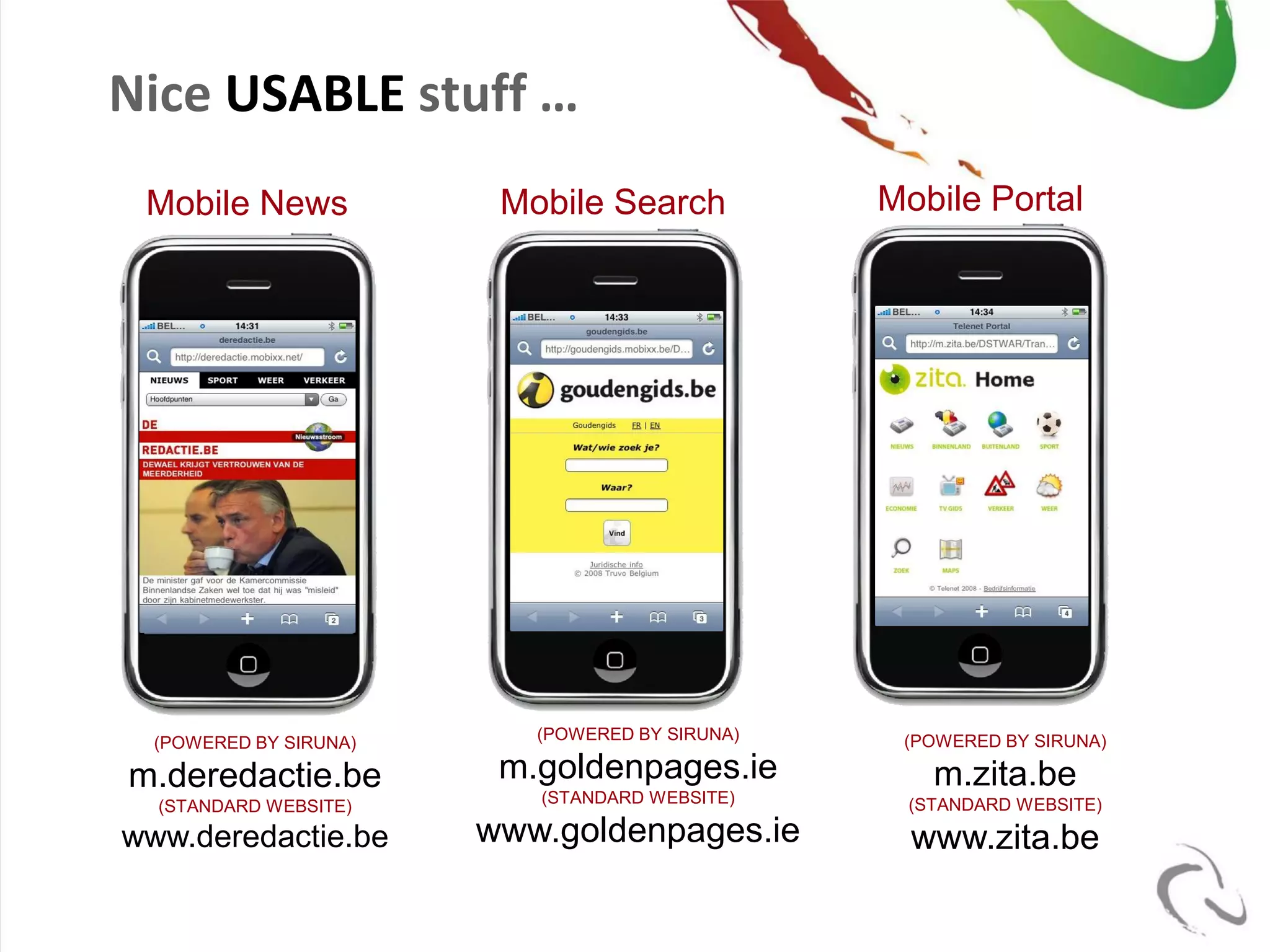
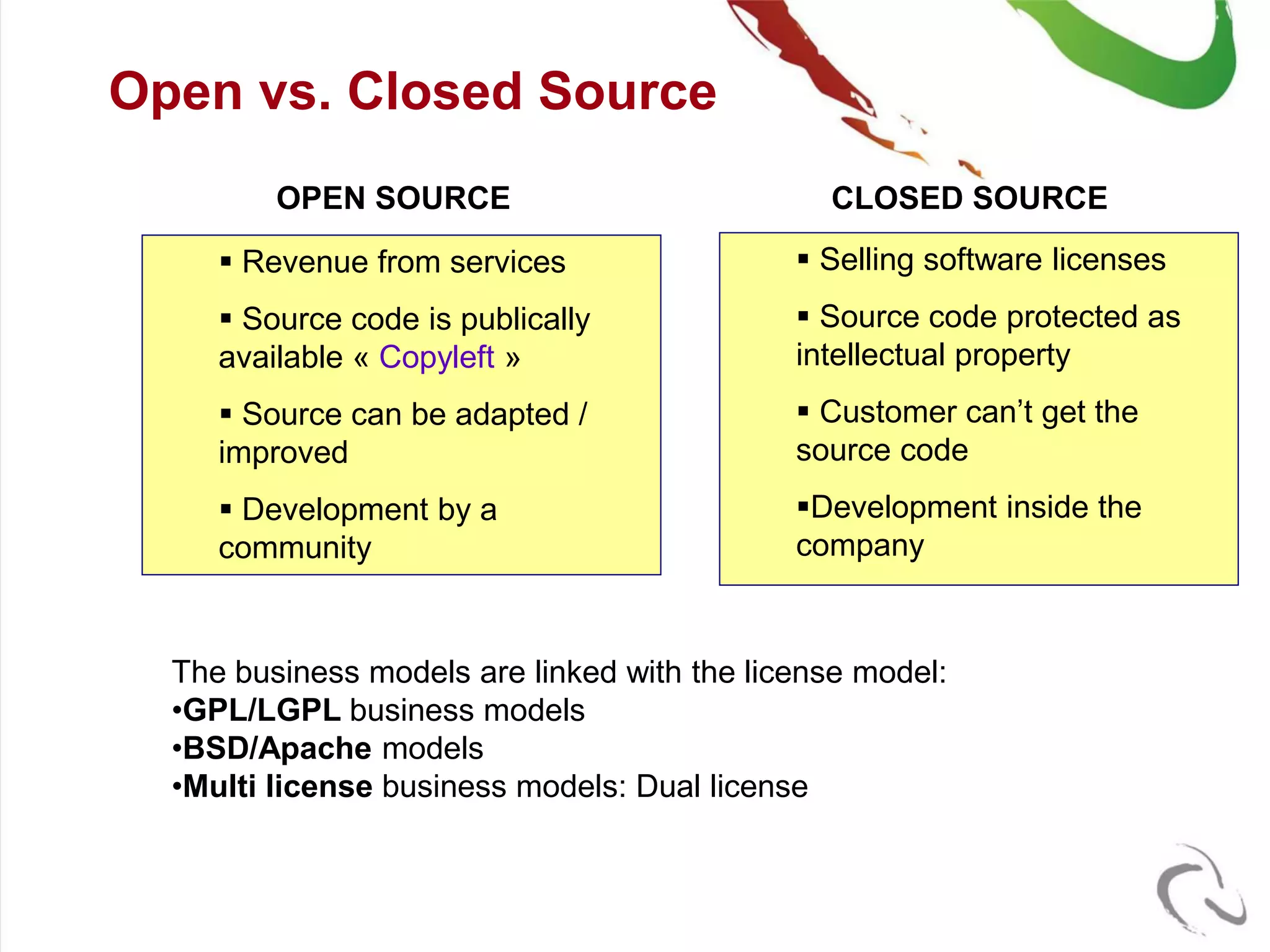
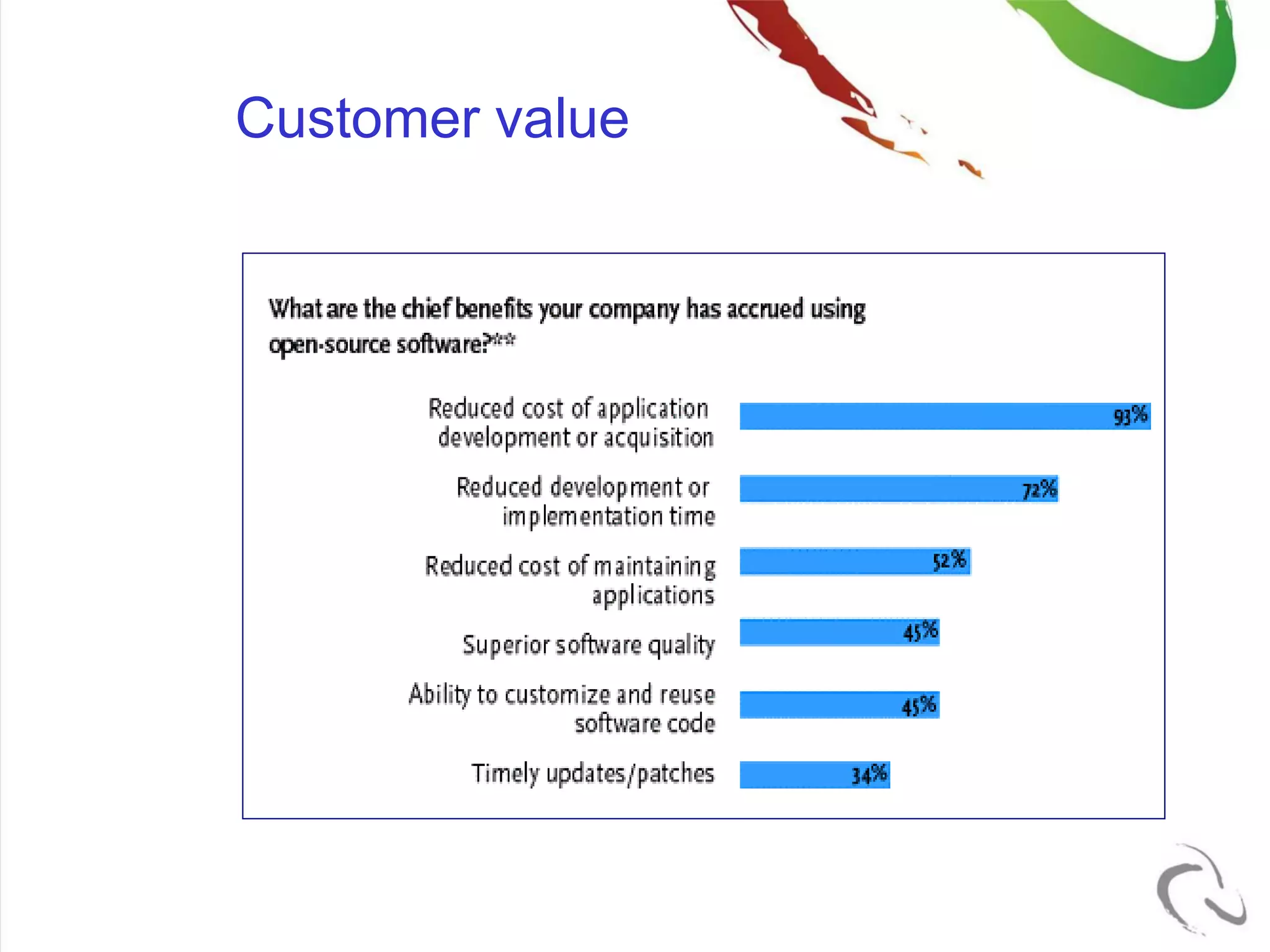
