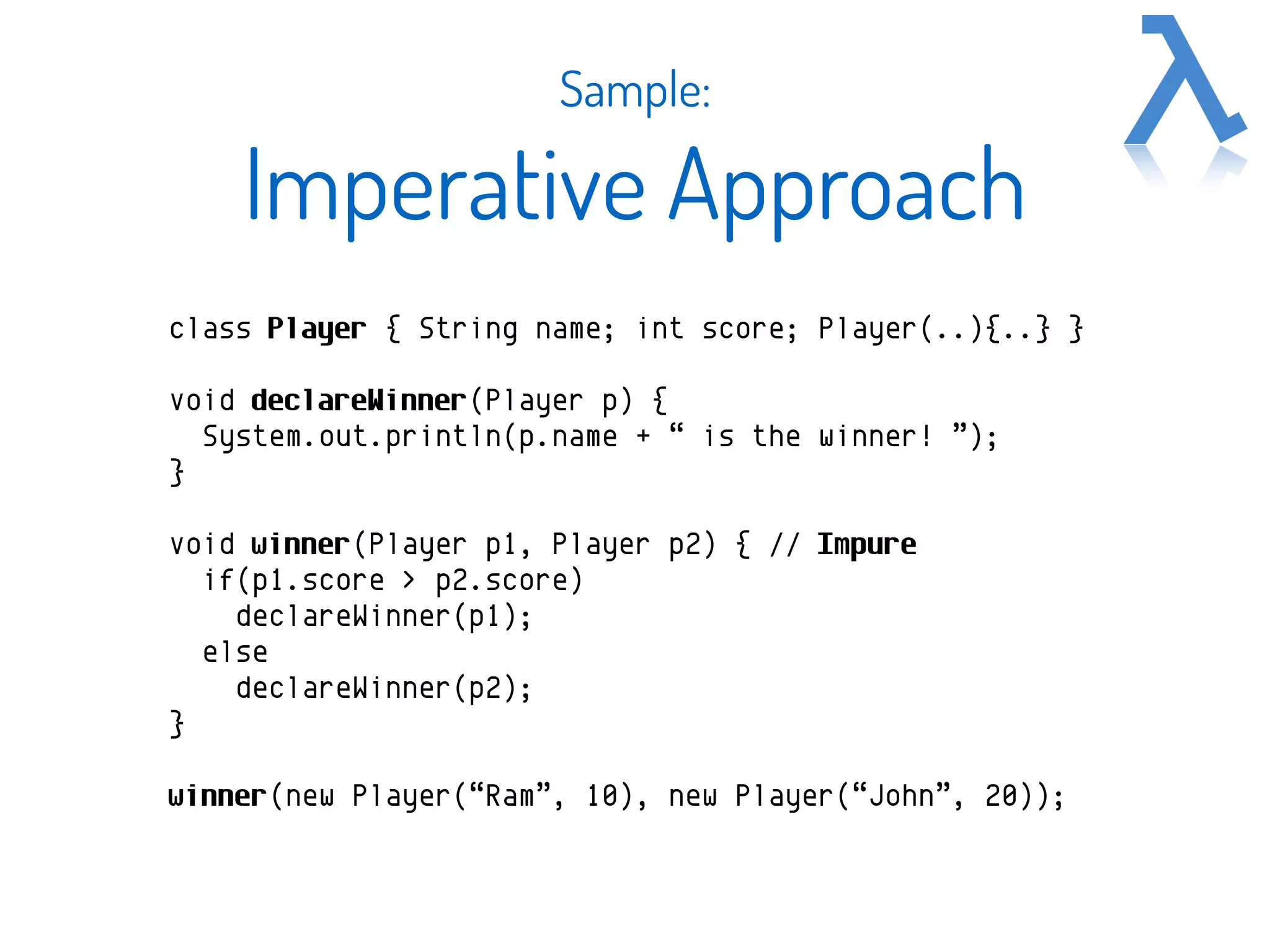
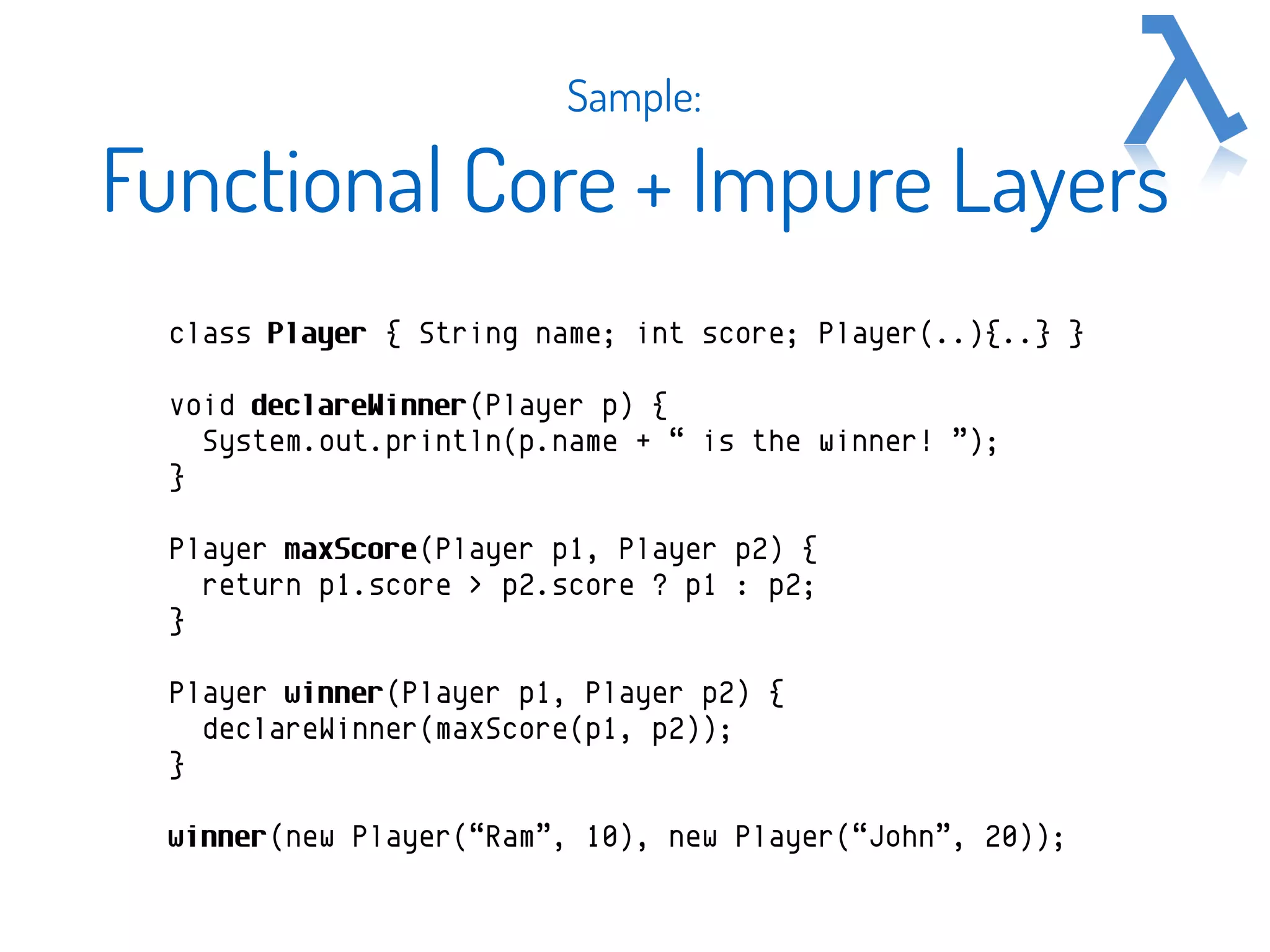
The document discusses functional programming (FP) as a programming paradigm emphasizing the evaluation of mathematical functions and minimizing mutable data. It traces the origins of FP from lambda calculus to modern languages like Java and Scala, highlighting its increasing relevance due to the limitations of Moore's Law and the demand for concurrency and scalability. Additionally, it contrasts imperative approaches with functional methods using programming samples to illustrate the concept.