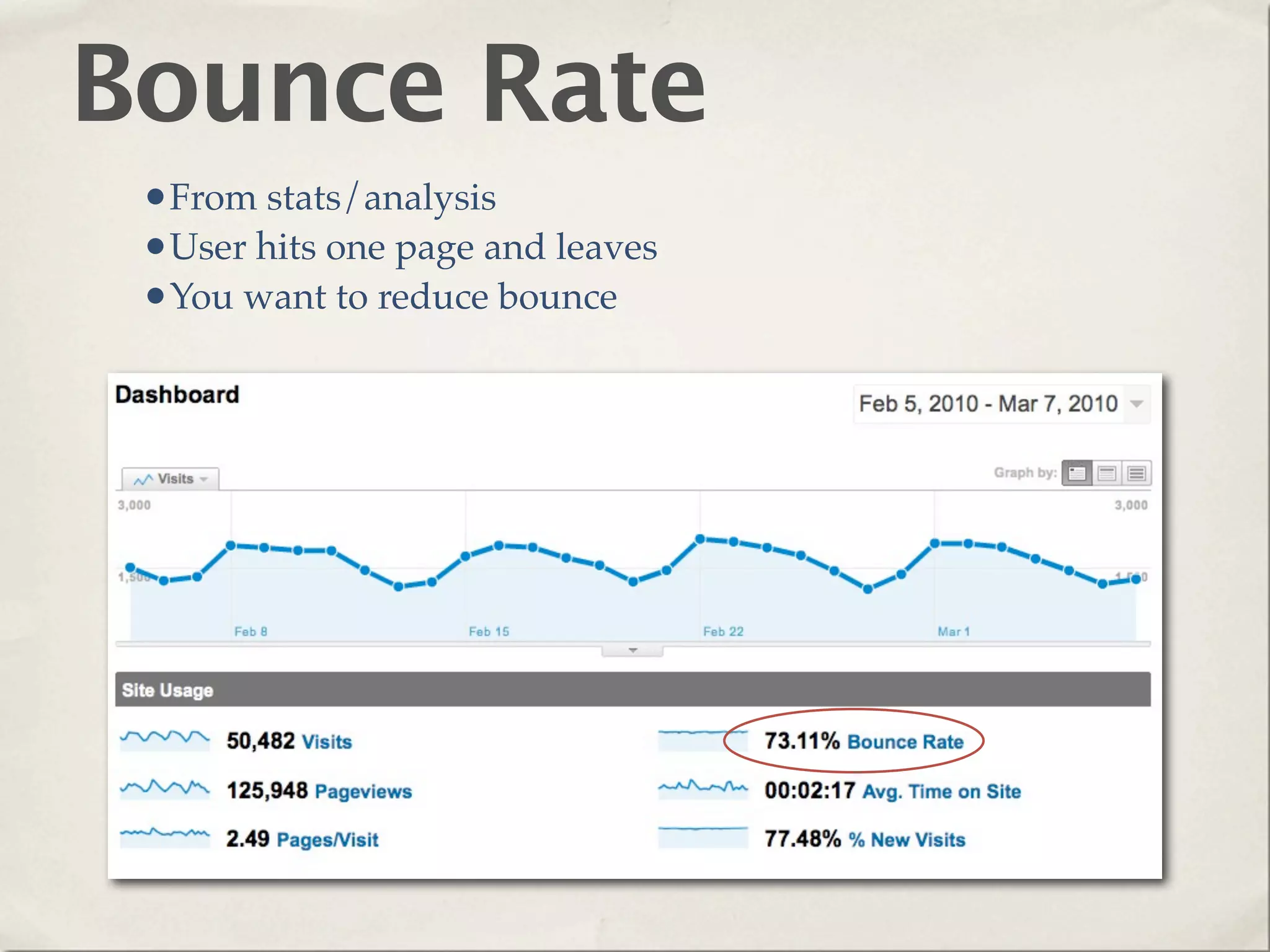
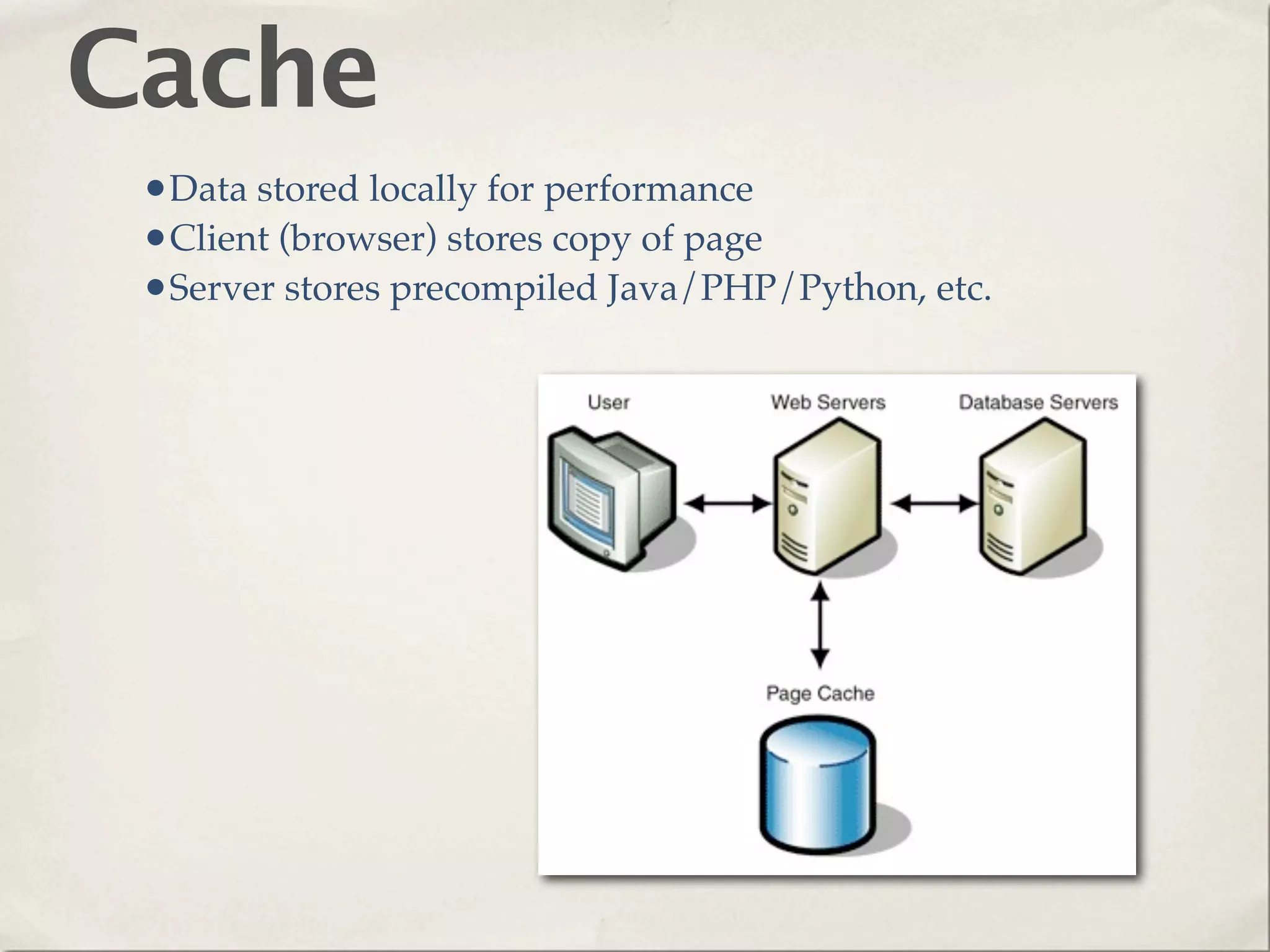
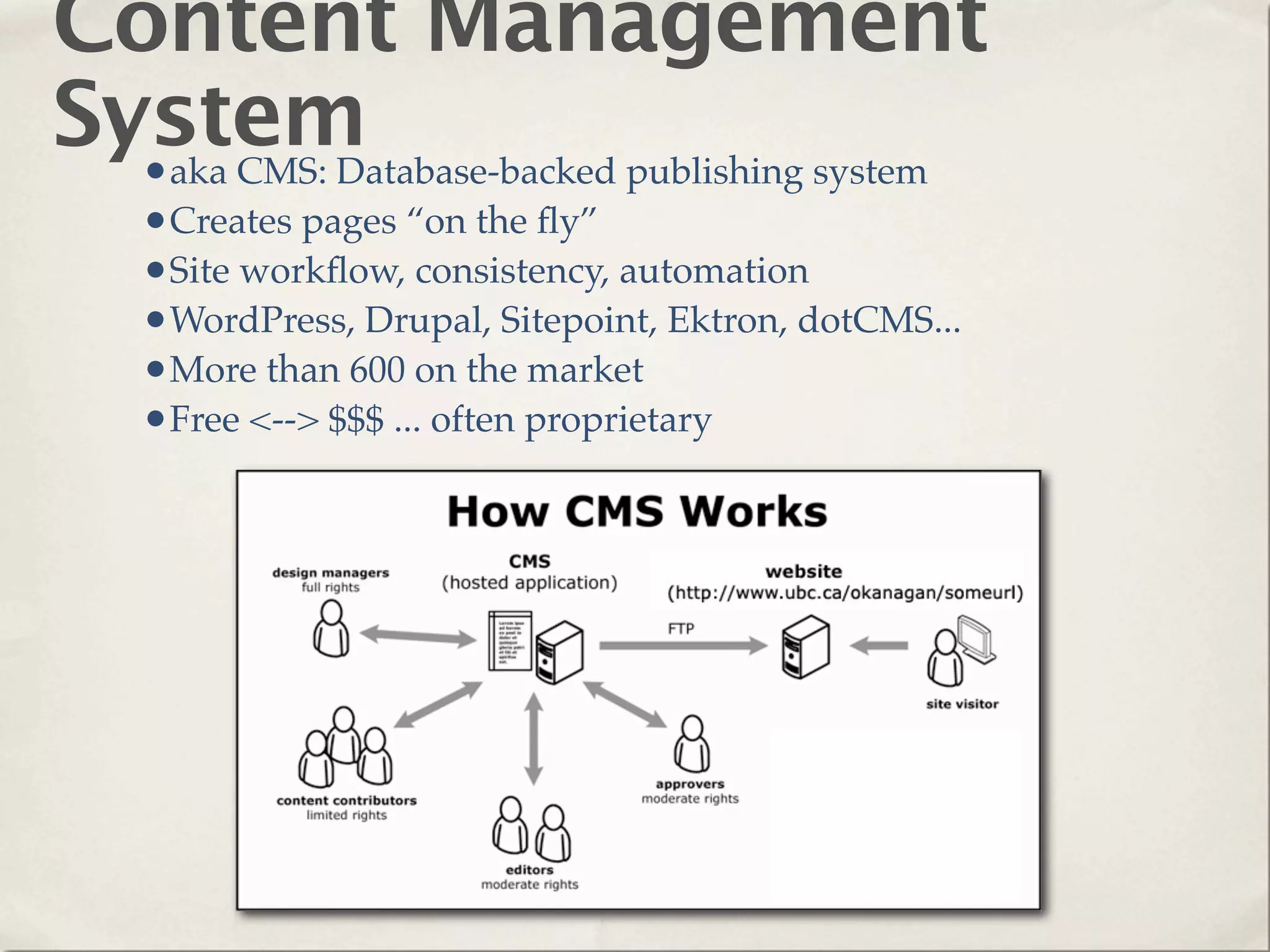
