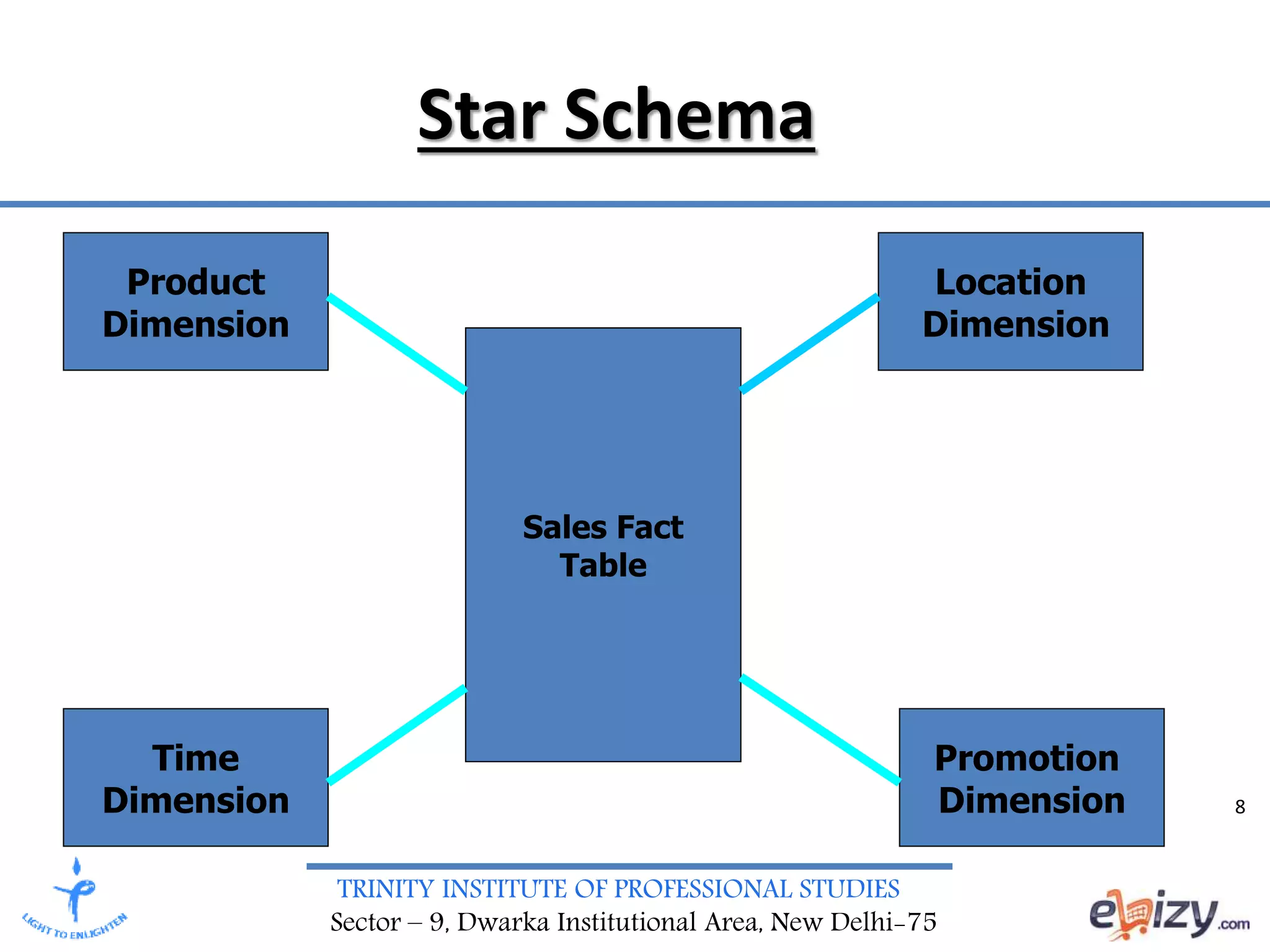
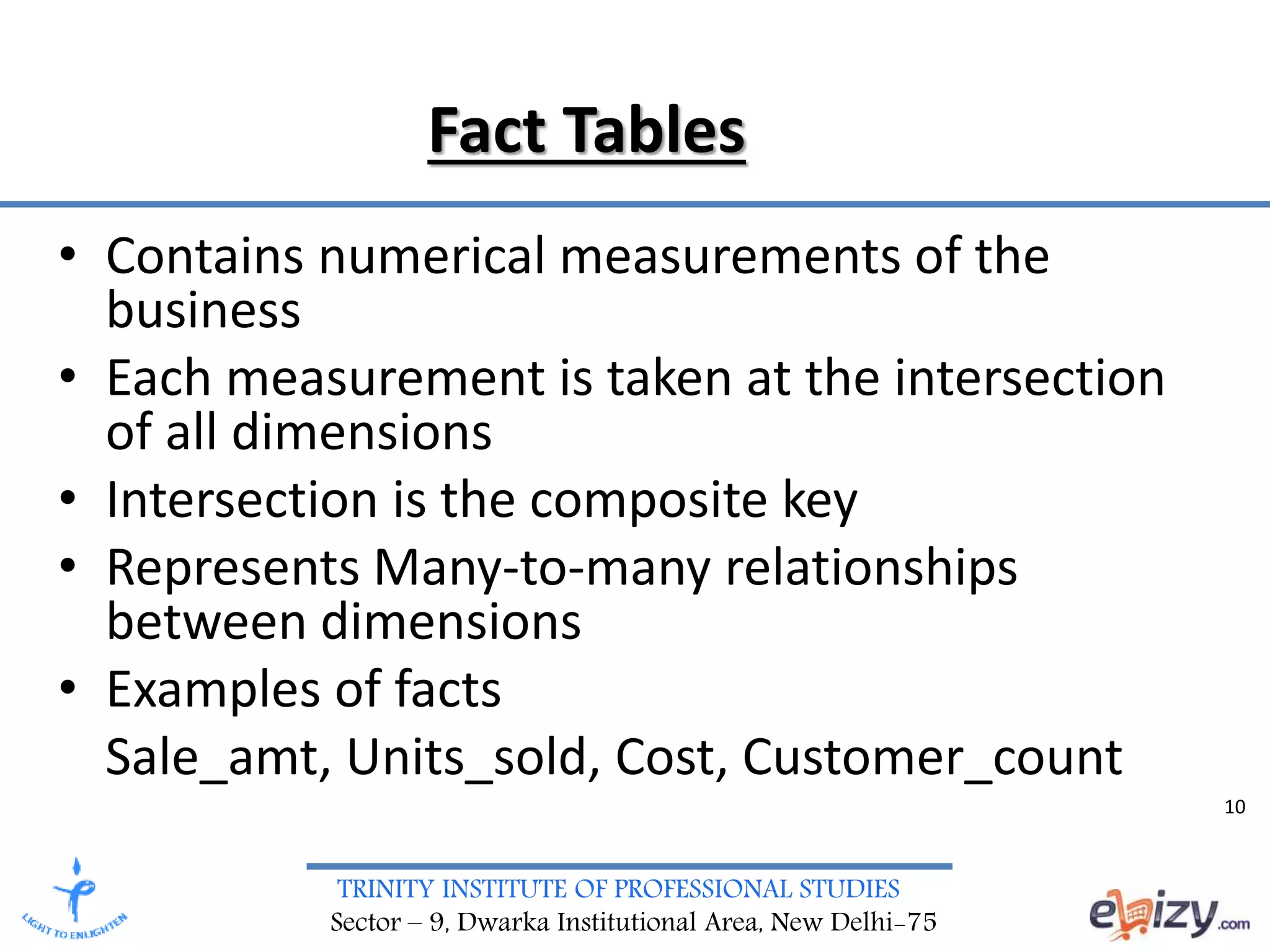
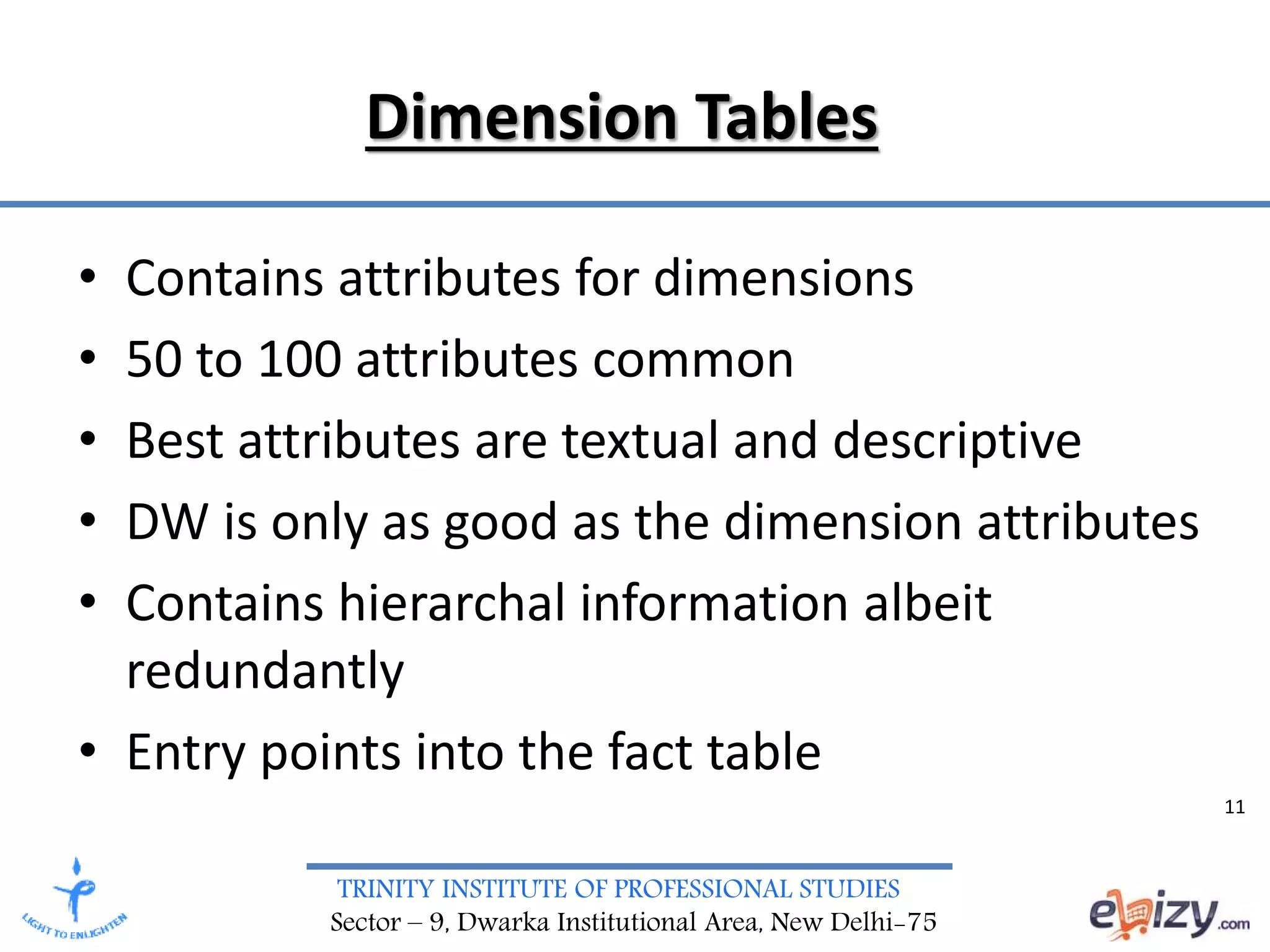
