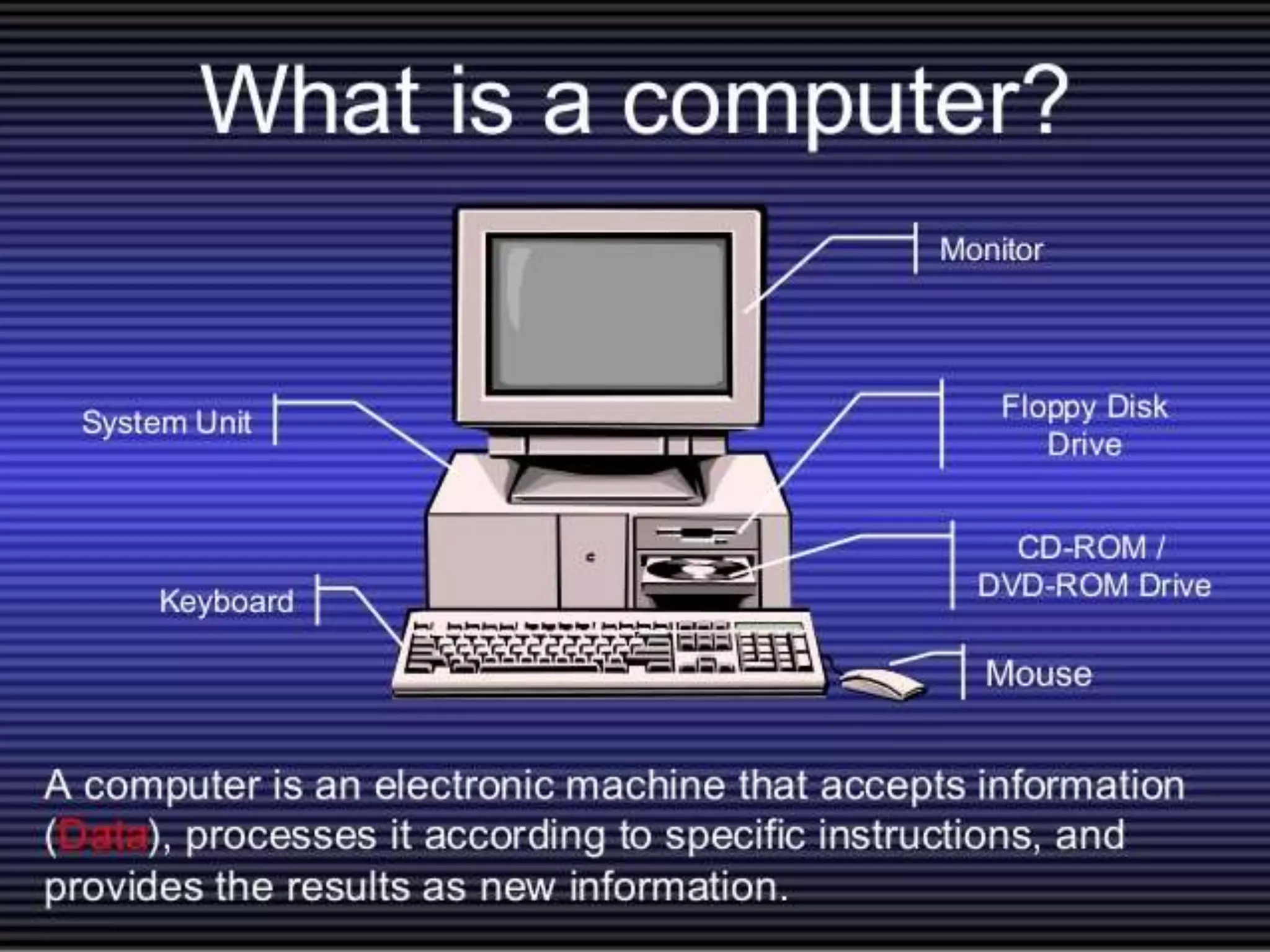
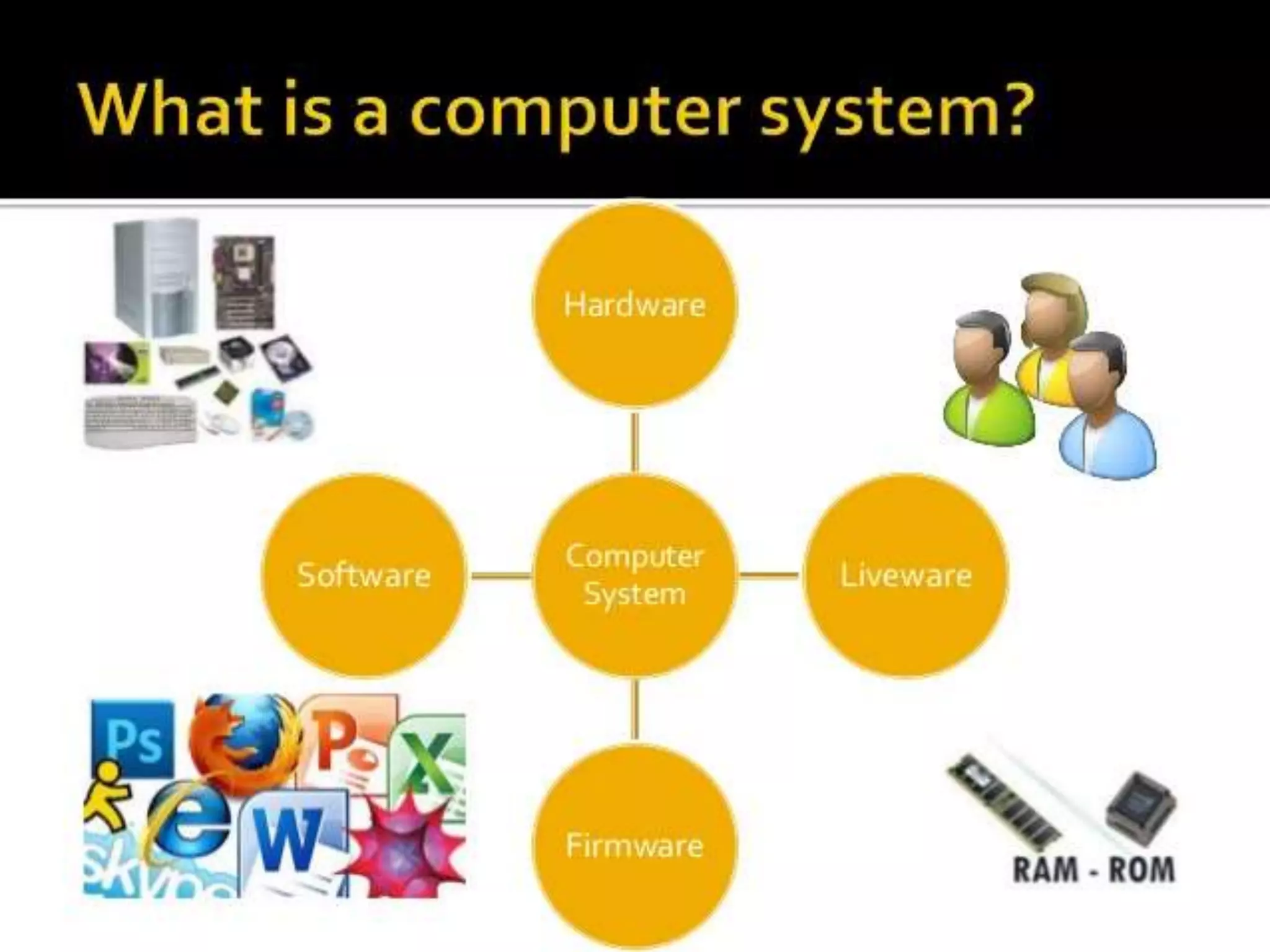
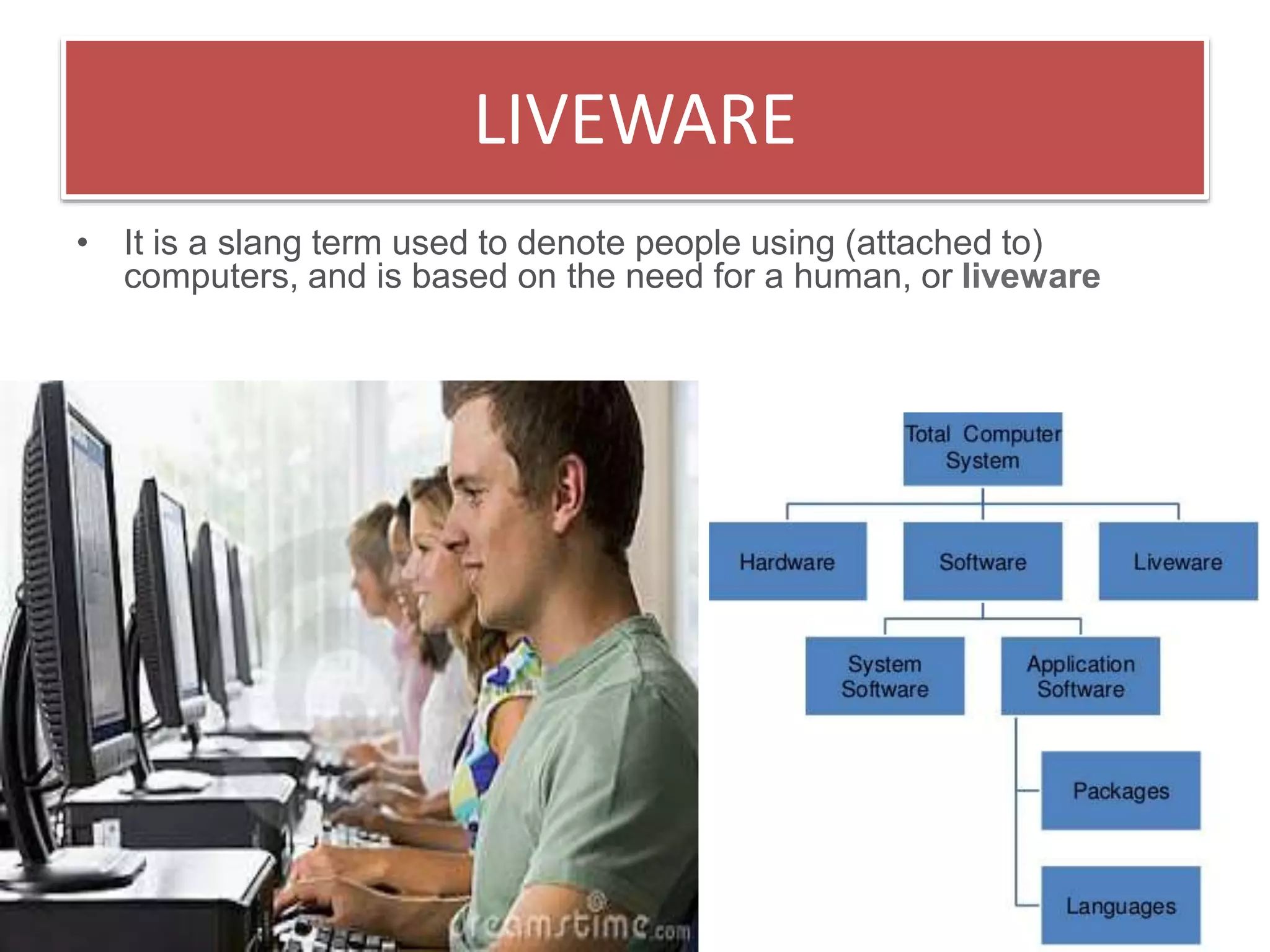
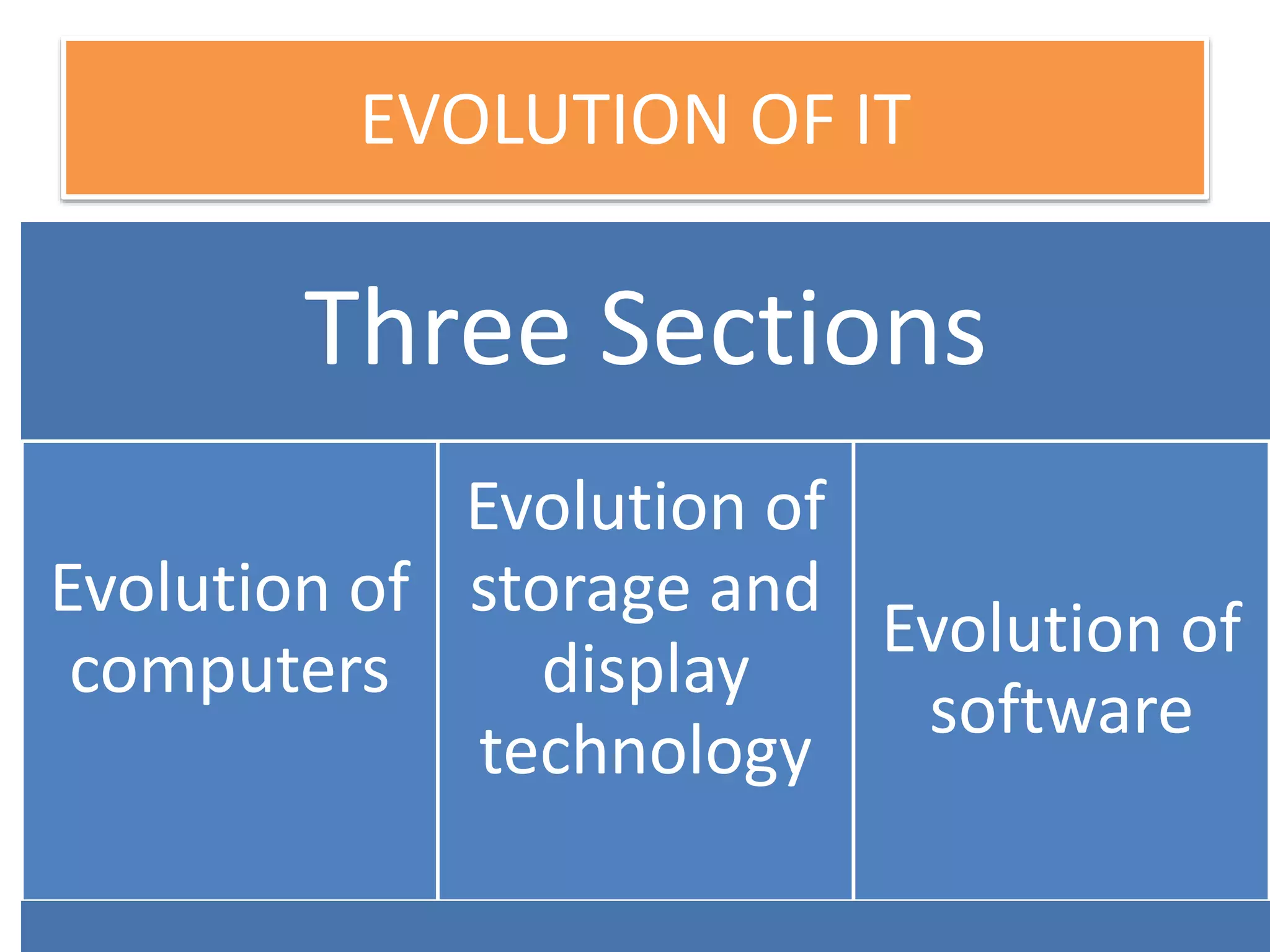
