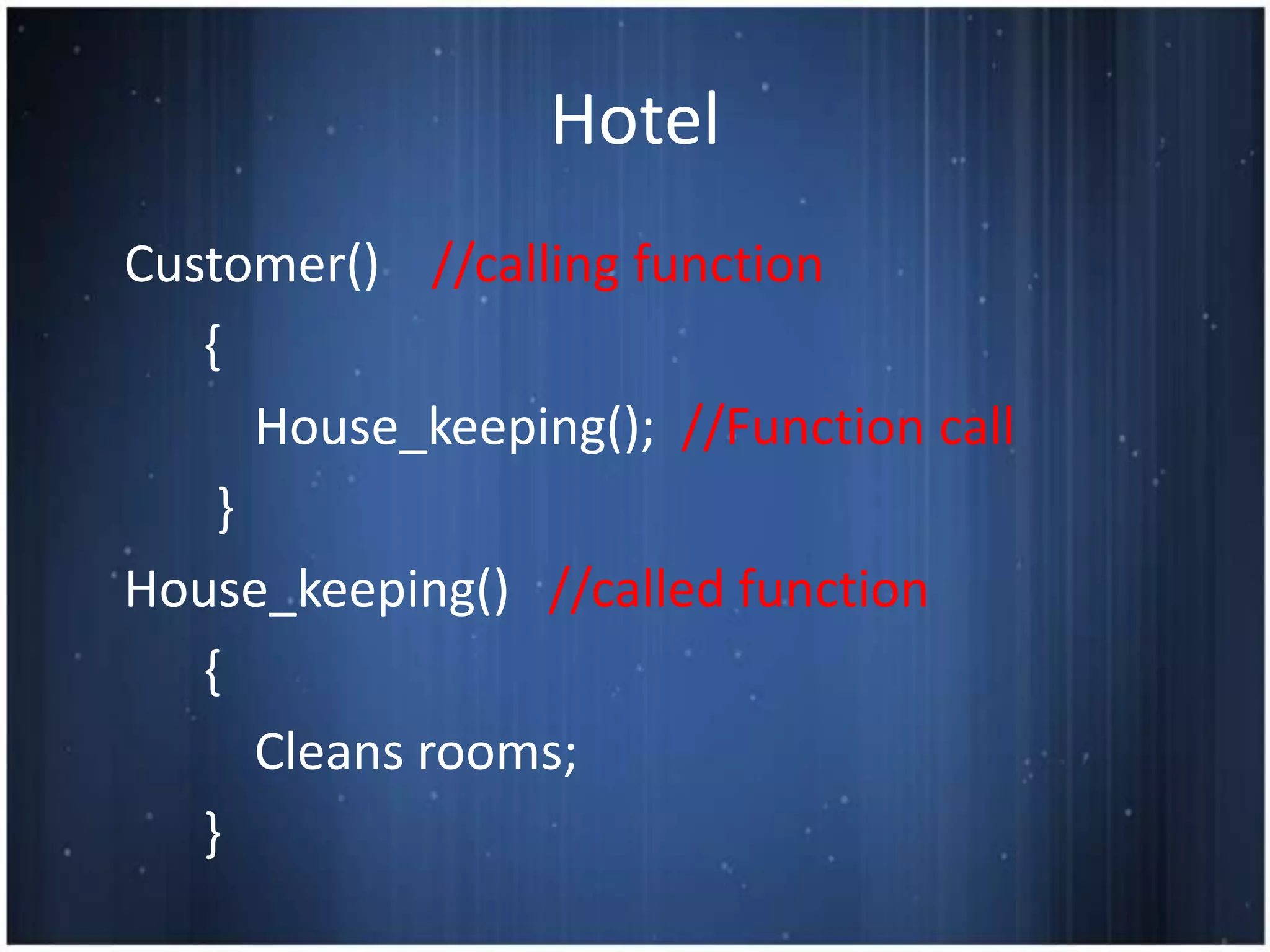
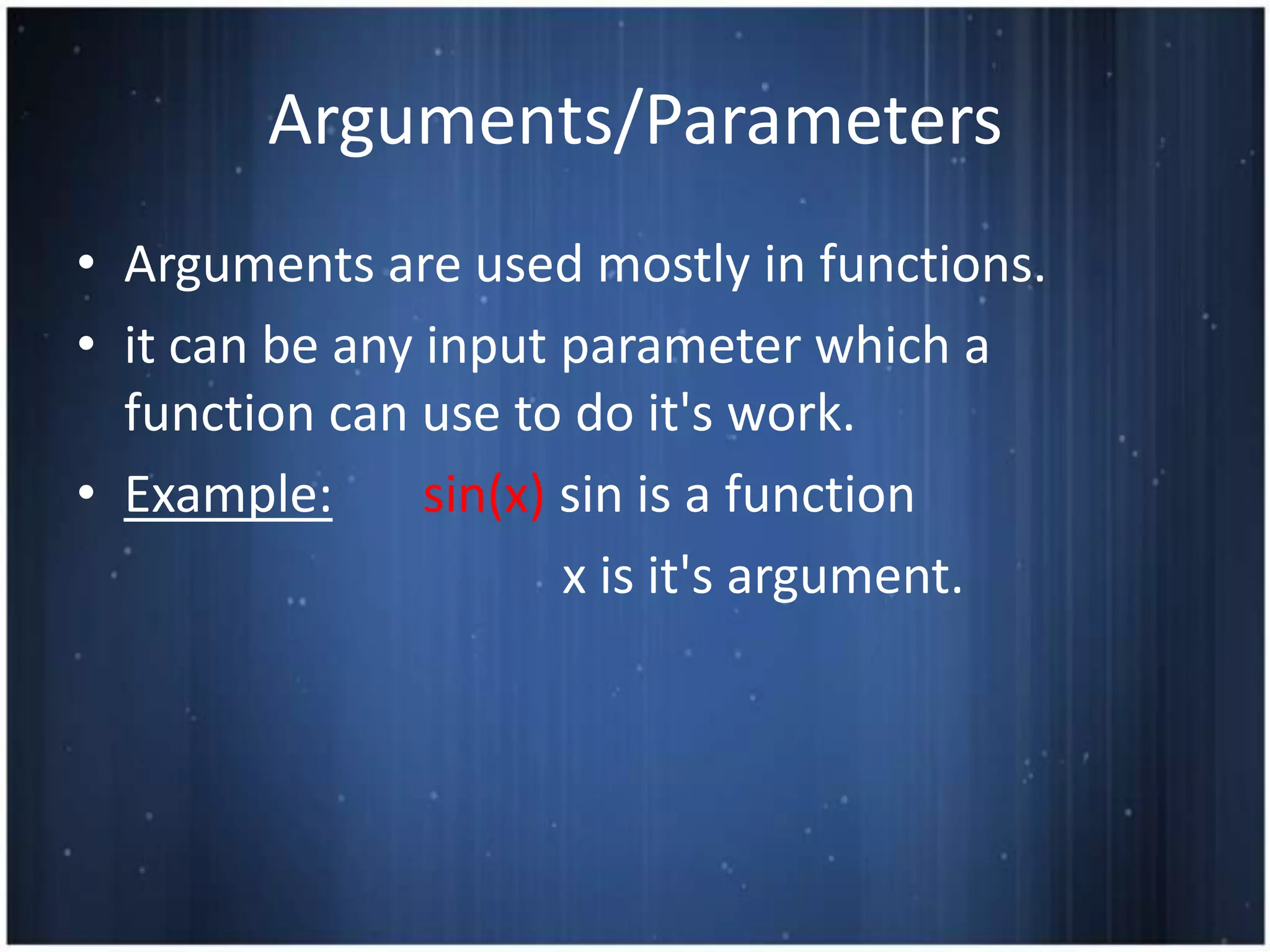
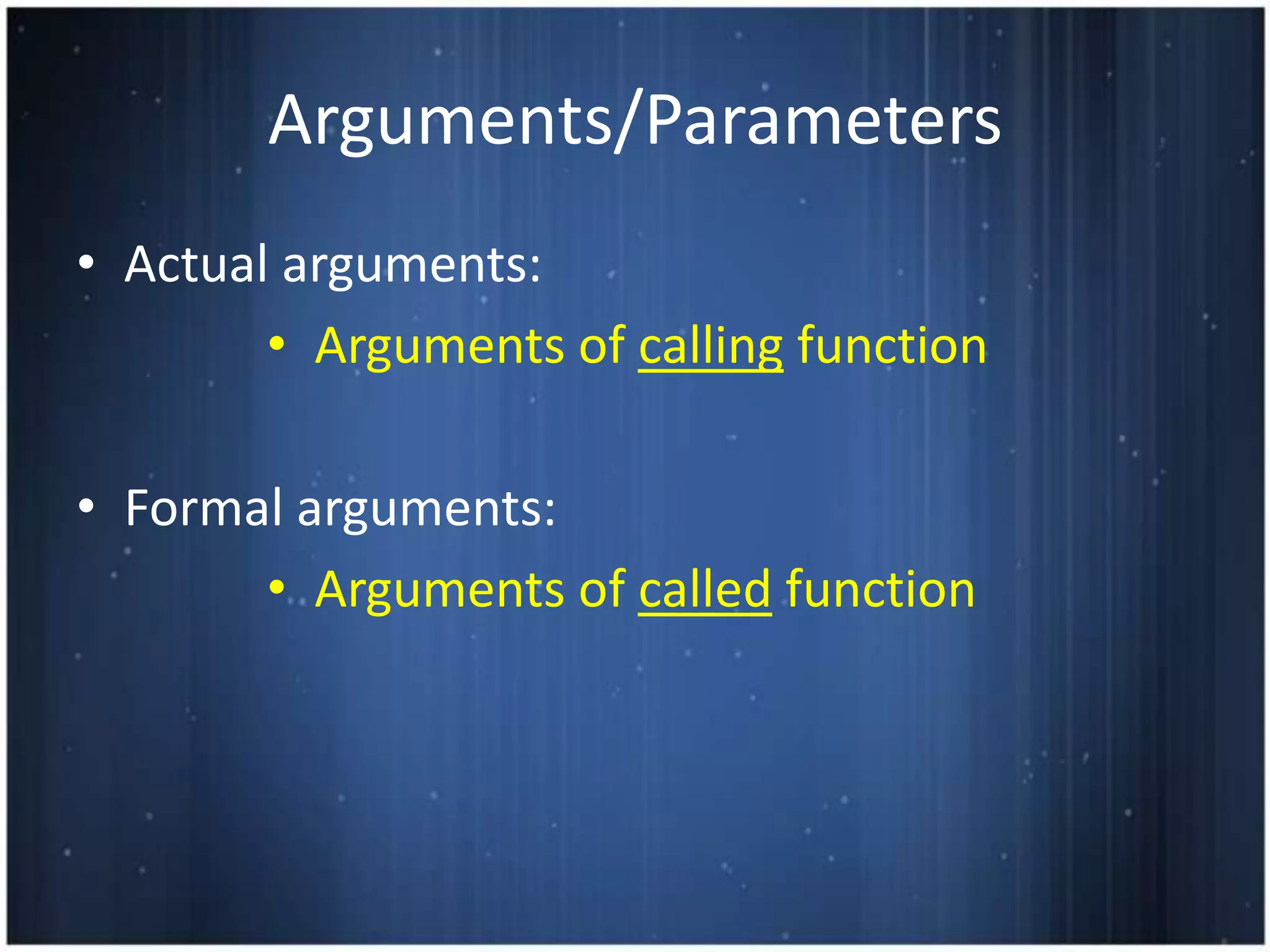
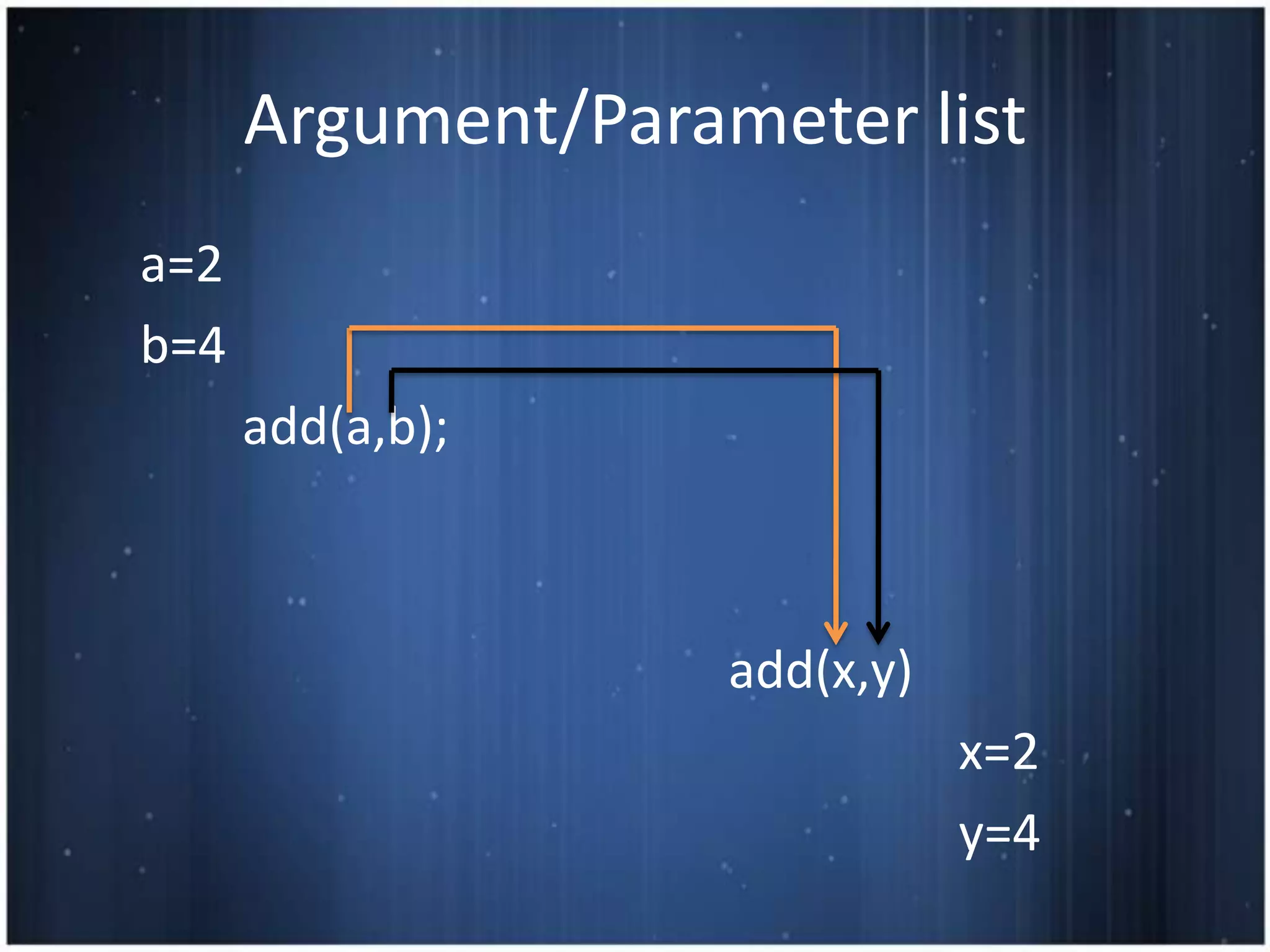
This document discusses functions in C programming. It defines a function as a block of code that performs a specific task when called. It provides examples of functions used in hotel management like front office, reservation, and housekeeping. It explains function definition, declaration, calling, parameters, arguments, return statements. It differentiates between actual and formal arguments and discusses call by value and call by reference methods of passing arguments to functions.