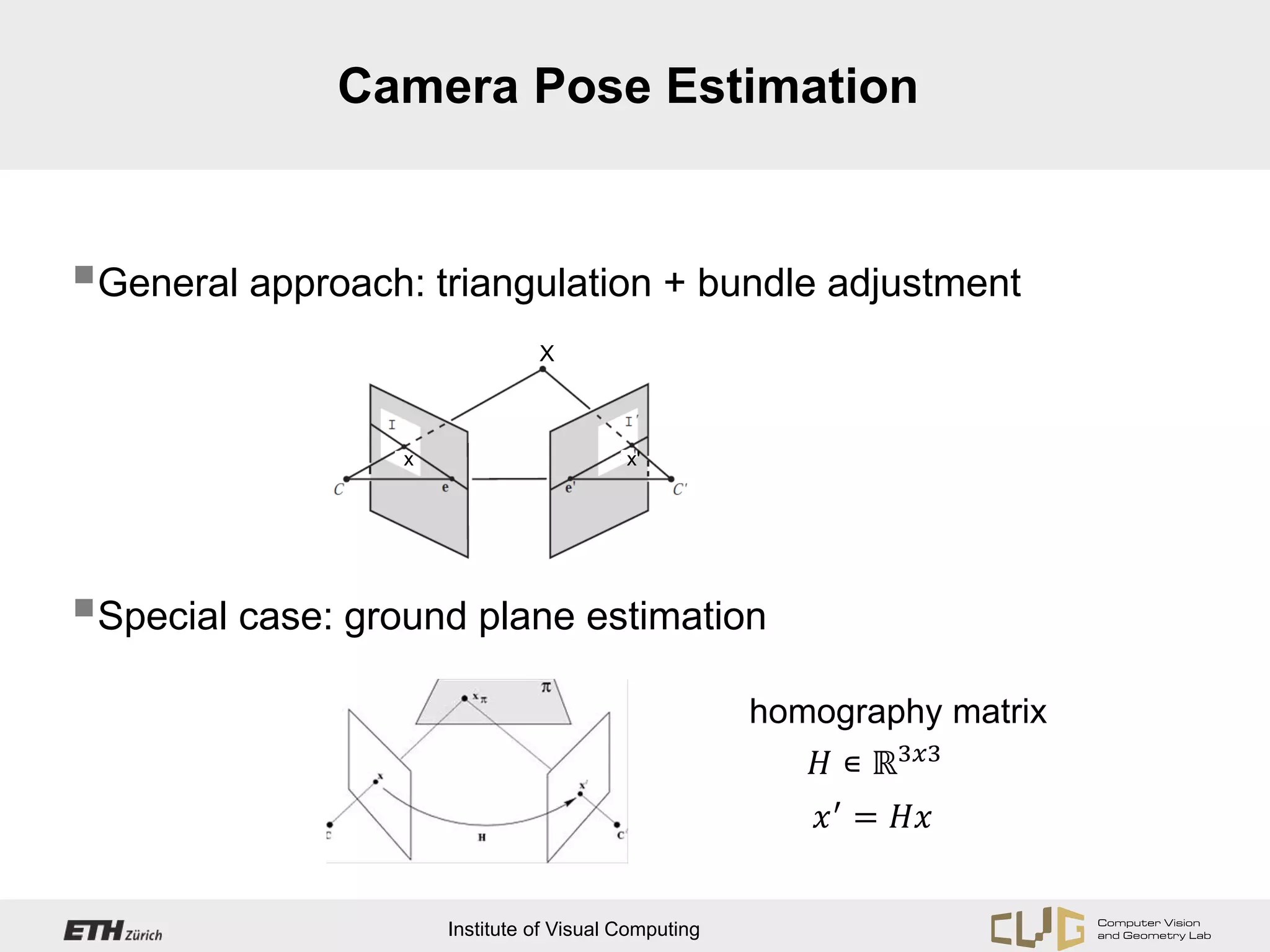
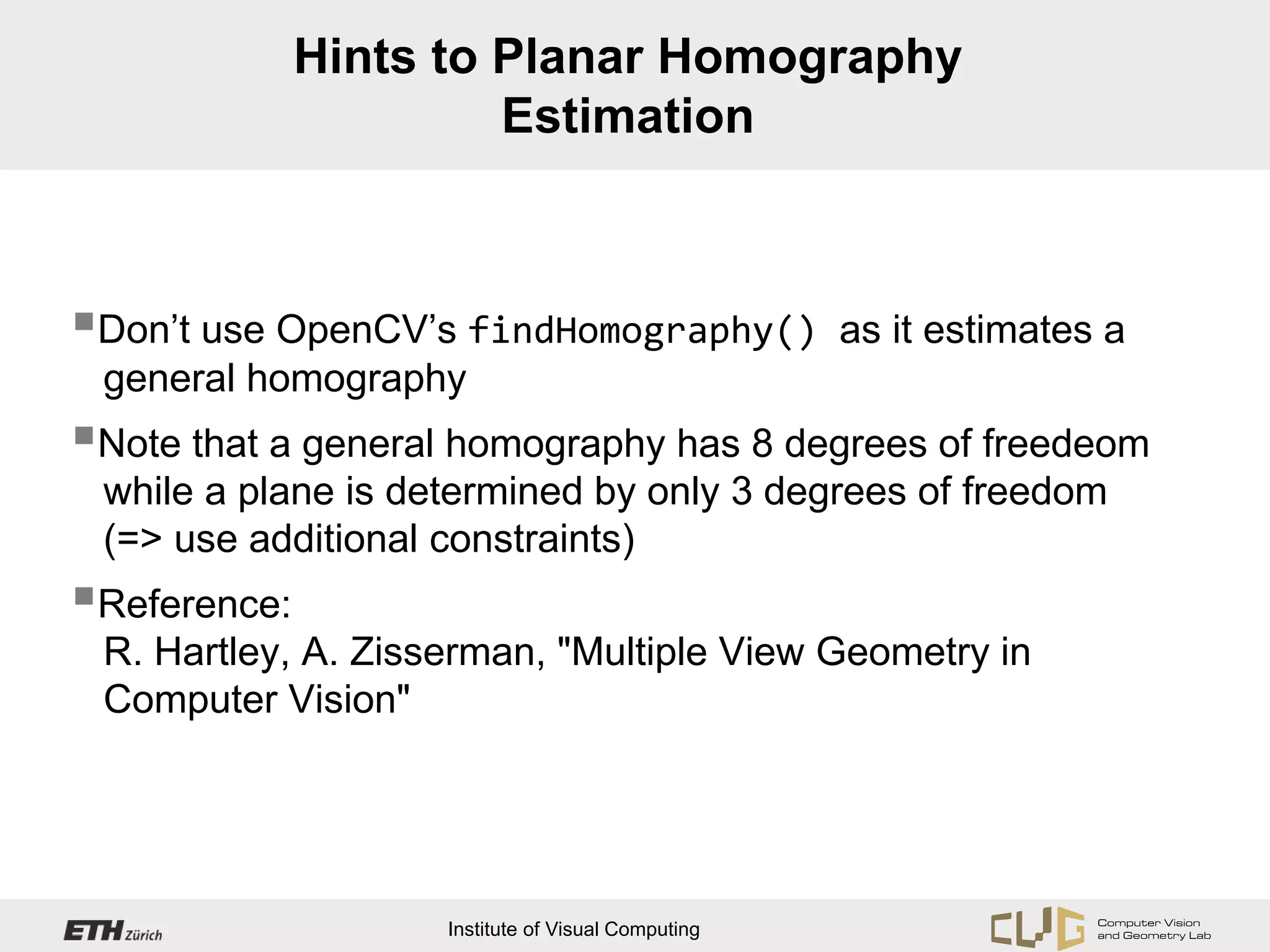
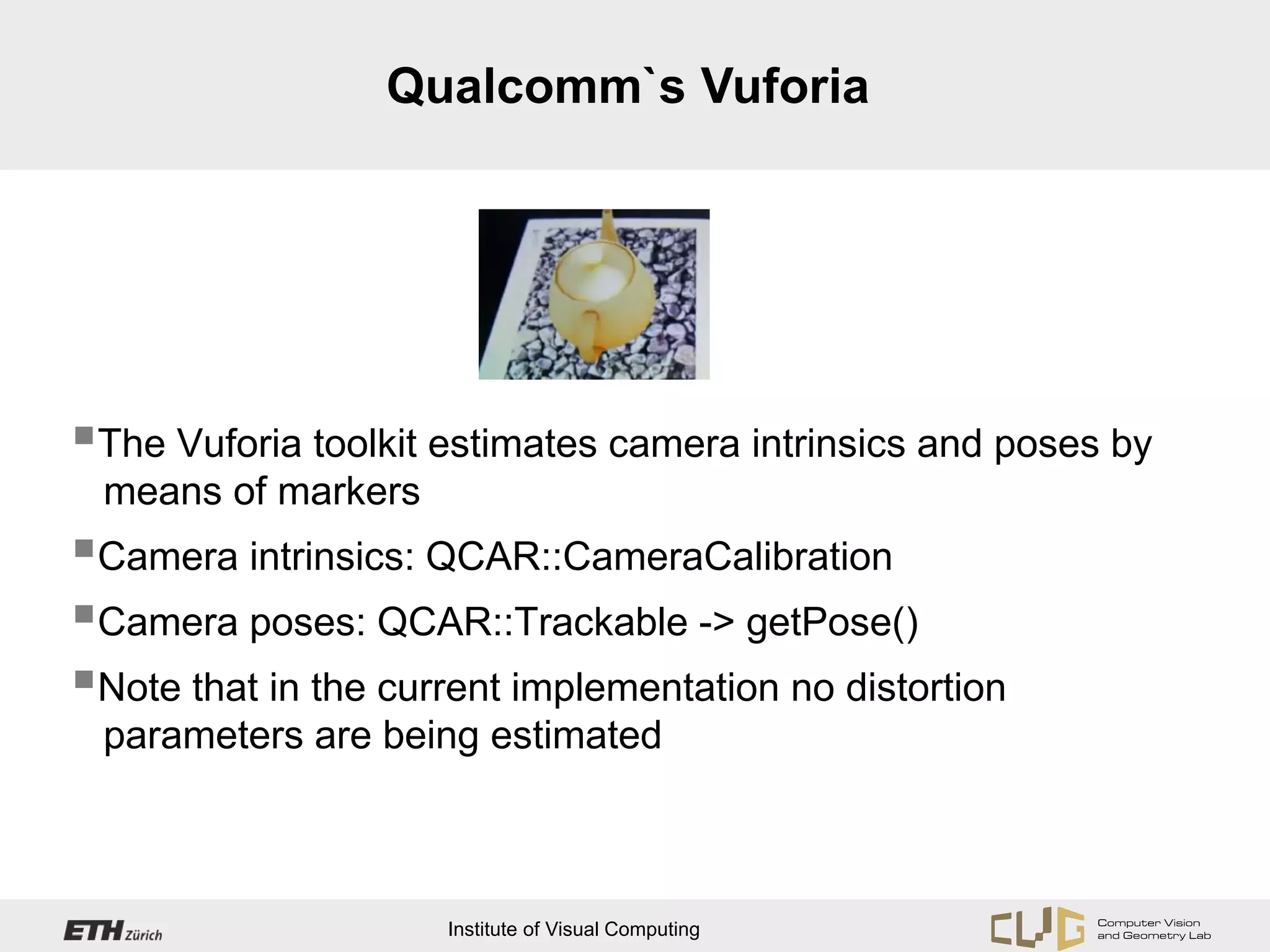
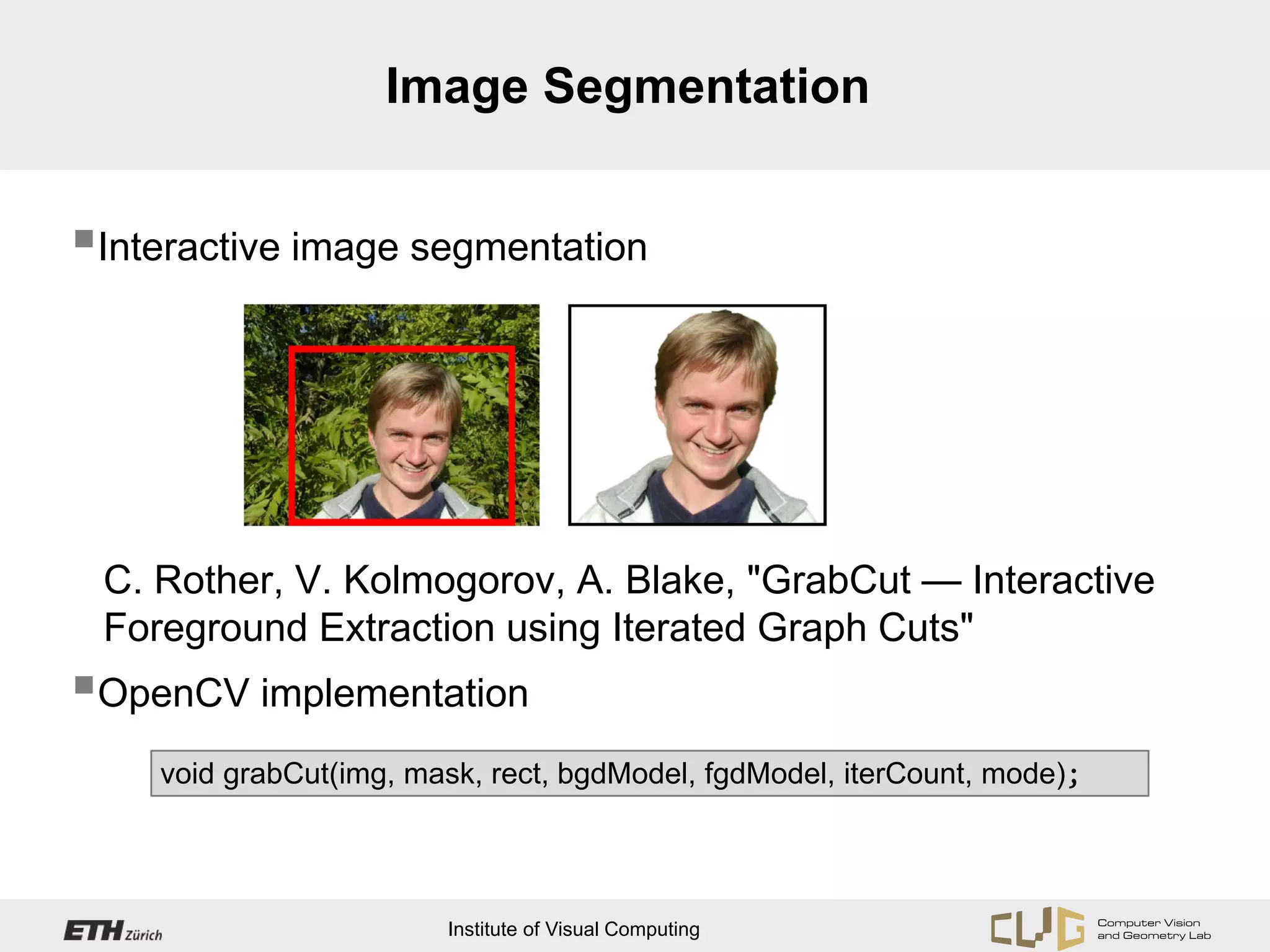
This document provides an overview of OpenCV, an open source computer vision and machine learning software library. It discusses OpenCV's core functionality for representing images as matrices and directly accessing pixel data. It