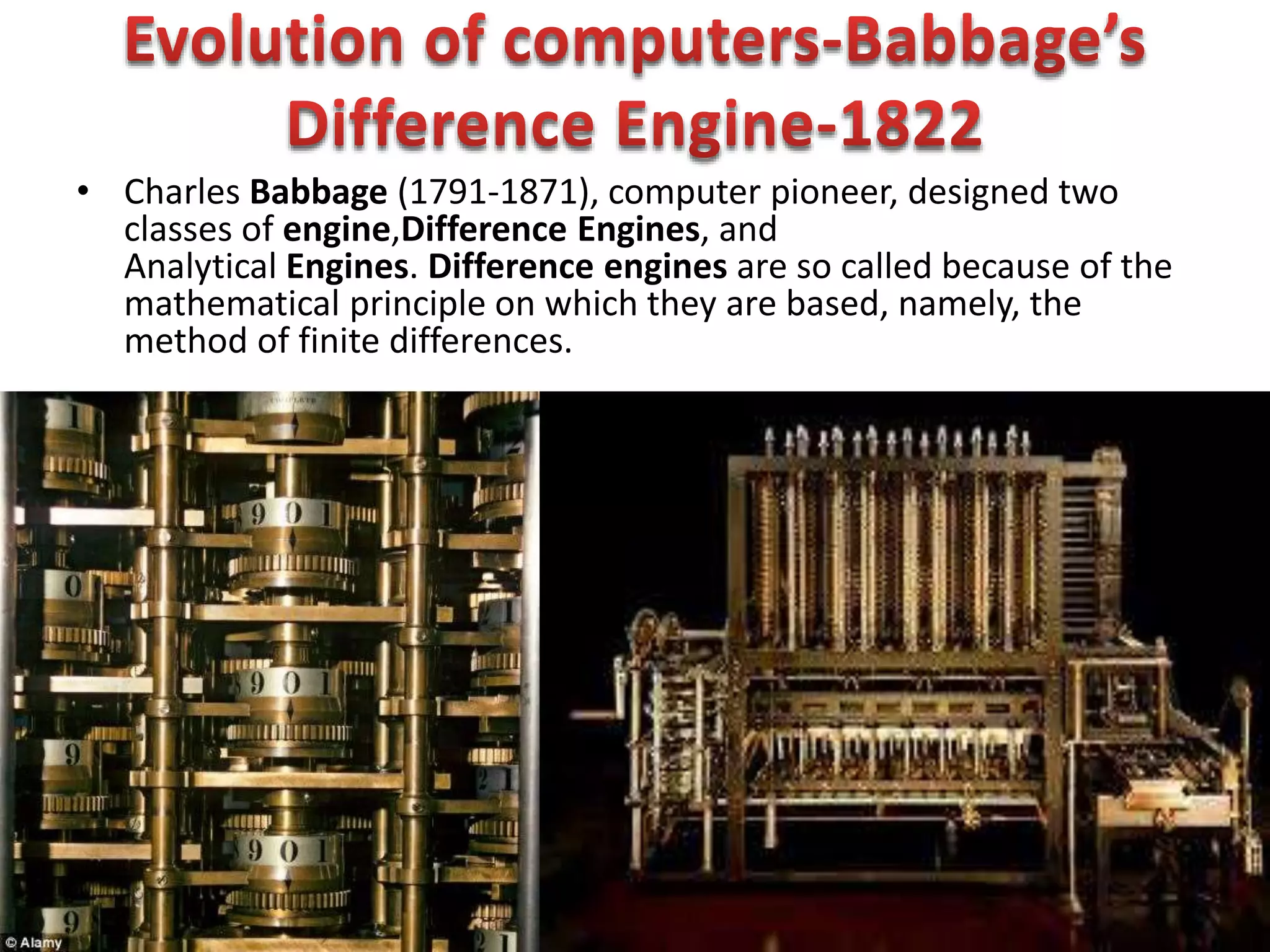
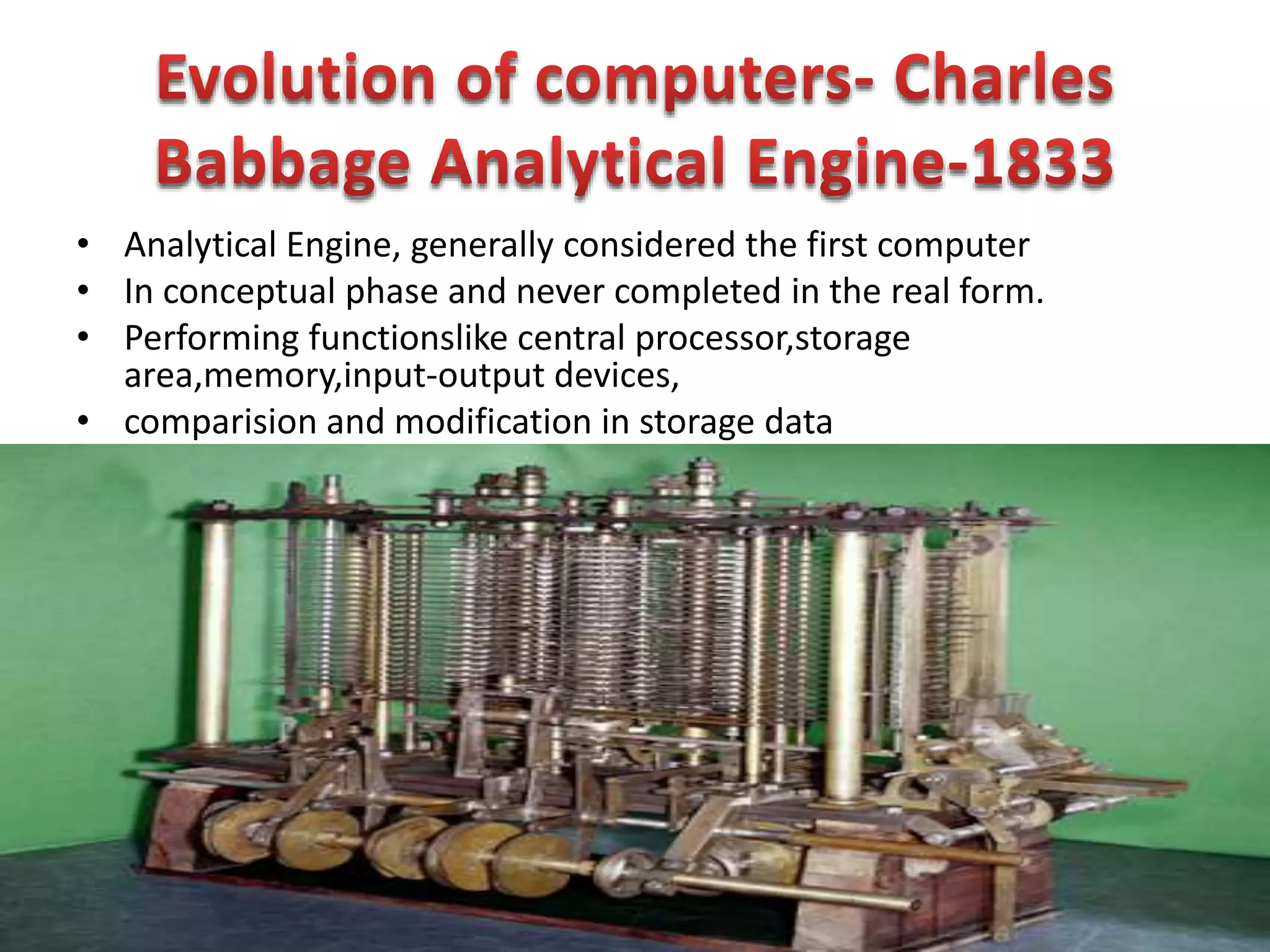
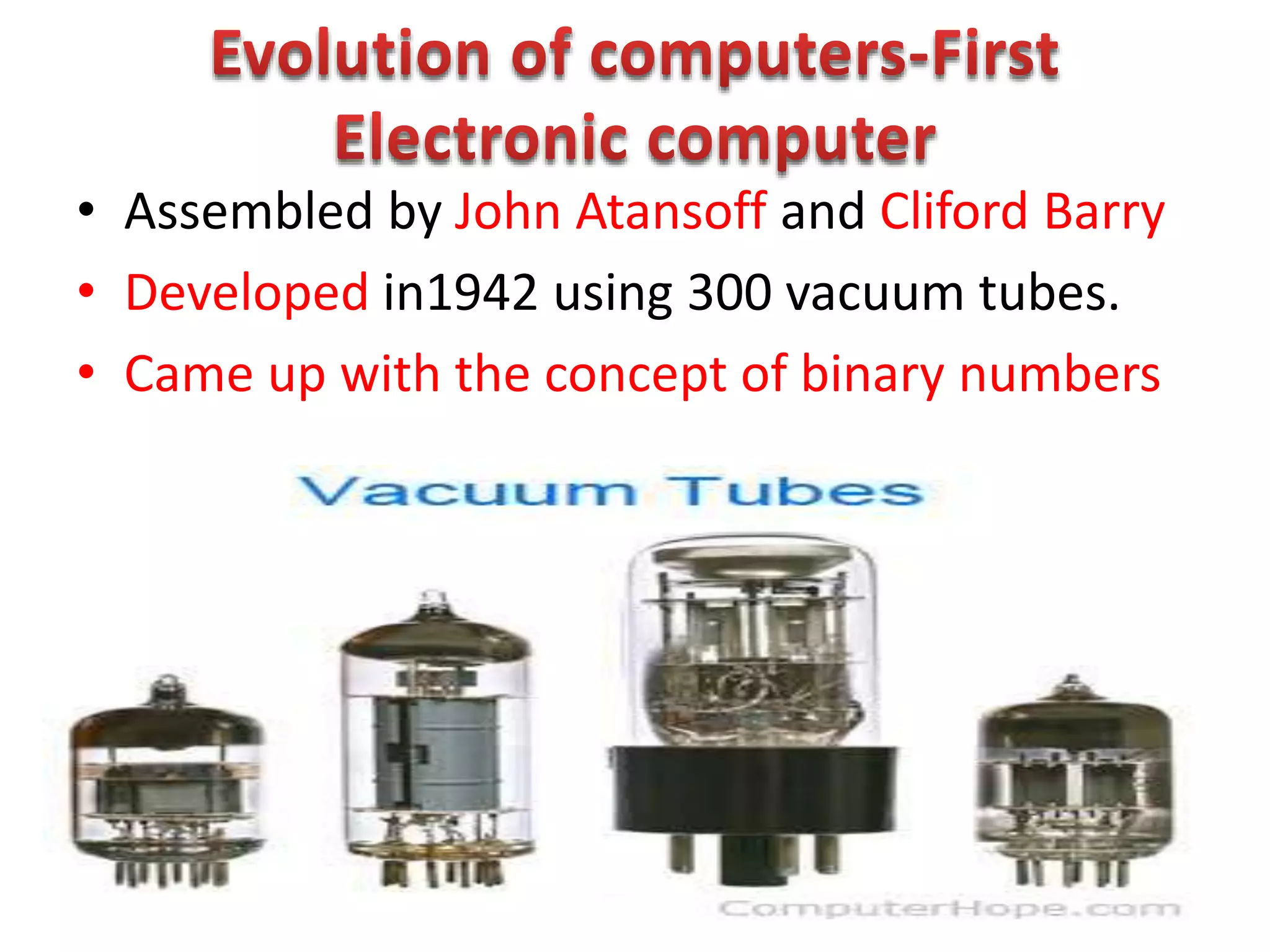
