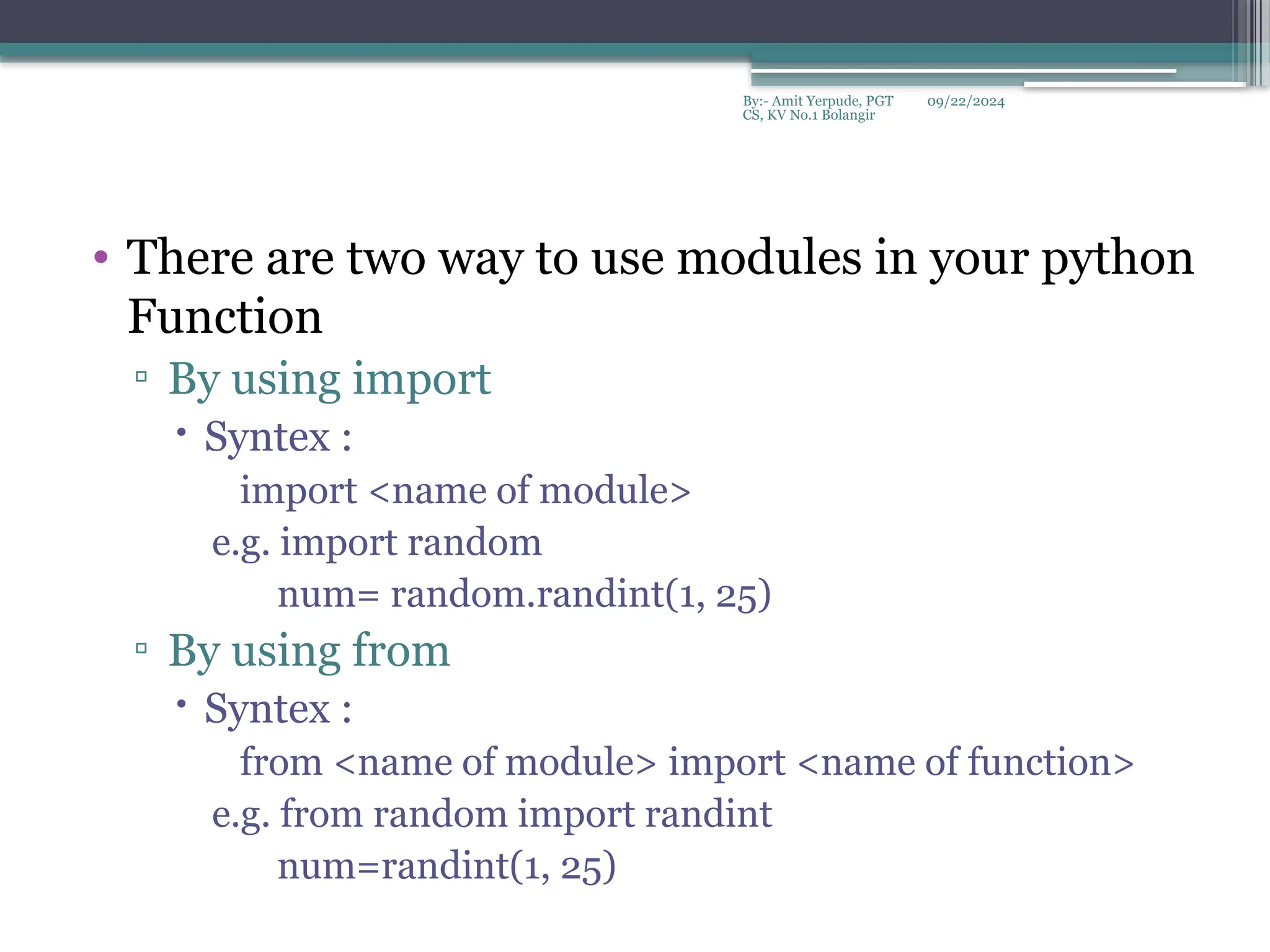
The document provides an overview of Python functions, including their definition, types, syntax, and usage of parameters. It discusses user-defined functions, built-in functions, lambda functions, and key concepts such as scope, lifetime, and argument types. Additionally, it includes examples of various functions to demonstrate their functionality and how to apply them in different scenarios.





![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
Defining a Function
• Here are simple rules to define a function in Python:
▫ Function blocks begin with the keyword def followed by the
function name and parentheses ( ( ) ).
▫ Any input parameters or arguments should be placed within these
parentheses. You can also define parameters inside these
parentheses.
▫ The first statement of a function can be an optional statement -
the documentation string of the function or docstring.
▫ The code block within every function starts with a colon (:) and is
indented.
▫ The statement return [expression] exits a function, optionally
passing back an expression to the caller. A return statement with
no arguments is the same as return None.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-7-2048.jpg)
![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
Syntax:
def function_name(parameters):
"function docstring"
statement1
statement2 ... ...
return [expr]
e.g.
>>> def hello():
"""
This Python function simply prints hello to the screen
"""
print("Hello welcome to the World")](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-8-2048.jpg)