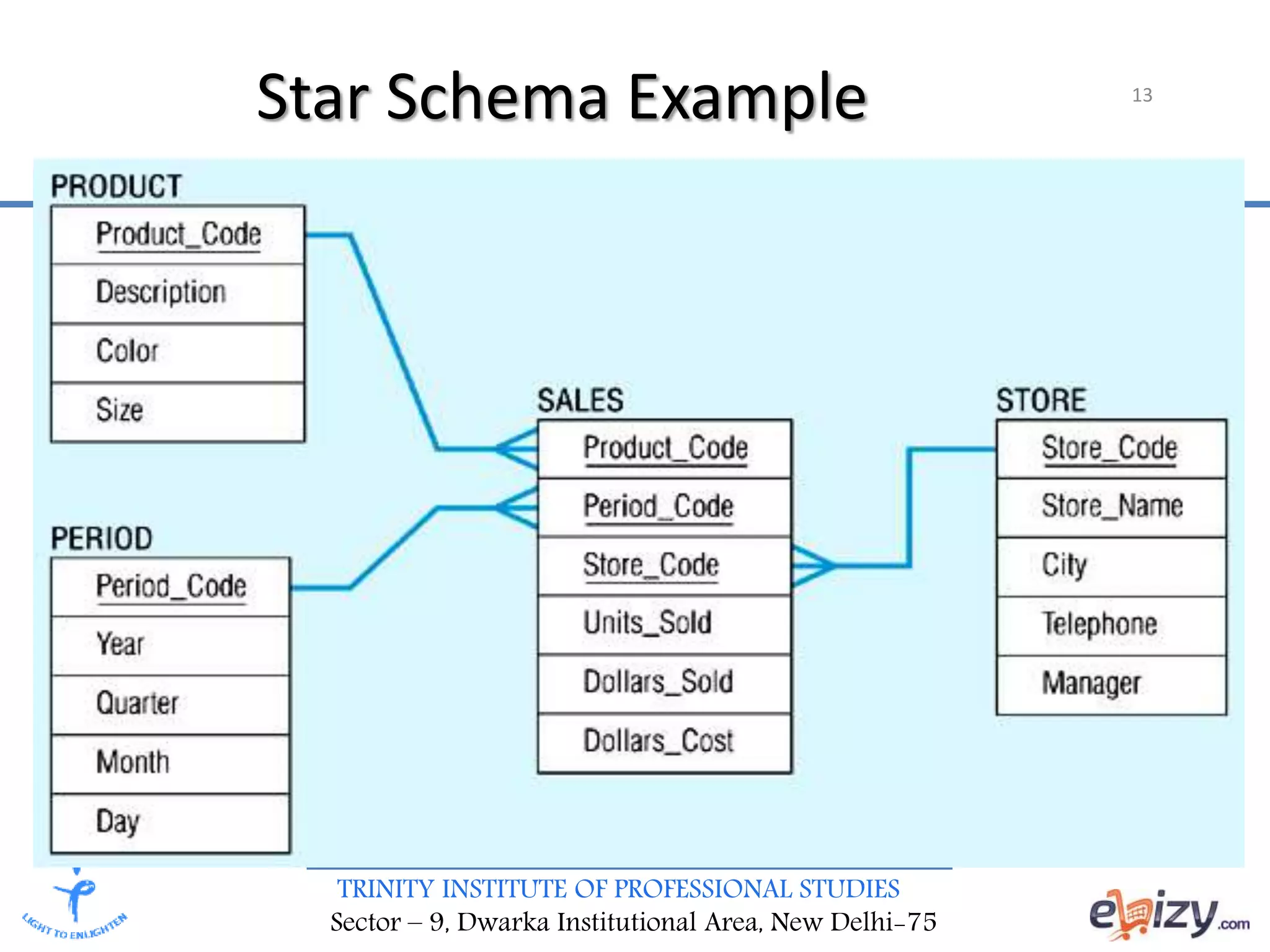
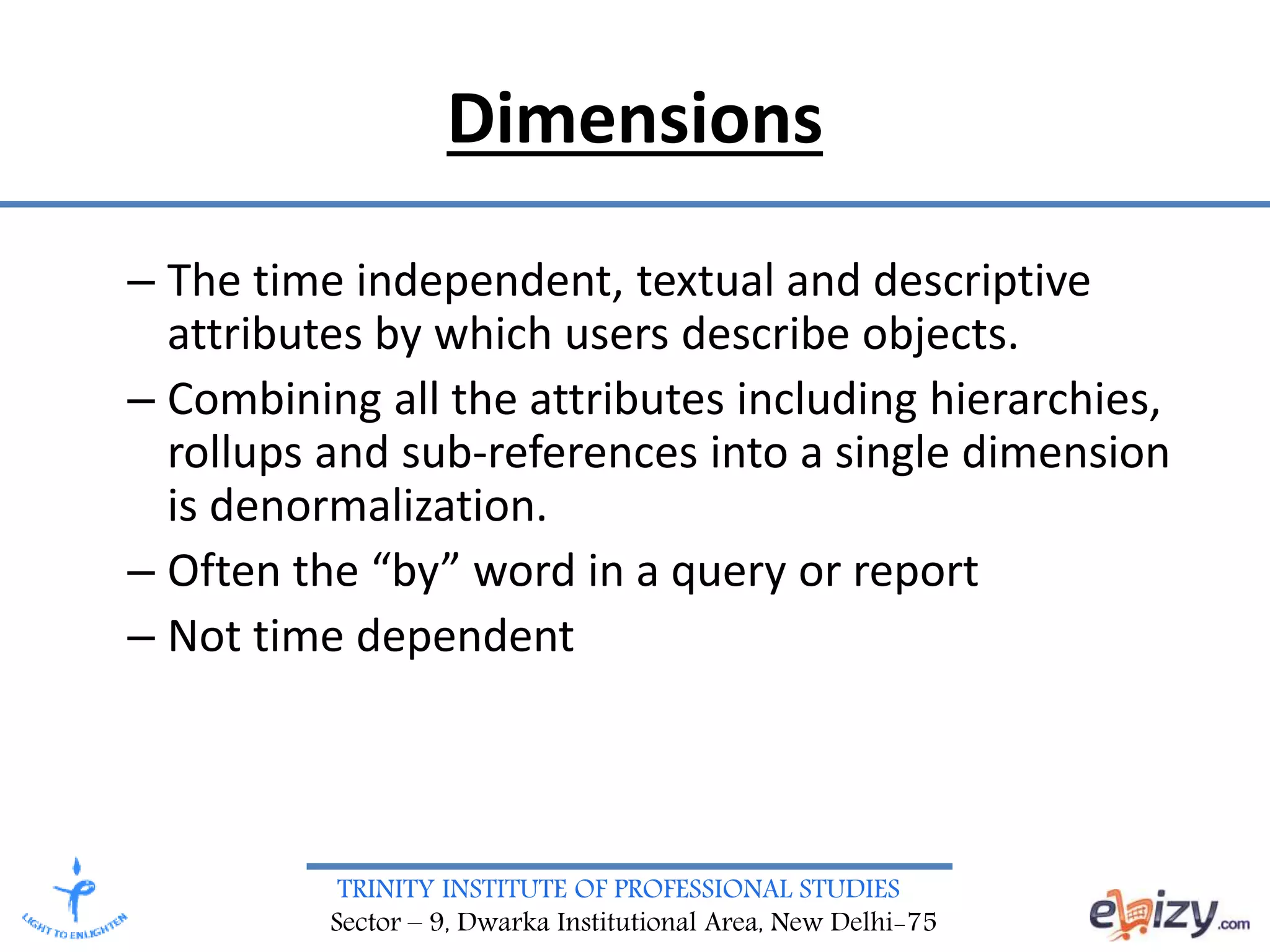
The document discusses the design requirements and differences between ER modeling and dimensional modeling in data warehousing. It emphasizes that while ER models are effective for transaction processing, they can pose challenges for end-users and are not ideal for complex queries. In contrast, dimensional modeling is presented as a more suitable approach for analytical needs, represented through star schemas that facilitate data retrieval and analysis.