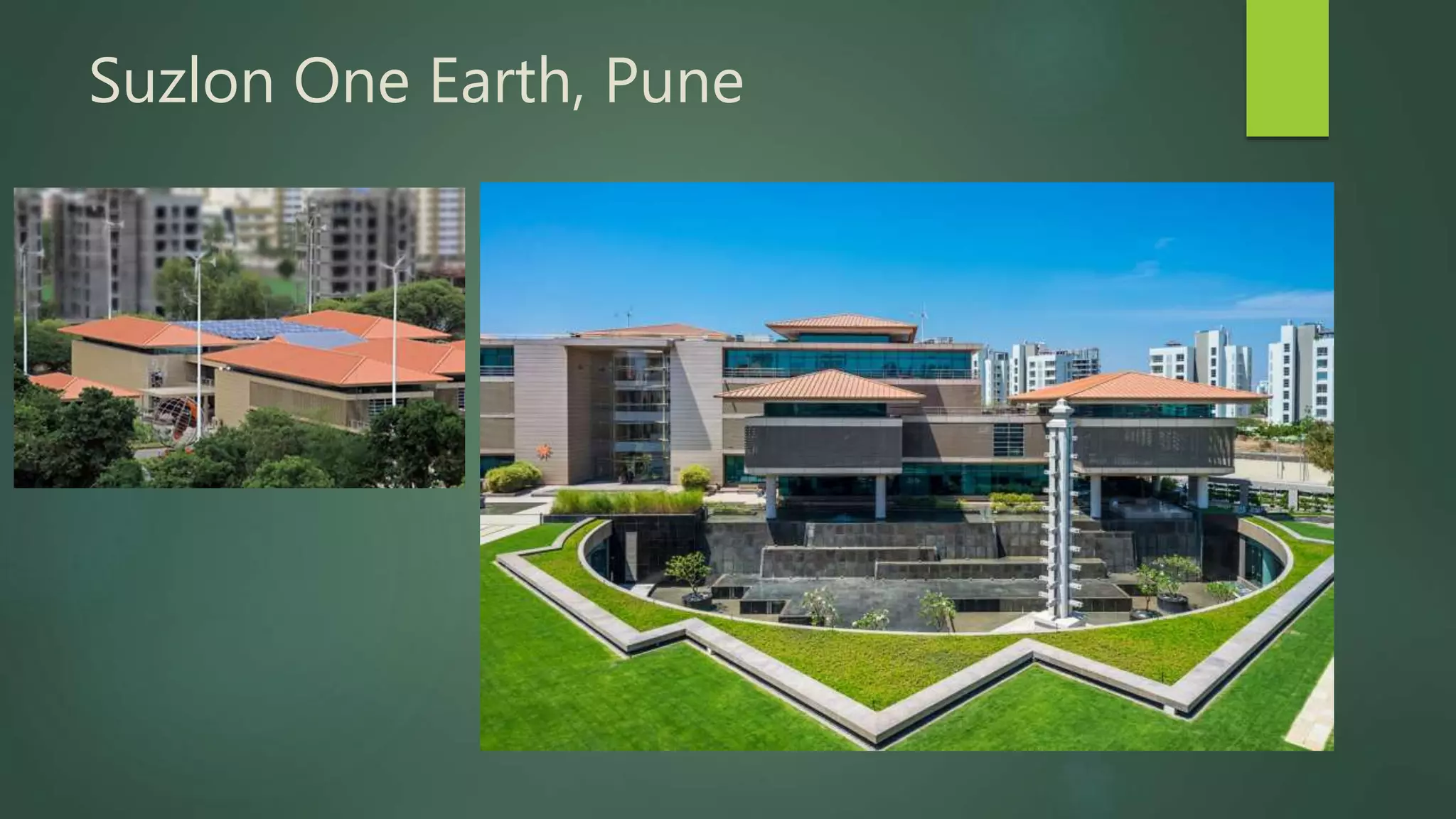
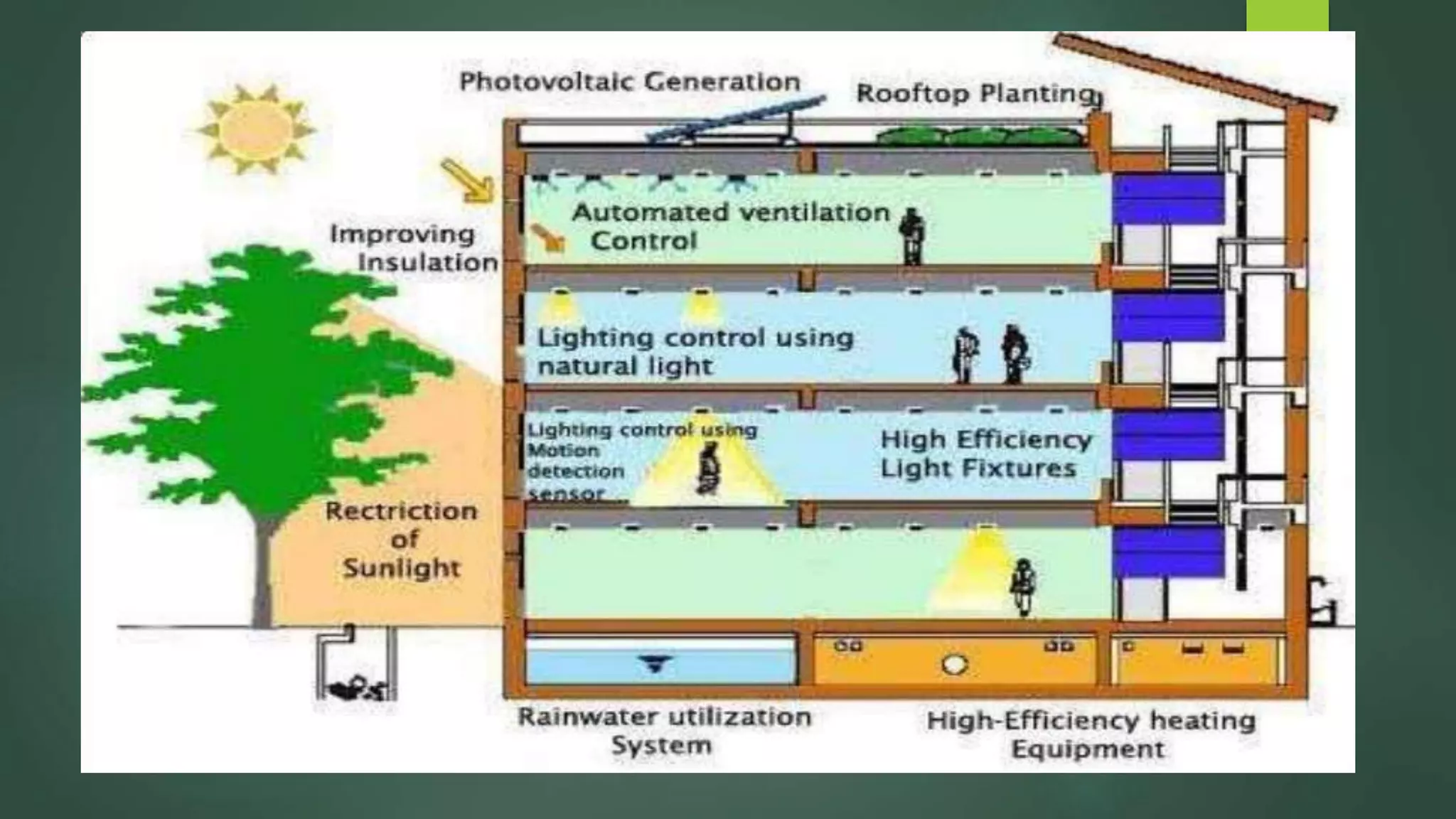
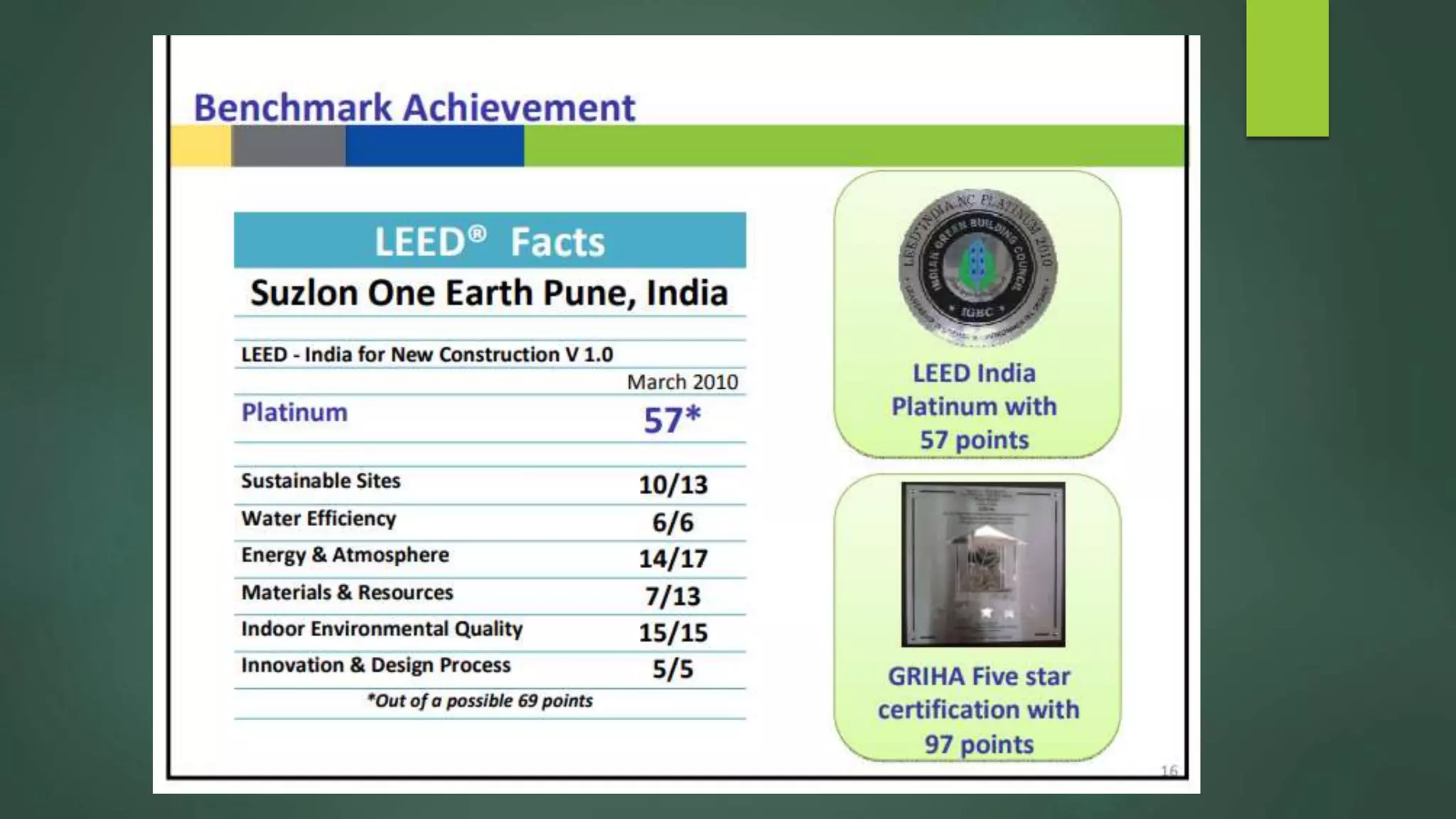