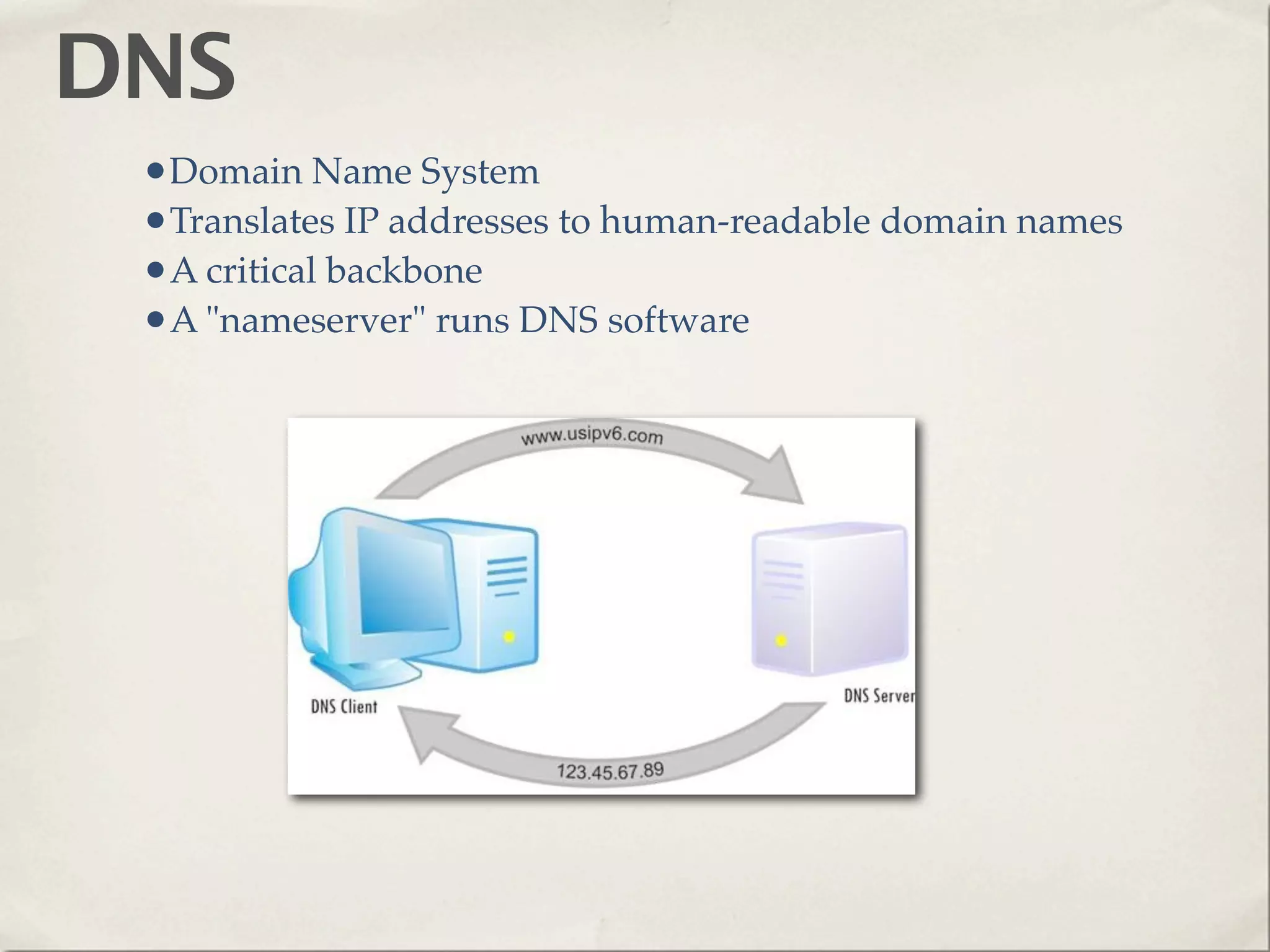
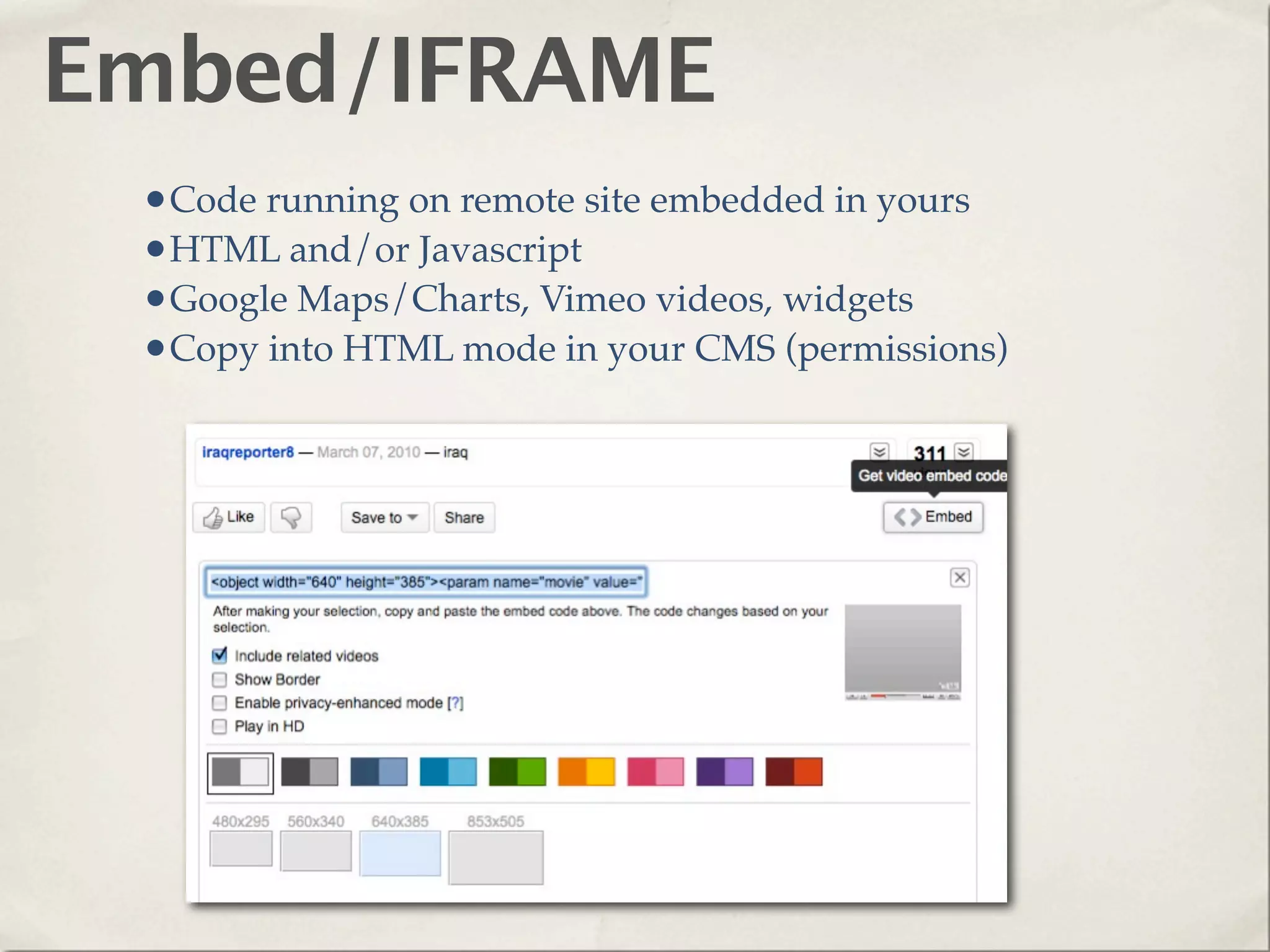
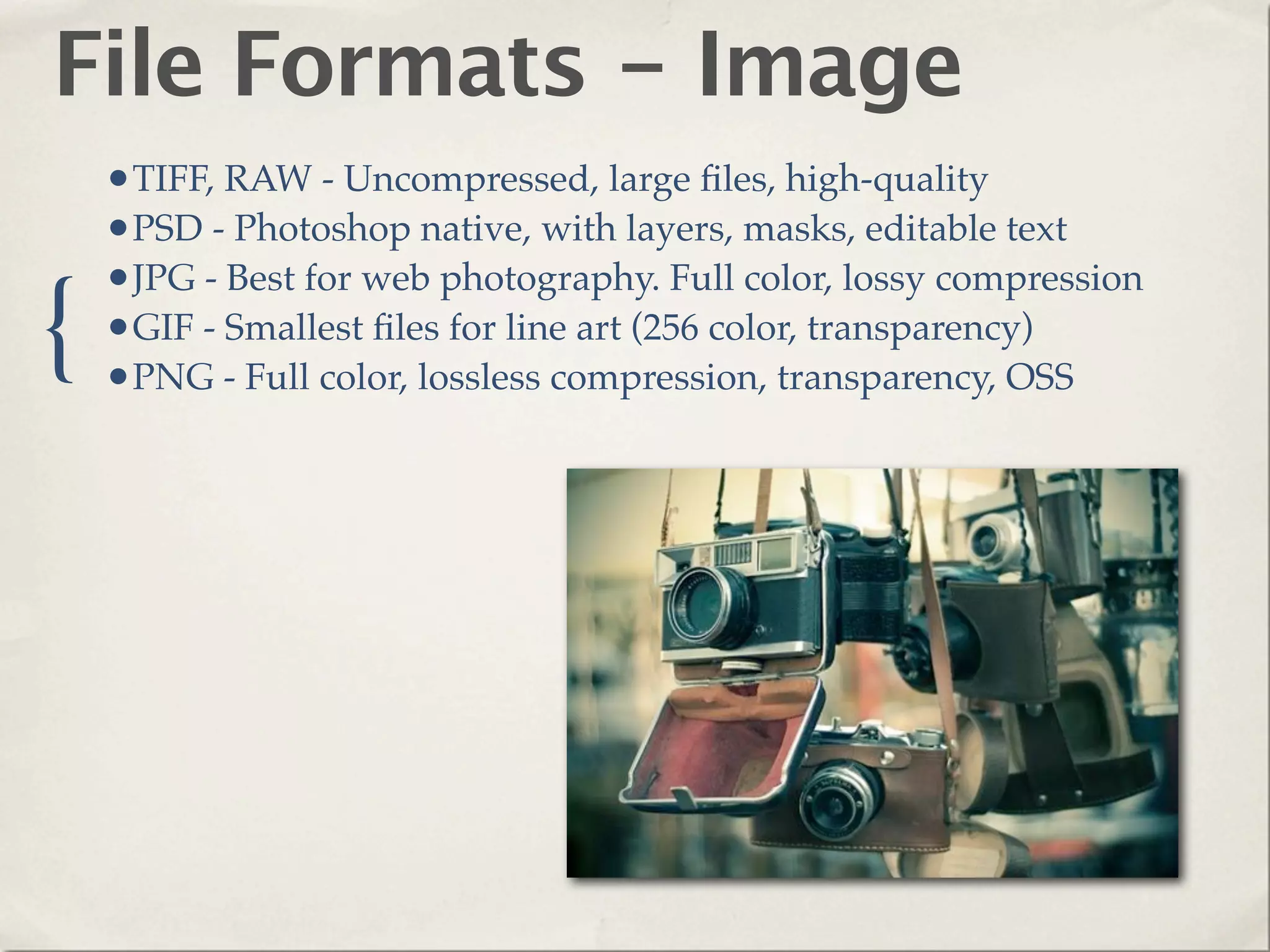
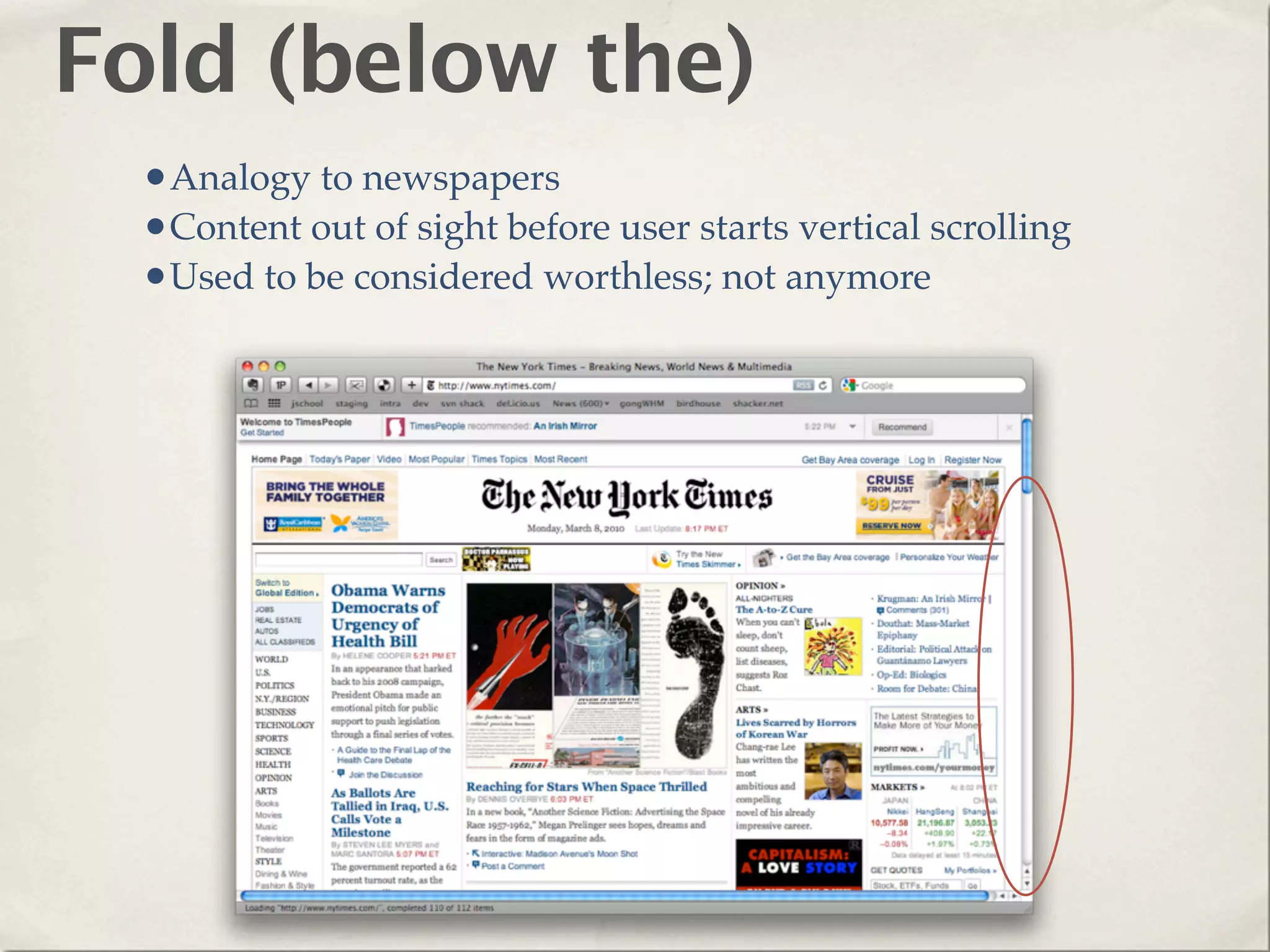