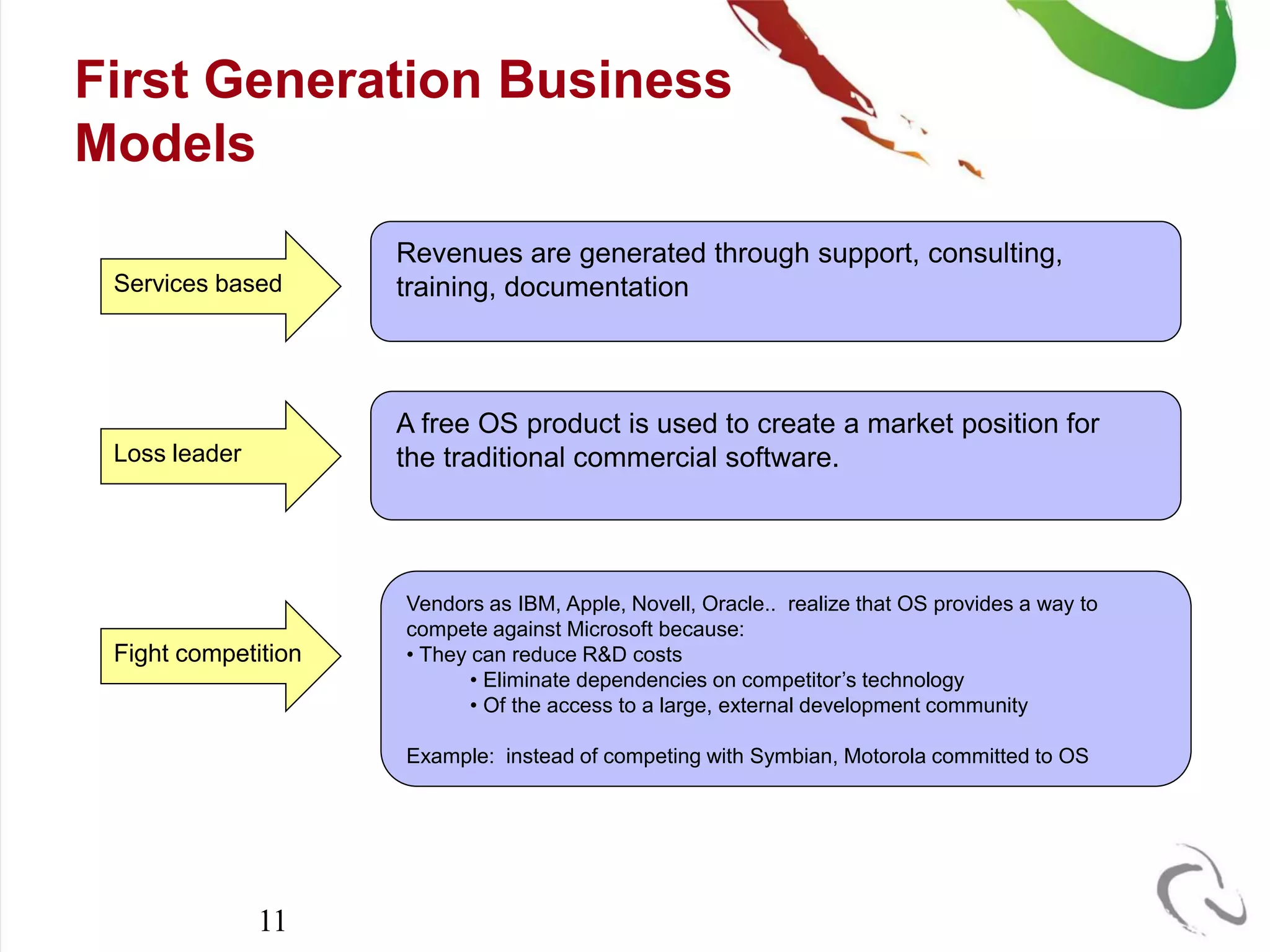
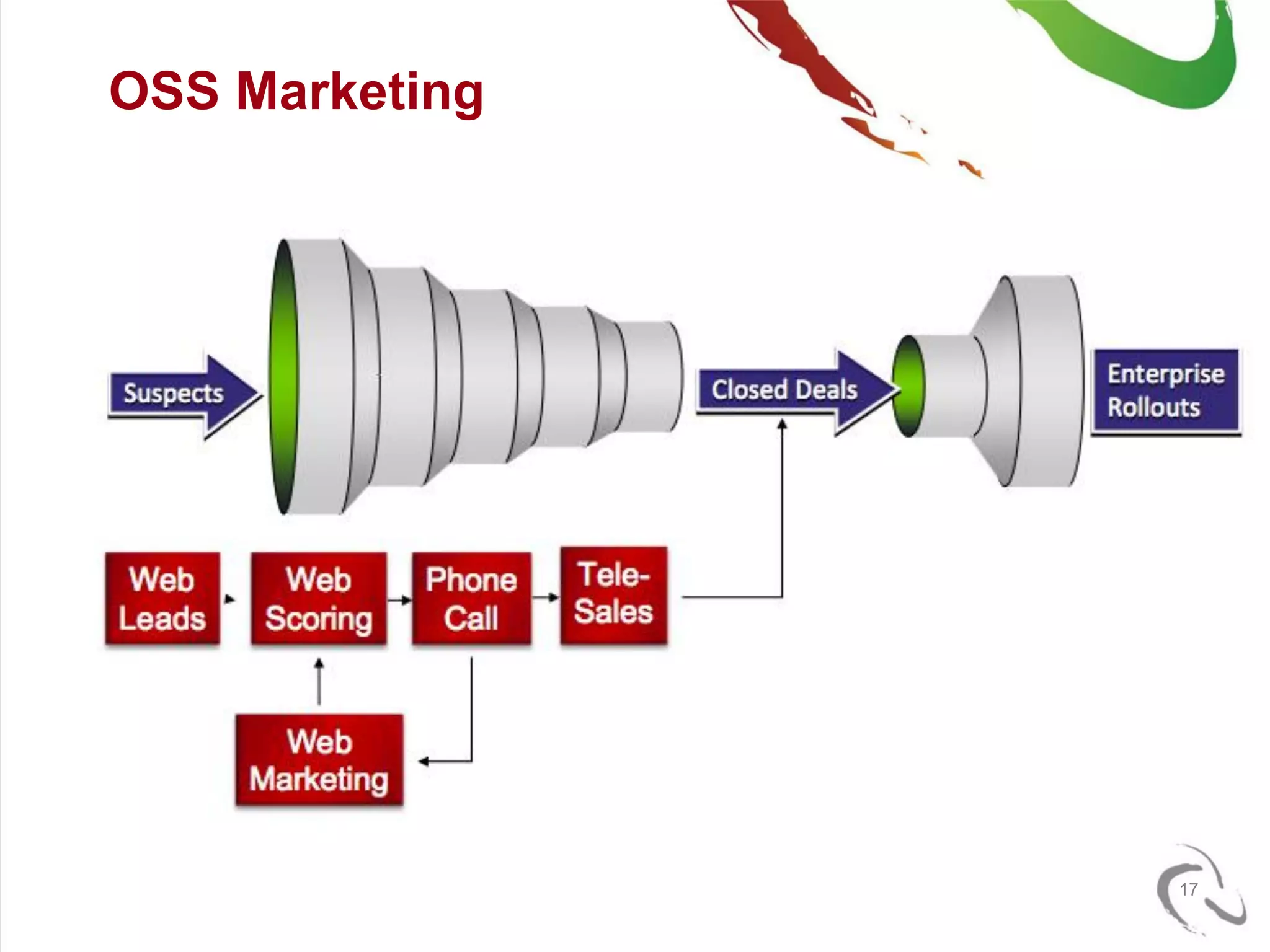