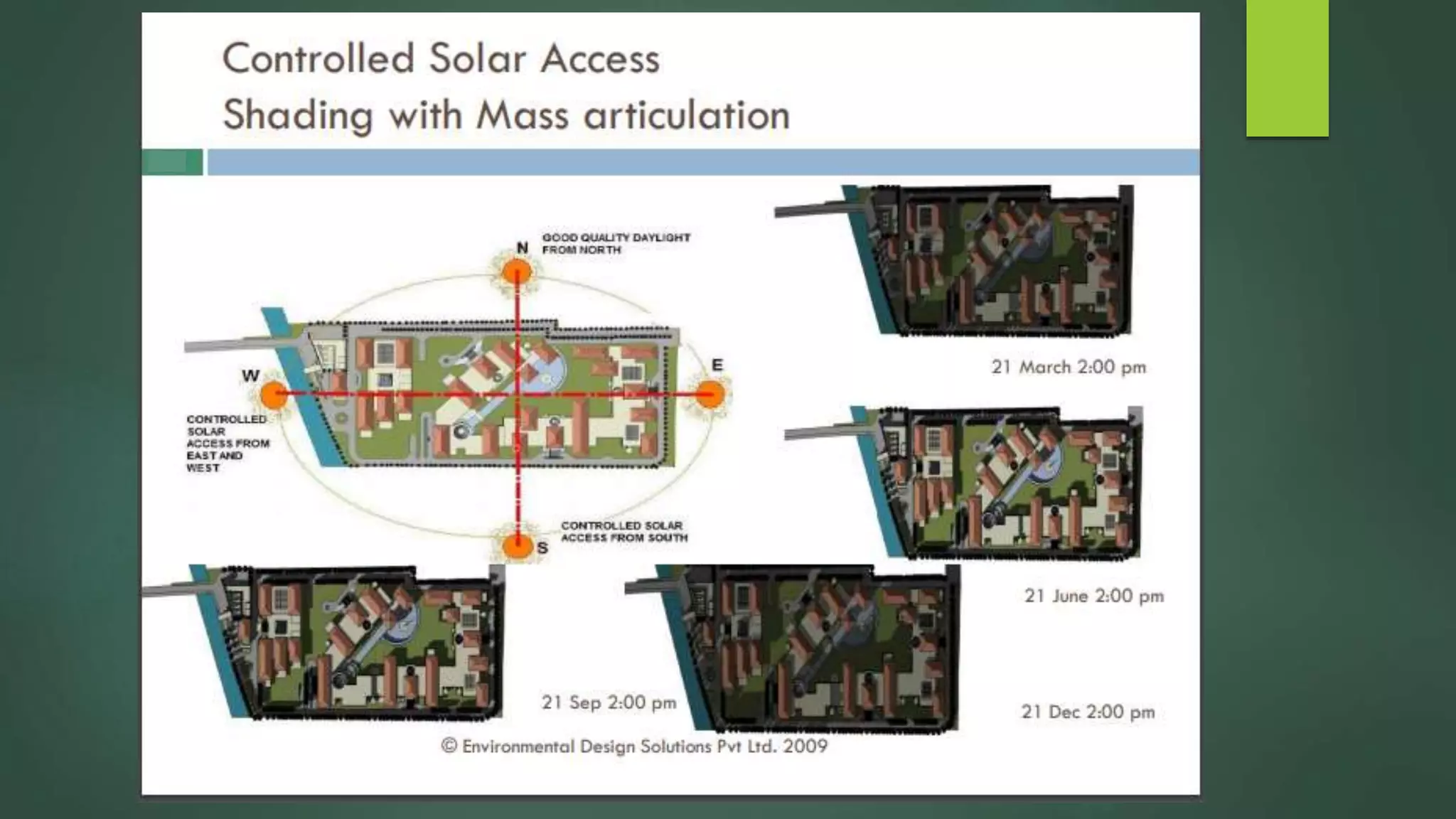
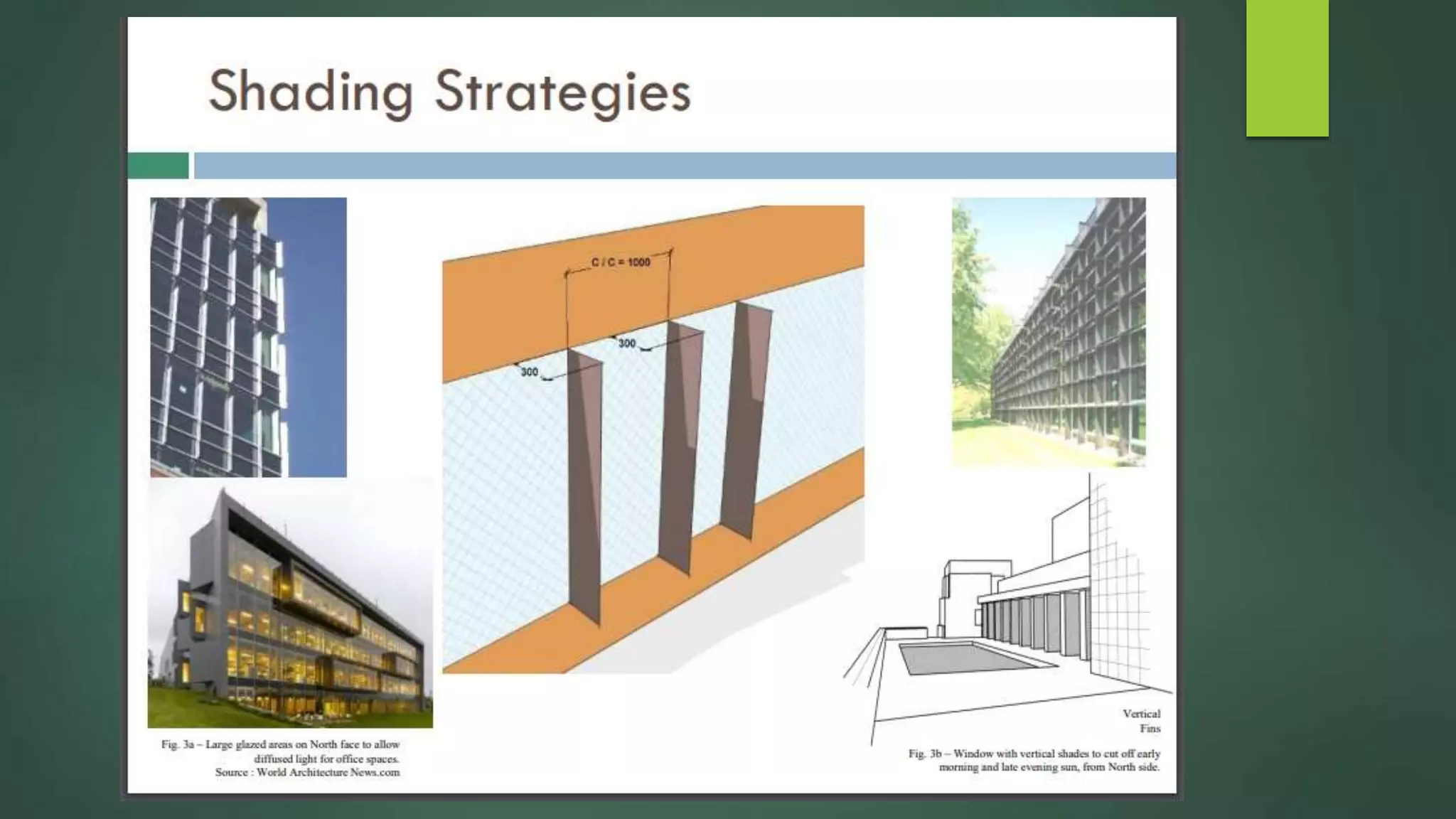
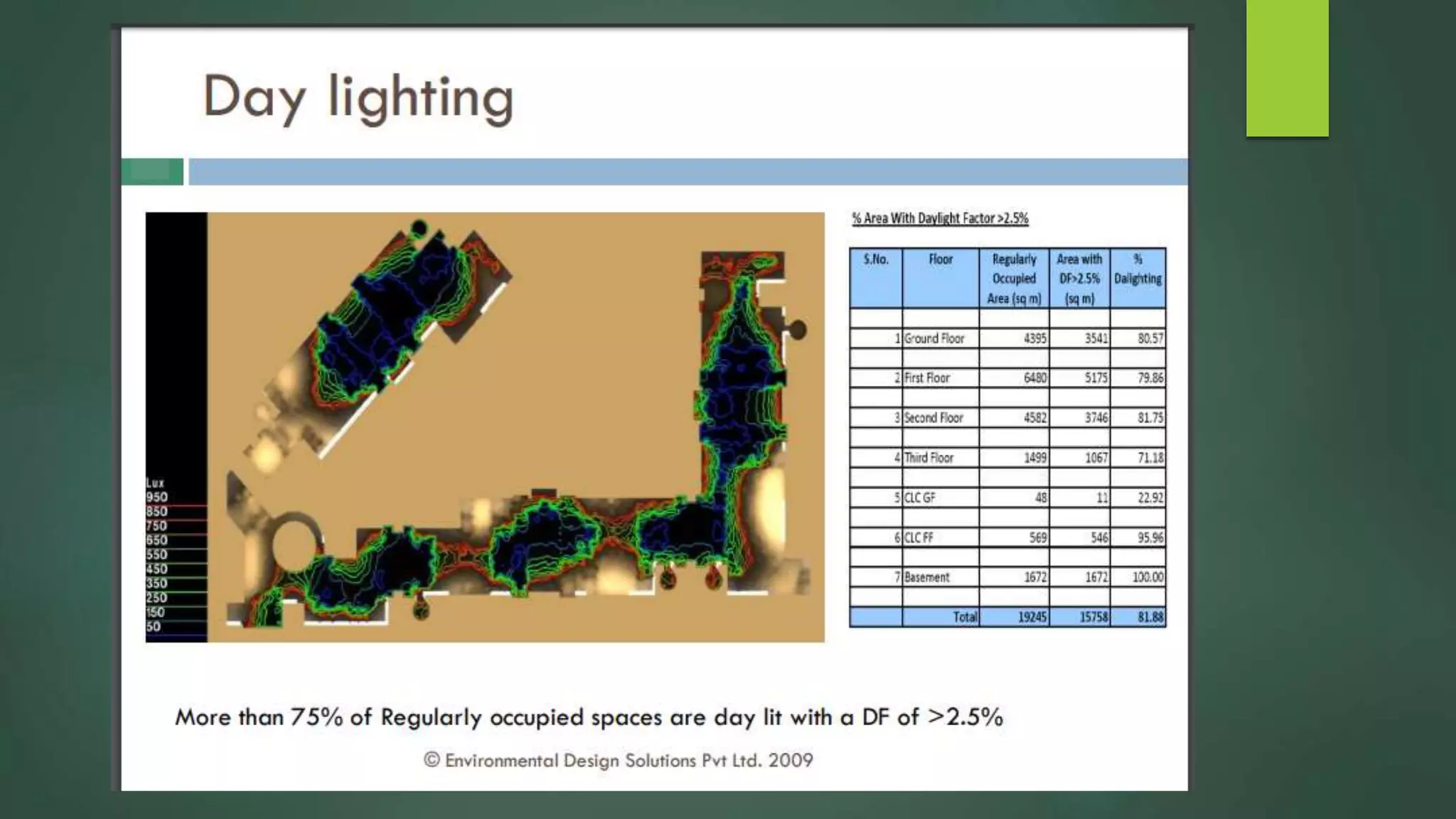