![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
List as argument
def add_more(list):
list.append(50)
print("Inside Function", list)
mylist = [10,20,30,40]
add_more(mylist)
print("Outside Function:", mylist)
Output :
Inside Function [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
Outside Function: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-23-2048.jpg)
![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
Dictionary as argument
def func(d):
for key in d:
print("key:", key, "Value:", d[key])
D = {'a':1, 'b':2, 'c':3}
func(D)
Output:
key: b Value: 2
key: a Value: 1
key: c Value: 3](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-24-2048.jpg)


![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
# call by value
string = “Hello"
def test(string):
string = “Hello Amit"
print("Inside Function:", string)
test(string)
print("Outside Function:", string)
Output:
Inside Function: Hello Amit
Outside Function: Hello
# call by reference
def add_more(list):
list.append(50)
print("Inside Function", list)
mylist = [10,20,30,40]
add_more(mylist)
print("Outside Function:", mylist)
Output :
Inside Function [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]
Outside Function: [10, 20, 30, 40, 50]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-27-2048.jpg)





![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
1. Write a Python function to find the maximum of three numbers.
2. Write a Python function to sum all the numbers in a list.
Sample List : (8, 2, 3, 0, 7)
Expected Output : 20
3. Write a Python function to multiply all the numbers in a list.
Sample List : (8, 2, 3, -1, 7)
Expected Output : -336
4. Write a Python program to reverse a string.
Sample String : "1234abcd"
Expected Output : "dcba4321”
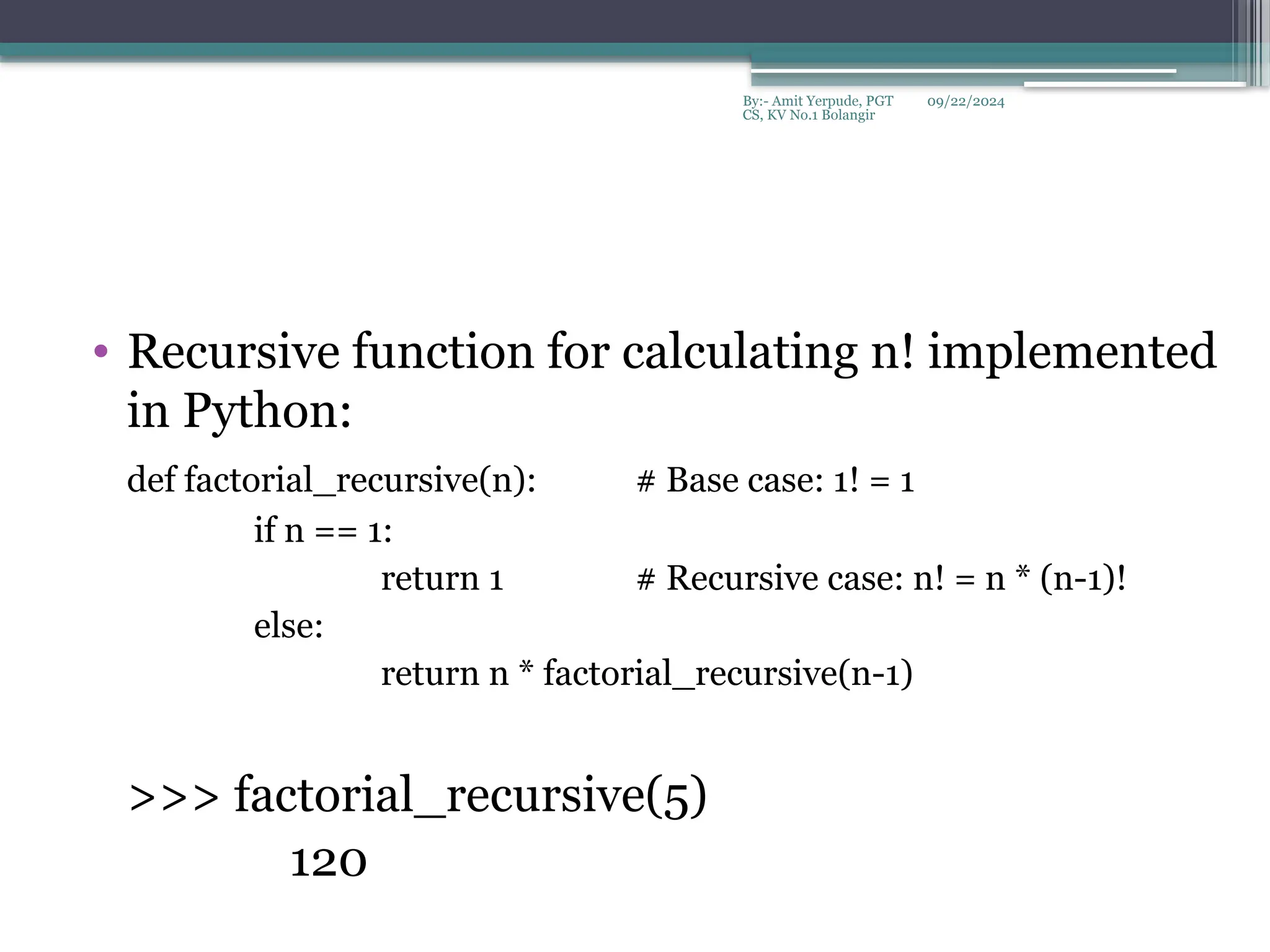
5. Write a Python function to calculate the factorial of a number (a non-negative integer). The function
accepts the number as an argument.
6. Write a Python function to check whether a number falls within a given range.
7. Write a Python function that accepts a string and counts the number of upper and lower case letters.
Sample String : 'The quick Brow Fox'
Expected Output :
No. of Upper case characters : 3
No. of Lower case Characters : 12
8. Write a Python function that takes a list and returns a new list with distinct elements from the first
list.
Sample List : [1,2,3,3,3,3,4,5]
Unique List : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-34-2048.jpg)
![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
9. Write a Python function that takes a number as a parameter and checks whether the number
is prime or not.
Note : A prime number (or a prime) is a natural number greater than 1 and that has no
positive divisors other than 1 and itself.
10. Write a Python program to print the even numbers from a given list.
Sample List : [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]
Expected Result : [2, 4, 6, 8]
11. Write a Python function to check whether a number is "Perfect" or not.
According to Wikipedia : In number theory, a perfect number is a positive integer that is
equal to the sum of its proper positive divisors, that is, the sum of its positive divisors
excluding the number itself (also known as its aliquot sum). Equivalently, a perfect number is
a number that is half the sum of all of its positive divisors (including itself).
Example : The first perfect number is 6, because 1, 2, and 3 are its proper positive divisors,
and 1 + 2 + 3 = 6. Equivalently, the number 6 is equal to half the sum of all its positive
divisors: ( 1 + 2 + 3 + 6 ) / 2 = 6. The next perfect number is 28 = 1 + 2 + 4 + 7 + 14. This is
followed by the perfect numbers 496 and 8128.
12. Write a Python function that checks whether a passed string is a palindrome or not.
Note: A palindrome is a word, phrase, or sequence that reads the same backward as forward,
e.g., madam or nurses run.
13. Write a Python function that prints out the first n rows of Pascal's triangle.
Note : Pascal's triangle is an arithmetic and geometric figure first imagined by Blaise Pascal.
Sample Pascal's triangle :
Each number is the two numbers above it added together](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-35-2048.jpg)


