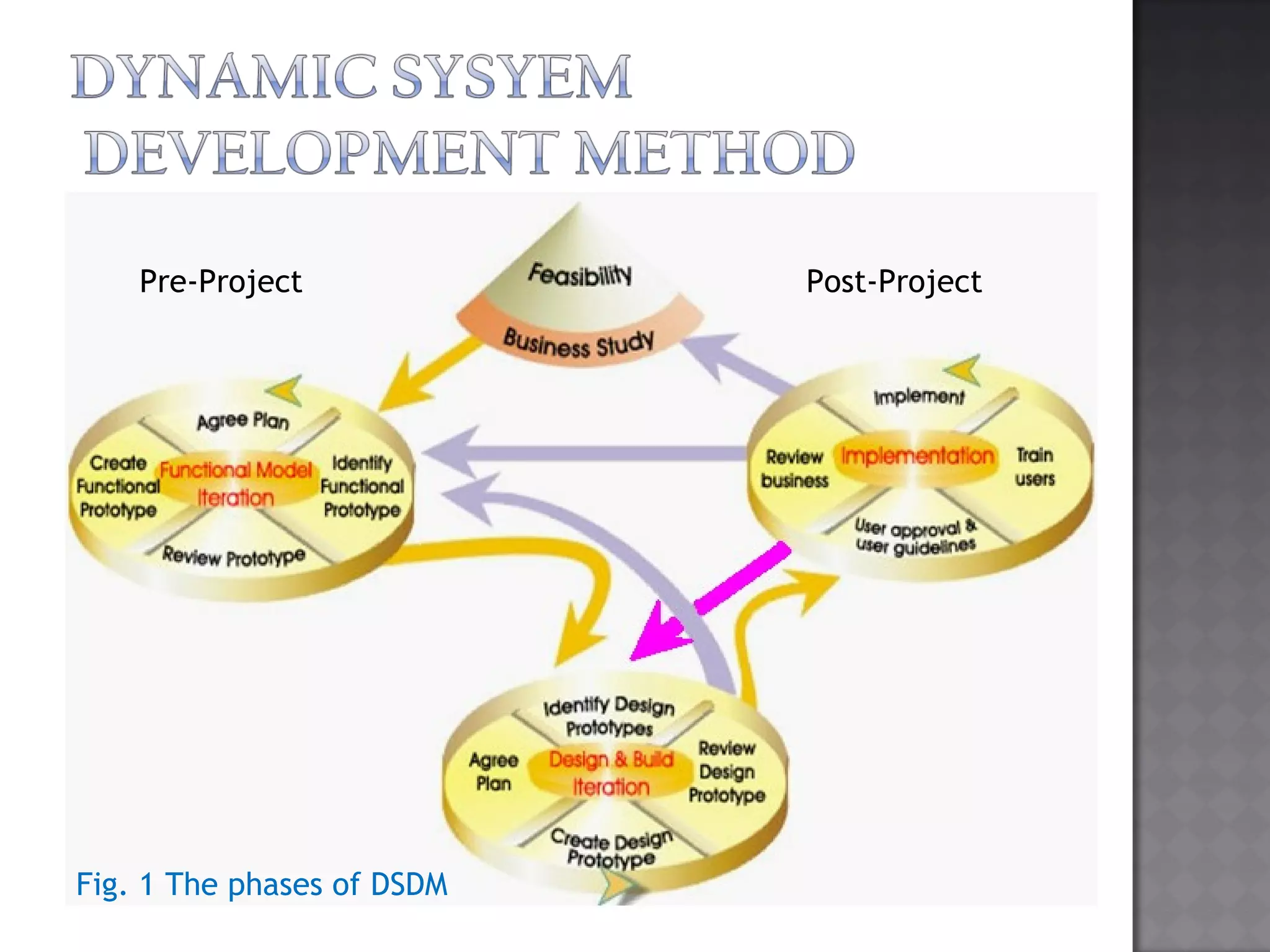
DSDM is a software development methodology based on RAD that emphasizes iterative development, user involvement, and adaptability. It aims to deliver working software frequently within budget and schedule while allowing changing requirements. DSDM was developed in the 1990s in the UK and uses principles like active user involvement, empowered decision-making teams, and reversible changes to facilitate iterative and collaborative development.