also covers topics like camera calibration, feature point extraction and matching, and estimating camera pose through techniques like structure from motion and planar homography. Hints are provided for Android developers on required permissions and for planar homography estimation using additional constraints rather than OpenCV's general homography function.



![Core Functionality
Each image is represented as a matrix
Basic class Mat for storing general n-dimensional arrays
(e.g. grayscale images, color images, voxel volumes etc.)
Fast access to its elements via pointers, e.g.
Mat mat;
mat.ptr<float>(i)[j] = …
Direct access to user-allocated data (e.g. video frames)
Mat image(height, width, CV_8UC3, pixels, step);
Institute of Visual Computing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-opencv-130319225542-phpapp01/75/ETHZ-CV2012-Tutorial-openCV-4-2048.jpg)

![Pinhole Camera
𝑃 = 𝐾[𝑅|𝑡]
Pinhole camera model projection matrix
𝑓𝑥 𝑠 𝑝𝑥
calibration matrix
𝐾= 0 𝑓𝑦 𝑝𝑦
0 0 1
𝑅 ∊ ℝ3𝑥𝑥
extrinsic parameters
𝑡 ∊ ℝ3
Institute of Visual Computing](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/tutorial-opencv-130319225542-phpapp01/75/ETHZ-CV2012-Tutorial-openCV-7-2048.jpg)