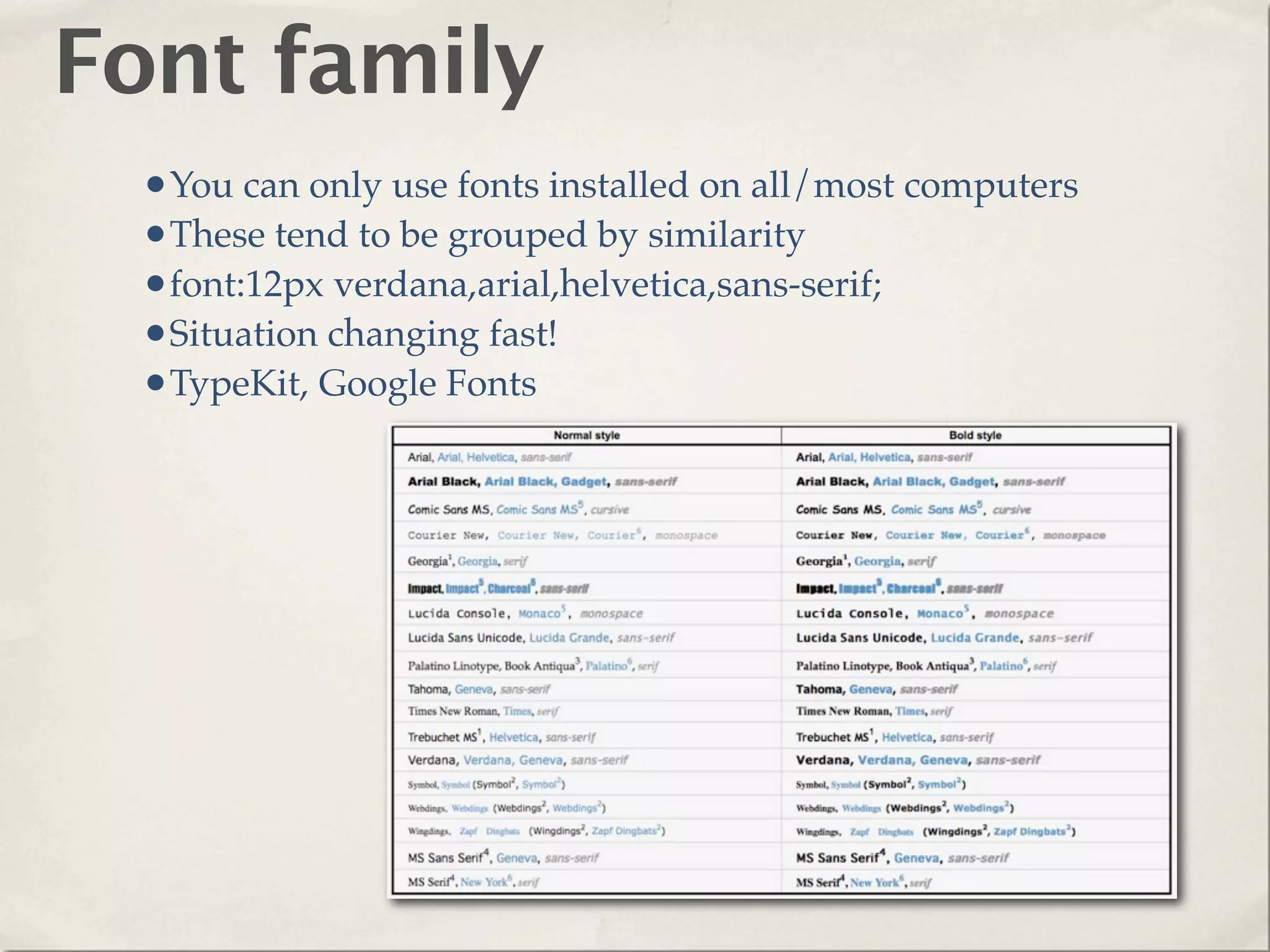
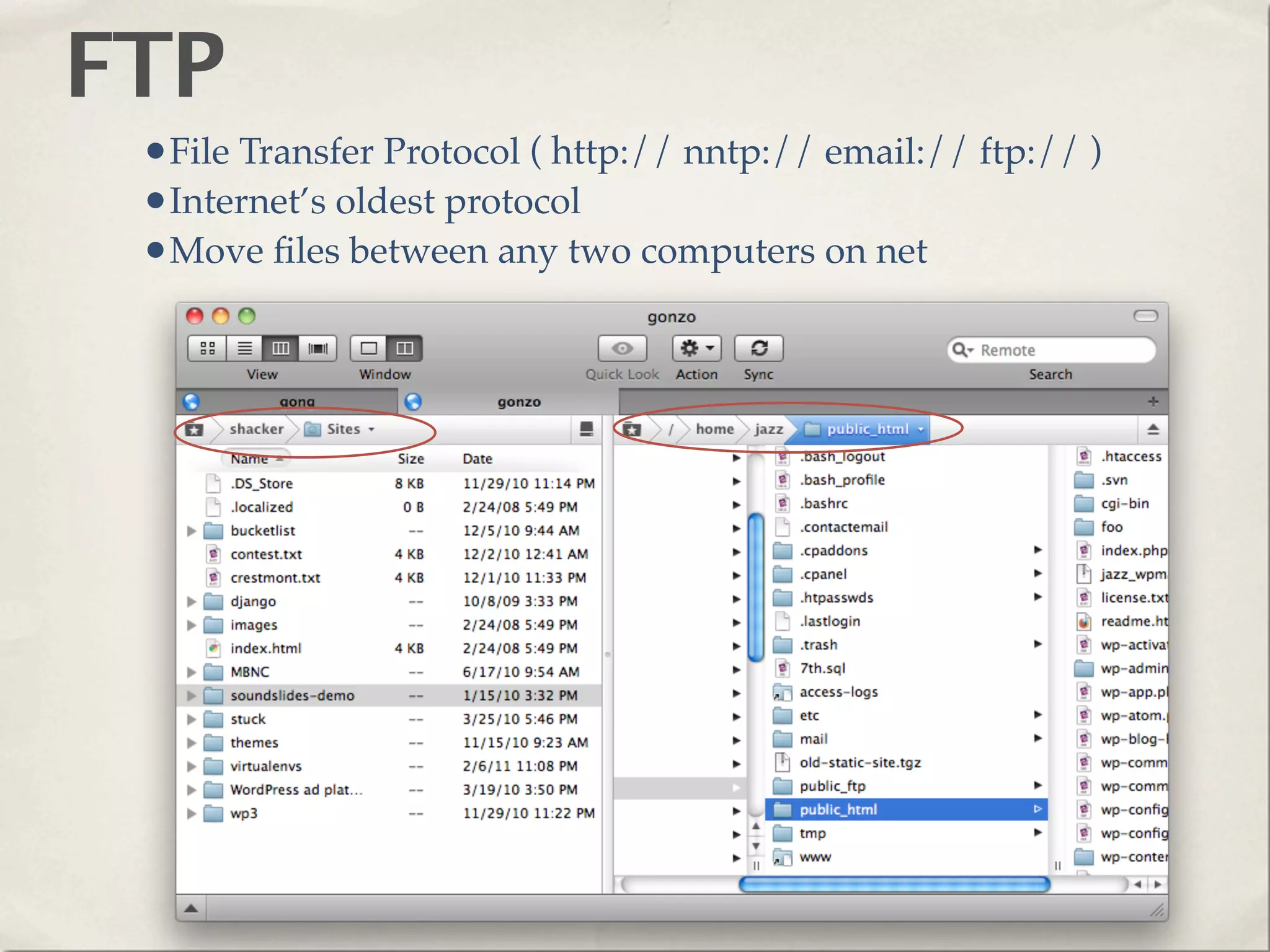
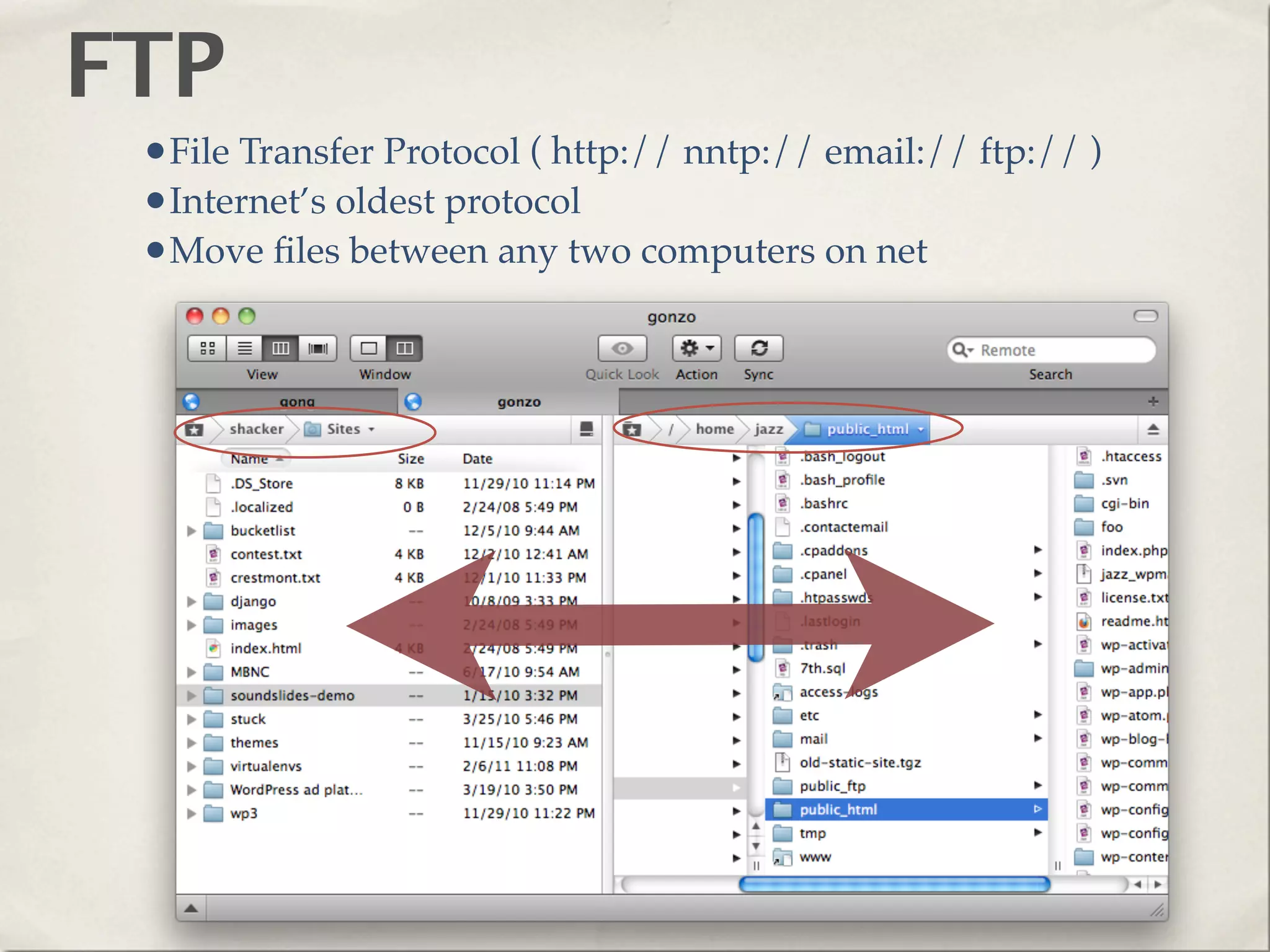
