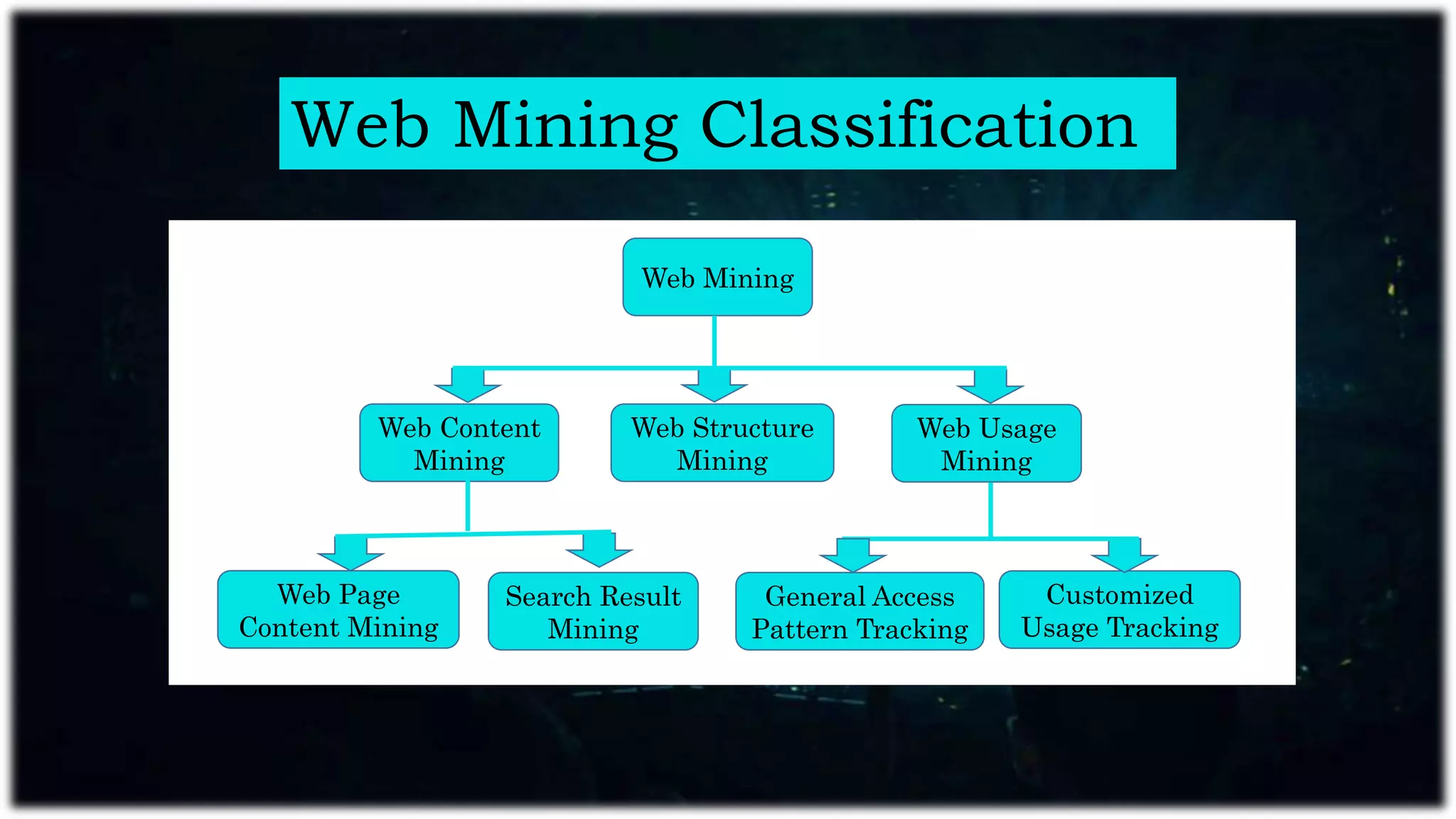
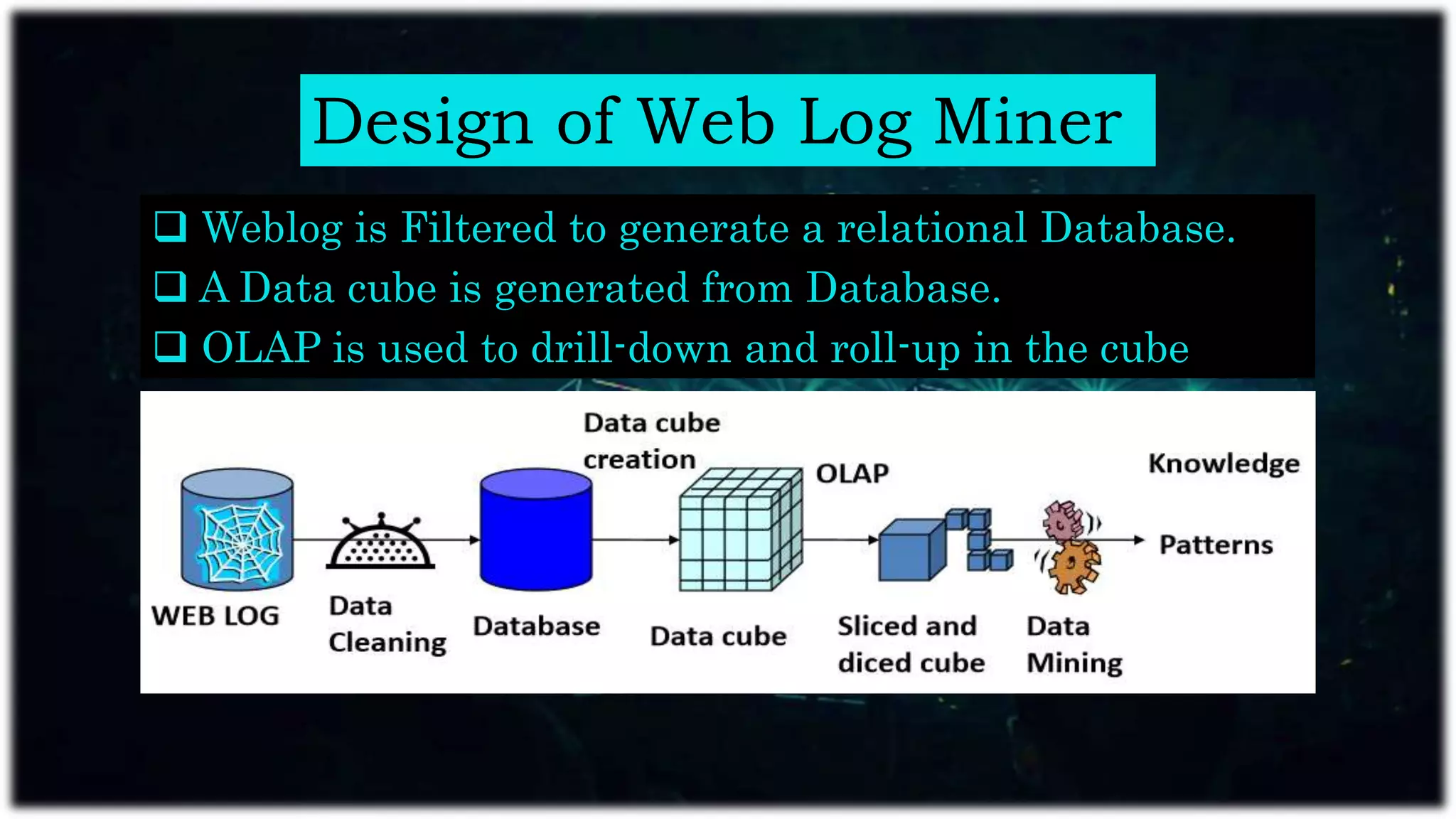
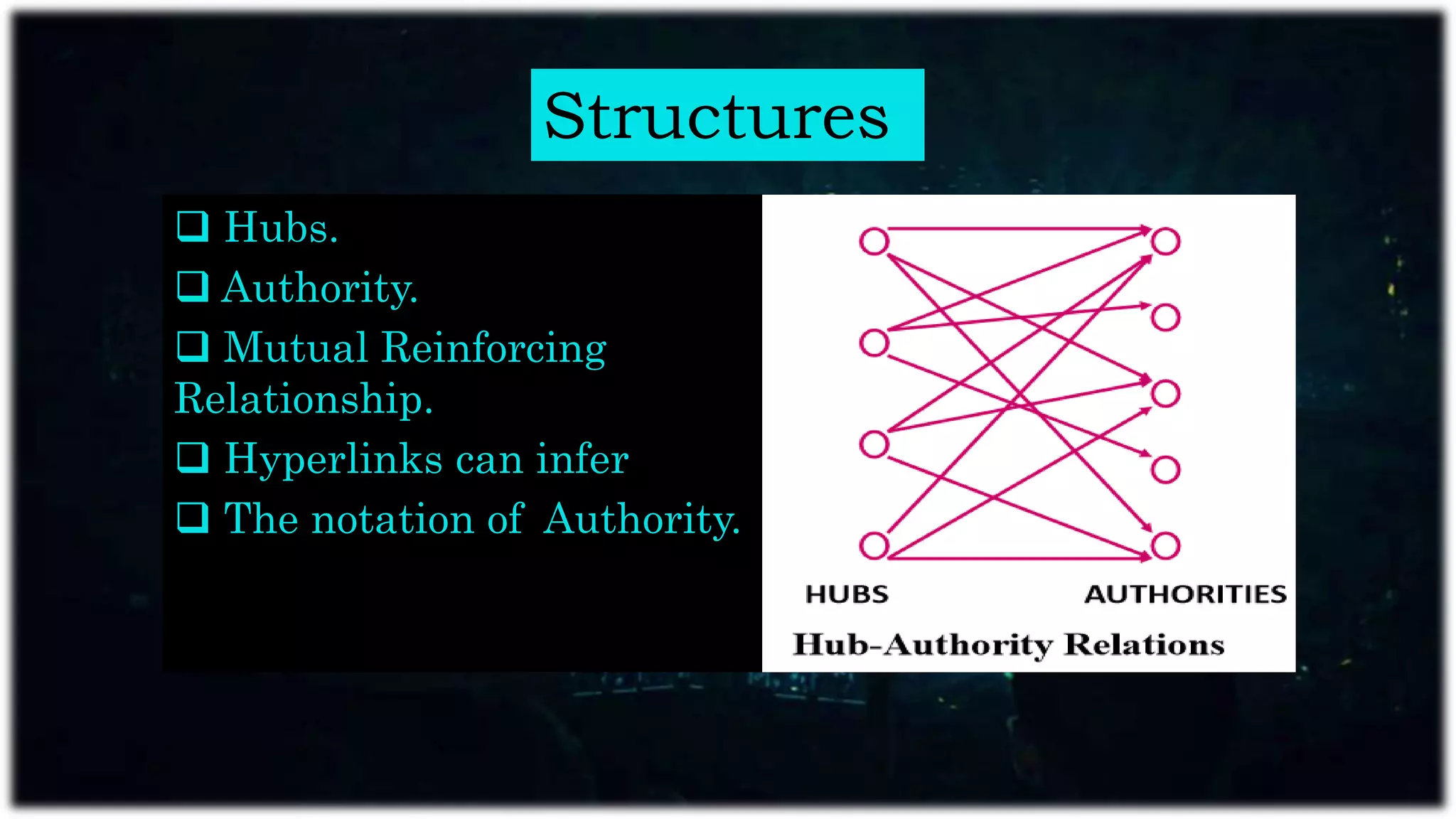
Web mining applies data mining techniques to extract knowledge from web documents and services, enhancing e-commerce through personalized marketing. It encompasses web content, structure, and usage mining, allowing for analysis of user behavior and resource discovery. Key applications include improving website performance, site design, and delivering personalized content.