![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
List of Functions in Python Math Module
Function Description
ceil(x) Returns the smallest integer greater than or equal to x.
copysign(x, y) Returns x with the sign of y
fabs(x) Returns the absolute value of x
factorial(x) Returns the factorial of x
floor(x) Returns the largest integer less than or equal to x
fmod(x, y) Returns the remainder when x is divided by y
frexp(x) Returns the mantissa and exponent of x as the pair (m, e)
fsum(iterable) Returns an accurate floating point sum of values in the iterable
isfinite(x) Returns True if x is neither an infinity nor a NaN (Not a Number)
isinf(x) Returns True if x is a positive or negative infinity
isnan(x) Returns True if x is a NaN
trunc(x) Returns the truncated integer value of x
exp(x) Returns e**x
expm1(x) Returns e**x - 1
log(x[, base]) Returns the logarithm of x to the base (defaults to e)
log1p(x) Returns the natural logarithm of 1+x
log2(x) Returns the base-2 logarithm of x
log10(x) Returns the base-10 logarithm of x
pow(x, y) Returns x raised to the power y
sqrt(x) Returns the square root of x
cos(x) Returns the cosine of x
hypot(x, y) Returns the Euclidean norm, sqrt(x*x + y*y)
sin(x) Returns the sine of x
tan(x) Returns the tangent of x
degrees(x) Converts angle x from radians to degrees
radians(x) Converts angle x from degrees to radians
gamma(x) Returns the Gamma function at x
lgamma(x) Returns the natural logarithm of the absolute value of the Gamma function at x
pi
Mathematical constant, the ratio of circumference of a circle to it's diameter
(3.14159...)
e mathematical constant e (2.71828...)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-40-2048.jpg)
![09/22/2024
By:- Amit Yerpude, PGT
CS, KV No.1 Bolangir
• random.random(): Generates a random float number between 0.0 to 1.0. The function doesn't
need any arguments.
>>>random.random()
0.645173684807533
• random.randint(): Returns a random integer between the specified integers.
>>>random.randint(1,100)
95
• random.randrange(): Returns a randomly selected element from the range created by the start,
stop and step arguments. The value of start is 0 by default. Similarly, the value of step is 1 by default.
>>>random.randrange(1,10)
2
>>>random.randrange(1,10,2)
5
• random.choice(): Returns a randomly selected element from a non-empty sequence. An empty
sequence as argument raises an IndexError.
>>>random.choice('computer')
't'
>>>random.choice([12,23,45,67,65,43])
45
>>>random.choice((12,23,45,67,65,43))
67
• random.shuffle(): This functions randomly reorders the elements in a list.
>>>numbers=[12,23,45,67,65,43]
>>>random.shuffle(numbers)
>>>numbers
[23, 12, 43, 65, 67, 45]
Python - Random Module](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/functioninpython-240922110519-82a5d89e/75/Function-in-Python-function-in-python-pptx-41-2048.jpg)