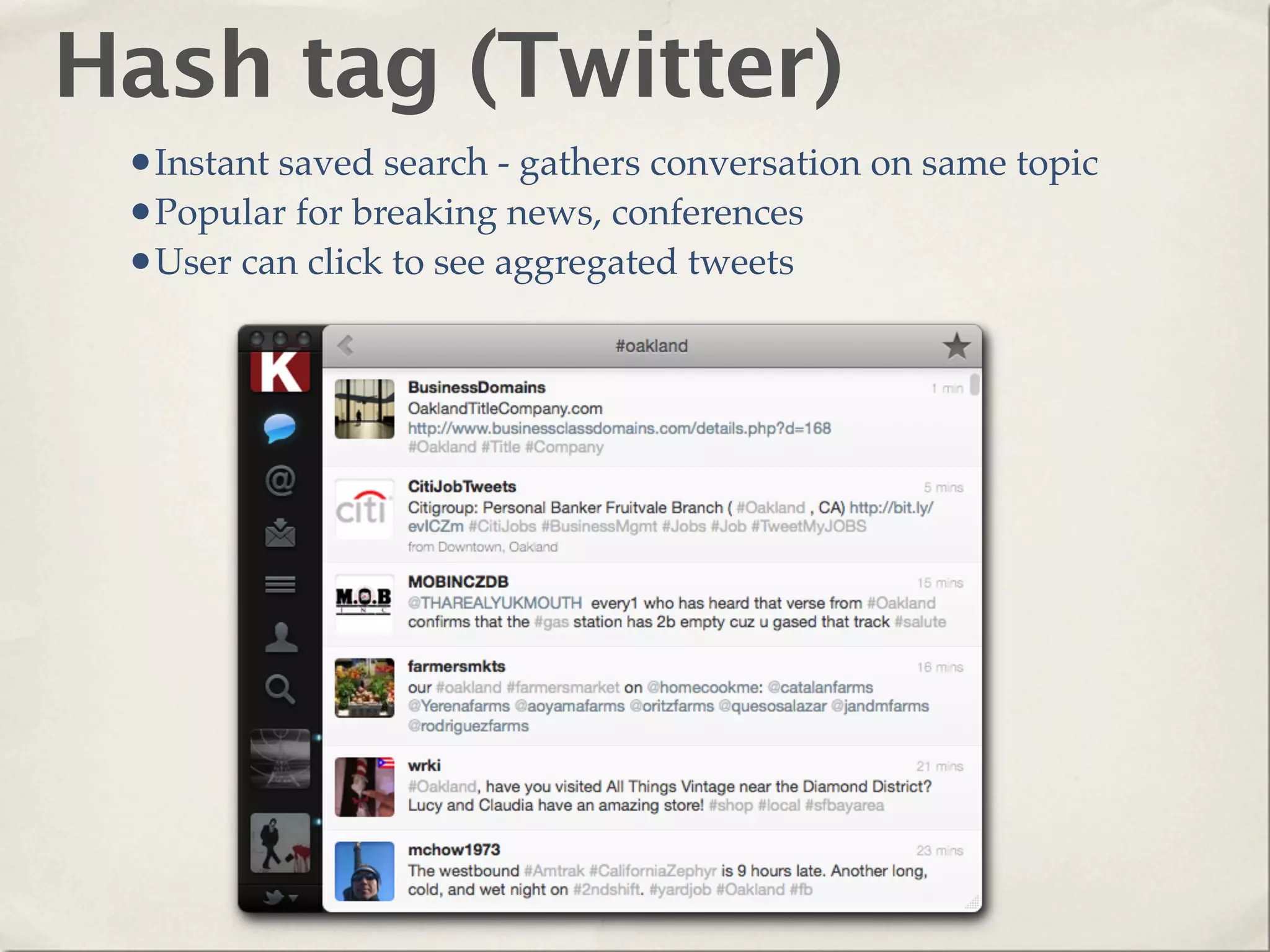
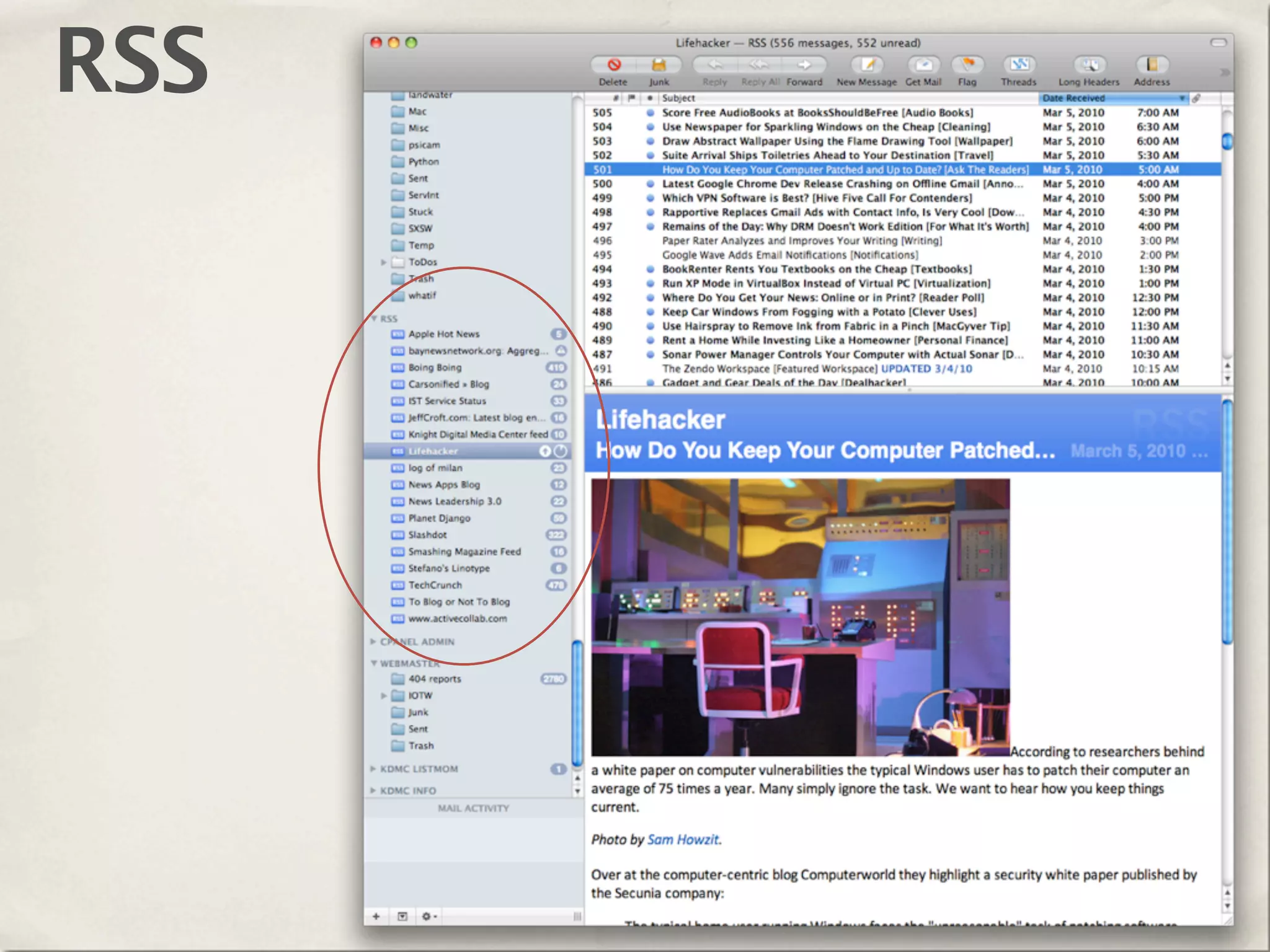
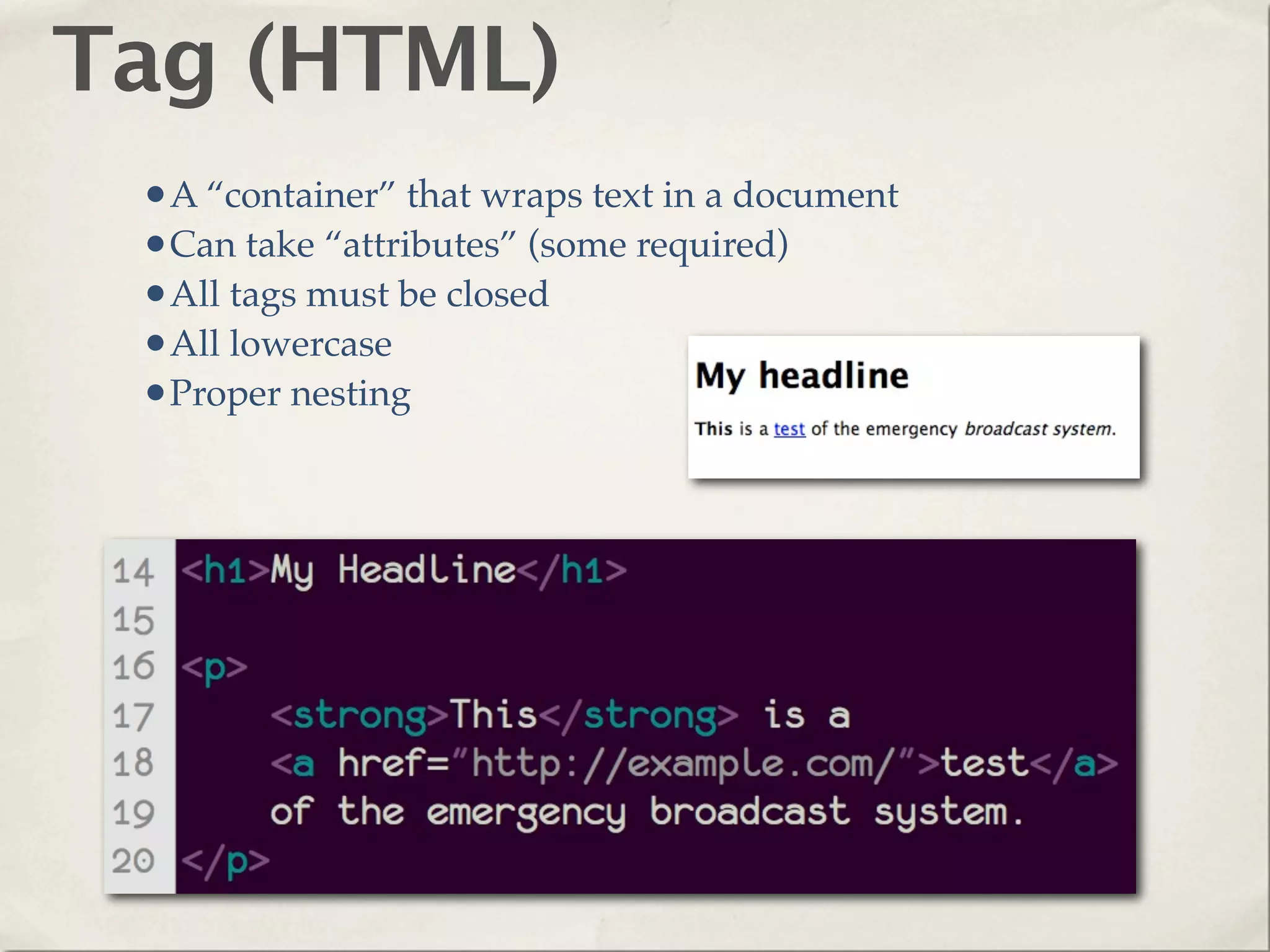
