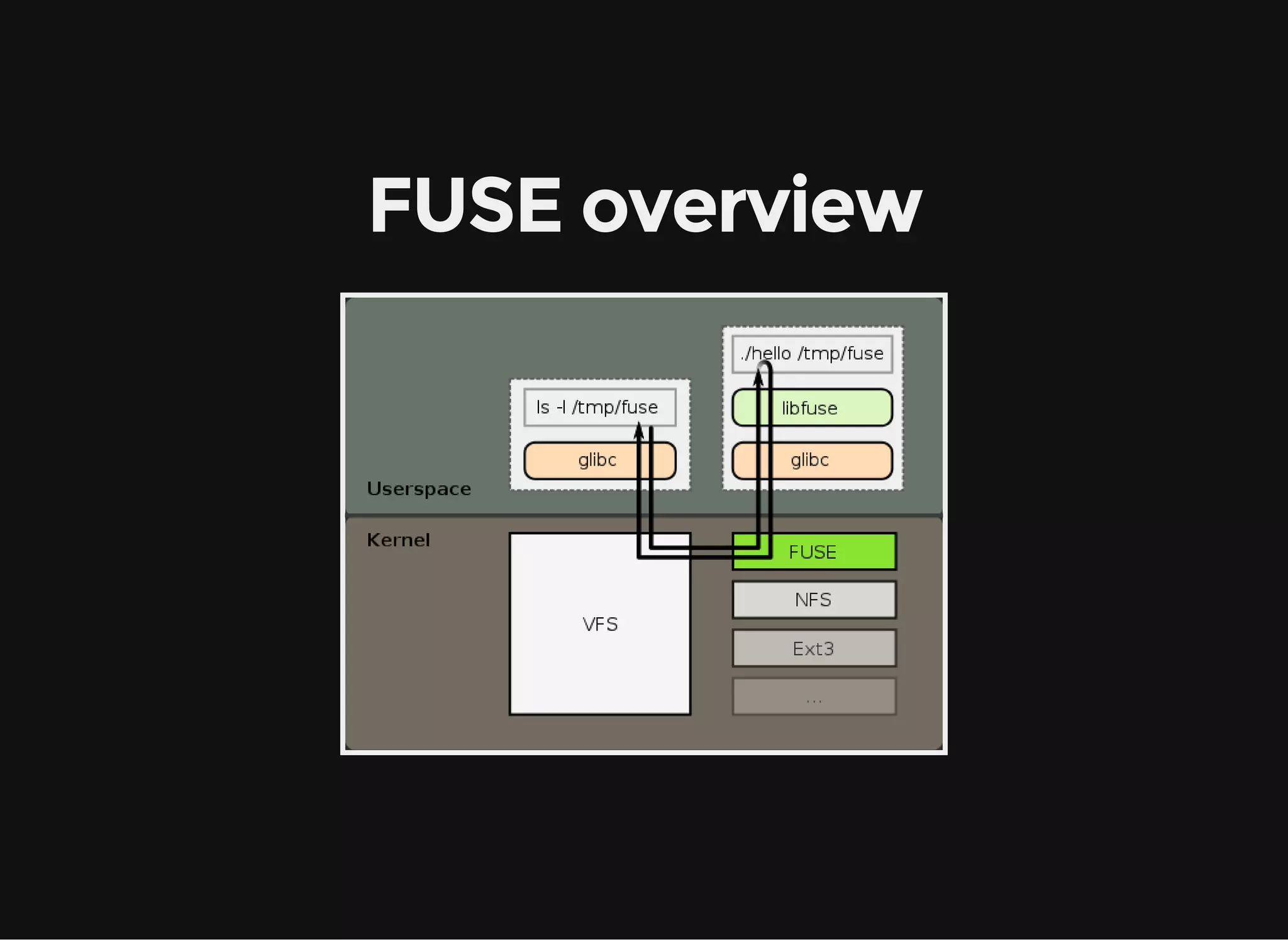
The document discusses writing flexible filesystems using fuse-python, detailing the Fuse API, installation process, and essential methods for filesystem operations. It highlights the advantages of Fuse such as ease of use for unprivileged users and support for multiple programming languages. Additionally, it provides examples of filesystem management methods and references various fuse filesystems available.