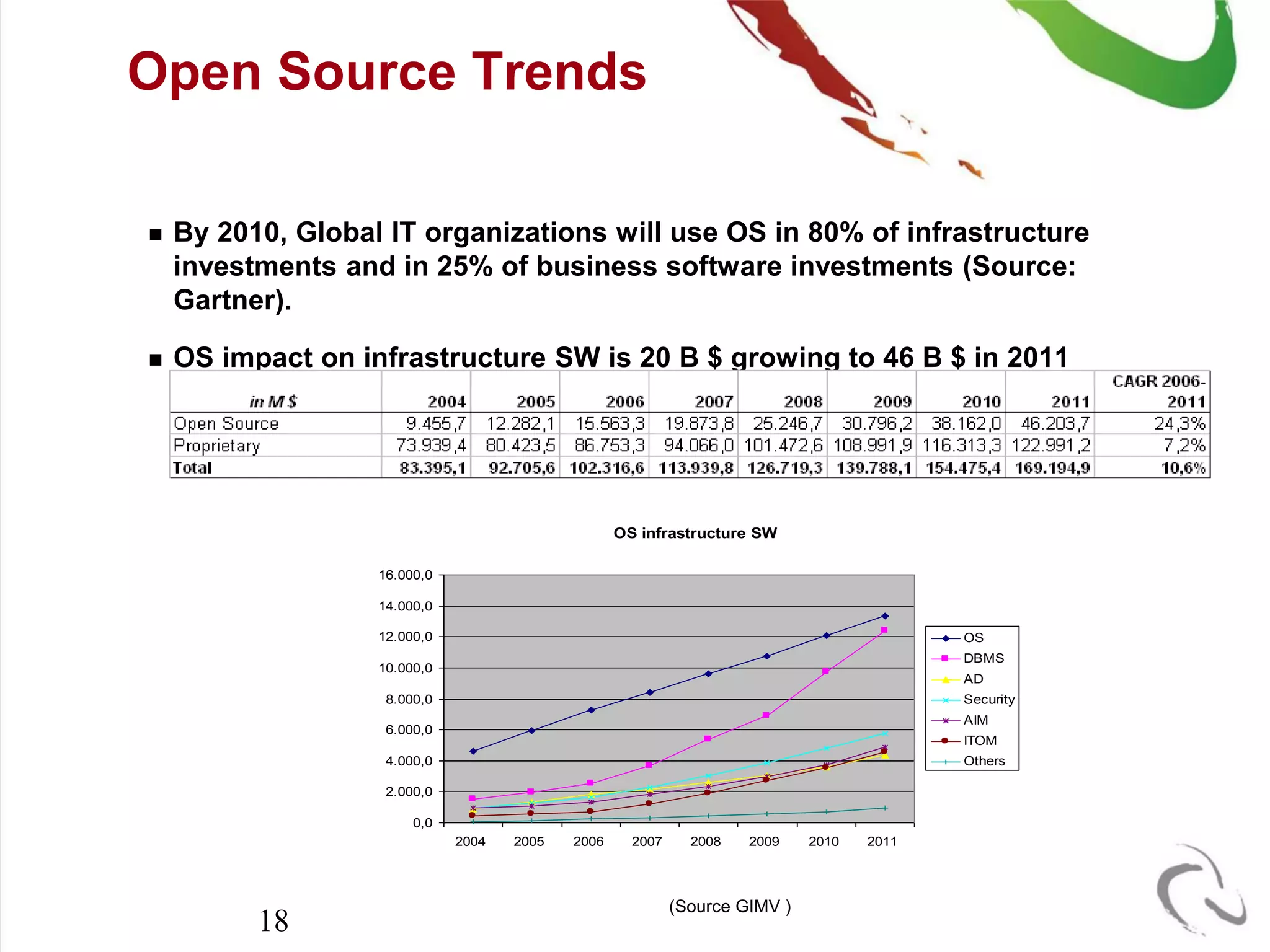
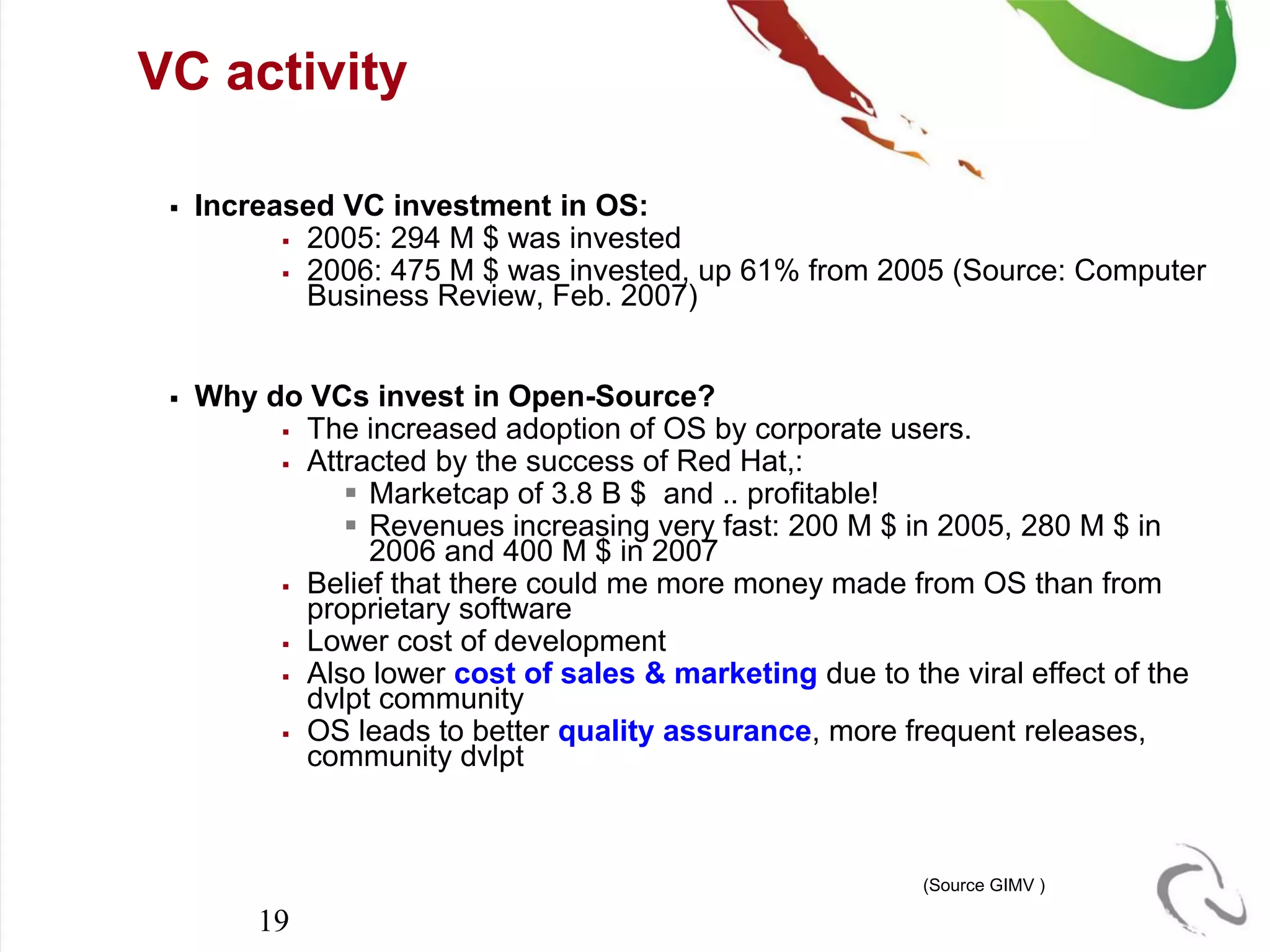
The document outlines the open-source business model employed by Siruna NV, which focuses on mobile web application development. It discusses the advantages of dual licensing and the relationship between open-source and closed-source approaches, emphasizing the importance of community involvement and cost efficiency in software development. Additionally, it presents trends in open-source investment and mentions notable acquisitions within the open-source sector.