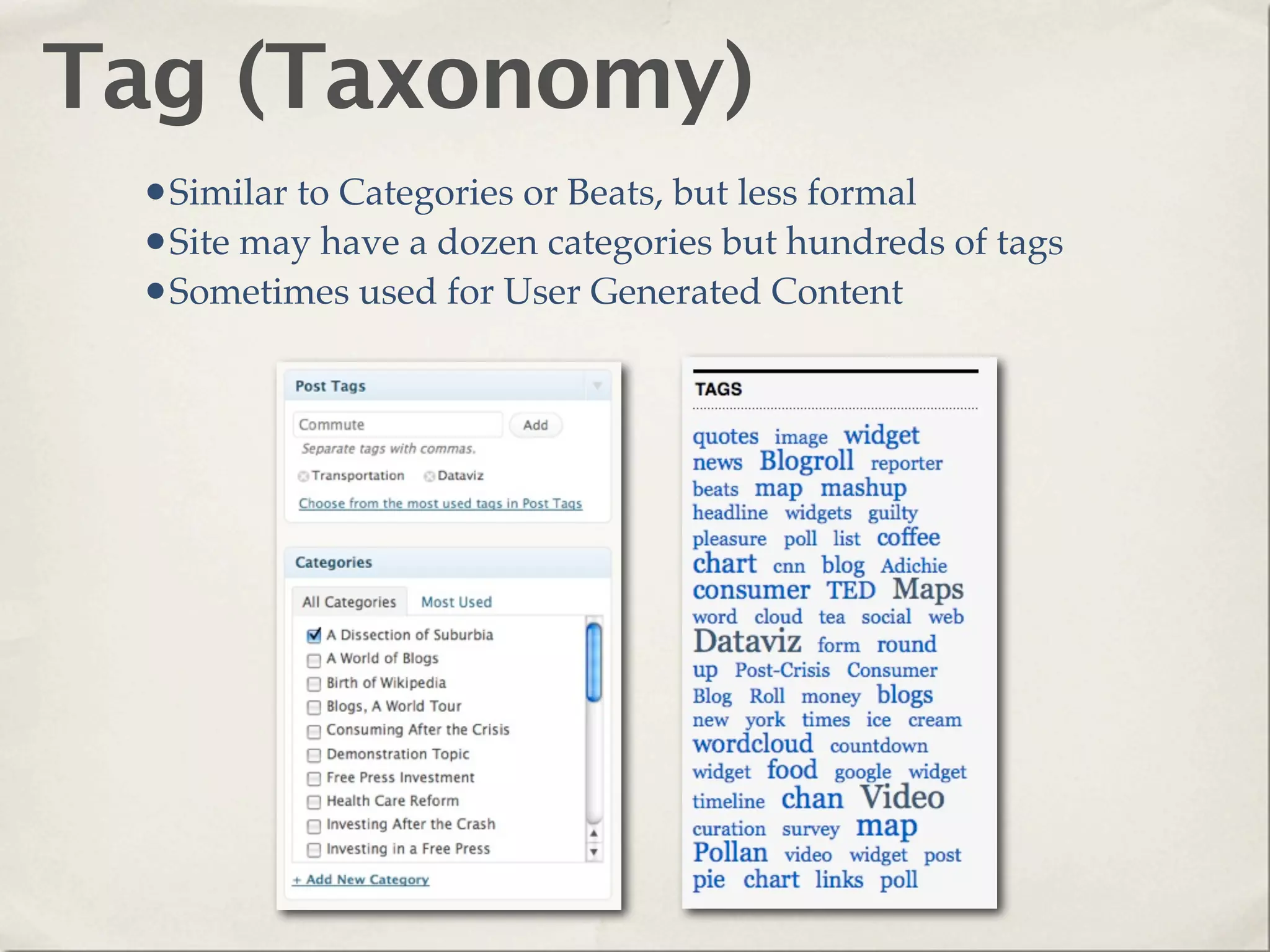
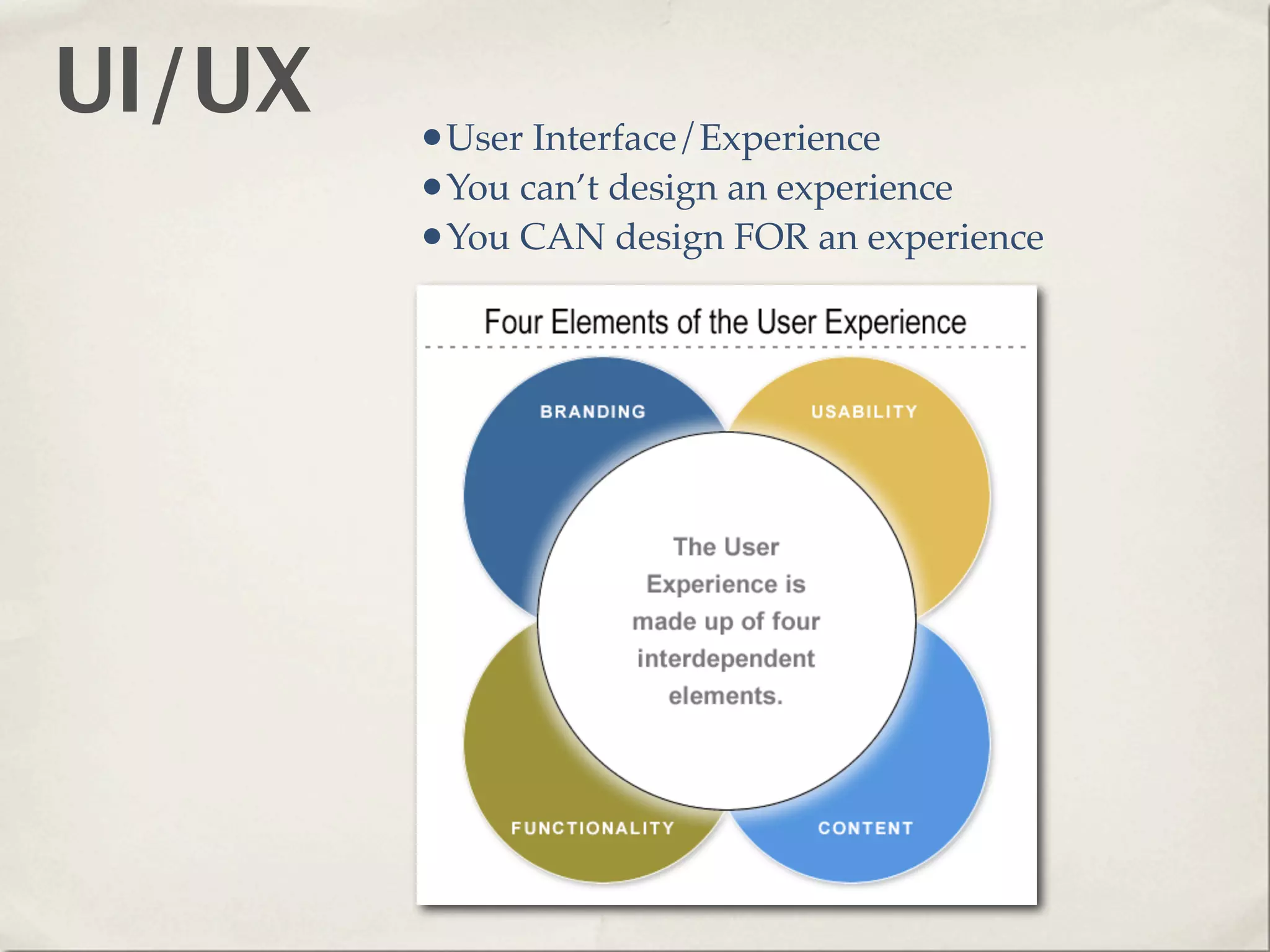
The document provides an overview of various web technologies and best practices, including AJAX, content management systems, file formats for audio, video, and images, and importance of usability and user experience design. It emphasizes the significance of web standards, semantic web, and responsive design to create efficient and user-friendly websites. Additionally, it outlines the structure and components of URLs, protocols, and the role of servers in web development.