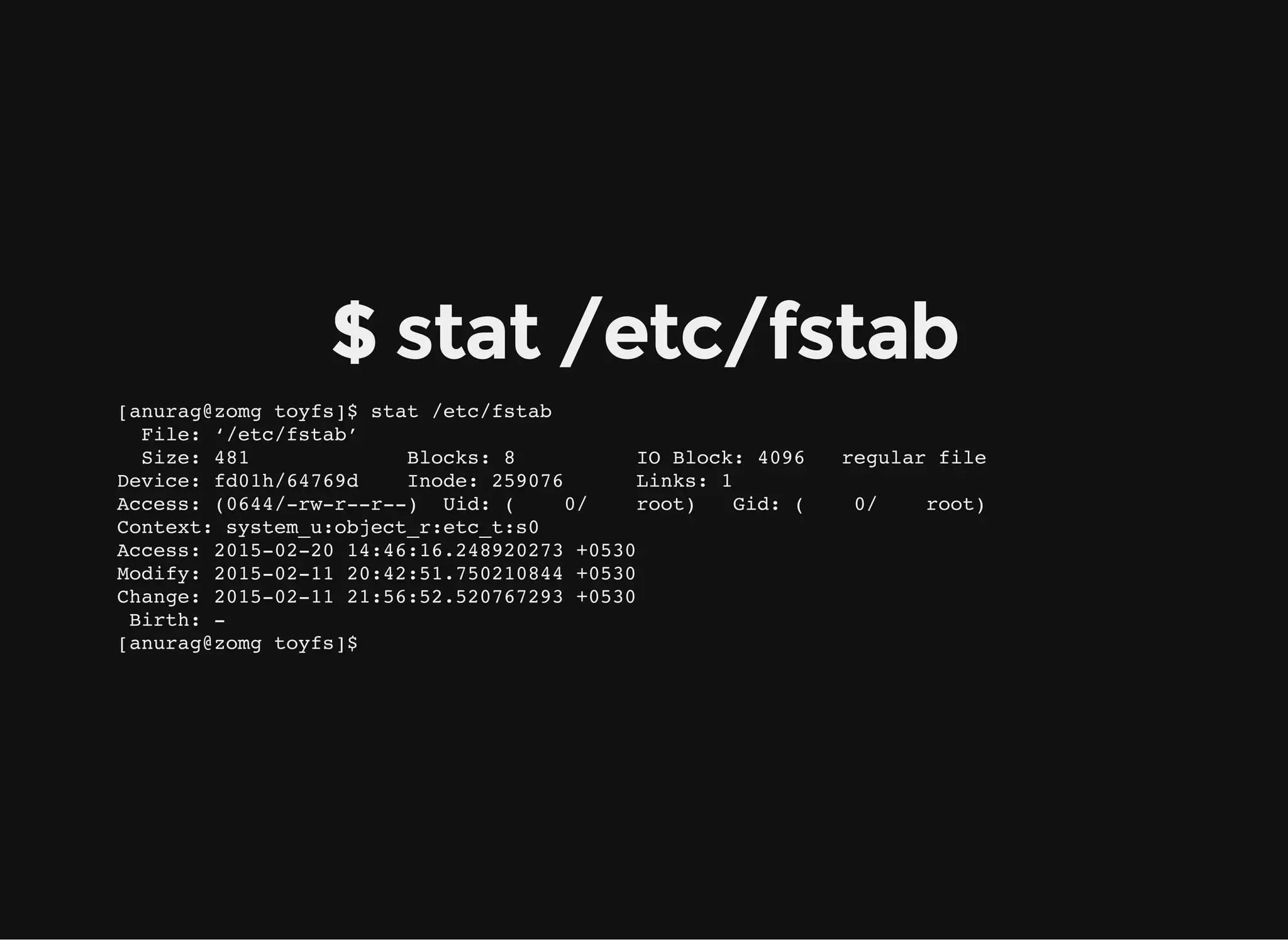
![$ stat /etc/fstab
[anurag@zomg toyfs]$ stat /etc/fstab
File: ‘/etc/fstab’
Size: 481 Blocks: 8 IO Block: 4096 regular file
Device: fd01h/64769d Inode: 259076 Links: 1
Access: (0644/-rw-r--r--) Uid: ( 0/ root) Gid: ( 0/ root)
Context: system_u:object_r:etc_t:s0
Access: 2015-02-20 14:46:16.248920273 +0530
Modify: 2015-02-11 20:42:51.750210844 +0530
Change: 2015-02-11 21:56:52.520767293 +0530
Birth: -
[anurag@zomg toyfs]$](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dzd14wxraafzf1vnbcdg-signature-8beddb31f59427bb47e0edbae8c91e4494be5facb98b49fa9eec79b54bc21a19-poli-150223023942-conversion-gate01/75/Writing-flexible-filesystems-in-FUSE-Python-18-2048.jpg)