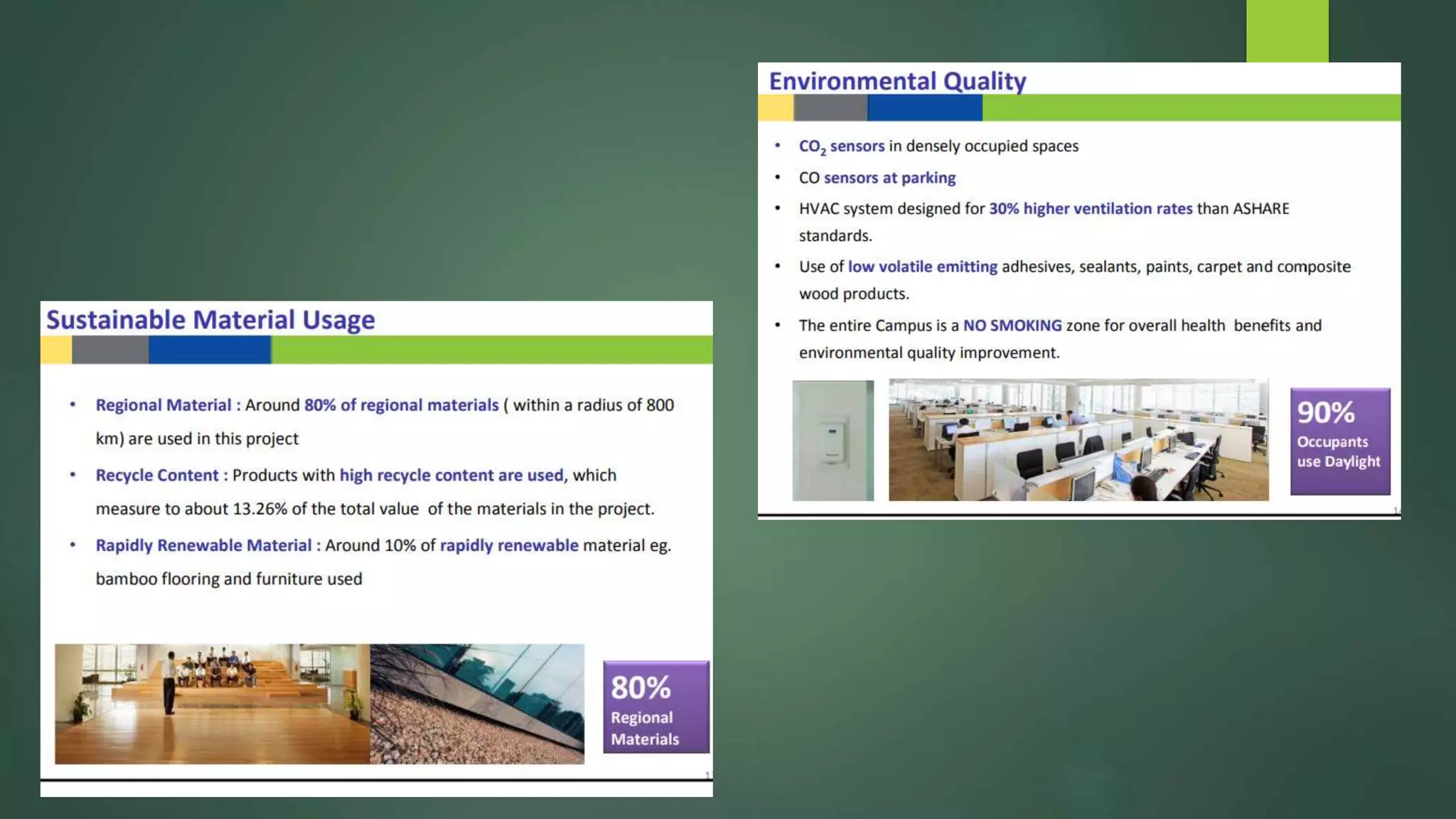
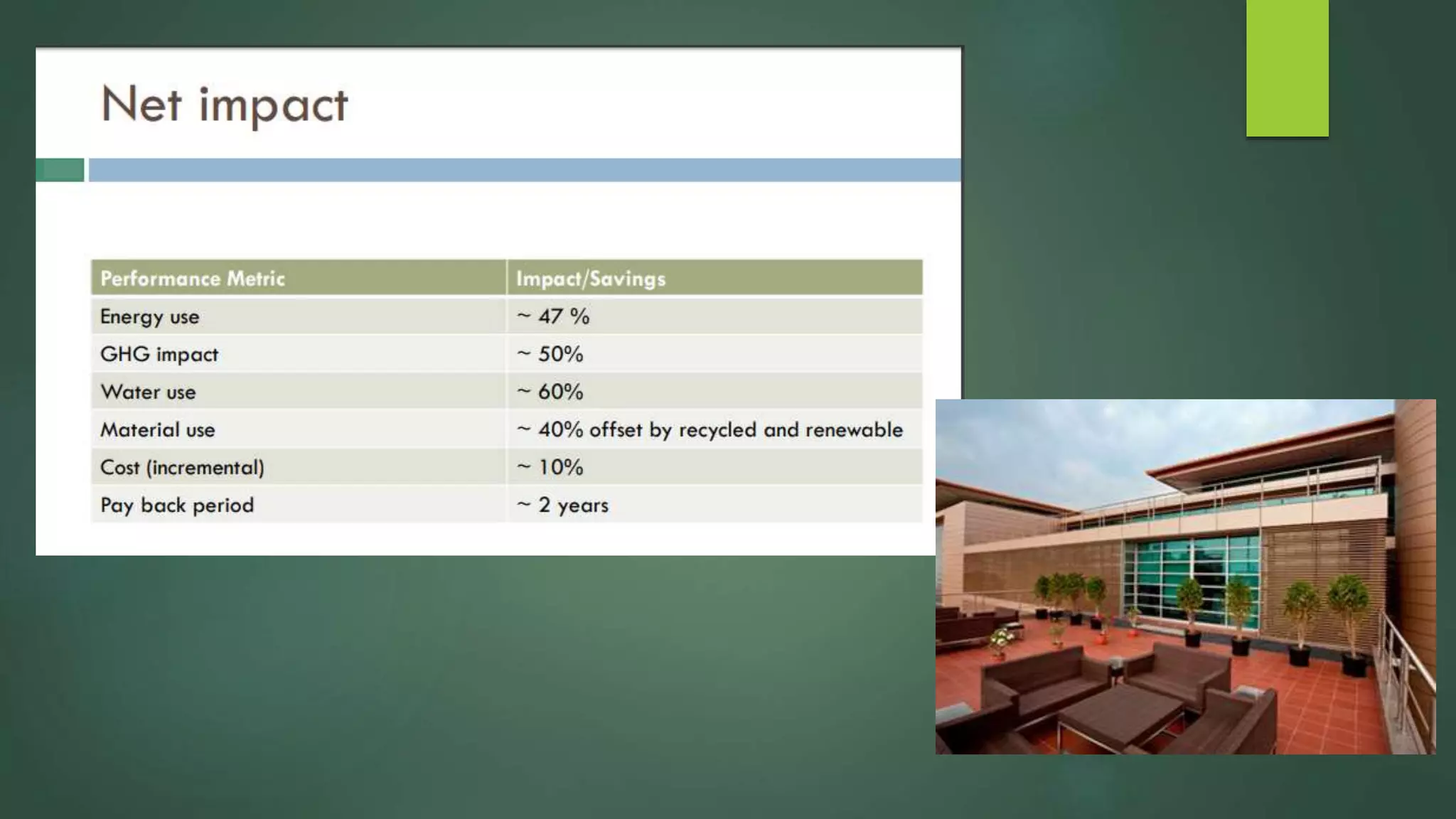
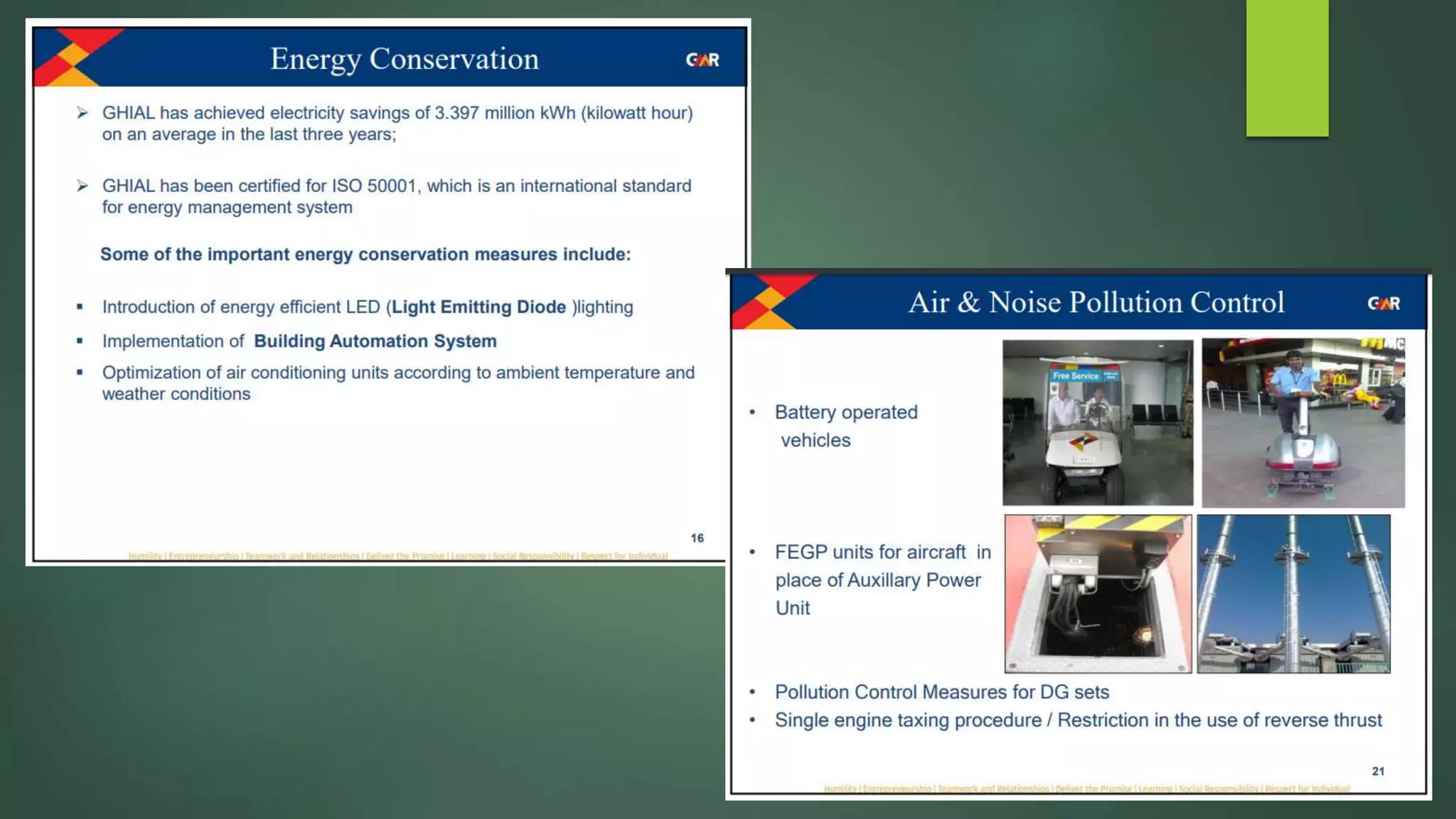
A green building is a structure that is designed to reduce environmental impact and improve occupants' well-being. It uses resources efficiently throughout its lifecycle by conserving energy and water and generating less waste. Green buildings provide environmental, economic and social benefits like reduced operating costs, improved air and water quality, and enhanced occupant health. While initial costs may be higher, green buildings save money over the long term. Examples of green building practices include using sustainable materials, maximizing natural light, and incorporating renewable energy systems.