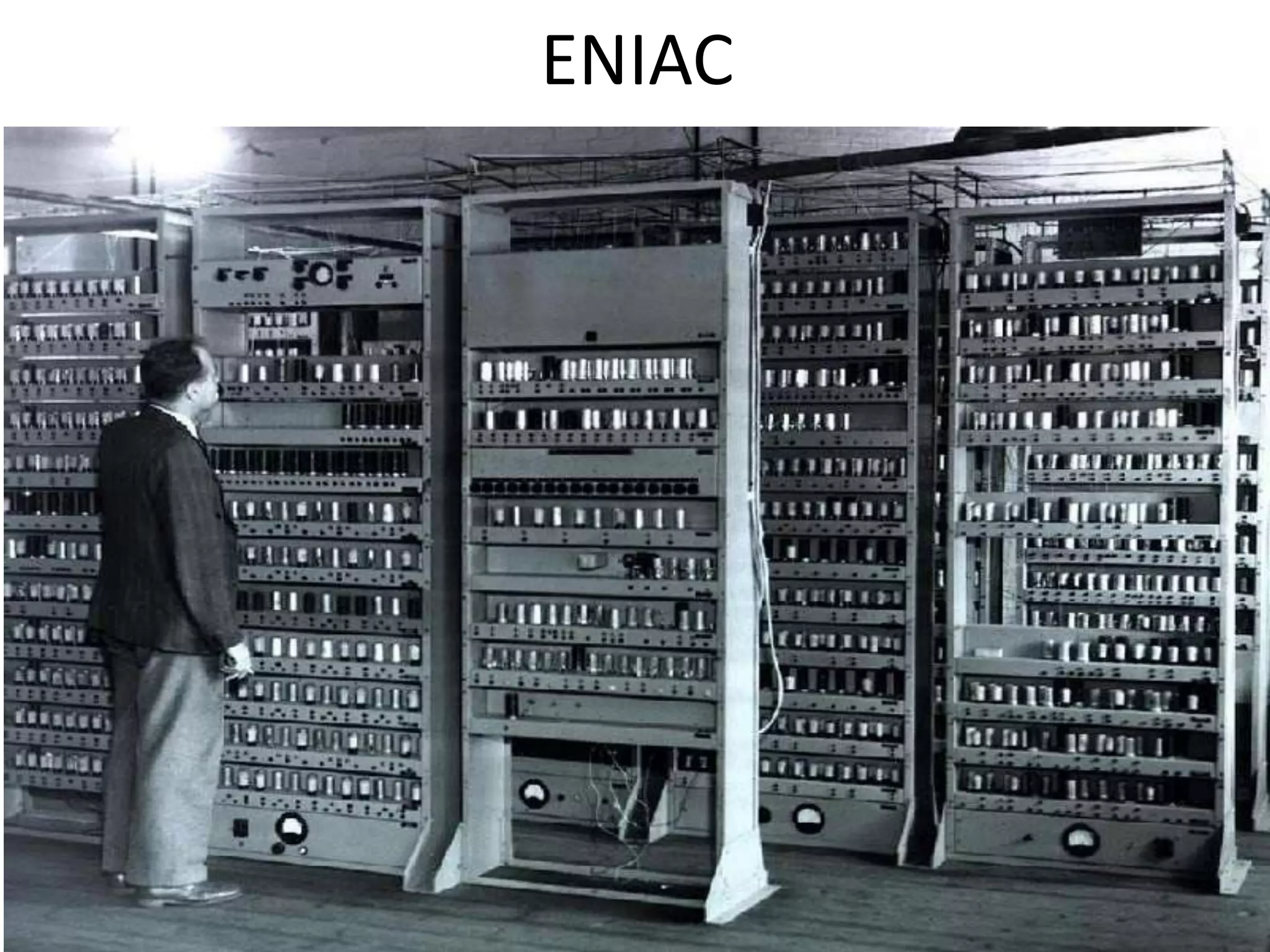
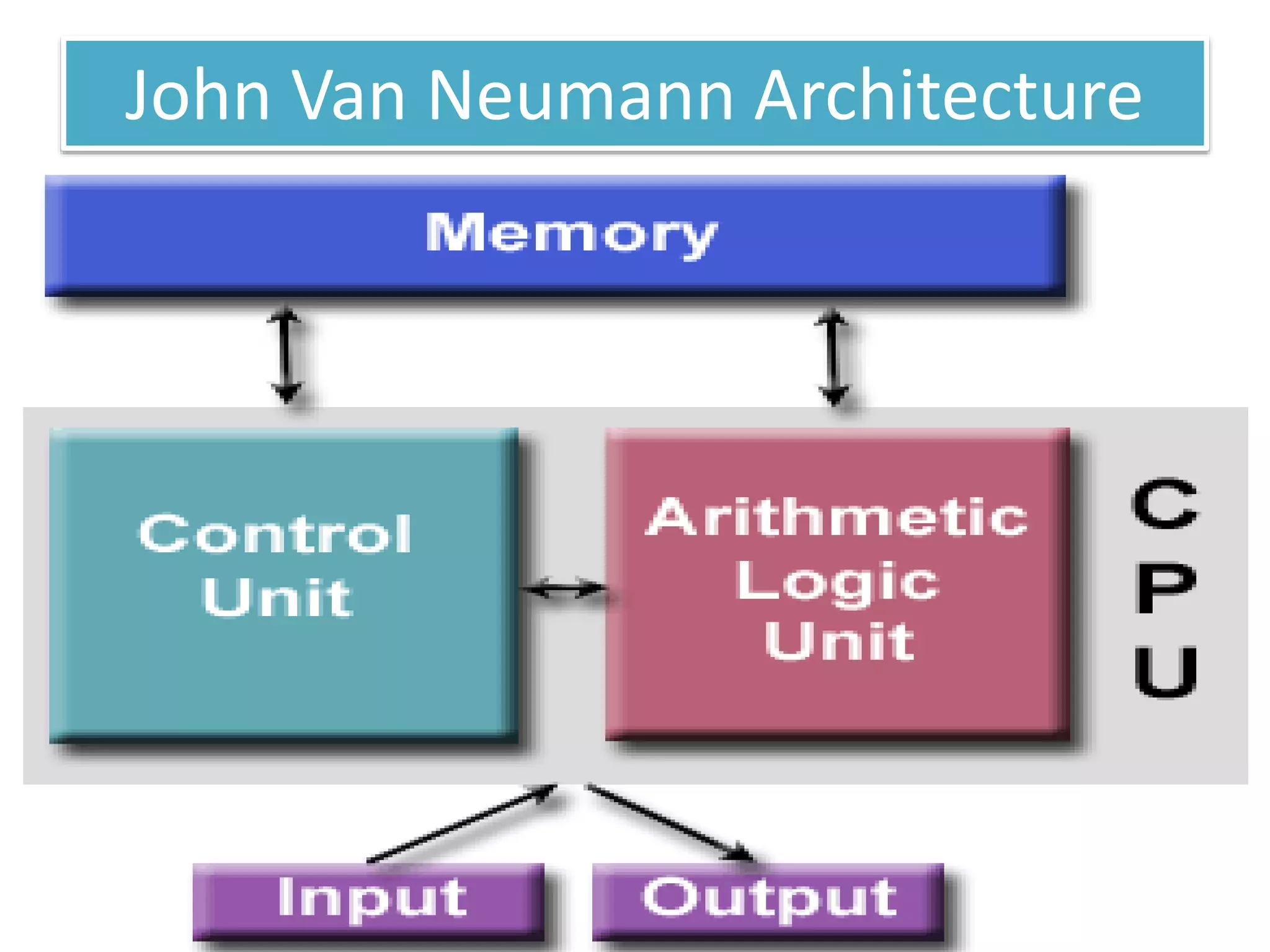
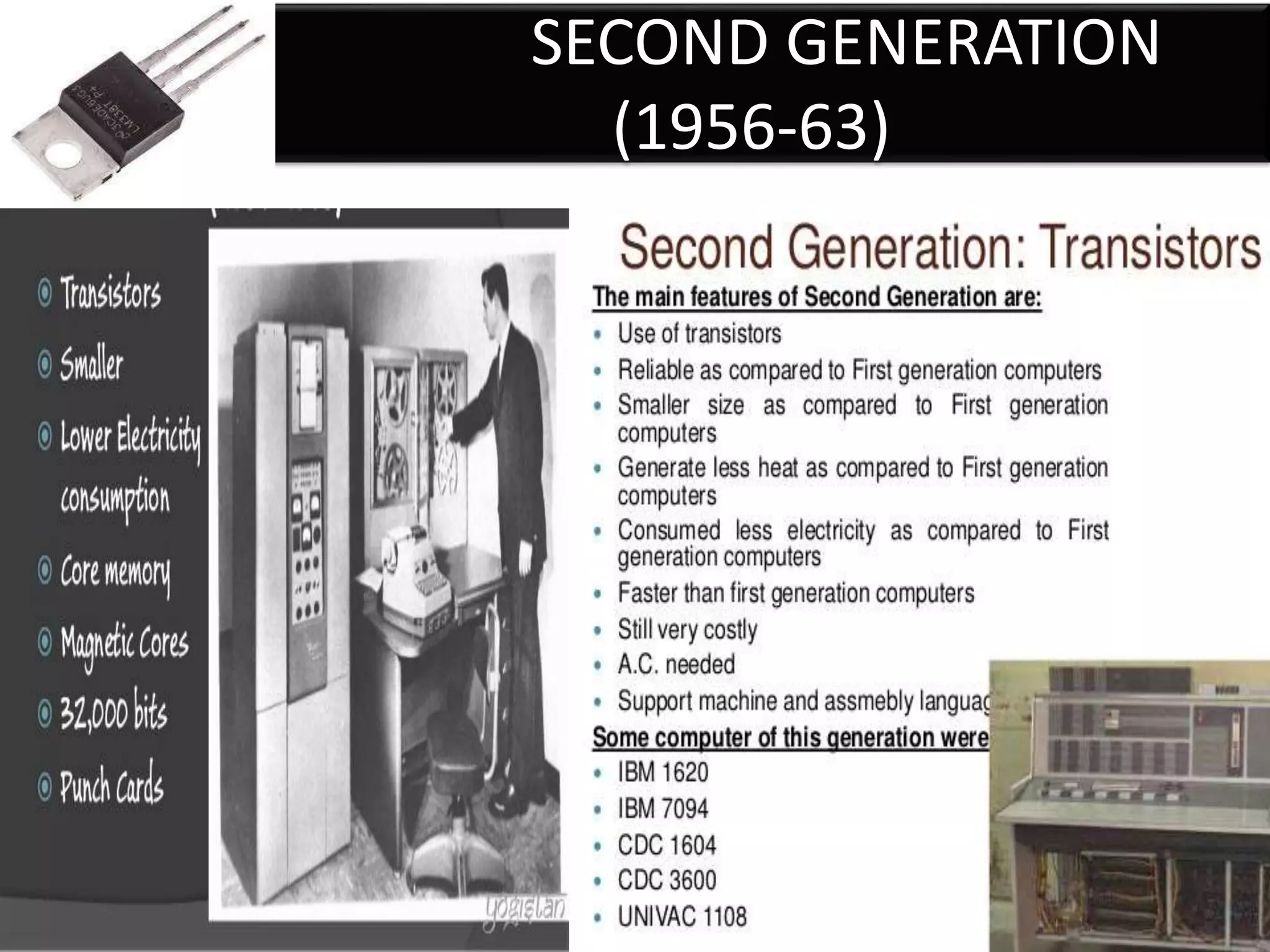
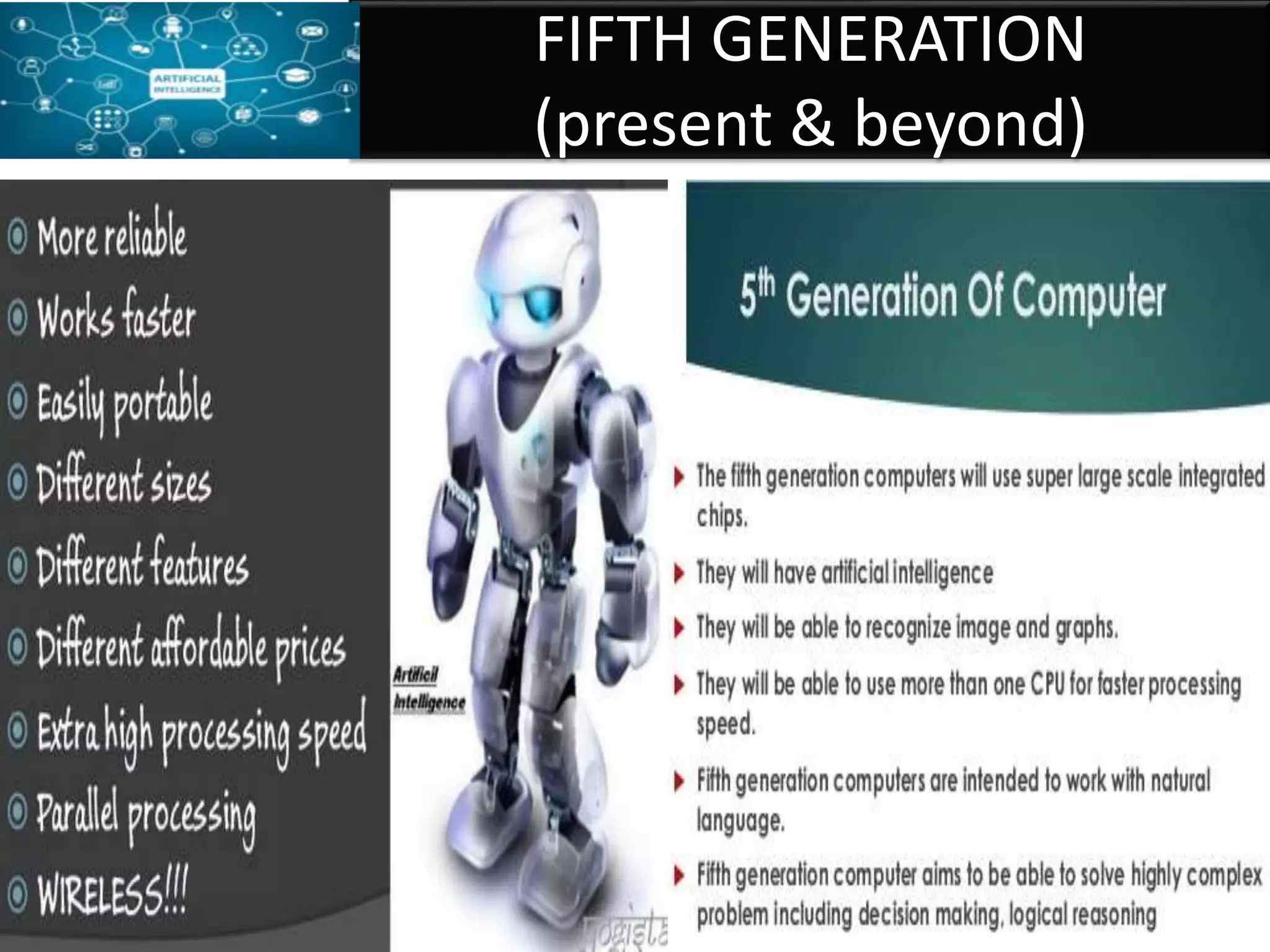
Firmware is pre-written programs stored in non-volatile memory like ROM that configure computers. It is not easily modifiable. Liveware refers to people using computers. The evolution of IT can be divided into the evolution of computers, storage/display technology, and software. Early counting devices included the abacus and Napier's bones, while early calculating machines were developed by Pascal and Leibniz. Hollerith developed punched cards for census data storage and their use later expanded to program looms. Babbage designed analytical engines to perform computations but they were not completed. The Atanasoff-Berry Computer used vacuum tubes and binary numbers. Subsequent generations saw developments like the Mark 1, ENIAC,