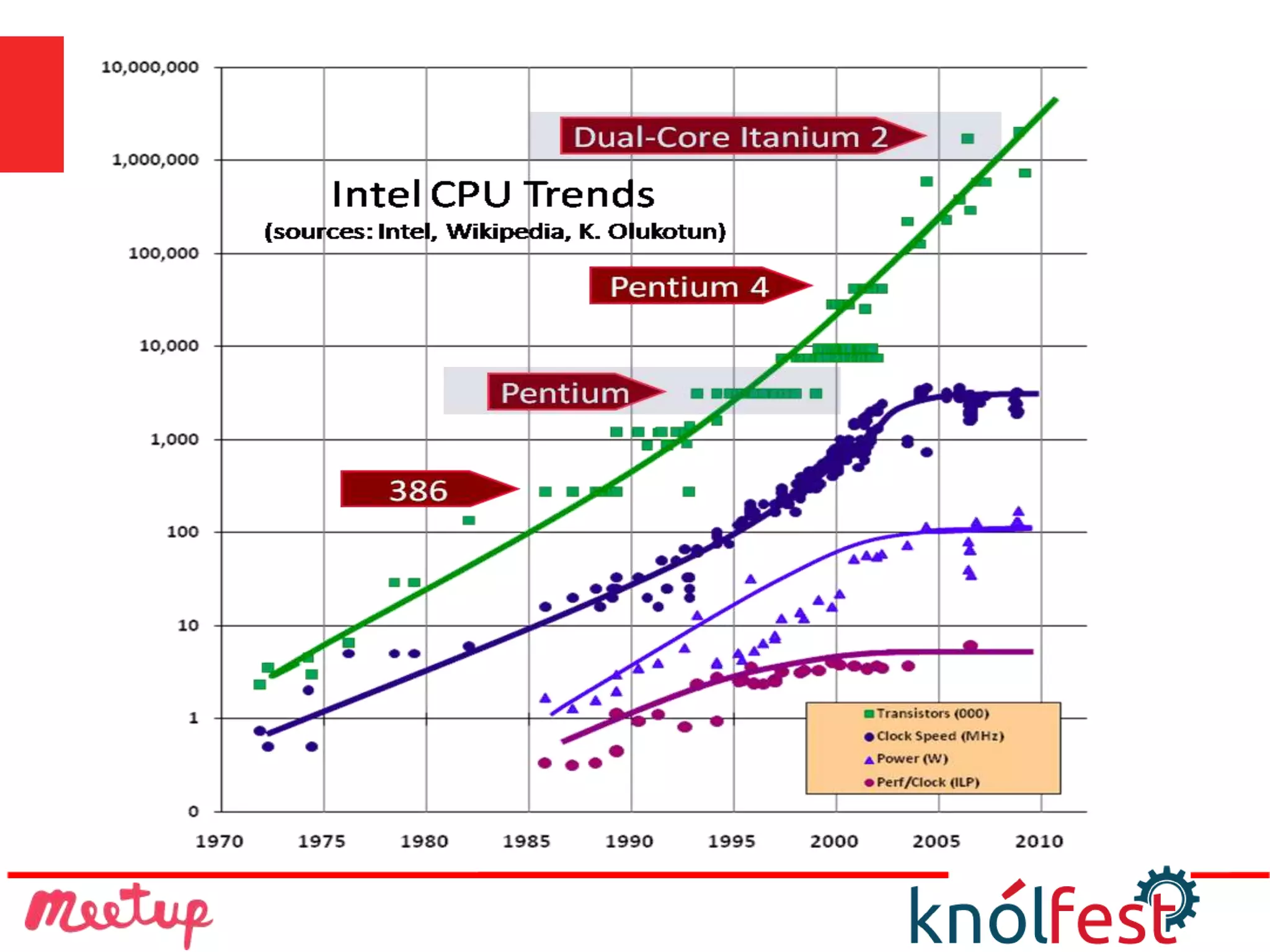
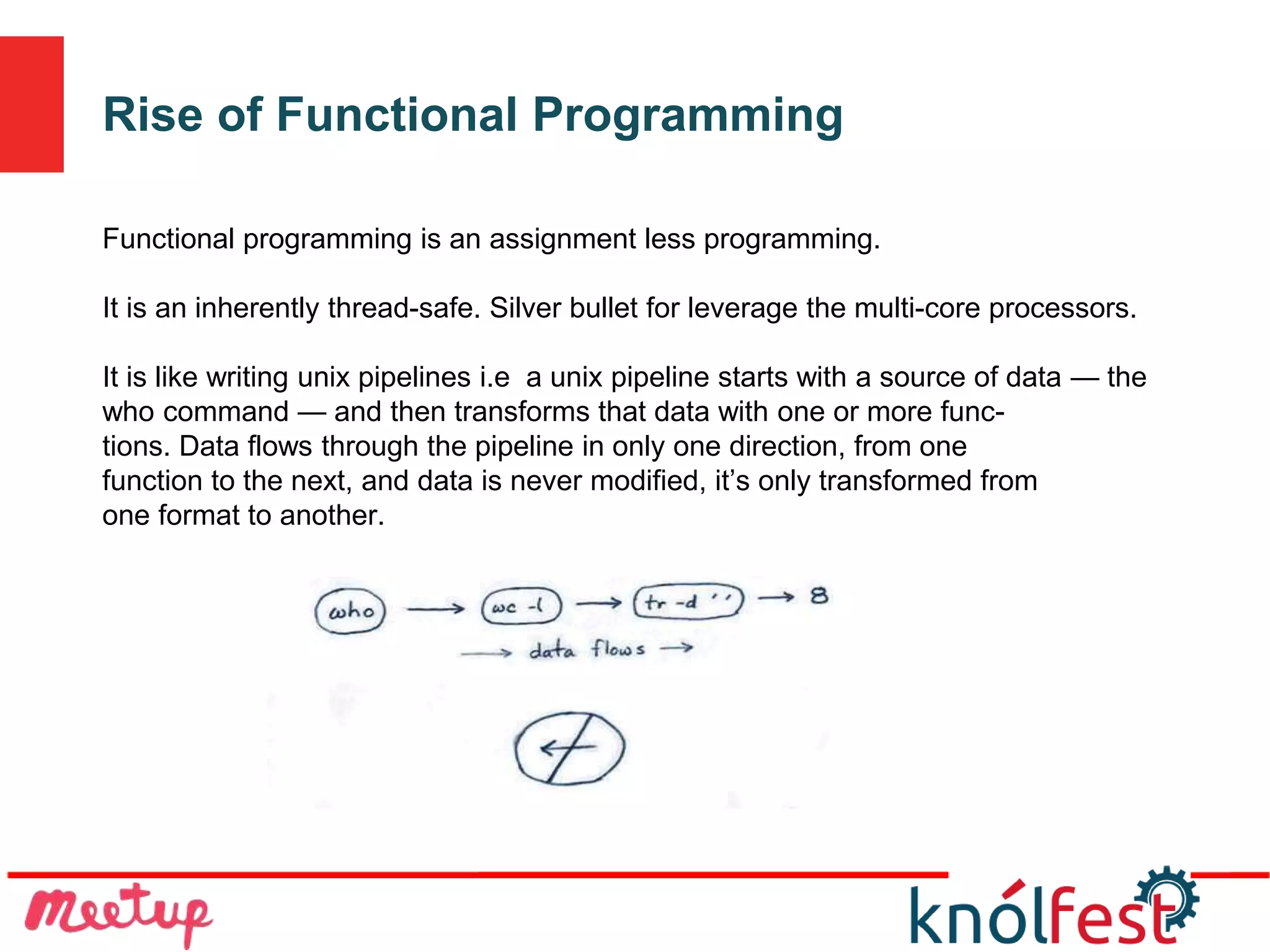
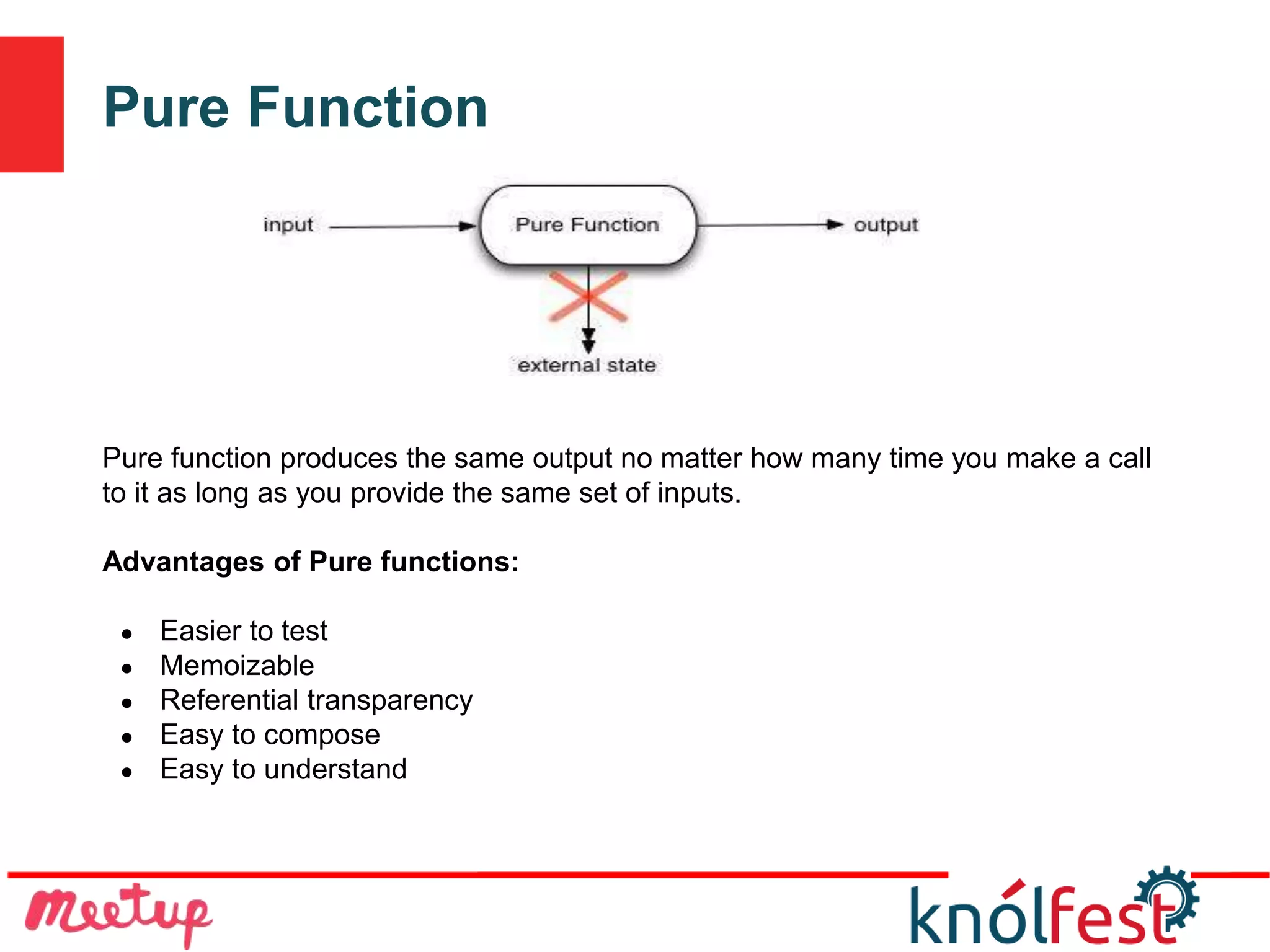
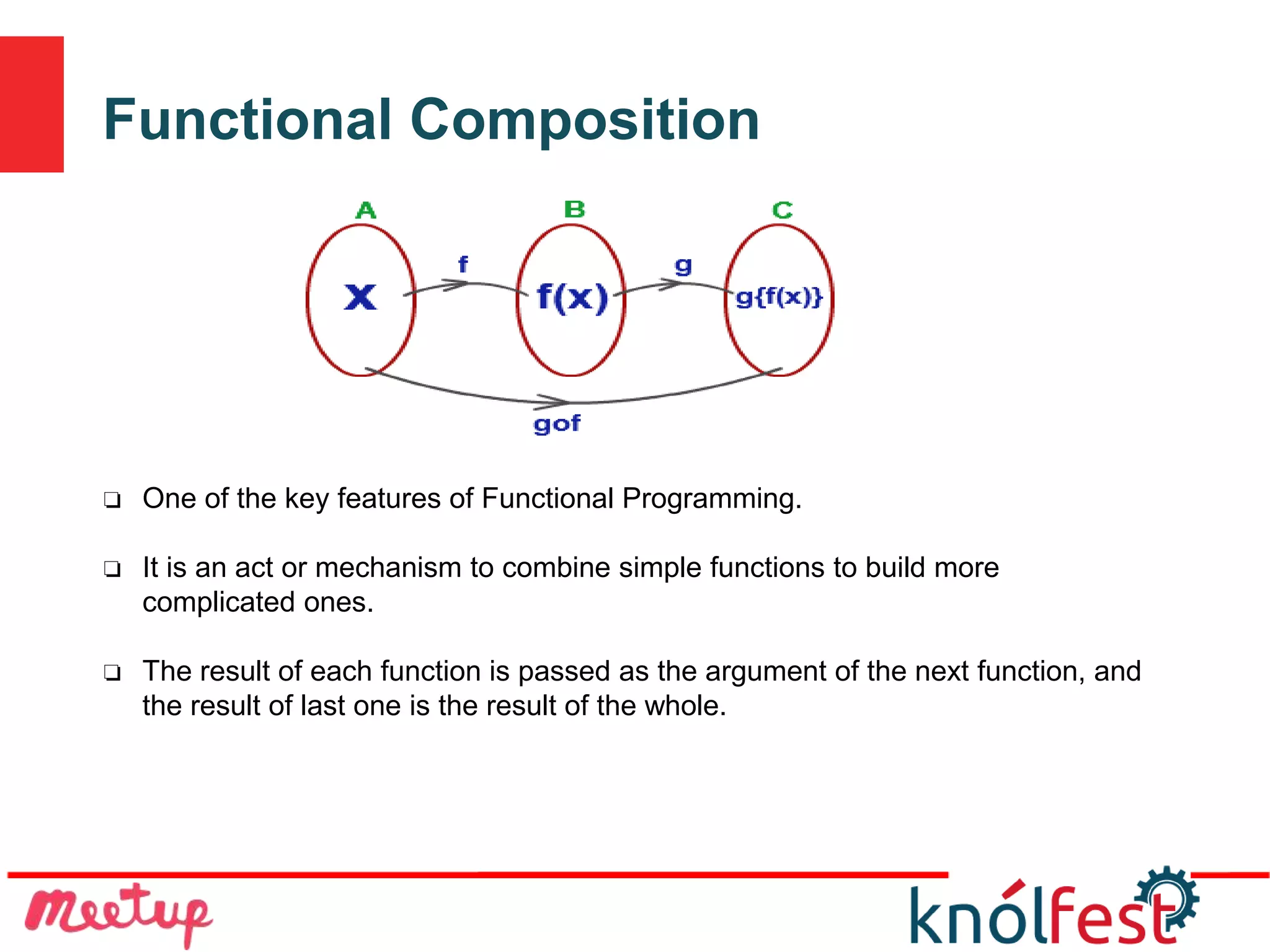
The document explores the transition from imperative programming to functional programming, highlighting functional programming's advantages like thread safety and ease of composition. It discusses concepts such as pure functions, functional composition, and lazy evaluation, emphasizing their roles in creating more efficient, understandable code. The conclusion posits that while functional programming is an older concept, it is well-suited for modern multi-core applications, offering a more concise and expressive alternative to other programming paradigms.