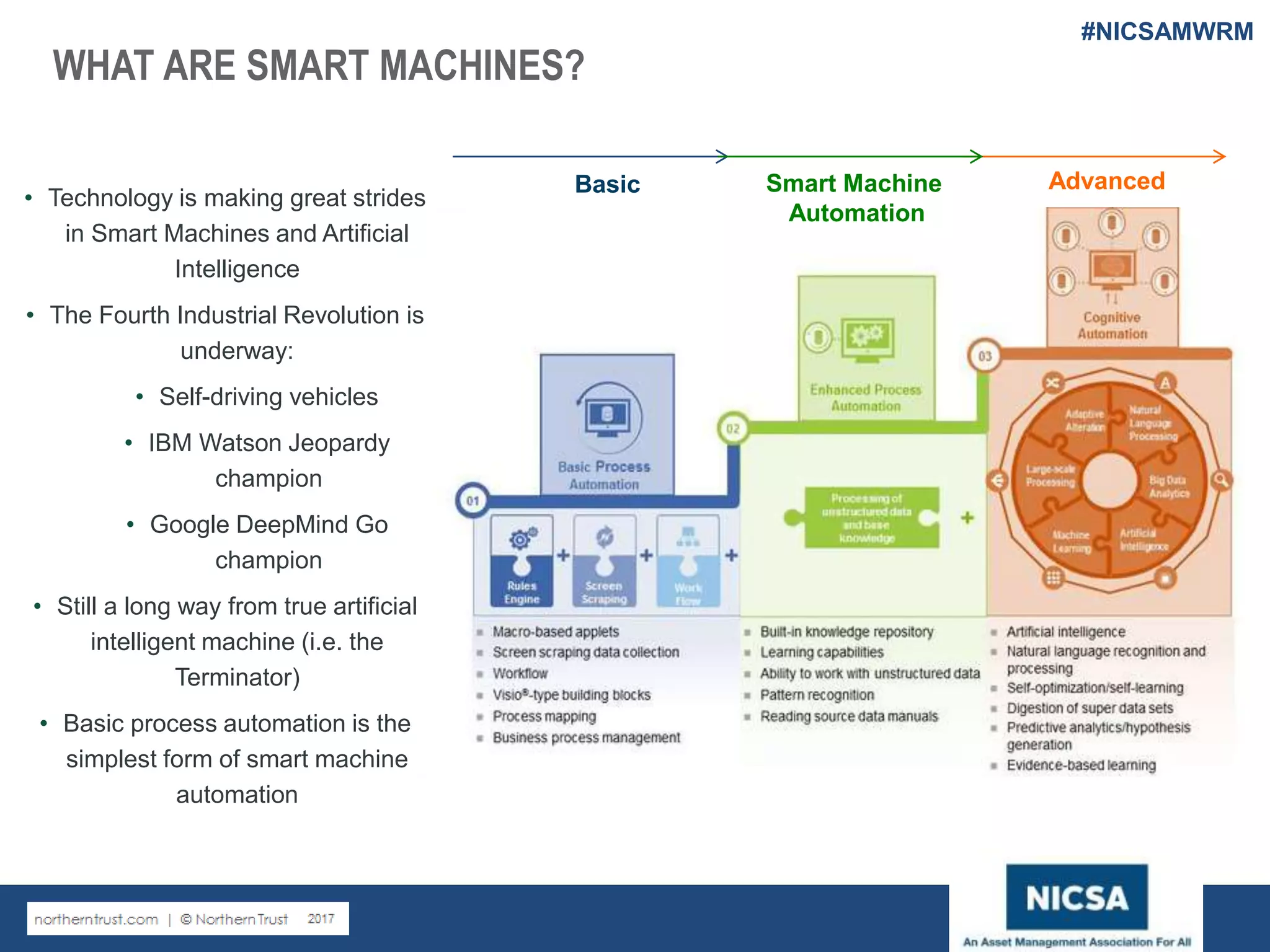
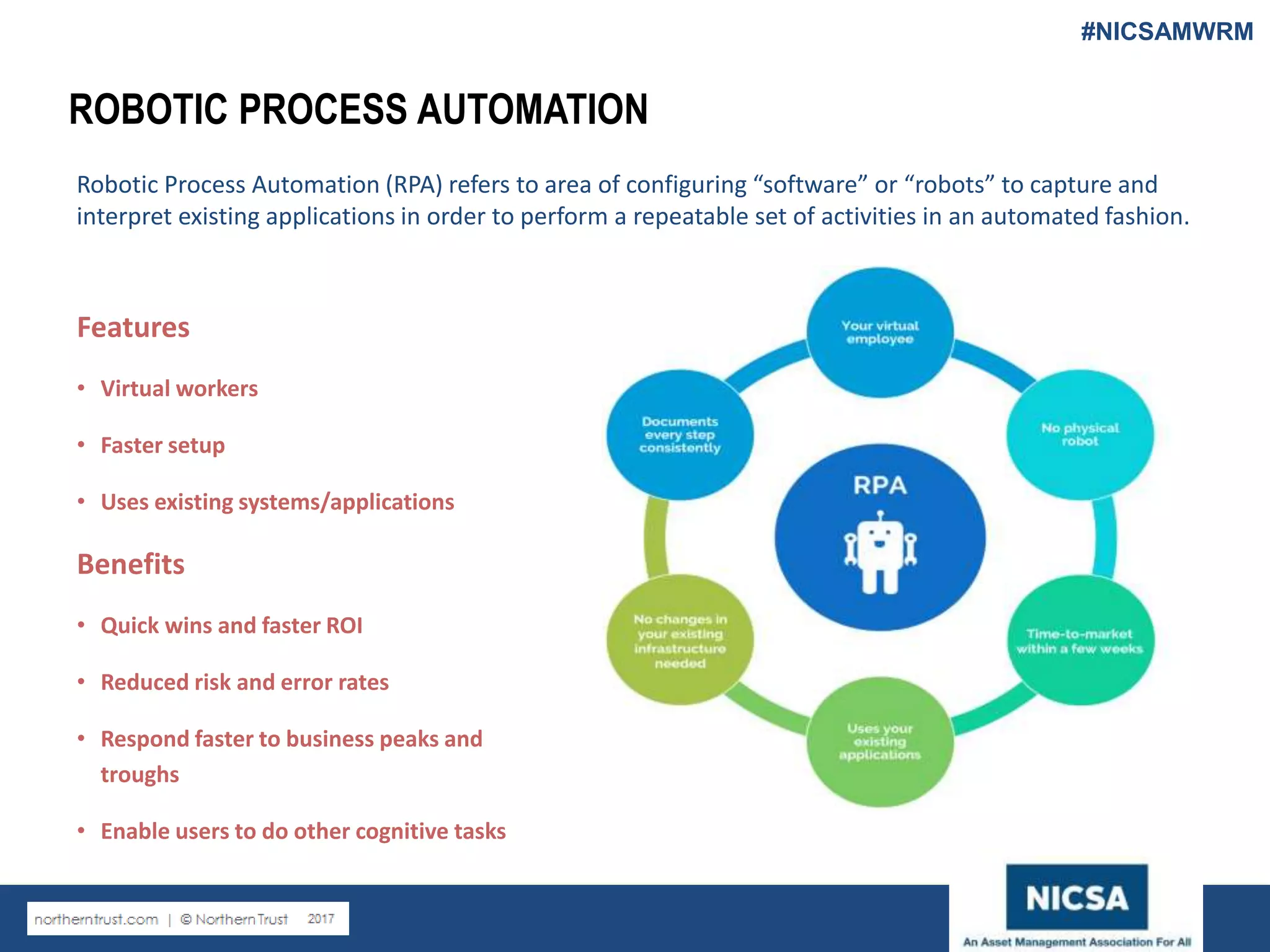
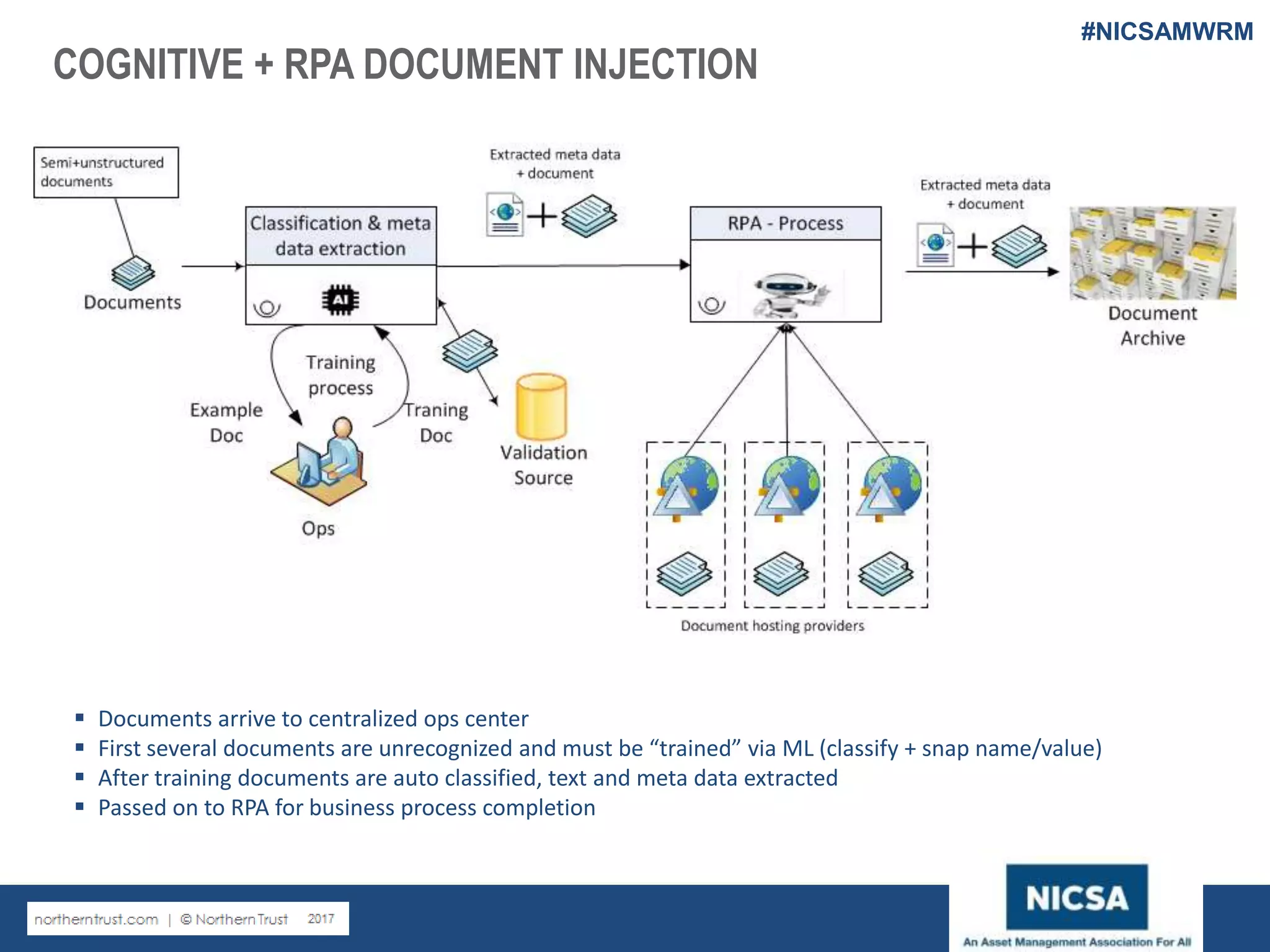
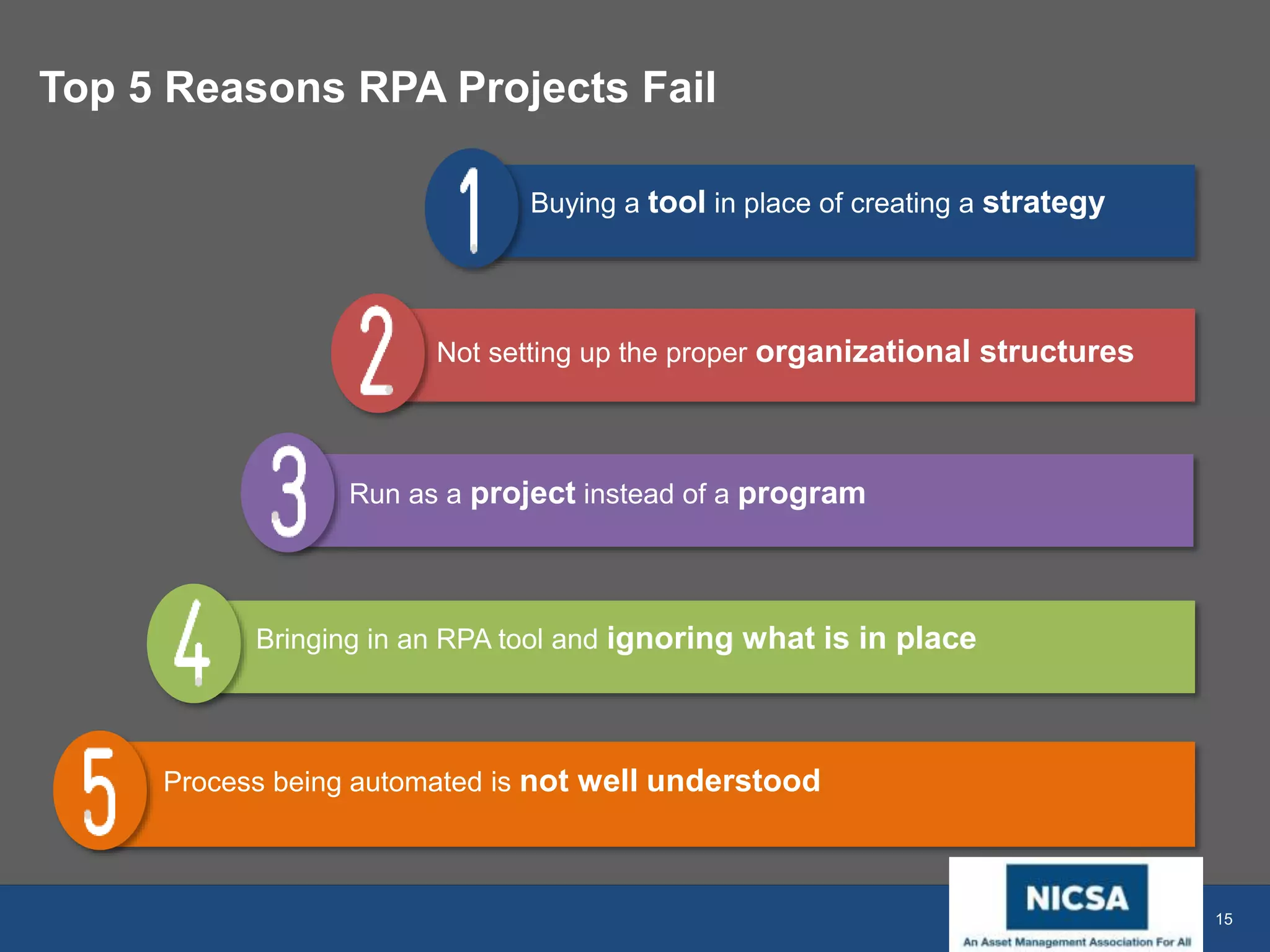
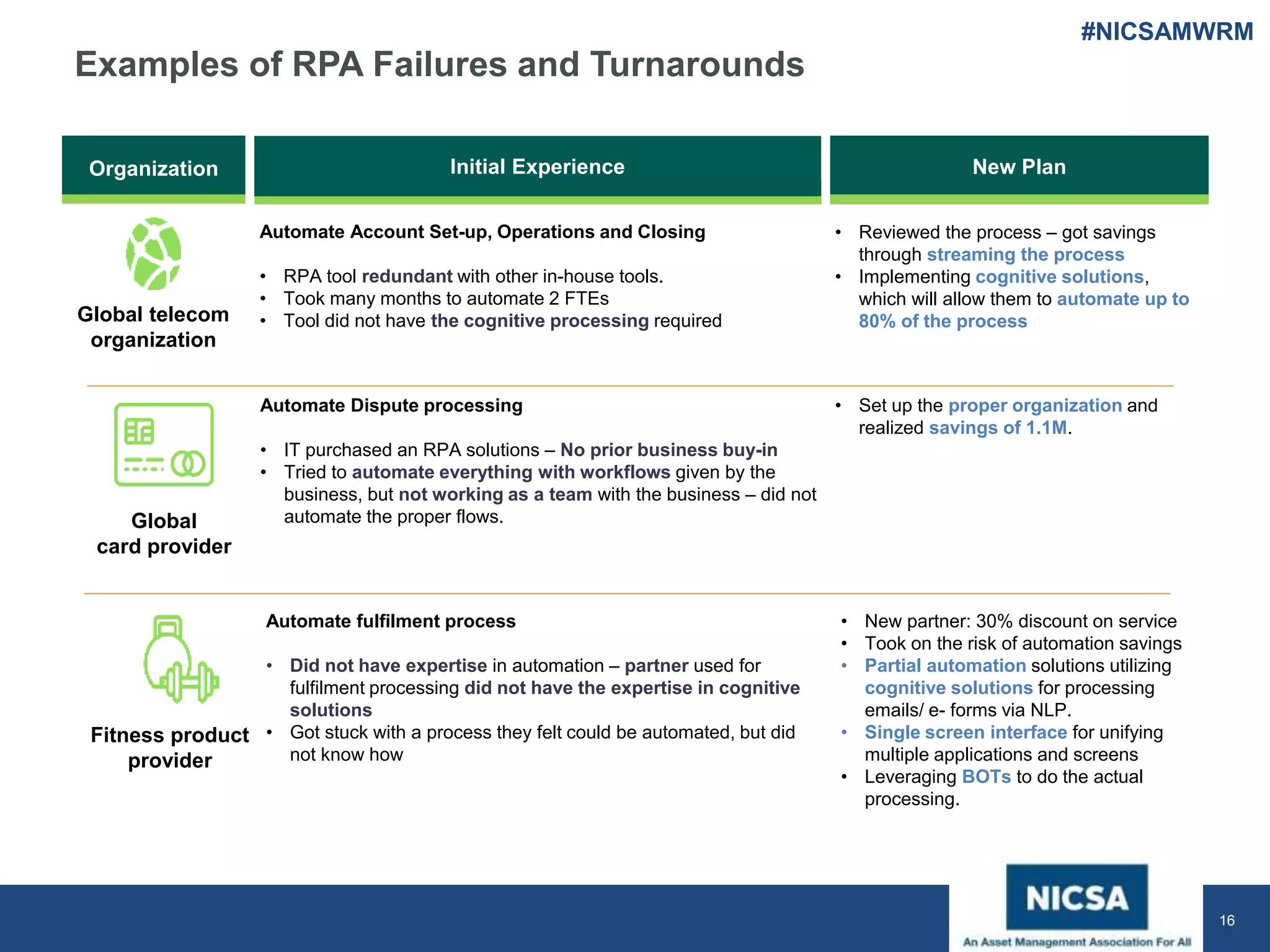
The document discusses the impact of robotic process automation (RPA) and cognitive intelligence (CI) in transforming professional landscapes, highlighting advancements in data science that have contributed to the Business 4.0 revolution. It details various use cases, potential benefits, and challenges of implementing RPA, along with examples of both failures and successful turnarounds in automation projects. Key insights emphasize the importance of strategic planning, user training, and adaptability in the face of rapidly evolving technology.